Creatinine is a special molecular product that occurs as a result of various chemical processes (metabolism) in human muscles. As a result of chemical reactions - protein metabolism - enormous energy is released into the body, which leads to muscle contraction. This is how creatinine appears. It comes exclusively from the creatine molecule, which is responsible for muscle tone and energy supply.
Once creatinine is created, the body no longer needs it. Therefore, it is excreted into the blood. Then, after moving throughout the body through the circulatory system, creatinine is delivered to the kidneys. The kidneys filter and the creatinine is completely excreted along with the urine. This filtration of the kidneys occurs constantly and without interruption throughout the day. Even when no physical activity is performed, the diet and time of day change. Therefore, creatinine as a by-product does not have time to negatively affect the human body.
Creatinine is necessary for the metabolism of muscle tissue, and it is always present in a small dose in the blood and urine of an absolutely healthy person. It is the level of creatinine in the blood that indicates whether the kidneys are functioning well enough. Only through the kidneys does it leave the body in the same quantity in which it is formed. And when there is a lot of creatinine in the blood, it means the kidneys can’t cope.
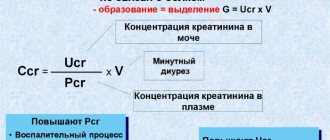
There is a special calculation used to determine GFR - glomerular filtration rate (kidney circulation). Glomeruli are microbundles of vessels in nephrons - kidney filters. This calculation is the most accurate analysis, which shows how much blood plasma the kidneys can filter from creatinine and excrete it into urine in 60 seconds. The resulting value is creatinine clearance.
Normal creatinine clearance values
Creatinine clearance is an indicator that is quite different in everyday life for various reasons - the psychological and physical state of the patient’s body, time of day, age and gender of the patient, body weight, improper kidney function.
The normal level of creatinine clearance varies from patient to patient. But there are general ideal norms of indicators:
- Up to 30 years of age for men up to 146 ml per minute, for women up to 134 ml per minute
- up to 40 years of age for a man, ideally 107-139 ml per minute (1.8-2.3 ml per second), for a woman under 40 years old 87-107 ml per minute (1.5-1.8 ml per second )
The creatinine clearance decreases by 1% every year. During the aging process in old age, the normal rate is already 54-105 ml per minute.
How to collect material correctly?
The optimal time to start the procedure is considered to be between 7 and 10 am. The exact time depends on the laboratory schedule at the medical institution.
The patient must follow certain rules:
- before the first meal, drink 0.5 liters of liquid;
- pour out the initial urine collection;
- perform a laboratory sampling of venous blood;
- throughout the day, drain all urine excreted into a sterilized container, noting the time of each urination and the volume of liquid;
- keep the material in a refrigerator;
- the last time urine is collected exactly 24 hours after the start of the procedure;
- Only 50 ml of urine taken from a common container is submitted for research.
Creatinine clearance is an indicator that requires precise fulfillment of the conditions for a proper study. Otherwise, an error may occur with an incorrect diagnosis, or the patient will have to retake the sample.
When and in what cases are creatinine clearance studies prescribed?
Creatinine clearance measures how fast blood flows through the kidneys. Changes in the norms of indicators when diagnosing creatinine clearance indicate a decrease in renal filtration and, as a result, renal failure, acute or chronic. Analysis of creatinine clearance is prescribed as a test of kidney function in the following situations:
- If renal failure is detected
- during pregnancy
- with pyelonephritis
- with congenital abnormalities of the kidneys
- in the diagnosis of diabetes and other endocrine diseases
- patients after hemodialysis
- for assessing muscle loads in athletes, astronauts
- in experimental medicine
Decoding the results
The study of ready-made tests is carried out by a urologist or nephrologist.
The interpretation of the results is carried out taking into account the individual parameters of the patient, the list includes:
- age;
- gender;
- body mass;
- blood pressure indicators.
All concomitant diseases that could affect these samples are taken into account.
Creatinine clearance is an indicator, changes in which can be associated both with improper kidney function and with problems in the functioning of the endocrine department. Therefore, additional diagnostic examinations are always required.
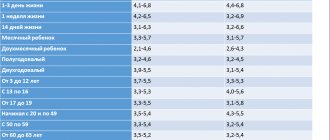
The results of the analysis are compared with the information in a special table:
| Age (years) | Indicators | |
| For women (l/h) | For men (l/h) | |
| Up to 12 months | from 0.06 to 0.1 | from 0.064 to 0.1 |
| Up to 30 | from 0.081 to 0.135 | from 0.088 to 0.147 |
| From 30 to 40 | from 0.075 to 0.128 | from 0.082 to 0.140 |
| From 40 to 50 | from 0.069 to 0.122 | from 0.075 to 0.133 |
| From 50 to 70 | from 0.058 to 0.116 | from 0.061 to 0.126 |
| After 70 years | from 0.052 to 0.105 | from 0.055 to 0.113 l/h |
Minor deviations from the above figures may be associated with increased sports loads and an excited state. Indulgence in high-calorie foods and consumption of large volumes of liquid leads to an increase in the amount of urine excreted and a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate. A significant decrease in results indicates a deterioration in renal function.
Definition, creatinine clearance formula.
To determine the functioning of the kidneys, there are 3 main ways to determine creatinine clearance:
- Analysis of urine collected by the patient over a 24-hour period
- Blood test using a calculation formula. This diagnosis is carried out most often, being the most convenient for the patient.
- Rehberg's test
Analysis of urine. When diagnosing the level of creatinine clearance in this way, the patient collects his urine in a certain volume in a clean container within 24 hours, refusing the day before and within exactly 24 hours from the time of the first collection of urine from caffeine and tea, beets and products with unnatural dyes. The container with collected urine should be kept either cool and dark or in the refrigerator. A urine test determines the ability of the kidneys to eliminate substances harmful to the body.
Blood analysis. There is a special formula for calculating creatinine clearance. The main parameters are the age and weight of the patient and, necessarily, the level of creatinine in the venous blood. The formula is: (140-age)*(body weight in kg)/(72*creatinine level in mg/dL). When calculating, a female patient needs to multiply the result obtained from the formula by the index 0.85
2 days before blood sampling, any physical activity is prohibited so as not to increase the daily normal creatinine level in the muscles. The day before the test, avoid meat, legumes, baked goods and fatty foods. You need to drink up to 2 liters per day. You should not eat in the morning before the test. Especially in this method, you need to pay attention to the children's formula, which differs from the formula for adults, because age is one of the main indicators in the calculation: child’s body length in cm/(0.0113 * creatinine level in the blood, µmol/l)*K . The “K” indicator in this formula is the coefficient of the age of the child patient. For children 2-14 years old and girls over 14 - the coefficient is 0.55, for boys over 14 - 0.7, for a full-term child under 2 years old - a coefficient of 0.45, for premature babies - a coefficient of 0.33.
When the clearance of endogenous (muscle) creatinine falls below the norm indicated in the previous chapter, this is an indicator of chronic kidney disease. At a level of less than 60 ml per minute, the kidneys are considered damaged, and at a level below 20 ml per minute, a severe form of renal failure is accurately established.
Reberg-Tareev test. This method is also called endogenous creatinine clearance, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and is considered more accurate. Collecting urine and taking a blood test at the same time. Before taking the test, you need to drink 0.5 liters of water, preferably in the morning on an empty stomach. The first urine is passed, it is collected during the second urination, when a blood test is taken at the same time. This test diagnoses many kidney disease problems. Normally, according to the calculation of the Reberg-Tareev test, the indicator is 65-125 ml per minute.
If the GFR result is underestimated, renal failure is detected. GFR with a result of 30-59 indicates chronic renal failure. A result below 30 means the kidneys are not functioning properly; dialysis is prescribed immediately.
Accepted laboratory norm of GFR by age
GFR (the norm for women varies between 90-110 ml/min) decreases as the body ages. Several equations are used to determine indicators. The norm may vary among different nationalities and ethnic groups. A low rate indicates impaired functional activity of the kidneys. A rate of 90-120 ml/min is considered normal.
Among women
GFR rates in women vary depending on age:
| Number of years | Indicators |
| 21-29 | 105-108 ml/min. |
| 30-40 | 95-97 ml/min. |
| 40-50 | 85-87 ml/min. |
| 50-60 | 80-85 ml/min. |
| 60-70 | 70-75 ml/min. |
| 70-80 | 60-65 ml/min. |
| 80-90 | 40-55 ml/min. |
In women over 60 years of age, levels of 55-70 ml/min are considered normal.
In men
GFR rates are slightly higher in men than in women:
| Age | Norm |
| 20-30 | 110-120 ml/min. |
| 30-40 | 100-110 ml/min. |
| 40-50 | 90-950 ml/min. |
| 50-60 | 80-8l/min. |
| 60-70 | 70-75 ml/min. |
| 70-80 | 60-65 ml/min. |
| 80-90 | 50-60 ml/min. |
Deviations from the norm in men under 50 years of age may indicate the development of inflammation of the prostate gland.
In children
Compared to adult patients, adolescent children have significantly higher rates of:
| Child's age | Indicators |
| A week | 40-41 ml/min. |
| 3-9 weeks | 60-67 ml/min. |
| Over 10 weeks | 90-97 ml/min. |
| 2-12 years | 130-134 ml/min. |
| 13-21 years old (girls) | 120-127 ml/min. |
| 13-21 years old (boys) | 135-140 ml/min. |
Indicators increase as the child grows older. This is due to the adaptation of the child’s body.
Norm and tests for the presence of creatinine in the blood
The blood creatinine level is a constant value and is measured in micromoles/liter. In order not to lose control of the proper filtration functioning of the kidneys, it is important to monitor the creatinine level using tests and kidney samples.
Prescribing a test for the presence of creatinine in the blood in cases where:
- assessment of kidney function is necessary in cases of detected chronic renal failure
- hemodialysis is prescribed with a critical level of creatinine in the blood
- urolithiasis is suspected
- the subject decided to become a kidney donor
When preparing for the test, 2 days before donating blood, avoid increased physical activity, do not drink coffee, tea, alcohol for 24 hours, do not eat meat and protein products, do not eat half a day before the test, drink only still water.
The main source of creatinine production is human muscles. Men's muscles are very different from women's. Therefore, normal levels of creatinine in the blood of men and women have different values; in men this figure is naturally higher. Also, in addition to muscle mass, nutrition and how active your lifestyle are are also important. Athletes and gym goers may have significantly higher creatinine levels due to the increased consumption of amino acids in the body. Those on a protein diet and meat eaters may also have elevated creatinine levels. The age and pregnancy of the patient also matters.
Normal blood creatinine level:
- in an adult male 70-110 mmol/min
- in an adult woman 50-93 mmol/min
- in newborns and children under one year of age 18-35 mmol/min
- in adolescents under 15 years of age 27-75 mmol/min
Indications for use
Using the creatinine clearance index, pathological conditions associated with impaired renal function are diagnosed by identifying deviations of indicators in the normal formula, up or down.
Inflammatory kidney diseases
- To determine renal failure.
- During pregnancy to assess the functional load on the urinary system.
- For congenital anomalies of the urinary system.
- Before and after hemodialysis in order to determine the need for the procedure and its effectiveness.
- For endocrine pathologies to identify metabolic and energy failures.
- For athletes to determine the functional state of the urinary and cardiovascular systems, as well as identify signs of doping.
- For chronic inflammatory kidney diseases.
- With high blood pressure.
- For experimental and scientific purposes to determine the boundaries of the norm and derive effective measurement formulas.
In medicine, several methods are used to calculate creatinine clearance; the Cockcroft-Gault formula is considered the most convenient and reliable.
Using the creatinine clearance index, pathological conditions associated with impaired renal function are diagnosed by identifying deviations of indicators in the normal formula, up or down.
- To determine renal failure.
- During pregnancy to assess the functional load on the urinary system.
- For congenital anomalies of the urinary system.
- Before and after hemodialysis in order to determine the need for the procedure and its effectiveness.
- For endocrine pathologies to identify metabolic and energy failures.
- For athletes to determine the functional state of the urinary and cardiovascular systems, as well as identify signs of doping.
- For chronic inflammatory kidney diseases.
- With high blood pressure.
- For experimental and scientific purposes to determine the boundaries of the norm and derive effective measurement formulas.
In medicine, several methods are used to calculate creatinine clearance; the Cockcroft-Gault formula is considered the most convenient and reliable.
Calculation of creatinine clearance is necessary to check kidney function. Indications for this procedure are:
- suspicion of pyelonephritis;
- kidney function in women during pregnancy, if pathologies are detected;
- renal failure;
- the presence of congenital abnormalities of kidney function;
- checking the functioning of organs after hemodialysis;
- if a person decides to become a kidney donor;
- checking kidney function in people exposed to heavy physical activity.
DETAILS: Complete urological examination for women
Increased creatinine in blood tests. Causes.
Sometimes the creatinine level in the blood changes slightly or greatly. This happens for various reasons:
- When creatinine does not leave the body due to kidney damage (urolithiasis, renal failure, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, uremia), decreased blood supply to the kidneys, severe shock.
- When there is an increased level of creatinine in the blood. There are a lot of factors here - endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus), frequent irradiation of the body, excessive physical activity (weightlifting, bodybuilding, improper diet (large amount of protein consumption), abuse of sports nutrition, with an increased content of growth hormone in the body (gigantism), severe skin injuries and operations, destruction of muscle tissue (compression) due to car accidents, various infectious diseases, loss of large amounts of blood, internal ulcers and tumors, anemia.
Symptoms of elevated creatinine are fatigue, fatigue, difficulty breathing, a feeling of exhaustion, and confusion.
Treatment for increased creatinine depends on the degree of the indicator. If this does not particularly affect the general condition of the body and the indicator is within the acceptable norm, doctors recommend a special diet, reduced physical activity, increased consumption of clean drinking water, diuretics, antioxidants to remove waste and toxins, and normalization of sleep. If the indicator deviates significantly from the norm, you need to contact a specialist who will select the right treatment.
Factors affecting glomerular filtration rate
The condition can be affected by a number of factors, which include:
- the presence of acute or chronic diseases;
- long-term use of drugs that stabilize blood pressure;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- obesity (regardless of degree);
- pregnancy (regardless of trimester);
- degree of basement membrane permeability;
- the number of structural and functional renal units (when they die, the filtration rate is slowed down);
- filter surface area (the number of functional nephrons is calculated);
- blood flow speed (at least 600 ml/min).
Filtration rates can be affected by a person's diet. If it contains a large amount of spicy, fatty or salty foods, then the SFC may be reduced. In elderly patients, there is a deviation from the norm (downwards). The time of collecting material (evening, morning) can also affect the final result.
Decreased creatinine in blood tests and its causes
A low creatinine level is also a pathology and has a negative effect on the body.
The reasons for it are as follows: low muscle mass, severe muscle injuries, a diet with low protein intake, cirrhosis of the liver, pregnancy, amputation of limbs, long-term treatment with allergy medications, a vegetarian diet, blockage of the urinary tract. In this case, you cannot independently prepare a diet based on diets and hunger strikes, and reduce sports activities to a minimum. Taking medications under the supervision of a doctor.
An increase, as well as a decrease, in the level of creatinine in the blood has quite serious consequences if you do not pay attention. Therefore, try to check with your doctor during blood tests to see if there are any abnormalities.