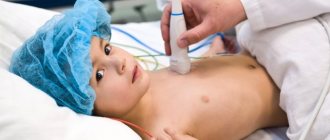
Otoscopy refers to methods for examining the ear - the external auditory canal, eardrum and tympanic cavity (in cases where perforation of the membrane occurs as a result of mechanical damage or a pathological process).
Otoscopy: indications
Otoscopy is a diagnostic procedure in otolaryngology. This is done using an otoscope. The technique is used to identify and treat diseases of the ear canal and eardrum. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to identify pathological changes in this area of the ear (as a rule, this concerns eczema or otitis media), as well as find a foreign object.
An otoscopy is performed by an otolaryngologist. In rare cases, a general doctor is allowed. If the situation is extreme, then the procedure will be performed by a worker from the ambulance team using a pocket device.
Indications for otoscopy are pathological changes. In particular, this applies to the following:
- Sulfur plug.
- Presence of purulent masses.
- Inflammatory processes and infectious damage to the eardrum.
- Injury to the eardrum (from various objects or during a blow to the head).
- Suspicion of eczema, otoscopy for otitis or other ear disease.
- Hearing impairment.
- Presence of bleeding from the ear.
- Pain and itching in the ears.
- The presence of a foreign object or suspicion of its presence.
- Rustling and splashing in the ears.
In addition, otoscopy is performed to evaluate the structure of the ear canal before making a hearing aid.
Ear diseases in dogs and cats
Ear diseases in dogs and cats - otitis - are very common and are a serious and multifaceted problem that requires comprehensive and consistent diagnosis.
What is the most common problem that a dog or cat owner faces? What symptoms require a veterinary examination?
- The animal shakes its head
- scratches his ears
- worries when ears are touched
- keeps his head tilted to one side
- Discharge and odor appear from the ears
- the skin of the external auditory canal turns red
- The animal becomes less active, its appetite decreases, and its temperature may rise—both local (the ears become hot) and body temperature.
Causes of otitis media
The causes of inflammation of the external auditory canal are varied, among them there are the main ones - primary, secondary and associated conditions. The veterinarian needs to find out what was the prerequisite for the development of otitis - parasitic infestations (Otodectosis, demodicosis), allergic reactions - adverse food reactions, contact allergies, atopic dermatitis), endocrine, immune-related diseases, foreign bodies in the ear canal, polyps, tumors. When making a diagnosis, the doctor also takes into account predisposing factors - the intensity of mechanical cleaning of the ears by the owner, the frequency of bathing, the shape of the ears, the thickness of the hair, and previous treatment.
A necessary condition for successful treatment is the cooperation of the doctor and the animal owner, the most complete information about the pet’s nutrition, the seasonality of ear problems, the frequency of treatments for external parasites (including the names of the drugs used).
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to examine the external auditory canal, otoscopy, scraping to exclude parasitic invasion, cytological examination - a stained smear of the contents, which allows you to find out what complicates the course of otitis - bacterial, fungal flora. Only on the basis of the data obtained is it possible to prescribe local or systemic drugs. Today, the range of drugs used is quite large and without carefully collected information, rational therapy for otitis media is impossible.
Endoscopic diagnostic method
An excellent diagnostic and treatment method for the treatment of otitis media is video otoscopy.
Otoscopy is an endoscopic diagnostic method that allows you to most effectively identify and differentiate diseases of the auditory canal. The procedure involves inserting a special instrument - an otoscope - into the external auditory canal. This endoscopic examination allows us to determine with a high degree of reliability various pathologies and ear diseases in dogs and cats:
- Inflammatory processes (otitis externa, middle ear, tumors, polyps).
- presence of foreign bodies (insects, plant seeds).
- damage to the eardrum.
- Allergic reactions, fungal infection.
- Causes of other types of pathology (vestibular syndrome, etc.).
Otoscopy is perhaps the only study that allows us to diagnose most of the listed problems in the early stages, which allows us to take timely preventive measures, as well as expertly select a set of treatment measures.
Otoscopy as a diagnostic procedure has no contraindications, is performed using anesthesia, and does not require complex preparation of the animal from the owners.
Only an appropriately qualified doctor in a clinic with specialized equipment can perform otoscopy!
Otoscope: what is it?
Previously, the examination was carried out with a regular funnel to widen the ear passage and a reflector, which the doctor wore on the forehead. The latter is required to display the light beam from the lamp and direct it directly to the inspected area. In modern hospitals, an otoscope is used for diagnosis.
It is a small device that an otolaryngologist uses in his practice. This is a device designed to examine the middle, external and internal parts of the hearing organ. An otoscope is a complex optical device that has the following structure:
- Long handle for comfortable holding of the device.
- Light source. It is xenon or halogen. More expensive devices use fiber optics.
- Cone-shaped tip. This is what is inserted into the ear canal.
Additional Information
No preparation for otoscopy is required. It is important to choose the appropriate size funnel (there are 6 sizes in total). When selecting the size, the doctor actively communicates with the patient. A funnel that is too wide provokes a cough and may cause discomfort.
After a preliminary examination, the doctor can remove any pus or buildup of earwax from the ear canal. If the wax is soft, the doctor removes it with an ear probe and cotton wool. If necessary, the outer passage is first washed to remove caked sulfur.
A pronounced bend of the anterior wall, covering the anterior quadrants, or bone growths (exostoses) can interfere with otoscopy.
In addition to the usual funnel and frontal reflector (a lens that concentrates light in the form of a “bunny”), you can use an otoscope. This is a medical device that has a light source and magnifying lenses in its head. When used, a disposable shell is placed on the distal (far) end of the otoscope for each patient.
The front lens can be removed if necessary, and instruments can be inserted through the device.
Kinds
Many models of otoscopes have been developed, which are divided into several types. The device itself is similar. The only difference is the presence of additional built-in devices.
The following types of otoscopes are distinguished:
- Diagnostic. An insufflator is installed on it. This is a special device that can be used to massage the eardrum.
- Operating. Has an open type of optics. In addition, special instruments are built in that may be needed during surgery.
- Pneumatic. This equipment accurately assesses the structure and condition of the eardrum and carries out tests. The housing is sealed.
- Portable. It has small dimensions, so it can even be stored in your pocket. This device is very convenient when traveling. A special clip is installed for fastening.
- With a camera. It has very small dimensions. Allows you to display an image on a monitor. Data can be recorded on any device.
These are the main types of device.
Preparation for otoscopy
Preparation for an otoscopy of the eardrum is carried out in the doctor's office. No preliminary measures are required from the person. The only thing is that it is prohibited to use any ear drops 3 hours before the procedure.
The doctor begins with an external examination. He determines whether there are contraindications or any obstacles to the procedure. This applies to trauma, severe swelling, and various congenital anomalies that make it impossible to insert the device into the ear canal.
Further preparation is as follows:
- processing of instruments for disinfection;
- elimination of sulfur plug;
- cleansing the ears of pus, dead cellular structures of epidermal particles - carried out if necessary;
- choosing an ear funnel depending on the diameter of the canal.
Normal otoscopic picture
During an otoscopic examination, the specialist collects some basic information about the condition of the ear canals and eardrum. By comparing this picture with the indicators accepted as the norm in this area, the doctor can judge the presence or absence of ear diseases. Ideally, during examination, the specialist observes the hairiness of the membranous-cartilaginous section and the presence of wax in the ears. The length of the external auditory canal should be about 2.5 centimeters. The eardrum itself has a pearlescent tint and is painted gray.
Typically, otoscopy should be preceded by external diagnostics, that is, an external examination of the ears and palpation to determine pain areas (if any). Doctors often complement this procedure and carry it out in combination with ear blowing, thereby examining the functions of the auditory tubes. Also, to complement the otoscopy picture, magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, computed tomography, audiometry are performed, bone and air conduction of the ears and the functionality of the hearing analyzer are examined.
The ear is one of the most sensitive organs of the human body. Often, when pathologies occur in the ears, simple medicinal methods are not enough, especially in cases where patients do not immediately seek help from specialists and self-medicate, delaying and aggravating the process. That’s why it’s important to see a doctor immediately if you have any problems with hearing, pain in the ears, or other symptoms.
Earwax is constantly secreted in the ears, an abundant flow of which can block the ear canal and cause plugs, which will ultimately lead to hearing loss (complete or partial). You cannot go deep into your ears on your own to remove wax plugs, since the eardrums are a very delicate matter that is easily damaged. Otolaryngologists remove plugs by washing them out under a pressure of water equal in degrees to the temperature of the human body. For this, a special syringe is used, which specifically delivers the flow and does not injure the eardrum.
Otoscopy is a method of medical visual examination of the external auditory canal and eardrum. If the membrane is perforated, the tympanic cavity can also be examined. Such an examination allows you to detect inflammation, accumulations of earwax, the presence of foreign bodies or pathological formations.
The study can be carried out using various medical devices: a simple ear specula and a head reflector (reflector), an otoscope (a device with a built-in light source and an optical system), a Siegle funnel (has an oblique cut angle and a lens, used to determine the mobility of the eardrum).
Cleaning Features
The ear canal is cleaned using two methods - dry or rinsing. In the first case, take a piece of cotton wool and smear it with Vaseline. They wrap it around an umbrella and wipe the walls so that pus, wax and other secretions are removed. The washing method involves using a Zhanne syringe. Warm water is drawn into it and injected into the cavity. When it is poured back, the area is dried with a cotton swab.
If the patient has a ruptured eardrum, then lavage is not performed. Otherwise, fluid may enter the middle ear, causing inflammation in it.
Rules
Otoscopy is a quick procedure. To examine the hearing organ, the doctor sits opposite the patient. His head is turned slightly in the opposite direction from the doctor. After this do the following:
- Select a funnel of the appropriate size.
- The concha of the ear is protruded upward and backward at the same time so that the ear canal is straightened.
- The funnel is heated to body temperature and then carefully inserted into the membranous cartilaginous area of the canal. It is forbidden to push it into the bone area, as this will cause pain. If the funnel is inserted incorrectly, it will rest against the walls of the ear canal.
- The doctor examines, moving the otoscope in the required direction. By the way, some people cough during these actions. This is due to the fact that the device acts on the vagus nerve.
- If necessary, puncture of the eardrum, microsurgical operation or removal of a foreign object is performed.
Otoscopes can be divided into “clinical” and “pocket”
Clinical otoscopes are equipped with a rheostat that allows you to adjust the level of illumination, a large glass lens, and a wide instrumental channel. Due to the presence of the listed options and a powerful feeding handle, this type of otoscope has a respectable size, weight and price.
Fortunately, you are unlikely to need a clinical otoscope - it is designed for intensive daily use, advanced diagnostics and instrument manipulation.
Unlike professional clinical practice, “home” diagnostics will be reduced to basic examinations :
- Examinations during illness, about one to two times a day;
- Detection of otitis media;
- Determining the type of otitis - catarrhal or purulent;
- Detection of wax plugs and foreign objects in the ear canal.
Pocket otoscopes of the E-scope series are suitable for basic diagnostics . These compact and inexpensive models were developed for family doctors, pediatricians and general practitioners. The body of the otoscopes is made of shock-resistant ABS plastic, which allows you not to worry about the safety of the device when traveling or when used at home. E-scope does not require expensive power supplies; it runs on two AA batteries. Pocket (A) and clinical (B) otoscopes.
In children
Carrying out ear otoscopy in children is practically no different from the “adult” procedure.
But there are a few key points to consider:
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to explain to the child all the actions, reassure him and indicate that everything will take place without pain.
- Parents or authorized representatives must be present with the child during the examination. The baby is placed in the arms, the legs are clamped with the knees, and the head is fixed on the chest. The hands also hold tightly.
- You will need funnels with smaller dimensions.
- The direction in which the ear concha is pulled back is different, which is the main feature. If in adults they pull up and back, then in a child they pull back and down at the same time.
How is it carried out?
When examining with any device, the patient's head is turned to the right or left at an angle of 900. After turning on the light, the doctor pulls the ear back up (in adults) or down (in children) with one hand, and carefully inserts the funnel with the other hand. Funnels are available in 3 standard sizes, their inner surface is matte. The examination provides the doctor with the following information:
- condition of the skin of the ear canal;
- condition of the walls;
- presence of pathological discharge;
- location of the tympanic membrane with identifying points - short process of the malleus, manubrium, umbilicus, anterior-posterior malleus fold, light cone.
If it is necessary to examine the mobility of the eardrum, a Siegle funnel is used, on the cone-shaped section of which a lens is installed. A canister is connected to the funnel, pressing which causes a vacuum of air inside the passage. Through the lens, the vibration amplitude of the membrane is clearly visible. This way you can determine not only the mobility, but also the elasticity of the scars, and perform a massage of the membrane.
Normally, the doctor sees the following picture:
- the skin inside the passage has hair;
- passage length 2.5 cm;
- there is a small amount of earwax;
- the membrane is not damaged, its color is grayish-pearlescent.
The cost of otoscopy in Moscow depends on the device used, the qualifications of the doctor and the complexity of the clinical case.