One of the modern diagnostic methods that is highly informative for pathologies of the heart muscle is CT of the heart and blood vessels.
This research method allows us to determine the structure of the organ and possible pathological changes. The main difficulty in studying the condition of the heart is that the organ is constantly working, so other diagnostic procedures may provide inaccurate and vague data. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital receive clear images during cardiac CT scans, since European equipment is equipped with a high-frequency sensor.
Brief anatomy
- The coronary arteries arise from the aortic bulb.
- They carry arterial blood directly to the myocardium.
- The left and right coronary arteries are the main vessels.
- The right coronary blood vessel runs along the posterior surface of the heart and gives off the posterior descending artery.
- The lateral coronary artery, located on the left, divides into the left circumflex and anterior descending blood vessels.
- In 15%, an intermediate vessel arises between them.
What does the examination show?
Computed tomography of the heart and blood vessels examines in layers. They are transferred to the monitor in the form of a clear three-dimensional image. The doctor has the opportunity to create a virtual model of the organ, in which any pathologies, cysts or damage are visible. Before surgery, such an image helps to develop an effective plan, take into account risks, and prepare for possible complications.
Among the results that a cardiac CT scan shows:
- injuries and wounds after damage;
- suppuration in the pericardial cavity;
- additional chords;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- rupture of the aorta or aneurysm;
- aortic valve diameter;
- blood clots and calcifications in blood vessels or on the walls of the heart.
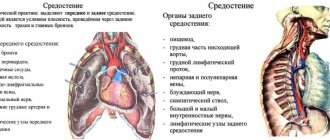
Using a tomograph, the heart can be examined in conjunction with the internal organs and the mediastinal area. This is important when diagnosing oncological tumors, which, when growing, put pressure on the organ, disrupting its function and affecting the ability to pump blood throughout the body.
Nakhodki
- First, the anatomy of the vascular system and its disorders are assessed. Many patients undergoing coronary artery (CA) CT angiography have undergone coronary artery (CA) intervention.
- It is necessary to carefully study the anamnesis and submitted documents in order to understand the changes in anatomy.
- Shunts can be detected - venous, arterial grafts that carry blood bypassing the “closed” section of the coronary artery.
A stent is a frame embedded in a vessel and ensuring its patency.
It is necessary to note the structural features of the vascular network, because Some abnormalities significantly increase the likelihood of myocardial infarction.
Then the patency of the vascular bed is assessed. The lumen of the artery can be narrowed due to parietal atherosclerotic plaques (ASP), incl. with inclusions of calcium or blood clot.
- The plaque is formed against the background of damage to the intima of the vessel by eddy flow of blood under high pressure, especially with arterial hypertension (AH).
- In the damaged area, a fat-like substance accumulates, which then calcifies.
- The more calcium in the plaque, the more stable it is, but the less treatable it is.
Narrowing
- The narrowing of the lumen is measured by the cross-sectional area of the vessel or its smallest dimension.
- The length of the narrowing is also determined.
The coronary calcium index is measured separately - an important criterion for the likelihood of developing damage to the heart muscle.
The lumen of the shunt or stent may also be narrowed. The narrowing is reflected in the description similarly to other zones.
Particular attention should be paid to the area of the anastomosis (ostium) of the shunt and artery. This is where significant stenoses occur in most cases.
Advantages of MSCT
To study the coronary arteries, a multispiral study with the largest number of rows of detectors is required.
The minimum is 32 rows, the best is 256 or 512. The more detectors, the higher the resolution can be achieved, and the more clearly you can see small vessels.
Computed tomographs with fewer detectors have low information content and are usually not used for coronary angiography. MSCT also allows you to evaluate:
- condition of the chambers and valves of the heart;
- accompanying findings in the scanning area from the lungs and bone structures.
Contrast tomography
Contrast agents help enhance the overall picture, visually separate organs from each other, and highlight the necessary areas of the body for further study. Contrast is indispensable when checking the cardiovascular system. It helps to examine in detail the anatomical features of the organ and makes the scanning results more accurate and reliable. In most cases, iodine-based preparations are used today - they easily penetrate soft tissues without causing side effects, and just as easily come out of them. Although these drugs are safe, in rare cases they cause allergic reactions in patients with individual intolerance and serious kidney pathologies. In the first case, a person may develop an allergic reaction, in the second, the body will not be able to quickly and effectively eliminate the substance. If their use is still necessary, the patient is given antihistamines. The contrast agent is administered intravenously or orally, depending on the area being examined. When diagnosing the heart, the first option is used.
The procedure with contrast lasts about 2-3 minutes, without it even less - 1-2 minutes. Usually the patient does not experience discomfort, but due to the contrast, unpleasant sensations are possible: itching, nausea, urticaria. All this passes without a trace within a day. If health deteriorates significantly, the patient must inform the doctor, who is observing the procedure in the next room through the viewing window, and the scanning will be stopped. Communication is carried out via a special built-in speaker.
Contrasting
For MSCT of the coronary arteries, the introduction of contrast is mandatory. A native study (without contrast) allows only to assess the presence of calcifications in the coronary arteries.
A contrast with a high content of iodine in non-ionic form is used:
- yopamiro;
- ultravist;
- omnipack;
- yomeron.
Contrast is injected into the cubital vein at high speed (4-5 ml/sec). To achieve this speed, an automatic injector is used.
Please note: coronary angiography is always performed with contrast.
A few words about coronary angiography
So what is she like? Cardiac CT is a special examination method that allows you to assess the condition of the arteries and capillaries. This type of laboratory research is very complex.
It is based on the fact that a special substance is released through the veins, thanks to which the tomograph is able to show the following pathologies:
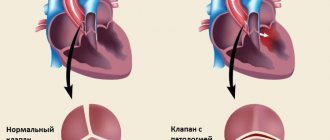
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- angina pectoris;
- acute and chronic inflammation of the pericardium;
- dilatation of the atria and ventricles;
- heart circulatory disorders;
- sclerosis;
- arrhythmia;
- thrombosis;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels.
Cardiac CT with contrast is performed layer by layer. Special sensors receive and record information about how X-rays are transmitted and absorbed by soft tissue. Step-by-step removal of sections allows you to obtain the most accurate clinical picture of the patient’s condition and make a diagnosis with almost one hundred percent accuracy.
Contraindications
- Myocardial infarction in the acute phase.
- Allergic reactions to contrast.
- Vein pathology.
- Renal dysfunction.
Execution frequency
- MSCT diagnosis of coronary disease is usually not associated with high radiation exposure.
- If indicated, the study can be performed as many times as necessary.
Typically the test is performed:
- before surgery;
- after operation;
- then at certain intervals to assess the patency of the recreated bloodstream.
If symptoms appear—compressive chest pain during exercise or at rest—MSCT may be performed earlier than planned.
How is MSCT of the coronary arteries performed?
After changing into light clothing, the patient lies down on a special table, which automatically extends from the scanner cavity. To monitor the heartbeat and pulse, special sensors are fixed on the limbs, whose operating principle is reminiscent of the process of taking a cardiogram. If it is necessary to administer contrast, a dropper or a small pump is installed, which automatically supplies the drug.
The table is placed in the CT scanner, which wraps around the patient. A full scan takes no more than 20 minutes. The patient must remain motionless, but doctors closely monitor the process from an adjacent room in case of vasospasm or heart attack. After the scan is completed, you can return to your usual activities without restrictions.
Preparation
First of all, it is necessary to exclude kidney pathology and take a blood test:
- for creatinine;
- urea;
- glomerular filtration rate.
To relieve tachycardia, dilate the coronary arteries, and eliminate arrhythmia, it is recommended to take the following under medical supervision:
- beta blockers;
- nitrates (under the tongue).
Attention: tachycardia and arrhythmia can significantly complicate the examination. Consult with your cardiologist before your procedure about possible measures to stabilize your heart rate and rhythm.
Decoding the received data
The radiologist will study the data obtained, creating different projections of the heart. This allows us to examine the slightest pathologies and the onset of the ischemic process. He does not make a final diagnosis, but describes the information received, indicating the size of the defect or chord. Subsequently, the images and descriptions are used by the cardiologist to prescribe treatment. On average, decoding takes 1–2 hours.
Methodology
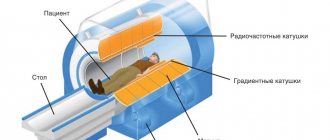
MSCT is performed with a device that synchronizes the patient's heart rate with the scan. The ECG synchronizer allows you to achieve:
- optimal image quality;
- significantly reduce the frequency of artifacts.
A catheter connected to a device that injects contrast is installed in the vein of the elbow.
- The patient lies down on the tomograph table, and the electrodes of the synchronizing device are fixed on it.
- Then the table slides into the tomograph ring.
- Contrast is introduced.
- Scanning begins.
Currently, imaging protocols are used to minimize radiation exposure.
The received data is transmitted to the doctor’s station, where they are post-processed using software. The programs allow you to:
- three-dimensional reconstruction of the vascular bed;
- automatically calculate the degree of narrowing of the lumen.
Maximum intensity projections (MIP) are also used.
How to prepare for MSCT of the coronary arteries
When performing an MSCT procedure without contrast, the patient requires virtually no preparation. It is necessary to obtain a referral from a cardiologist indicating a controversial diagnosis so that the radiologist can be convinced or refute the assumptions. You should bring comfortable cotton clothing without metal fasteners or buttons. It is better to use T-shirts that do not restrict movement and do not cause skin irritation.
If it is necessary to take a contrast agent, the patient is advised to stop drinking and eating for 3–6 hours. This will allow the drug to be fully distributed throughout the circulatory system and will make images of coronary blood flow as clear as possible. The day before the procedure, you should not consume foods and drinks that can affect your heart rate: strong tea, skin, fatty meat.
Some patients experience a feeling of anxiety and fear before the examination. For them, the doctor can choose a mild sedative on a natural basis. It is strictly forbidden to take medications containing nootropil, atropine: they can increase the heartbeat and distort data.
Alternatives
| Method | Advantages | Flaws |
| Traditional angiography | High resolution diagnostic and treatment procedure | All risks of invasive interventions, high radiation exposure |
| MRI coronary angiography | Emerging imaging modality, no contrast required, no radiation exposure | Duration of the study, the need for synchronization with heart rate, breathing |
Please note: Ultrasound is not performed to assess myocardial vascularization.
Frequency of performing cardiac CT
In the process of computed tomography, X-rays are used, and the patient receives a certain dose of radiation in any case. Ideally, the time interval between the two procedures should be 12 months. If absolutely necessary, a CT scan can be performed again 6 months after the first examination.
- The technique allows you to diagnose the disease at the very beginning of its development.
- During the scanning process, the doctor receives a three-dimensional image of the heart, which helps in making an accurate diagnosis.
- The duration of the study does not exceed 20 minutes.
CT scan of the heart and coronary vessels makes it possible to diagnose serious diseases at the initial stage of development, saving the lives of many people.
Research result
After the scanning procedure is completed, the results are processed by a computer program to obtain a three-dimensional reconstruction of the area being examined. MSCT data also makes it possible to analyze the condition of the coronary arteries (detect the presence of developmental anomies, determine the type of blood supply, branching options), determine the presence and type of atherosclerotic plaques, identify and clarify the degree of stenosis, determine the condition of shunts and stents when planning appropriate surgical intervention. Assessment of functional indicators takes into account the size and volume of the heart chambers, the thickness of the myocardial wall, the condition of the valves, etc.
The results of MSCT are given to the patient in the form of printed images. It is also possible to burn data to a CD (usually for a fee). In addition to the images, the cardiologist also issues a report (often deciphering the results and writing the report are also paid separately). Indications for further therapy or surgery are determined by a specialist at subsequent consultations.