A study such as magnetic resonance imaging, literally two decades ago, was not an independent diagnostic method. This was just an auxiliary technique. Today, this research method is completely independent, with the help of which it is possible to thoroughly examine not only the anatomy, but also the structure of the tissues of the pelvic organs. The diagnosis is made with great accuracy; at the same time, the cause can be established and the correct treatment can be prescribed in the future.
When is MRI performed in women?
MRI of the pelvis (preparation for women includes following a diet) can be performed in the following cases:
- the appearance of vaginal secretions that have no reason - the discharge can be periodic or constant;
- the presence of neoplasms that were identified using ultrasound (ultrasound) or during an examination by a gynecologist;
- the presence of inflammation in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- the doctor suspects endometriosis - this is the growth of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) beyond the organ;
- a neoplasm was noticed during pregnancy, but it was not previously detected;
- the woman has an acute or emergency condition - the doctor suspects rupture of the ovary, ureters or trauma to the bladder;
- severe discomfort in the lower abdomen, which manifests itself in different ways, the cause has not been identified;
- a woman cannot become pregnant, infertility cannot be treated;
- pain in the pelvic area occurs for unknown reasons;
- hereditary anomalies in the pelvis;
- the appearance of symptoms of gastrointestinal pathologies - this applies to the appendix and colon;
- the occurrence of symptoms of pathologies in the genitourinary organs - pain during emptying of the bladder, the presence of blood secretion in the natural fluid;
- before and after surgery in the pelvic area;
- to clarify the diagnosis when other methods (ultrasound, x-ray) have failed.
MRI is a procedure that helps visualize soft tissue with high precision. It makes the diagnosis easier.
This is what the pelvic organs look like on an MRI
Using MRI, it is possible to identify many pathologies in women:
- congenital structural defects - absence or underdevelopment, double organ;
- violation of size - increase or decrease;
- neoplasms in the organs of the genitourinary system and in the rectum; in addition, the procedure can determine metastases;
- pregnancy outside the uterine cavity;
- inflammatory pathologies – this applies to adnexitis, vaginitis, cystitis;
- appendicitis;
- adhesions in the pelvic area;
- excessive accumulation of fluid that appears as a result of inflammation.
Most often, MRI is prescribed by doctors to diagnose a tumor at an early stage, and this increases the likelihood of recovery. There are symptoms that require you to see a doctor for testing.
Signs:
- pain that is nagging and sharp;
- rapid weight loss;
- the appearance of blood in the urine or stool;
- a copious secretion that had not appeared before.
Indications for use
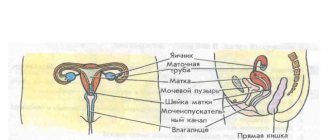
The female pelvis contains the internal genital organs (uterus with appendages, cervix, vagina), bladder and rectum, while the male pelvis contains the bladder, seminal glands, prostate gland and rectum. Considering that men and women have different organs located in the pelvis, the indications for MRI are also different.
Common indications for pelvic MRI for men and women are:
- pain in the pelvic organs of unknown etiology (usually prescribed after ultrasound);
- inflammatory processes in this area (infiltrates, abscesses);
- diseases of the bladder and lower ureters;
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the pelvis (cysts, tumors);
- metastases to the pelvic organs;
- developmental anomalies;
- prolapse of internal organs;
- rectal diseases.
MRI of the female pelvis allows you to evaluate the condition of the bladder, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, vagina, peri-uterine and peri-vaginal space, and lower intestines. Thus, the indications for its implementation in women (as opposed to men) are:
- bleeding from the internal genital organs of unknown origin;
- detection of a tumor or other neoplasm in the genital organs using other examination methods;
- endometriosis;
- infertility;
- adhesive disease.
In this case, a planned examination of the internal genital organs of menstruating women (uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries) is carried out on days when there is no menstruation.
The study in men is carried out to evaluate the condition of the prostate gland and vas deferens, bladder and rectum.
MRI is considered a good painless diagnostic method for establishing the location of tumors and the extent of their spread or metastasis. In some cases, this technique allows the doctor to decide on the patient’s management tactics, adjust the treatment program and predict its outcome.
Taking into account the wide range of indications, medical specialists of various profiles can refer for the procedure of magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvic organs: gynecologist, urologist, andrologist, proctologist, surgeon, traumatologist, oncologist.
Scheme of the procedure
MRI of the pelvic organs is carried out according to a specific plan:
- The person must remove all metal objects from himself, as the device is sensitive to them.
- Doctors ask the person to lie down on a special table.
- The limbs are secured with soft straps to prevent any movement. When performing an MRI, the patient should not move, otherwise the result will be inaccurate
- The table slides into the tunnel.
- If the administration of a contrast agent is necessary, it enters the body automatically through a pre-installed intravenous catheter.
- Next, you need to follow all the specialist’s recommendations (hold your breath, etc.); the device has a connection with medical personnel. There will be some noise during the procedure, so don't be alarmed.
- The table extends out of the tunnel.
- The procedure is over. The photographs are transmitted on film or disk, with an additional description. A person needs to wait for the transcript, which will be ready after 15 - 30 minutes. after research. If the workload is heavy, the description may be available every other day. Therefore, it is possible to send pictures by email.
The average duration of the procedure is 30 minutes. When a contrast agent is administered, the duration of MRI can be increased to 50 minutes. If a woman does not feel well during the examination, it is necessary to inform the staff.
Principle of the method
MRI of internal organs is based on the use of magnetic waves (not X-rays!), which are used to scan. The waves pass through the tissue, through all departments, and ultimately produce a three-dimensional image. Most often it is multilateral. It all depends on the number of pictures: the more pictures, the more reliable the information. In some cases, an MRI of the pelvic organs is performed with contrast, which increases the accuracy of the study. What is contrast? This is a substance that is administered intravenously for better visibility of blood vessels. A gadolinium-based drug is usually used.
MRI of the pelvis allows you to determine not only the presence of pathology, but also the extent of the disease. Using MRI of the pelvis with contrast, it is possible to study the condition of blood vessels and bone tissue.
Magnetic resonance imaging is significantly different from computed tomography, which uses X-rays to examine the patient. In this regard, it is distinguished by its safety. MRI results are quite accurate.
Main types of MRI
MRI of the pelvis (preparation for women includes avoiding alcohol several days before the procedure) is performed using different devices.
According to the classification, tomographs are of 2 types:
- Open. Otherwise called a low-floor device. Thanks to the design, it is possible to examine women with excess body weight, when a closed device is contraindicated. Due to the free approach from all sides, the open device is recommended for use by people with claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces) and children. Its cost is lower than that of the 2nd option, but the image quality is worse. Such devices are suitable for examining children without the use of anesthesia.
- Closed. Another name is high-field device. These devices have high frame resolution due to strong magnets located on all sides. The diagnostic tunnel has a limited diameter. A tomograph is often used to diagnose oncology. The device can detect tumors smaller than 1 mm.
Classification by type of MRI:
- With contrast agent. This study is the most accurate. The process uses the substance gadolinium. When performing an MRI, contrast “illuminates” the area under study, and damaged tissue is clearly visible. The substance is administered during the inflammatory process after surgery to remove a hernia or in case of infectious infection.
- No contrast applied. This method is used if high accuracy of images is not needed. And also when the doctor does not suspect a neoplasm.
Some compare MRI to computed tomography (CT) and ultrasound. Therefore, they do not know which procedure is better. The differences between MRI and CT are indicated in the table.
| Comparison parameter | MRI | CT |
| Harmfulness | The MRI process uses a magnetic field, hence the name. The procedure does not have strict limits for use. That is, how many times a year can an MRI be done. | CT scan is the use of X-rays. The disadvantage of the procedure is that you cannot exceed the dose for a certain period. |
| Image quality | As a result of the procedure, high-quality images of soft tissues are obtained. Therefore, MRI is preferable to perform for examining the pelvic organs. | CT is used to diagnose bone tissue. |
| Time of the study | From 30 to 50 min. | If the patient cannot lie in one position for a long time, he is recommended to have a CT scan. Its implementation is short-term – up to 60 seconds. |
The difference between MRI and ultrasound is shown in the table:
| Comparison parameter | MRI | Ultrasound |
| Availability | The procedure is not always available for execution. | Ultrasound examination is more accessible than MRI. |
| Price | MRI is more expensive than ultrasound. | The equipment is cheaper. Therefore, the price of pelvic ultrasound is less than that of MRI. |
| Image quality | MRI is an informative procedure. | Less information content. But if the diagnosis was made by ultrasound, then an MRI may not be done. |
What is MRI
MRI is based on radiofrequency pulses directed at the area being examined. Magnetic waves create fields with high voltage, allowing you to obtain high-quality images. During the procedure, the woman should take a comfortable position lying on a table that slides into the chamber of the device. The equipment is equipped with coils, thanks to which the required area is examined.
Tomographs come in open and closed types. In the first type of equipment, the magnetic field is located only above the organ being diagnosed, which makes them the most convenient for patients. However, this type has less power, which affects their research capabilities. Typically the procedure lasts from 20 to 60 minutes.
Thanks to the magnetic effect, multiple images of the organ under study are transmitted to the monitor, which make it possible to fully study the tissue structure. Since the images are taken digitally, they are stored and subsequently studied.
Most often, in order to examine organs located in the pelvic area, it is recommended to conduct an extended MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent. When the contrast enters the blood, it reaches the organ being examined in literally 2 minutes and is distributed in the area where the study takes place. This diagnosis allows you to obtain the largest amount of information necessary for the doctor.
Absolute contraindications
There is a list of absolute contraindications to MRI:
- implants containing metal;
- an allergic reaction to the contract substance, if it must be used during the procedure;
- kidney failure (for MRI with contrast), since the substance is excreted by the organs, the disease may worsen;
- presence of a pacemaker or neurostimulator;
- presence of an insulin pump.
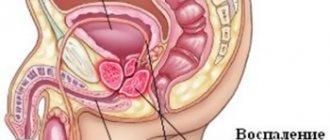
Diagnosis of men
The male population who has crossed the 40-year barrier is at risk for developing pathologies of the genitourinary system. Moreover, the disease often develops unnoticed by them, when the appearance of symptoms indicates an advanced stage of the disease. In this situation, pathological foci often affect nearby organs. This makes it difficult to recover quickly.
How does MRI affect the human body?
MRI of the pelvis in men allows you to timely determine the presence of prostatitis, cancerous tumors, adenomas, and disruption of the circulatory system that feeds these organs.
This allows you to detect pathology at the initial stage, prevent its chronic course and treat the consequences with surgical interventions. Without contrast, this information cannot be obtained.
Indications for conducting a contrast study are:
- impaired sexual function;
- presence of suspicion of oncology and metastases;
- injury to the abdomen, penis, lower back;
- frequent and painful urination.
A contrast agent makes it possible to clarify the diagnosis; it is usually used when minor neoplasms and altered conditions of not only soft but also bone tissues are detected on non-enhanced MRI. If a man is suspected of having prostate cancer, then it is possible to accurately identify the pathological focus using magnetic resonance imaging with an endorectal sensor placed in the rectum of the person being examined for the entire duration of the procedure. This examination can replace a biopsy.
Relative contraindications
These contraindications include conditions in which MRI is undesirable.
But in case of urgent need, the procedure is used for diagnosis:
- Pregnancy. If something threatens the mother’s life and it is necessary to do an MRI, the procedure is performed. This item is included in the contraindications not because the equipment harms the health of the expectant mother or fetus, but because of insufficient knowledge of the effect. The doctor may recommend an MRI or replace the test with another one.
- Children's age up to 5 years. A child cannot always remain in one position for a long time. And an MRI takes more than half an hour. Therefore, restless children may be given anesthesia.
- Claustrophobia is the fear of enclosed spaces. To solve this problem, there are open devices.
- Unstable nervous system. If a person cannot lie in a motionless position for a long time or is afraid, the procedure should not be performed in a closed apparatus. But this problem can be solved with the help of sedatives.
- Muscle spasm.
- The presence of metallic paint in the tattoo.
- Obesity, weight more than 130 kg. The same goes for a large waist circumference. The tomograph chamber is narrow, so a person may not fit inside. But now there are open devices.
MRI of the pelvis with contrast
Contrast based on gadolinium chelates has passed all clinical trials and is approved for use in magnetic resonance diagnostics
Contrast provides clearer visualization: on tomograms, the contours and size of the tumor, its interaction with nearby structures, the condition of blood vessels, and potential metastasis are seen much better. In modern diagnostics, a paramagnetic agent is used based on gadolinium chelates, a rare earth metal that in its native state is dangerous to the body, but when used in the form of dissolved salts does not lead to any serious consequences in 98% of patients. The drug is excreted by the kidneys. Contrasting is not applicable if:
- a generalized allergic reaction such as angioedema or anaphylaxis to the administration of the drug has previously been observed;
- the patient is diagnosed with end-stage chronic renal failure (glomerular filtration rate less than 30 ml/minute);
- the woman does not rule out pregnancy in the early stages, which she plans to prolong.
Paramagnetic agents, which provide higher-quality images during MRI of the pelvic organs, are much better tolerated and have a smaller list of adverse reactions than iodine-containing substances for CT. Contrast-induced nephropathy/systemic fibrosis is incidentally rare. Minor allergic reactions - redness of the injection site, urticaria-type rash were reported in 10% of patients.
When a paramagnetic is administered, unpleasant symptoms from the autonomic nervous system may appear: a metallic taste in the mouth, a diffuse feeling of heat, salivation, nausea, headache, which does not require cancellation of the procedure. After 2-5 minutes the phenomena stop on their own. To minimize the likelihood of their development, you need to eat a light breakfast 40-50 minutes before, for example, a sandwich with sweet tea or a few spoons of porridge boiled in water.
The contrast is delivered into the vein using an injector during certain phases of the study or administered by a nurse.
Preparing women for a planned study
MRI of the pelvis requires preparation. Women need to follow the rules so that the results of the procedure are as accurate as possible. Preparation includes the use of medications and proper nutrition. An MRI of the pelvis (preparation for women includes taking medications) can be performed urgently.
When planning a study, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages for 2–3 days.
- In the evening, before the study, it is necessary to take laxatives if the woman has problems with the gastrointestinal tract. For example, in case of frequent constipation. It is also recommended to use medications if an enema is contraindicated.
- If there are no problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to do a cleansing enema in the evening (12 hours before the procedure) and in the morning. It is better to purchase an Esmarch mug from a pharmacy chain, since compared to a conventional device, it can hold up to 2 liters of water. For this purpose, use warm boiled or purified water. You cannot do an enema at a cold temperature, otherwise there will be muscle spasms.
- The last meal should be at least 5-6 hours before the test.
- It is not recommended to empty the bladder 3 hours before the MRI, as the picture of the disease is disrupted. If a person cannot tolerate it, urination is allowed. But then (in 30 - 60 minutes) you need to drink 1 - 1.5 liters of liquid to fill the bladder.
- You should not smoke 1 – 2 hours before.
If an MRI with contrast agent is prescribed while breastfeeding, it is recommended that the child be weaned for 24 hours after the examination. All milk must be expressed and discarded. To speed up the process of removing the contrast agent, a woman should drink plenty of fluids.
Medications
Medicines help eliminate gas formation, which interferes with the procedure, or calm a person with great emotionality. Commonly prescribed medications are listed in the table.
| Classification of drugs | Group Description | List of medications |
| Laxatives | The products soften feces and help remove them from the body. | Guttalax, Microlax, Duphalac |
| Reducing flatulence | The drugs help reduce gas formation, resulting in clearer images. | Espumisan |
| Antispasmodics | Medicines reduce spasms. | Spazmalgon, Spazgan, No-shpa |
| Sedatives | Medications help cope with anxiety | Valerian, Afobazole, Tenoten |
| Antiemetics | Medicines reduce intestinal motility. | Metoclopramide, Domperidone |
At the discretion of the doctor, the list of medications may be changed.
Diet before MRI
It is recommended to maintain proper nutrition 2–3 days before the test. Thanks to this, visualization of organs improves.
A woman must adhere to the following rules:
- refuse fried, salty, smoked foods;
- reduce the consumption of salt, sweet foods and baked goods;
- exclude legumes, potatoes, raw vegetables;
- It is not recommended to eat fatty fish and meat;
- exclude fast food, dried fruits, spicy seasonings;
- get rid of carbonated drinks, coffee and tea.
You can eat the following foods before an MRI:
- porridge – buckwheat, millet, pearl barley;
- lean meat and fish;
- low fat dairy products;
- stewed and boiled vegetables;
- dishes steamed, boiled or baked in the oven;
- boiled eggs – 1 pc. per day.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to minimize gas formation.
This can be done by observing the following rules:
- Meals should be taken at the same time;
- eat 5 – 6 times a day (servings 200 – 300 g) with breaks between meals of 3 – 4 hours;
- drink 1.5 - 2 liters of pure still water per day.
Nutrition before the procedure
In order for magnetic resonance imaging to give high-quality results, you should take care of the condition of the intestines: during the procedure, there should be no foci of gas formation or fermentation, flatulence and bloating, as they distort the images. You can avoid extremely unpleasant signs only with proper nutrition.
So, 2–4 days before an MRI, you need to either exclude or consume to a lesser extent such foods as:
- grape;
- packaged juices;
- alcohol;
- confectionery;
- cabbage;
- peas;
- beans;
- coffee;
- baking;
- fried foods;
- fast food;
- milk.
The following drinks should predominate in the diet: pure water and green tea. It is best to stick to fractional meals for several days: meals should be small. The basis of nutrition can be cream soups, steamed fish, slimy porridges and other easily digestible dishes.
What should you warn your doctor about?
Before undergoing an MRI, a woman should consult a doctor. The specialist studies information about previously conducted studies and conclusions.
Since MRI involves a magnetic field, it is necessary to warn the doctor about the presence of the following conditions:
- Pregnancy. This is especially true in the early stages, since at this time the child is just beginning to develop, the fetus is sensitive to all influences.
- Pacemaker - MRI machine may not function correctly or fail.
- The presence of metal elements on the human body that can become magnetized. For example, dentures, implants, fragments. The paragraph also concerns bullets, staples, and screws. The tomograph can move these objects in the tissues, the woman will feel severe pain. In the worst case, death is possible.
- Claustrophobia and tendency to panic attacks. The doctor may suggest taking sedatives. But, in any case, it is necessary to warn the doctor.
- Pain that prevents a person from lying in one position for a long time . The specialist recommends taking antispasmodic drugs.
- Lactation. The doctor should explain that after the procedure you should not feed the child for about a day.
Contraindications to the procedure
Despite the fact that MRI is a safe and painless procedure, it still has a number of contraindications. They mainly concern the features of the methodology. The device creates a strong magnetic field, so this study is strictly prohibited for persons with:
- cochlear implants;
- metal stents, clips or staples (for example, on blood vessels);
- artificial valves in the heart;
- implanted neuro-, pacemakers or defibrillators;
- shrapnel, bullets or other metal objects in the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended for women in the first trimester of pregnancy. There is no reliable data on the harm of a magnetic field for a baby, but the risks of pathologies occurring during this period are so high that it is better to temporarily abandon such an examination in favor of other methods, for example, ultrasound diagnostics.
Is there a relationship between the menstrual cycle and MRI?
The most optimal time for the procedure is the first phase of the menstrual cycle. That is, no later than 7–12 days of the cycle. In the first phase, it is better to evaluate the endometrium (whether its development corresponds to the day of the menstrual cycle), the myometrium when identifying various gynecological diseases - fibroids, ovarian tumors.
In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the endometrium thickens and its structure changes. Additionally, blood circulation in the uterus increases, and the myometrium becomes heterogeneous. Therefore, if the study is performed during this period of time, the doctor may recommend additional testing on another day of the cycle. This will help make the correct diagnosis.
If a woman has reached menopause, an MRI can be performed at any time. The same applies to suspicion of oncology or if the procedure is done to determine the extent of the tumor. An MRI may be performed on an emergency basis. But it is better to agree on the exact date of the procedure with your doctor.
MRI of the pelvis, preparation for which in women is similar to the rules for men, with contrast does not require compliance with separate rules.
Deciphering the analysis and further actions
After completing the procedure, the specialist evaluates the resulting images and draws up a conclusion. Typically, pelvic MRI readings in women are performed on the same day. The images will accurately indicate the presence of both tumors and inflammatory processes, pathologies, blood flow disorders in the vessels, and injuries to the pelvic bones.
How long will the preparation and examination itself take?
The time of the procedure depends on the need to administer a contrast agent. If required, the duration may exceed 50 minutes.
The average preparation time is from 4 to 7 days. Additionally, the time depends on the menstrual cycle.
Alternative Methods
Due to the high cost of MRI, many people wonder whether there are alternative research methods. These diagnostic methods include ultrasound diagnostics and CT. However, compared to them, tomography has many advantages. First of all, ultrasound cannot provide such a complete picture of the disease as MRI, and computer methods have a serious minus radiation exposure to the patient.
The same amount of information as with magnetic tomography can only be obtained through hysteroscopy or laparoscopy, which examine the body through surgery. MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent allows you to non-invasively identify even the smallest formations, thereby increasing the chances of a complete recovery.
Side effects in women
The procedure is completely safe and does not harm human health. After an MRI, negative effects occur in 2% of 100 cases.
The following side effects are identified:
- itching and burning sensation;
- cough;
- feeling of suffocation;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- redness of the skin.
Most often, consequences appear when the procedure is carried out incorrectly or the preparatory rules are neglected.
Operating principle of MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging combines the best features of CT (this examination is called X-ray computed tomography) and ultrasound (ultrasound). Thanks to this, the use of pelvic MRI in women allows one to obtain detailed information regarding the condition of the bladder, rectum, ureters, uterus, ovaries, sigmoid colon, peritoneum, lymph nodes and other soft tissues.
In the field of gynecology, great attention is paid to the safety of the examination, since the woman’s health directly affects the development of the unborn child, even if the woman is not pregnant at the time of the medical examination. That is, the following requirements are imposed on diagnostic methods:
- safety;
- no x-ray exposure;
- high information content;
- non-invasive (non-surgical method) or minimally invasive.
Regarding radiation exposure, it should be noted that the use of diagnostic methods based on X-ray irradiation does not make it possible to carry out procedures frequently. Everyone knows very well that radiography and fluorography can be done no more than once every six months. But usually monitoring the patient’s health and the progress of treatment is required, and for this it is necessary to conduct examinations quite often. Only techniques that do not involve radiation exposure can help here. Magnetic resonance imaging is one of these methods. Using MRI of the pelvic organs, you can not only identify their current condition, but also give an accurate prognosis for the future.
The operating principle of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is based on the creation of a high-intensity electromagnetic field with a special configuration. This field creates radio frequency waves that are generated by the tomograph. An MRI machine consists of a movable table and a camera; its type can be closed or open. It contains magnetic coils that scan the desired area of the body. The subject is placed on the table in a supine position; the procedure takes an average of half an hour.
The images on the tomogram are obtained as follows. In the human body there are a huge number of hydrogen atoms, the nucleus of which is formed by a proton. These protons are constantly in motion, rotating around their axis. A magnetic resonance imaging scanner creates a high-power magnetic field, and under its influence, protons change their trajectory. After the device’s impact on a certain area stops, the protons return to their places, and energy is released. It is received by the tomograph coil, and the received information is processed on a computer. The amount of emitted energy depends on the density of the tissues: the denser they are, the more energy. A computer program, having received data on different energy values, can build a corresponding image.
Magnetic resonance imaging provides images of organs and tissues in the form of sections. Their thickness reaches 3 mm, they can be viewed from a variety of projections. Since the resulting data will be presented in digital form, it will be possible to subsequently study the condition of the pelvic organs and other parts of the body in more detail.
MRI prices
The cost of the procedure depends on the city and specific organization. The average price of a study is from 2000 to 6000 rubles.
The procedure is often prescribed by doctors to women to examine the pelvic organs. The study helps to identify pathologies at an early stage of development. MRI requires special preparation - proper nutrition, quitting smoking, and so on.
By following these measures, visualization of organs can be improved. Sometimes side effects occur after an MRI. This happens in 2% of cases if the doctor performed the procedure incorrectly or the woman was poorly prepared.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
MRI OMT with contrast: indications and contraindications
There are many indications for MRI; this type of diagnosis has improved the detection of pathology of the pelvic organs at an early stage
Indications for pelvic MRI with contrast include the following:
- the need to clarify the diagnosis in case of ambiguous data from previous diagnostic methods;
- tracking changes in dynamics;
- preoperative planning;
- suspicion of a pathological process in the pelvic organs.
Complaints that are considered as indications for MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast in a woman, taking into account the general clinical situation:
- absence of a desired pregnancy within 12 months, subject to regular sexual contact without contraception;
- dyspareunia (pain during intimacy);
- repeated self-termination of pregnancy with normal tests;
- the appearance of bloody discharge in the interval between regular menstruation, a change in its character: more abundant, scanty, with large blood clots, the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- pain in the lower abdomen of unknown etiology;
- dysfunction of urination: the need to strain, a feeling of incomplete emptying, urine mixed with blood, frequent urges, etc.;
- irregular bowel movements: diarrhea, constipation, bloating, bloody stool.
Common symptoms that are suspicious of a neoplastic process in the pelvic organs: weakness, fatigue, unexplained fever, sweating, weight loss, anemia. MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast is performed as part of the general diagnosis if changes in the hormonal background are detected: increase/decrease in FSH, LH, prolactin. According to indications, the search can be expanded: the brain (pituitary gland), which is responsible for the production of biologically active substances that regulate the functioning of the female reproductive system, is additionally examined.
Contraindications for MRI
The risk of MRI in some cases outweighs the benefits; before going to the clinic, read the contraindications
There are a number of contraindications to MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast:
- Metal objects in the body. Any implants with electrical, magnetic or mechanical activation (cardiac and neurostimulators, insulin pumps), cochlear devices, ferromagnetic clamps, brackets, orthopedic structures will cause artifacts to appear on the images during the procedure. There is a risk of failure of equipment providing vital functions. Metal shrapnel, shavings or a bullet under the influence of a magnetic field can begin to move, as a result of which neighboring tissues are injured. The intrauterine device, as a means of contraception, can also lead to image defects.
- Inability to remain still during pelvic MRI with contrast. Some neurological pathology (Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, etc.), psychiatric illnesses in the acute stage, severe curvature of the spine, severe pain are an obstacle to magnetic scanning. For tremors and obsessive movements, the examination can be performed after the administration of sedatives, which is also important for patients suffering from claustrophobia. Immersion in medicinal sleep is one of the ways out in this situation, but the issue is always resolved on an individual basis.
- Obesity. If you have a high body mass index, it will not be possible to do an MRI of the pelvic organs for technical reasons: too much weight (120 kg or more) will not allow the patient to move inside the device. For this category of people, scanning is performed on open-type tomographs, which significantly reduces the quality of diagnosis due to low power, or they resort to other testing methods. Sometimes it is recommended to follow a diet for 1.5-2 months in order to lose weight and undergo a full examination.
An MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast in a woman has an additional obstacle to performing: pregnancy in the first trimester. In world practice, there is no data on the teratogenic effect of a magnetic field on a developing embryo, but it is more rational to conduct research after the 12th week of gestation, when the main formation of organs and systems of the fetus is completed. According to vital indications, magnetic resonance scanning can be performed at any time. MRI of the pelvic organs helps in diagnosing intrauterine malformations of the fetus, but there must be compelling reasons for carrying out the procedure, for example, if ultrasound detects abnormalities that are suspicious of a serious pathology in both the mother and the unborn child. Compared to other research methods - cordocentesis, amniocentesis - magnetic resonance scanning has no side effects.
Diet before magnetic resonance imaging with contrast
An examination of a woman’s reproductive sphere is carried out when the bladder is filled with fluid. You need to drink about 1 liter of water an hour before the MRI procedure. If necessary, a cleansing enema is done no later than 4 hours. Cleansing the circulatory system is an important part of preparation. The distribution of gadolinium inside the arteries determines the structure of the wall and verifies the areas of deposition of atherosclerotic plaques.
Principles of diet before abdominal MRI
What not to eat before an MRI scan of the abdomen:
- Gas-forming drinks - milk, tannin, coffee;
- Products that provoke fermentation - black and white bread;
- Legumes – peas, beans;
- Fresh fruits are high in fiber.
You can eat food that is easily digestible and steamed. Raw fruits and vegetables provoke increased gas formation. It is better to treat with steam.
Diet before pelvic tomography - what you can eat:
- Dried bread;
- Stewed, boiled vegetables;
- Fish, lean meat;
- Kissels, compotes.
Taking enterosorbent medications will help improve digestion and reduce gas formation. Medicines prevent unwanted gastrointestinal motility.
Is it possible to take medications prescribed by a doctor before an MRI? The relevance of the answer requires a preliminary assessment of health status. Antispasmodics are allowed, enterosorbents are taken according to indications.
Can I drink alcohol while preparing for a pelvic MRI? The answer is negative. Refusal of alcoholic beverages 2 days before the study is an important rule of the preparatory stage. Ethyl alcohol changes the course of metabolic reactions, makes a person excited, which distorts the results of tomography.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Magnetic resonance imaging is carried out by technologists, photographs are interpreted by radiologists, and highly specialized specialists can also be involved in the examination process.
Before carrying out the procedure, you must remove from yourself all things and objects that may be attracted by the magnetic device of the tomograph (including metal buttons and fasteners, earrings, magnetic cards). Change into cotton clothes.
During the test, the patient is placed on a couch, the body is fixed using belts (during the procedure, you must lie absolutely still).
When diagnosing the pelvis in a closed tomograph, sedatives can be used.
During operation, the device produces certain sound effects (humming, clicking), to prevent the audibility of which you can use earplugs.
When the resonance tomograph begins to work, sensations of increased temperature appear in the pelvic area and the whole body. This condition is a normal reaction of the body to the operation of the electromagnetic field.
If there are indications for continuous administration of a contrast solution, an intravenous catheter is inserted into the patient, through which a contrast agent is automatically infused. Its entry into the body is accompanied by a cold or hot sensation that spreads with the bloodstream.
What does a pelvic MRI procedure reveal?
The range of pathological changes diagnosed through the study is wide. MRI images of the pelvic organs demonstrate:
- Tumor formations.
- Metastasis.
- Structural abnormalities of the pelvic organs, acquired or congenital. Pathological changes in the prostate, testicles and other structures.
- Endometriosis.
- Cystic formations.
- Pathological changes in blood vessels.
- Adhesions in the fallopian tubes.
- Inflammatory process.
- Various injuries to internal organs, surgical pathologies (for example, rupture of a cyst or ovary).
- Adenomyosis.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Bone tumors.
- Arthrosis, femoral neck fractures.
The procedure is non-invasive, that is, the study does not require violating the integrity of the tissue. Thanks to the high accuracy of the method, pathology is detected at the initial stages.