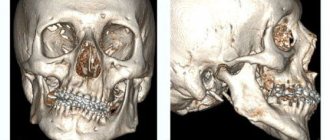
MRI of the jaw is a diagnostic method based on the phenomenon of magnetic resonance, which manifests itself when tissue is exposed to a magnetic field. It provides complete information about the condition of the organ, identifying its pathologies. In case of violations of the motor function of the jaw, an MRI of the temporomandibular joint is also done. What are these procedures, why are they prescribed, and how to properly prepare for them?
Indications for MRI of the jaw
Magnetic resonance imaging of the jaw and TMJ (temporomandibular joint) has the following indications:
- Swelling of half the face;
- Malocclusion;
- Bruxism (teeth grinding);
- Spasm of the masticatory muscles;
- Congenital dislocation of the TMJ;
- Acquired injuries and dislocations;
- Planning for facial surgery;
- Diagnosis before treatment of jaw injury;
- Preparation for prosthetics or implantation;
- Assessing the outcome of the operation and the effectiveness of treatment;
- Decreased range of jaw movements;
- Pain in the joint when opening and closing the mouth;
- Increased sensitivity or numbness in the chin, cheeks and temples;
- TMJ diseases: arthritis, gout, arthrosis, ankylosis (their symptoms are pain, clicking when opening the mouth, swelling of the face on the side of the affected joint).
The study is also prescribed for chronic diseases of the ENT organs (MRI of the throat and larynx), since they can be provoked by inflamed conditions of the joints or tooth roots. MRI of the temporomandibular joints is mandatory before surgery in maxillofacial surgery.
MRI of the jaw and maxillofacial joint is an expensive procedure. Therefore, it is carried out only when the results of other diagnostic methods turned out to be uninformative.
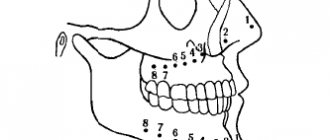
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the jaw joint
MRI shows a reducible dislocation.
The arrow indicates an intra-articular formation, which is displaced anteriorly when the jaws are closed (a) and returns to its place in the open position (b). An oral and maxillofacial surgeon will recommend an MRI of the jaw joint in preparation for several procedures:
- installation of implants;
- plastic surgery;
- dental prosthetics.
The doctor will prescribe an examination when there are such signs:
- pain when chewing;
- facial asymmetry;
- redness and increased temperature in the joint area (inflammatory processes);
- arthrosis;
- malocclusion;
- injuries of the lower and upper jaw, previous surgeries, etc.
The indication for the use of a contrast agent is a suspicion of a neoplasm for better visualization of soft tissues (muscles, ligaments, etc.). Repeated examinations are done to reflect the dynamics of the condition and the speed of recovery after interventions.
MRI of the jaw is highly informative and safe at any age. However, there are some exceptions. Scanning is not done during pregnancy in the 1st trimester, and then only under strict indications. For children, it can be performed as early as 4 weeks of age. In the diagnostic department, if there is a referral, the child is given an MRI from the age of 5, and with the introduction of contrast - from the age of 12.
You will be denied if your body weight exceeds 120 kg. This limitation is due to the technical features of the device: the device may not withstand more weight and may break.
MRI of the maxillary joint cannot be done in situations where:
- a pacemaker and other devices have been installed;
- there are metal foreign bodies not only in the face, but throughout the body (staples, stents, pins, etc.);
- systems that support the patient’s life are used (hemodialysis, artificial ventilation, etc.).
Metal objects in the body are not always an obstacle to performing the test. If the alloy is non-magnetic, it will not affect the process in any way.
Restrictions to enhanced scanning are:
- allergic reactions to a contrast agent;
- end-stage renal failure.
The doctor will determine whether you need an examination; he will assess the presence of contraindications and indicate the timing of your return to monitor the dynamics.
What pathologies can the examination reveal?
Magnetic resonance imaging takes high-quality layer-by-layer images in various planes. It clearly visualizes the structure of the jaw and mandibular joint, helping to determine the condition of the articular tubercle, head, fossa and cartilage, as well as the soft tissues of the face.
Pathologies that MRI will show:
- Erosion of cartilage tissue;
- Excess synovial fluid in the TMJ cavity;
- Displacement of the articular disc relative to the head of the mandibular bone;
- Inflammatory diseases of bone and soft tissues of the face;
- Anomalies in the structure of the dentition that affect the formation of the bite;
- Tumors and tissue destruction caused by them;
- Bone changes due to injuries and degenerative processes.
A special feature of this examination method is the possibility of dynamic scanning, when the patient opens and closes his mouth while inside the MRI machine. This helps in identifying ligament pathologies, causes of disc displacement and assessing the contractility of the muscular apparatus of the jaw.
How to prepare for the procedure
One of the important advantages of magnetic tomography is the lack of preliminary preparation and adherence to a certain diet.
Before the examination itself, it will be necessary to deposit all personal items containing metal: keys, glasses, belt, bracelets, rings, chains, bank cards, remove piercings and dentures. Such objects may affect the operation of the magnet. The doctor must be warned about the presence of tattoos, braces or fillings, as they may become hot during diagnosis and cause discomfort to the patient.
If your clothing has metal buttons, zippers, or buckles, you will most likely be asked to change into a hospital gown.
If necessary, contrast, sedatives, local anesthesia or anesthesia are administered.
How does the procedure work?
You cannot move during an MRI scan. Otherwise the picture will turn out blurry. With an MRI of only the temporomandibular joints, you will have to remain motionless for 15-20 minutes, and with an MRI of the jaw and the entire face - up to 1 hour. How can a patient prepare for the procedure, and what awaits him inside the device?
Is preparation required?
An MRI examination does not require special preparation, nor does an examination of the nose and sinuses. The patient only needs to remove all things made of metal: it interacts with the magnetic field of the device and distorts the picture. Diagnosis may be hindered by:
- Glasses;
- Hairpins;
- Jewelry and watches;
- Underwires in women's bras;
- Zippers, buttons and metal decor of clothing;
- Mobile phone, bank cards, etc.
If MRI in the presence of metal objects is unacceptable, is it possible to perform the procedure on patients with metal and metal-ceramic crowns, pins and stump inlays, implants? Yes, their presence is not a reason to abandon the most informative diagnostic method. But the doctor must be warned about this. It is better if you take an X-ray of the jaw in advance and bring the photo to the diagnostic office. But usually dentures and braces do not pose obstacles to MRI, since they are made of materials that do not interact with the magnetic field.
Sometimes patients experience fear before the procedure. In such a situation, it is recommended to take a sedative in advance. But it should not have a hypnotic effect: during MRI of the mandibular joints, you will have to listen and follow the doctor’s instructions.
Methodology
The patient is asked to lie on the MRI table with his back down. His head is placed within the range of the device’s magnetic coils and fixed so that it remains motionless during the procedure. Then:
- Images are taken in the oblique frontal and oblique sagittal planes with the mouth closed. This procedure takes one minute. It will take the same amount of time to get an image of the second joint.
- Pictures are taken in an oblique sagittal projection with the mouth slightly open (another minute for each mandibular joint). When opening the mouth slightly, the patient should not push the lower jaw forward.
- The TMJ is scanned with the mouth very wide open. To do this, you will have to lower the lower jaw as far as possible and move it forward (a minute for each joint).
- With an MRI of the jaw, it will take some more time to scan the soft tissues in different planes.
During the diagnostic process, a loud noise is produced. Earplugs are permitted to protect your ears. If noise-reducing headphones are available in the exam room, the patient will be asked to wear them.
Application of contrast agent
To obtain clearer images of the jaw, magnetic resonance imaging with contrast is performed. This means that before scanning the mandibular joints, the patient is intravenously injected with a contrast agent - a coloring liquid based on the metal Gadolinium, which has no contraindications, does not cause allergies and is quickly eliminated from the body.
MRI of the jaw with contrast allows you to see tumors with a diameter of 1 mm, which significantly increases the information content of the study. This diagnosis is prescribed for suspected cancer.
How is an MRI of the temporomandibular joint done?
MRI image of the TMJ and anatomy of the joint
No special preparation is needed before MRI. The patient is allowed to eat. If an enhanced scan is being done, a light snack 40-45 minutes before will help reduce signs of activation of the autonomic nervous system after drug administration (increased salivation, feeling hot, dizziness). We advise you to approach the office 10-15 minutes in advance so that you can slowly remove all metal objects (earrings, hairpins, etc.). The latter is necessary so that the images are not distorted and are informative.
The child should describe in detail the process and what sounds he will hear. One of the parents can remain in the tomograph room during the entire procedure to communicate with the baby and reassure him.
The examination begins with a short preparation-instruction, then the person is placed on a mobile table. The patient is secured with straps to ensure complete immobility during the procedure. Next, the table is placed inside the ring of the device. Medical workers leave the premises, but maintain contact using a radio transmitter.
With MRI with contrast, a native image of the jaw joint is first taken, after which a special drug is injected intravenously. The dose is calculated individually by weight. The contrast agent, quickly leaving the bloodstream, is distributed in the intercellular space. Enhanced tomography will more reliably detect soft tissue pathology and the presence of tumors.
A feeling of fear may arise in a confined space. Therefore, if you have claustrophobia, tell your doctor before having the procedure. Specialists will select a sedative or sedative drug. It is possible to perform an MRI under general anesthesia, but only in a hospital setting.
Advantages of the magnetic resonance imaging method for examining the jaw
MRI of the jaw and its joints has the following advantages over computed tomography of the facial area and head:
- No exposure. The patient's body is not penetrated by X-rays; only the magnetic field affects the tissues;
- High-quality images due to the sensitivity of the device to various types of cells;
- The ability to improve the quality of images by introducing a contrast agent into the body;
- Possibility of obtaining three-dimensional images of the jaw and mandibular joints;
- Both hard and soft tissues are equally visible.
Magnetic resonance imaging has only one drawback - the high cost of the procedure. However, the legislation provides for certain cases when diagnostics are carried out free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
What an MRI of the jaw shows cannot be shown by radiography, which only gives a general idea of TMJ diseases. Therefore, if it is possible to choose between these studies, preference should be given to MRI, especially if the doctor insists on this diagnostic method.
Duration of the procedure
MR diagnostics of one zone of the maxillofacial region on a closed-type tomograph generating a voltage of 1.5 Tesla takes 10 minutes.
An examination using an open tomograph with a lower magnetic field voltage will require the patient to remain motionless in the device for 30 minutes.
An ultra-high-field tomograph will complete the examination in 5 minutes.
MRI with contrast will increase the examination time by 2 times, regardless of the magnetic field voltage of the tomograph, since the procedure takes place in 2 stages.
Contraindications
MRI of the jaw has only one absolute contraindication - the presence of a pacemaker. The procedure in this case may pose a threat to the patient’s life.
Relative contraindications are as follows:
- Epilepsy;
- Age less than 5 years;
- Pregnancy and lactation period;
- Extreme obesity;
- Kidney dysfunction;
- Claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces).
Relative contraindications are cases where MRI is not advisable. But the procedure is possible if the doctor deems it necessary.
Difficulties during the diagnostic procedure may arise in the presence of metal inclusions in the mouth: metal pins, stump inlays, implants, crowns, bridges and braces. The patient should check with his dentist in advance whether an MRI with such structures is acceptable. Modern materials for prosthetics are not ferromagnetic, but it is necessary to ensure that there is no danger.
Contraindications for the study
Magnetic resonance imaging, unlike computed tomography, is prohibited for patients with electrical or metal implants (for example, middle ear hearing aids, artificial pacemakers, endoprostheses, etc.). The magnetic field can disrupt the operation of such devices and lead to undesirable consequences for human health.
As for metal products, they can heat up during the procedure and cause the appearance of “artifacts” on the equipment screen, thereby complicating diagnosis. MRI of the maxillofacial joint in the presence of braces and metal crowns is only possible if they are made of materials that do not respond to magnetic waves.
Specially synthesized polymers and titanium have these properties. But before doing an MRI of your teeth, it is better to consult with your doctor, who will determine its feasibility and safety. Some of the relative contraindications include increased body weight (more than 130 kg) and claustrophobia. An alternative, if you are afraid of closed spaces, are open-type tomographs.
The weight limit is individual for each specific device
The use of contrast during the procedure is contraindicated for pregnant and nursing mothers, people with severe renal and liver failure, or a history of allergies to dyes.
Cost of the procedure
The cost of MRI of the jaw depends on the newness of the device, the number of joints scanned and the list of additional services. Here are the average prices (in rubles):
- MRI of one temporomandibular joint – 5,000;
- MRI of two joints – 6,000;
- Scanning of the jaw with functional tests (1 joint) – 8,000;
- Scanning of the jaw with functional tests (2 joints) – 10,000;
- Contrast (10-20 ml of substance) – plus 2,000-4,000 to the cost of MRI;
- Saving images to disk – plus 500 for diagnostics;
- Recording pictures on a flash drive – plus 1,000.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the upper and lower jaws is the safest and most informative diagnostic study. It detects not only TMJ pathologies, but also soft tissue diseases, as well as gumboils, cysts and tumors. MRI of the jaw and mandibular joints has virtually no contraindications and allows you to choose the most effective treatment methods.
MRI of the temporomandibular joints with functional testing
On MRI of the TMJ there is a “stuck disc” (a - open mouth, b - closed).
The arrow indicates the posterior surface of the cartilaginous formation, which, regardless of movements, remains in the mandibular fossa. If the TMJ is affected, an MRI is performed with functional tests in the following positions: with the mouth closed, slightly open and completely open. This approach allows you to visualize the entire movement process in different projections. Using the results obtained, the doctor will understand at what point the failure occurs.
Normally, the bones do not touch, but pathological mobility of the disc leads to friction and pain. The latter can change position in various directions, the most common being anterior displacement.
An example of another pathology that functional tests help to establish is fixed, intermittent dislocation and subluxation. The specialist will see in the image with the mouth closed the displacement of the intra-articular formation, and in the open state it will return to its place. The described result will indicate intermittent dislocation of the jaw joint.