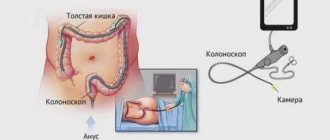
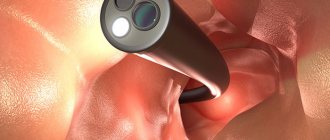
Colonoscopy is the most informative examination of the intestines. It is prescribed for suspected tumors and a host of other dangerous diseases. After 40 years, it is recommended for preventive purposes. Is it painful to have a colonoscopy? This question always arises in the patient’s mind immediately after the doctor’s appointment. It is difficult to give a definite answer. Much depends on the physiology and age of the patient, as well as on the disease that led to the appointment of the study.
Importance of the procedure, decision to use anesthesia
By performing this hardware examination, it is possible to determine the type of disease, the form of the pathological process, the degree of intestinal damage and the involvement of neighboring organs and tissues in the inflammatory process. About 10-15 years ago, this manipulation was considered painful. During the procedure, the endoscopist, directing the tube in the desired angle, could cause pain, because the intestines are equipped with an incredible number of nerve receptors. The painfulness of endoscopic examination forced many patients to refuse, agreeing to X-rays, ultrasound, MRI and computed tomography. But the disadvantage of such hardware manipulations is the inability to take biomaterial for examination for the presence of cancer, determining the infectious source + type of pathogenic flora. To eliminate the painful factor, doctors began to perform colonoscopy under local or general anesthesia.
Why do you need a colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy of the intestines is it painful - the question is certainly asked to the doctor, and many patients try to avoid such a study. In fact, there are not many indications for use, but the study helps to detect a lot of serious pathologies in a timely manner, and ultimately prevent death. Colonoscopy is prescribed in the following cases:
- rectal discharge (mucus, blood or pus);
- constant stool disturbances;
- sudden weight loss or anemia of unknown origin;
- pain in the intestinal area;
- suspicion of a neoplasm in the intestine, the need to perform a biopsy of intestinal tissue;
- removal of polyps and foreign bodies.
Colonoscopy using anesthesia
By lowering the pain threshold, the endoscope can be inserted into the rectum painlessly and without fear of any consequences such as intestinal spasm due to the patient’s anxiety, bleeding due to sudden body movements due to pain, and lastly: the inability to complete the examination due to screams and the patient’s refusal to be fully examined.
Forms of pain relief during colonoscopy:
- Local anesthesia
: an anesthetic substance is injected into the rectum, which inhibits the sensitivity of nerve cells in a certain area and for some time. The pain reaction does not disappear completely, so during the procedure there is discomfort when the endoscope comes into direct contact with the mucous membrane. Pain in this case may occur due to the injection of air into the colon, as well as the presence of inflammatory foci, bleeding or purulent ulcers, polyps or neoplasms of benign or malignant types.
- Use of sedatives
: Before a colonoscopy, the patient is given intravenous or intramuscular sedatives. After the onset of drowsiness, a colonoscopy of sections of the large intestine is performed. Hypnotic substances reduce the pain threshold of intestinal receptors, and the device passes painlessly in all parts. The advantage of such anesthesia: no anesthesia equipment is required, and the patient’s quick recovery after colonoscopy.
- General anesthesia
: performed only in stationary conditions, that is, in the operating unit. Before the procedure, anesthesia is selected, a test is performed to rule out allergies, and the dosage is determined. After the drug is administered, the patient falls asleep, and the colonoscopy is performed absolutely painlessly. Indications for this type of anesthesia are a high reaction to pain, childhood, adhesions and erosions in the intestines.
Attention! Patients recover from general anesthesia slowly with some consequences: dizziness, nausea, sometimes vomiting, pain around the perimeter of the abdomen. In connection with such reactions and clinical manifestations, plus the exclusion of complications such as bleeding, peritonitis, patients must be observed for several days in the hospital.
Is a pain-free colonoscopy possible?
Diet after intestinal colonoscopy
Even if we take into account all possible pain sensations during an examination of the intestines, under certain circumstances it is possible to undergo this procedure absolutely painlessly without using pain relief methods.
This requires a coincidence of the following factors:
- the experience of the endoscopist, his ability to carry out the procedure with the least discomfort for the patient;
- the presence of modern equipment that provides maximum comfort and a high degree of information content;
- a successful combination of physiological characteristics of the subject - the structure of the colon, pain threshold and the absence of pathologies of internal organs;
- Complete mutual understanding and coordination of actions between the diagnostician and the patient will relieve discomfort during the procedure.
The right clinic and experienced doctor are the key to a painless colonoscopy
It is because of these factors that you need to carefully consider the choice of a clinic for a colonoscopy in order to take advantage of the opportunity to undergo an important procedure without anesthesia and absolutely painlessly.
Indications for colonoscopy under anesthesia
The controversial question “What is the best way to undergo a colonoscopy with or without anesthesia?” remains relevant, pain frightens many patients, they must make a decision and choose the type of anesthesia. After studying many sources, our journalists found that the majority choose colonoscopy through sedatives. The option is very suitable for three reasons: it does not cause pain, intoxication and complications. As a result, this option is considered by a medical council, which takes into account the patient’s sensitivity to the drug, concomitant diseases of systems and organs (cardiovascular, endocrine, diabetes mellitus, tumors, central nervous system diseases) and the degree of gastrointestinal damage.
Colonoscopy is performed when:
- constant complaints of pain in the epigastric region of the abdomen + pain along the perimeter of the segments of the large intestine;
- complaints of dyspeptic processes with the presence of pus + streaks of blood in the stool;
- chronic constipation;
- the presence of fresh blood during bowel movements;
- specific stool for internal bleeding;
- constant urge to defecate;
- hemorrhoids;
- chronic anemia;
- poisoning;
- increased gas formation with dyspeptic symptoms;
- suspected malignant or benign tumors;
- sudden weight loss of unknown etiology;
- Crohn's disease;
- confirmation of the diagnosis and for the purpose of collecting histological materials;
- to exclude relapse of the disease.
After surgery to remove a colon tumor, it is recommended to perform a colonoscopy to rule out recurrence. If there have been incidents of intestinal cancer in the family, there is a need to be examined and undergo a hardware examination of the digestive organ to exclude pathology.
What to do after an intestinal colonoscopy?
After the manipulation, you should follow a therapeutic diet for some time to reduce the load on the digestive system. During surgical procedures, it is necessary to exclude physical activity, control the regularity of bowel movements and immediately respond to signs of constipation.
Intestinal restoration after colonoscopy is aimed at:
- Normalization of internal microflora;
- Elimination of unpleasant sensations;
- Prevention of long-term post-manipulative complications.
How to restore the intestines after a colonoscopy?
If only a diagnostic examination took place, then there are no special recommendations after the diagnosis. A smooth transition from a slag-free diet to a normal diet (introducing fiber and fresh vegetables and fruits, maintaining plenty of fluids to gradually stabilize stool) will be sufficient.
If, in addition to diagnosis, endoscopic surgery was performed, then it is important to maintain a therapeutic diet for 3 days after the manipulation and prevent intense stress on the intestines. Usually this time is enough for the mucous membranes to recover.
Patients should practice careful hygiene of the perianal space to prevent infection.
What to do if your stomach hurts?
For abdominal pain, it is important to determine the location and intensity of the symptoms. After colonoscopy, the pain is moderate, nagging in nature, localized from the navel down. Often the pain radiates to the anus.
The following medications are prescribed to relieve abdominal pain::
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-Shpa) to relax the muscles of the peritoneum and intestines.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin).
- If pain occurs in the epigastrium , stomach area and stool disturbances, you can take Duspatalin, Festal.
- For signs of heartburn along with abdominal pain - Gastal, Maalox.
Normally, any pain should disappear 2-3 days after the colonoscopy. The persistence of unpleasant symptoms indicates the persistent development of complications.
Restoration of intestinal microflora
Disturbance of intestinal microflora is usually caused by intensive preparation for the study:
- The use of medicinal laxatives,
- Slag-free diet
- An additional enema for colonoscopy to exclude residual effects in the intestinal cavity.
Effective means to restore the balance of microflora are the following::
- Lactofiltrum;
- Lactusan;
- Duphalac syrup;
- Mezim Forte;
- Creon;
- Kreazim.
Effective agents are Acipol, Linex, Bifidumbacterin. The course of treatment with prebiotics is 14-20 days. Additionally, you should include fiber, fruits and vegetables, dried fruits, natural juices, fruit drinks, and compotes in your diet.
Normalization of microflora is an important aspect of a healthy digestive process.
List of contraindications
The procedure for examining segments of the colon through an endoscope has become the number one tool in making the correct diagnosis. But despite the positive side of the diagnostic method, there are contraindications for its implementation.
Colonoscopy is not recommended if:
- increased reactivity of the body to anesthetics;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- pernicious anemia;
- cardiovascular failure;
- suffered a heart attack or stroke;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- urolithiasis;
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy.
Even with such contraindications, if there is a critical need, this procedure is performed. All stages are discussed in advance, and when it is performed, in addition to the endoscopist, several doctors are present (anesthesiologist, resuscitator, oncologist, surgeon). Considering the risks of the procedure, doctors are ready to provide specialized assistance in case of unforeseen circumstances such as bleeding, respiratory arrest, heart rhythm disturbances, perforation of the intestine due to ulcers, polyps or tumors. Before the procedure, the patient must be prepared according to a special scheme, which determines the results of the study and the patient’s condition before and after the investment.
Popular publications:
- Black feces Why? Causes? — 01/07/2015 05:06 — Read 42232 times
- Video capsule endoscopy: frequently asked questions - 11/12/2013 17:02 - Read 42017 times
- Capsule endoscopy. Description, reviews, advantages and disadvantages - 03/24/2013 17:15 - Read 37824 times
- Abdominal syndrome. Abdominal pain - 01/10/2015 05:02 - Read 21563 times
- Capsule colonoscopy - indications, contraindications, price - 10/30/2015 07:20 - Read 16751 times
Key words: Colonoscopy, intestinal colonoscopy, colorectal cancer, colon cancer, polyps, colonoscopy indications, diet during colonoscopy
- < Back
- Forward >
Stages of preparation for colonoscopy
Before the diagnostic procedure, the entire intestine must be clean, that is, there should be no feces in it. The mucous membrane should not have the slightest “garbage”; it can be perceived as pathological phenomena. Therefore, there is a whole scheme of preparatory manipulations: laxatives, diets, cleansing enemas.
Steps for bowel preparation:
Dietary preparation: exclusion of fatty and spicy foods. For three days, the diet should be composed of frequent split meals:
- light breakfast at 8:00: crackers and unsweetened green tea;
- 10:00 a.m.: low-fat kefir, hard-boiled egg;
- 12:00 o'clock: a glass of juice or jelly with a piece of gray bread, and a piece of low-fat fish;
- 14:00: mushroom or potato soup, mashed potatoes with a steam cutlet (or pasta, rice), a glass of green tea and sweet crackers with raisins;
- 17:00 hours: a piece of boiled chicken meat, white bread;
- 19:00 hours: a glass of low-fat kefir, crackers, baked apple.
Alcoholic drinks, carbonated water, fruits, vegetables, cereals, rye bread, legumes, fatty meat products, mayonnaise, hot seasonings are prohibited in the diet. This diet will effectively free the intestines from feces.
Cleansing procedures: enemas with warm water and laxatives such as Senadexen, Duphalac. Plus, you will need to replenish fluid in the body by consuming 2 liters of warm boiled water or mineral water without gases. This is done the day before the diagnostic procedure; if the colonoscopy is scheduled for 15-16 hours in the afternoon, before this time in the morning it is recommended to drink another 1.5-2 liters of liquid.
On the appointed day, the patient should not eat food; colonoscopy with anesthesia is performed on an empty stomach. Very important: if the patient is worried, agitated or undergoing neurosis, after consulting the attending physician, it is recommended to take a sedative that is compatible with the anesthetic and will not affect the quality of anesthesia.
Should I have a colonoscopy or not?
I doubted for a long time whether to have a colonoscopy or not. I heard comments about this from a therapist, that injections are given for pain relief, that it is unpleasant and painful. And in general, to put it simply, the procedure itself is not pleasant, when something is shoved into the anus. It's a shame!
But constant problems with the intestines, pain, bloating, food restrictions and a feeling of uncertainty, etc. they were not allowed to live in peace. Doctors could not make a specific diagnosis.
All this made me consider this study as an option for solving accumulated problems.
So I started researching various colonoscopy sites on the Internet. I looked for people's reviews, read articles. So I came across the site prokishechk.ru, which I was very happy about. On it I read details about the preparation and the procedure itself. Therefore, I decided to write my review of intestinal colonoscopy for this site in gratitude. I think that people who read this article will support me and will also write their reviews on this site, thereby helping and supporting those who have yet to do so.
Performing a colonoscopy under general anesthesia
After the preparatory stage, the patient is sent to the treatment room. Taking off all clothes below the waist, he lies down on the couch, on his left side. Your knees should be bent. Next, an anesthetic is injected into the vein, after 10 minutes you can insert an oiled endoscope into the anus. Using special practiced movements, the endoscopist guides the tube through the sections of the large intestine. The monitor shows the condition of the intestinal mucosa. At this time, you can remove suspicious areas, as well as take material for histology and eliminate polyps. Once the procedure is complete, the tube is removed. The patient is woken up, if he feels well, sent home, otherwise, his well-being is monitored for a day in a hospital setting. The entire procedure lasts from 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the diagnostic purpose and pathology. You can drink or eat food an hour after the procedure.
What can a patient do to have a painless colonoscopy without the use of anesthesia?
Much depends on the individual reactions and experience of the doctor. The subject has only 2 things in his power:
- Conduct full preparation.
- Get ready psychologically.
How to prepare for an intestinal diagnosis?
The process begins 3-5 days before the procedure. First, a person follows the rules of a slag-free diet:
- Small portions;
- Meals 3-5 times a day;
- Refusal of foods that cause constipation, flatulence;
- Eating only approved foods;
- Drink plenty of clear drinks - weak black or green tea, compote, fruit drink, clarified juice, etc.;
- On the last day, no dinner.
The preparation is completed by cleansing the intestines with special preparations with a laxative effect. The most common are Fortrans, Lavacol, Moviprep, Flit phospho soda, Endofalk. These are dosage forms for the preparation of aqueous solutions. The result is a volume of 2 to 4 liters. Every 10-20 minutes drink a glass in small sips. Most of them have an unpleasant taste and a side effect is nausea, so you should not take the medicine in one gulp, so as not to provoke vomiting. The dosage regimen depends on the time for which the colonoscopy is scheduled. There are 3 options:
- Diagnostics tomorrow morning, which means you need to drink the entire amount this evening.
- Study in the middle of the day. Half of the laxative is consumed late at 21:00-23:00, the second part early in the morning.
- Procedure after 14:00. The entire solution is used from 6:00.
Typically, more than 2 hours should pass between the start of the colonoscopy and the end of the drug. After 40-60 minutes of administration, frequent and prolonged bowel movements begin. During this period, a person spends almost all his time in the toilet. At the end of the preparation, a yellowish or clear liquid comes out instead of feces - this indicates that the result has been achieved.
Attention! Preparing for a colonoscopy is 50% success. If it is not carried out, then the examination will be impossible.
How to deal with fear?
Look at the situation from a different side. Colon cancer is the third most common deadly disease. Neither men nor women are immune from it. Oncology begins with a small formation - a polyp, which occurs in half of people over 50 years of age. You can remove the growth during a colonoscopy in a couple of movements.
The procedure lasts 20-30 minutes, and during this period the doctor can save your life by destroying the potential germ of a cancerous tumor. For the sake of such a result, it is worth enduring pain, which, according to experts, is still not critical, as, for example, during childbirth or serious burns.
Behavior rules:
- Do not squeeze;
- Relax as much as possible;
- Don't twitch;
- Thinking that these sensations are temporary, and you know that in a few minutes they will end;
- Before a colonoscopy, you can take a herbal sedative, for example, valerian tablets.
An example of a psychological trap! The patient wonders whether MRI or colonoscopy is better. And out of fear, he chooses the first option. As a result, he will face the same lengthy preparation, high cost for the procedure, and as a result, the appointment of a second option in order to clarify the data obtained from MRI.
Pros and cons of colonoscopy under anesthesia
After familiarizing yourself with the stages of the procedure, the question: “What is the best way to undergo a colonoscopy with or without anesthesia?” fades into the background. There are strong arguments for performing colon diagnostics under anesthesia, namely:
- There is no unbearable pain.
- The patient does not experience discomfort, bloating, weakness, or dizziness.
- The endoscope tube moves unhindered, examining the entire mucous membrane.
- Polyps can be removed painlessly.
- Histological material is taken qualitatively.
- During a colonoscopy under anesthesia, you can safely take pictures and carefully examine suspicious areas.
- The procedure does not last long.
- The patient regains consciousness immediately after the colonoscopy.
The only disadvantage of diagnostic hardware examination of the intestine is the cost and some side effects. Diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract using anesthesia varies in cost from 4,000 to 20,000 rubles. But these disadvantages depend on the financial situation of the patient, on the level of service of the medical center and on the complexity of the diagnosis plus the patient’s concomitant diseases and age.
Possible causes of pain during colonoscopy
Still, you shouldn’t expect severe pain to appear during the study. Whether a colonoscopy is painful depends on a lot of factors. It is worth mentioning right away that the endoscopist will do everything possible to ensure that the procedure is as comfortable as possible for the patient. Among the main reasons that can lead to discomfort or pain are:
- passing the endoscope through physiological bends, especially pronounced in the area of the liver and spleen;
- inflating the intestines with air - it is necessary to straighten the natural folds of the intestine;
- the presence of polyps, neoplasms, foreign bodies or cracks in the intestinal lumen;
- individual features of the intestinal structure.
Unintended consequences of colonoscopy
Side effects include
general condition such as fever, weakness, fainting, nausea, vomiting, as well as streaks of blood in the stool on the second day after the procedure.
Rare cases include perforation of the intestinal walls + damage to the spleen, this happens with erosive colitis and Crohn's disease, when the intestinal walls are very thin and the endoscope can pierce the intestinal walls. Even with this risk, a colonoscopy is necessary to detect and rule out cancer. Such complications also occur due to the incompetence of the doctor or under accidental circumstances. To avoid such incidents, it is better to find a good specialist or a medical institution with a decent reputation in advance. For your attention: the answer to the question of how best to undergo a colonoscopy with or without anesthesia can only be obtained from your attending physician, and your right is to agree with the opinion of a specialist!
Contraindications to the procedure
Despite the fact that colonoscopy under anesthesia is a common procedure, some people will still be better off avoiding this test. So, the examination is contraindicated in the following cases:
- in the presence of acute infectious diseases;
- peritonitis or suspicion of it;
- severe blood clotting disorders;
- late stages of heart failure;
- presence of heart valve stenosis;
- allergies to anesthetic medications;
- neurological and psychiatric diseases;
- epilepsy;
- during pregnancy.
It should be noted that none of the listed conditions is a complete contraindication to performing a colonoscopy examination under anesthesia. It is extremely important to discuss the individual characteristics of the body with the endoscopist so that the specialist can decide on the advisability of diagnosis, taking into account the possible benefits and risks of the procedure. If a study is scheduled, you need to pay attention to preparatory measures. This measure will help make the doctor’s task easier, and will also have a positive effect on the patient’s condition during and after the procedure.
When does pain indicate serious consequences?
Complications after intestinal colonoscopy practically do not occur. But there is a possibility of several adverse outcomes.
Bleeding
If the pain is accompanied by bloody discharge in the stool, then this is a consequence of:
- Damage to the mucous membrane with a colonoscope;
- Improper wound treatment when removing polyps or adhesions;
- Injury to internal hemorrhoids;
- Formation of anal fissure due to careless actions during the procedure.
In any case, you must urgently contact a proctologist to find out the cause of the bleeding. Normally, old blood may come out in the form of black and brown clots after surgical procedures. Fresh scarlet blood is considered dangerous.
Perforation of the intestinal wall
It is very difficult to pierce the membrane of a healthy adult organ. But in children, the elderly and patients with ulcerative colitis or other pathologies, the wall is very thin and easily damaged. In this case, the contents of the intestine enter the abdominal cavity, which ends in peritonitis and sepsis. Perforation occurs due to the unprofessionalism of the coloproctologist, sudden movements of the patient without anesthesia, and problems with the equipment.
Symptoms:
- Cutting pain in abdomen from every movement;
- Uneven swelling;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Pale skin;
- Frequent pulse;
- Subsequently, a sharp increase in temperature.
To confirm, an x-ray of the abdominal cavity is taken. If the perforation is confirmed, then emergency surgery is performed.
Carefully! A patient with signs of intestinal perforation should not move; an ambulance must be called immediately.
Infection
A prolonged increase in temperature, deterioration in general health, abdominal pain and purulent discharge from the anus are signs of an inflammatory process as a result of infection. This happens extremely rarely. The patient requires additional diagnostics: blood and stool tests, bacterial culture. Antibiotics are prescribed for treatment.
Splenic rupture
Severe pain on the left under the ribs, radiating to the shoulder blade and shoulder, as well as rapid pulse, low blood pressure, cold sweat, weakness, nausea and vomiting, may be symptoms of a ruptured spleen as a result of a strong blow to the intestines with an instrument. This is a dangerous condition because total internal bleeding occurs. Need urgent medical attention.