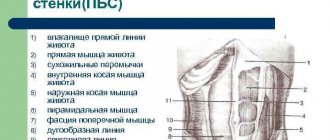
What is an X-ray? Most people have passed it at least once, but not everyone knows what it represents. X-ray is a common test for visualizing internal tissues and has been used for decades.
It helps the doctor examine internal organs, diagnose, monitor and treat diseases.
There are some risks associated with taking an x-ray. But for most people, the potential benefits outweigh the risks. The doctor independently decides how necessary it is for a particular patient to use this research method.
Why do X-rays take place?
The method is used to diagnose and further treat patients by recording images of the internal structure of the body to find out whether or not a specific disease is present, whether there are foreign objects, structural damage or abnormalities.
The doctor orders an x-ray to:
- examine the area in which the person is experiencing pain or discomfort;
- monitor the progression of a diagnosed disease, such as osteoporosis.
Diseases for which an X-ray machine must be used:
- bone cancer;
- breast tumors;
- enlarged heart;
- blocked blood vessels;
- lung diseases: pneumonia, emphysema, tuberculosis and lung cancer;
- heart disease, congestive heart failure;
- causes of shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain;
- digestive problems;
- broken bones, fractures in the chest, including the ribs and collarbone, fractures of the bones of the upper spine;
- infections;
- osteoporosis;
- arthritis;
- if necessary, find out the location of the swallowed object.
The essence of the examination technique
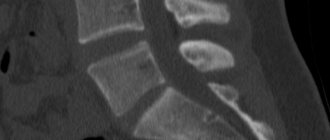
X-ray of the head shows the condition of bones, joints, soft tissues
The possibilities of modern radiography are very wide. Its essence lies in the fact that all tissues of the body absorb x-rays to one degree or another:
- the apparatus tube sends them to a certain point - the photographic film;
- some of these rays freely reach the target, others are absorbed by bones and soft tissues;
- the higher the density of the fabric, the fewer rays reach the film;
- As a result, an accurate and understandable pattern with shadows of different intensities is formed in the picture.
From this picture, specialists can determine the condition of bones and internal organs.
What will a head x-ray show?
For ease of interpretation, x-rays are taken in several projections
During the diagnosis, groups of skull bones such as the vault, facial skeleton and base are visualized. All of them are connected to each other by seams in the form of a jagged element. Only the lower jaw moves, working through the joints. Different projections of images help to assess the integrity and shape of these elements.
X-rays can be used to diagnose:
- congenital pathologies of the sella turcica: decreased bone density, destruction, increase;
- suspect the presence of benign or malignant tumors of the pituitary gland;
- signs of intracranial hypertension - finger-like impressions on the inside of the bones;
- osteomyelitis – due to defects inside the bone tissue;
- subdural hemorrhages of a chronic nature - due to calcifications inside the skull;
- calcification by meningitis and oligodendrogliomas of the brain;
- tumor processes due to displacement of the pineal body;
- changes as a result of metabolic pathologies, as in Paget's disease.
Radiography occupies an important place in both the primary and final diagnosis of pathologies.
Types of X-ray
Sight X-ray of the jaw
Types of examination are classified in several ways. According to the purpose of the diagnostic procedure:
- Overview. Prescribed for skull injuries, bone abnormalities, cracks, hematomas, increased pressure inside the head. The entire area is being examined for possible violations.
- Sighting. The condition of any area is studied if there is a suspicion of a pathological process in it. It is often used to diagnose blood vessels, eye sockets, jaws, and nasal bones.
There are also different types of skull radiography based on the nature of the projections: left and right lateral, anteroposterior, axial, posteroanterior.
The most commonly used are direct and lateral projections. To accurately determine the lesion, other methods may be prescribed. Thanks to the different angles, even the smallest deviations from the norm are detected.
The next type of classification is based on the type of tissue being examined.
- Brain examination. Performed if tumors, calcifications, hypotension or high blood pressure are suspected, as well as with symptoms of inflammation and hematomas. This technique is often called CT scanning because it requires slice analysis. Advanced equipment is used.
- Diagnosis of skull bones. Indicated for fractures, osteoporosis, cracks, osteosclerosis, concussions and congenital anomalies.
- Temporal bone analysis. A separate type of procedure that is used for temple injuries, acute otitis, inflammation of the mastoid process, or tumors in this area.
- Ear diagnostics. Intended for analysis of external, middle or internal organs. The aiming method is used.
The type and method of examination depend on medical indications. Sometimes combined approaches can be used, for example, when studying the temporal lobe, they do an analysis of the ear or the brain.
How to prepare for an x-ray
An x-ray is a standard procedure performed in an x-ray room. Often a person does not need special preparation for it. Depending on the area being examined, your doctor and radiologist may need to wear loose, comfortable clothing.
Some hospitals may provide you with a hospital gown to wear during the x-ray. Doctors may ask the patient to remove any jewelry or metal objects.
Important! You should always tell your doctor or radiologist if you have metal implants from previous surgeries. They can block x-rays and prevent clear images.
Sometimes the test requires a contrast material (alternatively called contrast dye), which is injected before the x-ray. This is a substance that improves the quality of images. It contains iodine or barium compounds. Depending on the purpose of the procedure, contrast dye is introduced into the body in several ways:
- through the liquid that a person drinks;
- through a catheter;
- through an enema.
If a patient is prescribed an x-ray to examine the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor recommends fasting for a certain period of time. Avoidance of certain liquids may be necessary. Sometimes doctors, in order to take an x-ray, prescribe medication to cleanse the intestines.
What are ligament ruptures and sprains?
Ligaments are dense bands formed by connective tissue. They connect bones, fix the joint and provide movement in the desired direction. If the ligaments experience tension that exceeds their elasticity and density, they are injured.
In this case, a microtear or partial rupture of the ligaments may occur, which is called a sprain. A complete rupture is said to occur if the integrity of all fibers is broken.
If we consider the causes of microtears of ligaments, the most common among them will be sudden movements. Often, bruises and falls as a result of direct mechanical impact on them lead to damage to the ligamentous apparatus.
Similar cases can occur with injuries at home, at work and during training. Also contributing to stretching are shoes that are too wide or narrow, obesity, degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the joints due to arthrosis, previous injuries and infectious diseases, and flat feet.
How the procedure is performed
A radiologist performs an examination in a hospital radiology department, dentist's office or clinic.
X-rays are done when the patient is prepared for it. The radiologist will tell him how to position the body to obtain clear images. He may ask you to lie down, sit or stand in different positions.
The procedure is performed while the patient stands in front of a plate containing X-ray film or sensors. Sometimes doctors are asked to lie down or sit on a platform and move a camera connected to a steel arm above the body to capture the area that needs imaging.
It is important to remain still until the image is obtained. Stillness is the guarantee of a clear image. The test is completed once the radiologist is satisfied with the images obtained.
Types of tears and sprains
This pathology is classified according to severity and location.
Depending on the severity, the following degrees of damage are distinguished:
- Mild is a micro-tear of fibers, while motor function is not impaired, pain is moderate.
- Medium – incomplete rupture of fibers in several places, partial rupture of the capsule is possible, swelling and hemorrhages appear, movements are painful, support is difficult.
- Severe - complete rupture of fibers is characterized by severe pain, severe swelling and hemarthrosis, the joint becomes unstable.
What are the potential side effects of X-rays?
X-ray devices comply with radiation safety requirements and are tested by specialists. X-rays are used in small quantities to produce images of the body.
The level of radiation exposure from an X-ray machine is considered safe for most adults, but not for a developing fetus. Pregnant women should talk to their doctor to find a safer alternative. Doctors will offer them another method, such as an MRI.
Information! What is MRI read on this page
If the patient uses contrast material, it may cause side effects. These include:
- hives;
- itching;
- nausea;
- metallic taste in the mouth.
In rare cases, the dye causes a serious reaction: anaphylactic shock, low blood pressure, or cardiac arrest. If a person suspects that they have a severe reaction to a substance, they should consult a doctor immediately.
Treatment of tears and sprains
The treatment tactics for sprained ligaments in the leg, shoulder or hand are determined by the traumatologist, taking into account the severity of the injuries. What to do if a ligament is torn? If the tear is minor, tight bandaging is recommended, which brings the ligaments together.
It is recommended to apply cold every 4 hours. On the first day, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets and ointments. Injections are used if necessary.
After a few days, you can replace the cold with warm compresses and start doing simple exercises. Proven folk remedies will also be effective. They are used as compresses and help relieve pain and swelling.
- Grated raw potatoes are applied several times a day to the damaged area.
- Raw onions are mixed with sugar and placed on gauze over the sprained area.
- Washed and crushed aloe leaves are mixed with honey and made into a compress.
In case of severe damage, a splint, orthosis or plaster is applied.
How are sprained joints (ligaments) treated? For mild to moderate damage, immobilization can be used; for severe damage, surgery can be used.
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- complete rupture, when independent recovery is impossible or there is a risk of improper formation of ligaments;
- severe hemorrhage into the joint cavity;
- separation of bone tissue.
The rehabilitation period can last from several weeks to several months. At this stage, physiotherapeutic procedures will be effective: magnetic therapy, UHF, paraffin therapy, massage.
Exercise therapy plays an important role in restoring impaired motor functions. You should start with simple exercises, gradually increasing the load so that the patient does not feel pain.
Providing emergency assistance
Before the EMS team arrives, urgent measures must be taken. What to do in case of a concussion, a small reminder with recommendations will help:
- lay the patient horizontally, with the head on a hill;
- the patient should not be given food or drink;
- provide a flow of fresh air;
- make a cold lotion;
- the patient should be completely at rest - avoid watching TV, playing games on the phone, laptop or tablet.
If the patient is unconscious, then he cannot be moved or transported! The patient must be placed on the right side, the left leg and upper limb bent, the head turned to the right and pressed to the chest with the chin. This ensures free air circulation, and the victim will not be able to choke on his own vomit.
Concussions and brain damage are treated only after diagnosis; only a specialist can recommend what medications to take and how much. If it is not possible to seek help in time, then during the recovery period you should follow some rules:
- Painkillers are contraindicated.
- Alcohol tinctures, alcohol is prohibited.
- Physical activity is excluded.
Even if a concussion is not accompanied by negative symptoms for 14 days, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics at a medical institution, which will prevent serious consequences for human health.
Contraindications
The radiation exposure during an x-ray of the ankle joint is no more than 0.01 mSv, which corresponds to less than one day of natural radiation. The maximum annual exposure dose is 150 mSv. Thus, the harm from ankle x-rays is minimal.
However, X-rays are not taken unless absolutely necessary:
- Pregnant women. The contraindication is due to the negative impact of rays on the fetus and possible disruption of the structure of DNA and RNA, which can lead to the formation of malignant tumors.
- During lactation. It is recommended to express milk after the x-ray examination.
- Children under 15 years old. Accelerated metabolism and cell growth make young children especially sensitive to radiation. When performing X-rays on infants, they are completely covered with protective devices.
- People who regularly undergo studies based on the X-ray principle to determine treatment tactics.
Attention! It is recommended to take no more than one photo per day.
Mild: symptoms
After a bruise has occurred, a hematoma usually appears at the site of the injury. Pain sensations are localized at the site of injury. This is a situation that can be dealt with quite easily on your own at home.
Providing assistance on your own, much less ignoring the situation, is strictly prohibited. You should contact a medical facility.
There are symptoms for which you should call a doctor immediately. Independent transportation is dangerous for humans.
- the appearance of clear discharge or blood from the ears and nose;
- increase in body temperature to 38 degrees and above;
- additional damage present in the back of the head, on the back;
- seizures;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- inability to move independently;
- loss of ability to focus;
- damage to the speech reflex;
- deformation of the pupils;
- feeling of difficulty breathing;
- loss of consciousness.
After a concussion, the patient exhibits general cerebral signs of injury, head contusion:
- severe vomiting, feeling of nausea;
- a concussion is accompanied by the main symptom – lack of consciousness (short-term or long-term);
- migraine attacks, disorientation, dizziness;
- pupils of different shapes;
- hyperactivity or vice versa, lack of sleep;
- limb spasms;
- after the patient comes to his senses, he may experience discomfort when exposed to sudden noise or bright light;
- confusion of speech, consciousness, memory loss.
During the first 24 hours, the patient may experience the following symptoms due to a concussion, damage to the skull, or brain:
- Dizziness.
- Feeling nauseous.
- Migraine, lack of sleep.
- Skin poverty.
- Disorientation in space.
- Loss of appetite, excessive sweating.
- Lack of concentration, weakness.
- Fatigue, discomfort.
- “Unpleasant” flushes to the scalp.
- Extraneous ringing in the ears.
Features of pediatric craniography
An X-ray of a child’s skull is a procedure that requires a more thorough approach. In most cases, the specialist prefers ultrasound. X-ray diagnostics are used as a last resort, since the bone elements of the brain are still in the stage of growth and formation, and excess radiation can lead to negative consequences.
Frequent indications are head trauma, including birth, and skull fracture. The procedure is similar to the examination of adults. The only problem is the need to be in one position during manipulation, which is very difficult for children. The presence of parents or the use of sedatives and sleeping pills may be required before diagnosis.
Rehabilitation after injury
Throughout the entire recovery period - from 2 to 5 weeks after the injury (depending on the severity of the pathological condition), the patient must adhere to the recommendations of the attending physician and maintain complete rest. Any mental or physical stress is prohibited.
It is necessary to realize that after a TBI of any severity, the development of symptoms of a dangerous disease is possible in people who systematically consume alcoholic beverages, including epileptic seizures.
A concussion is a dangerous pathological condition of the brain that can provoke the development of serious illnesses. At the first sign of injury, you should urgently call an ambulance or consult a specialist.
Only a qualified doctor can explain how to treat a concussion in order to prevent the development of a dangerous pathological condition. The lack of adequate, comprehensive therapy can lead to irreversible consequences, especially in the presence of serious and dangerous injuries to humans.
How dangerous is the research?
X-ray of the skull is accompanied by low radiation exposure to the patient’s body (approximately 0.12 mSv). This figure is less than 5% of the dose that a person is allowed to receive per year. For comparison, we can say that a person receives the same amount of radiation while relaxing in the sun on the beach in one hour.
However, it is not recommended to take an X-ray of the head (as this method shows, described above) more than 7 times a year.
X-ray diagnostics are carried out solely according to indications and its purpose is to determine the presence of a fatal disease. This is why there are cases of more patient radiation than reported in the medical literature. For example, a skull fracture is considered an emergency. If it is suspected, diagnosis is carried out even during pregnancy. Women carefully cover their chest and stomach with a lead apron.
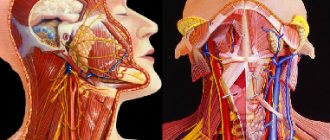
CT scan of facial soft tissues
A native study using X-ray radiation does not provide an idea of the soft tissue formations of the face and head, therefore only contrast CT can act as an analogue of MRI. After administration of an iodine-containing solution, layer-by-layer images can be used to determine:
- areas of hidden inflammation;
- neoplasms (tumors, cysts);
- disturbances in the blood supply to the examined area and pathology of facial vessels;
- abnormalities of soft tissue development.
A CT scan of the face reflects the condition of the underlying bone and cartilaginous structures, eye sockets, paranasal sinuses, temporomandibular joints, teeth and gums.
What is MRI of soft tissue structures?
Soft tissue MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic method that helps obtain high-quality, detailed images of the structures being studied.
The action is based on the influence of a magnetic field on hydrogen atoms that make up water molecules, the content of which varies in different organs.
The change in the direction of hydrogen molecules is recorded by special sensors and converted by digital processing methods into an image.
MRI helps to obtain a layer-by-layer image of soft tissue structures: muscles, their fascia and tendons, synovial membranes, fatty tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
Since soft tissues contain a large amount of fluid, MRI is the preferred method for diagnosing pathological formations in this location.