Great invention
The year 1895 became significant in the life of Wilhelm Roentgen. They discovered radiation, which in the future was called X-rays. To conduct experiments, the German scientist invented a special tube with which he studied little-known radiation. To make it possible to use these rays, various devices were invented. This is how the X-ray machine appeared.
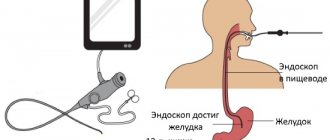
It began to be used in surgery. Later, photographing the human body, where soft tissues transmit rays and bones block them, began to be called fluoroscopy. The first X-ray photograph in the history of mankind was a photograph of the hand of the inventor's wife with a wedding ring on her finger. It was truly a great invention.
After some time, X-ray tubes began to be used not only for medical purposes. They have become essential in many industries. The scientist was approached with numerous offers to sell the rights to use the invention, but he refused because he did not consider it profitable. At the beginning of the twentieth century, X-ray tubes became widespread and used throughout the world. Today, scientists from different countries have made numerous discoveries not only in medicine, but also in space and other fields.
Story
A partial synonym for the term “radiology” is the concept of “radiology diagnostics,” although today it includes a much broader meaning than at the very beginning of the formation of this science, and combines several specialties.
So, this medical discipline appeared in the 19th century. Its founder is rightfully considered to be the physicist Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, a professor at the University of Würzburg, who discovered X-rays while working with electrical discharges. He investigated the new phenomenon and managed to take photographs of his own hand and that of his wife. Realizing the importance of the discovery, he devoted several years to its detailed study - from the autumn of 1895 to the spring of 1897 and published thematic articles.
The discovery of X-rays was truly revolutionary. Devices appeared that made it possible to take pictures, which expanded the capabilities of medicine and attracted many talented scientists to its new branch. From 1912 to this day, radiation diagnostics has been actively developing in Russia and remains a leader in the field of research technologies.
Device
The X-ray machine consists of:
- From one or more tubes, which are called emitters.
- A power supply device designed to provide electricity and regulate radiation parameters.
- The X-ray machine includes tripods with which you can control it.
- A device that converts x-rays into a visible image that can be observed.
And now a little more detail. The device is protected by a thick lead casing. The atoms of this metal absorb X-rays well, which ensures the safety of personnel and accurately directs the rays to the object of study through a hole made in the housing. Such devices work successfully at airports. With their help, luggage is quickly checked for the presence of metal objects.
Who gets x-rayed at home?
On-site diagnostics are necessary for people with limited mobility and people with disabilities who find it difficult or impossible to visit a clinic on their own.
As you get older, your risk of osteoporosis increases, which causes your bones to become brittle. Even slight falls can result in fractures. The doctor will take an urgent X-ray of the femoral neck, upper or lower extremities, and also apply a plaster or splint in a timely manner.
- Causes of pain in the left lower abdomen in men and women
- Colposcopy of the cervix, what is it?
- Which flower protects against computer radiation?
Classification
Depending on the operating conditions and design, X-ray machines are:
- Stationary: they are equipped with special X-ray rooms.
- Mobile: they are designed for use in operating rooms and trauma departments, wards, and at home.
- Transported to their destination in special vehicles.
- Portable, dental, impulse.
Depending on their purpose, X-ray machines are divided into:
- To specialized ones, which, according to the conditions and methods of research, are fluorographic and tomographic.
- General purpose devices.
Depending on the area of application, devices are distinguished:
- Dental.
- For urological studies.
- Neuroradiology.
- Angiography.
How to build a career
A practical radiologist goes from a resident to the head of the department. If he has the desire and appropriate professional qualities, he can make a managerial career - take a place in the hospital administration and even become the chief physician.
Scientific activities are also possible. Radiology provides many topics for research work, and a specialist can:
- To attend graduate school.
- Collaborate with specialized departments as an assistant.
- Publish scientific articles, give lectures and conduct seminars according to your knowledge and qualifications.
Working at the department of a medical university involves teaching. A physician may devote full time to scientific research, writing reports, articles, papers, and teaching students, or combine this activity with working with patients in an office or radiology department.
How to get a photo?
X-ray rays passing through the body are projected on film. But they are absorbed differently by tissues, depending on their chemical composition. Calcium, which is part of bones, absorbs X-rays the most. Therefore, they will be bright and white in the picture.
Muscle, connective tissue, fluid and fat do not absorb the rays as intensely, so they will appear in shades of gray in the image. Air absorbs X-rays the least. Therefore, the cavities containing it will be the darkest in the image. This is how the image turns out.
Wage
Radiologist is one of the most in-demand professions in the modern job market. This doctor can work in a public clinic or hospital, and in a private institution; some specialists have two or three places of employment.
In Russia, a radiologist can earn from 20–30 to 60–100 thousand rubles. The average salary is 36,400 thousand rubles.
The list of vacancies in different regions is quite wide, and there are offers from foreign clinics. A significant advantage when finding a job is knowledge of various diagnostic techniques, including the latest. The value of a radiologist in the labor market directly depends on practical experience and level of qualifications.
"Arina". X-ray machine
This equipment is widely used in the oil and gas industry not only in our country, but also in neighboring countries. The Arina pulse portable X-ray machine is unpretentious in operation. It is successfully operated both at low temperatures (-40) and at high temperatures (50 degrees above zero). This is a small-sized device, so its weight is light. It is easy to maintain.
The wide radiation angle allows for directional and panoramic illumination. If you use a special power source, the Arina device becomes completely autonomous. It includes an X-ray unit and a portable control panel. They are connected to each other by a twenty-five meter cable. The digital X-ray machine "Arina" has several varieties. They differ from each other in design:
- "Arina-1" has built-in batteries, which makes working in the field much easier, and low power. This allows you to work with the device without using special protective measures.
- The Arina-3 X-ray machine is equipped with external batteries, which lightens its weight. The advantages include the possibility of translucent steel up to 40 mm thick, and the disadvantages are the lack of protection against overheating.
- "Arina-7" is the most popular pulse device in our country. It is capable of shining through steel up to 80 mm thick and has an increased operating voltage of up to 250 kV.
Responsibilities
The specialty of a radiologist requires that the doctor will:
- Determine indications for radiological examinations in accordance with the patient’s medical history and medical history.
- Select optimal methods and develop diagnostic testing plans.
- Operate medical equipment and take radiographs, including the use of contrast agents.
- Proficient in tomography techniques (computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging).
- Analyze research results, enter them into documented documentation and draw up a conclusion for the attending physician.
The radiologist must be familiar with the issues of normality and pathology of the human body, know the features of “radiation symptoms” and describe them when detected in the images, provide specialized medical care in accordance with the professional standard. His responsibilities also include assessing the completeness of the research scheme prescribed by the attending physician, justifying and describing additional methods if necessary to include them in the primary list. The radiologist is responsible for the safety of testing, supervises the work of subordinate personnel - laboratory assistants, nurses, and provides consultations on radiation diagnostics.
Dental X-ray machine
A high-quality diagnosis for any disease allows you to discover the very cause of the disease and quickly cure it. A dental X-ray machine can be found in any dental clinic today. With its help, the problem is instantly identified and the correct diagnosis is made. This device is safe due to the low level of radiation, so it can be placed directly in the dental office, which will save work space and time for the doctor and the patient.
The Pardus-02 dental X-ray machine is the most popular for dental diagnostics. With its help you can get targeted and panoramic images. The transition from one shooting to another takes one minute. Using a panoramic image, the doctor assesses the general condition of the patient’s teeth, and targeted images allow him to monitor the treatment process.
Description and characteristics of the profession
A radiologist is a doctor who conducts radiation studies of the body and interprets their results. It helps the treating doctor find out the causes and characteristics of various pathologies, including space-occupying formations - cysts, abscesses, tumors. His competence also includes participation in preventive measures. In Russia, for example, this is an annual fluorography in order to timely detect signs of a dangerous infection - pulmonary tuberculosis.
A radiologist works with complex diagnostic equipment and performs research as directed by attending physicians; he can find employment in such institutions as:
- Clinic.
- Multidisciplinary hospital.
- Sanatorium (if medical work is provided there).
Modern radiologists take not only well-known photographs, but also carry out diagnostics using computer and magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound (ultrasound studies). Additional directions are available after specialized training (from several weeks to months).
The radiologist does not give recommendations on therapy, he only deals with diagnostics.
Nevertheless, he works closely with attending physicians - therapists, surgeons of various profiles. Based on his conclusion, these specialists establish a diagnosis, make a choice in favor of surgery or conservative therapy, and plan tactics for providing care to the patient. Therefore, the importance of high-quality work by a radiologist cannot be overestimated.
Digital ward X-ray machine
This device performs the functions of a C-arm and a tomograph. With its help, you can quickly obtain digital projection images of any part of the human body. The digital X-ray machine is designed to work both in specialized rooms and departments, and in hospital wards, which allows you to examine the patient before, during and after surgery, without moving the patient. This device is of particular importance for performing cranial tomography to detect malignant tumors.
The ward X-ray machine has:
- Vertical tripod with a moving carriage and an X-ray monoblock mounted on it.
- A movable base with brake pedals installed on it.
- Two caster wheels at the front and rear.
Depending on the field of research in which the devices are used, they differ into several types:
- Dental – for research in dental practice.
- For research in urology.
- For diagnostics of blood vessels (angiography);
- For neurodiagnostics. To start the operation of the X-ray machine, electricity is supplied to its control panel, which, after regulation, goes to the main transformer. After this, the amplified voltage is redirected to the emitter, generating the appearance of rays. The X-ray beam easily penetrates the skin of the subject and reaches the muscles and bones. They, in turn, absorb radiation with varying intensities.
Bones absorb rays to the greatest extent due to the presence of calcium in them. Because of this, they appear in intense white in the final image. Gray in the image shows muscle tissue, fat and fluid. This is not due to such intense absorption of radiation. It has the least effect on the air region. Therefore, those places inside the body that contain air will appear in the image as the darkest. The converter processes the data obtained from the X-ray and displays it on the image. It clearly shows the bones and organs being examined. Often, internal structures are filled with contrast liquid to make them appear more clearly in the image. This method makes it more likely to detect various changes and make an accurate diagnosis.
X-ray examination is a fairly simple and inexpensive procedure that provides a two-dimensional image of body structures, which is necessary for diagnosing many common diseases.
We'll tell you how it works.
X-ray portable device LORAD LPX
Commercial and military aerospace programs are designed with the reliability of all components supporting high-tech processes in mind. Since the cost of producing parts is very high, their quality must be constantly monitored. For this purpose, a portable X-ray machine of the LORAD LPX series is used.
These devices come in different models: liquid and air cooled. But all of them are designed for continuous operation, which turns out to be very profitable. Devices in this series are used in various climatic conditions, but liquid-cooled devices are considered the most common, since they are not a source of ignition. This is especially important when fuel cells are being examined and flammable substances are released into the air. Air-cooled devices are used in cases where it is possible to supply air for cooling or when the requirements for fire and explosion safety are not very high.
About security
Despite the fact that when performing fluoroscopy at home, less powerful devices are used, the rules of protection still remain inevitable. The patient is put on a leaded apron or skirt, and the thyroid area is covered with a special collar made of leaded rubber.
In addition, modern portable X-ray tubes (for example, the Toshiba brand) are practically free, thanks to successful engineering discoveries and multi-level protection, of both scattered and lateral radiation. This makes the examination safe, both for the doctor and for others.
In conclusion, it must be said that this type of examination, such as home radiography, not only increases the level of comfort and reduces stress (for example, when examining children), but can also significantly reduce the burden on the outpatient radiology sector.
Mobile X-ray unit
These devices are the most popular in medical institutions. They have small dimensions, so they are very convenient to use. To examine a patient, they can be used directly in the ward. A mobile X-ray machine can be easily placed in any room. There are no age restrictions for obtaining images, and there is no need to move the patient. This is especially important for bedridden patients.
Mobile devices show accurate results, which is why they are widely used everywhere. They are equipped with wheels, thanks to which they have good maneuverability, and this is important when transporting. Mobile X-ray machines are used when performing instrumental interventions, to monitor the treatment of many diseases in the field of traumatology, orthopedics, urology, endoscopy, vascular surgery and others.
Mobile devices include devices designed to work in the field. They are installed and transported on special transport with a separate room, autonomous power supply and a personal darkroom. Such devices are installed in railway cars and on ships.
Indications and contraindications for home examination
During an on-site x-ray examination, almost all types of x-rays can be performed, except methods with contrast. Typically, the size of the photograph onto which an image can be projected does not exceed 40 by 40 cm.
Usually, an X-ray at home is called to perform a study of the bronchopulmonary system, for example, when the patient has not been diagnosed with pneumonia, indications for hospitalization have not yet been identified, but his condition is of moderate severity against the background of bronchitis with an increase in temperature and the addition of a cough, possibly pain in the chest and the appearance of purulent sputum. Then an X-ray of the lungs is performed at home.
X-rays at home can be prescribed for bedridden patients
In addition, the following areas are most often imaged:
- hip joint with a fracture of the femoral neck in bedridden patients;
- ankle joint if injury is suspected;
- knee joint;
- examination of the spine for acute pain.
Of course, the radiologists who arrive are ready to take pictures of the skull bones, sinuses, and wrist joints, but you need to understand that people prefer to have an x-ray at home if they have limited mobility, and this is obvious.
Contraindications for doing an x-ray at home are exactly the same as for inpatient examinations, for example, the first trimester of pregnancy.
There is one more feature. Considering that the power of the X-ray tube in portable devices is still not high enough, then if the patient’s body weight is more than 120-130 kg and the intensive development of subcutaneous fatty tissue, the visualization of some details (for example, pulmonary fields) will leave much to be desired.