Home » Colonoscopy » Can a woman have a colonoscopy during pregnancy - and in what cases?
April 27, 2020 Colonoscopy
Pregnancy is a state of the body when restrictions or even prohibitions are imposed on the use of a number of medications and the performance of certain medical procedures. Let's figure out whether it is possible to do a colonoscopy during pregnancy - that is, an examination of the intestines using an endoscope with an optical device inserted into the body through the anus.
What it is
This is a procedure that is prescribed if it is necessary to examine the condition of the intestinal mucosa of the expectant mother.
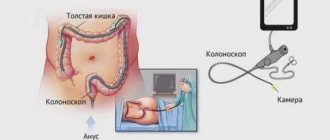
For the study, a special tube is used - an endoscope. It is carried through the anal sphincter into the pregnant woman's body. As a result, it is possible to study the features of the condition of the mucous membrane, its anatomical structure, and diagnose possible adhesions and neoplasms.
Only a proctologist for pregnant women can tell about the need for manipulations. Colonoscopy when carrying a child is prescribed quite rarely and only in case of urgent need. You cannot decide to undergo this examination on your own.
Is it possible to have a colonoscopy during pregnancy?
Colonoscopy refers to an endoscopic type of examination, during which the condition of the intestinal mucosa is assessed. The pregnancy period is a long-awaited and wonderful moment for every woman. At this time, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health, since the female body works for two.
Indications for use
Colonoscopy is an instrumental examination of the colon and rectum from the inside, designed to identify any abnormalities in the structure and collect biomaterial for histological analysis of the affected area.
Compared to other diagnostic measures, the procedure has a number of advantages, namely:
- high information content;
- relative safety;
- no harmful radiation.
This type of study is prescribed by a proctologist or gastroenterologist based on the totality of the patient’s characteristic symptoms:
- abdominal pain of various localizations;
- bleeding from the rectum;
- prolonged constipation, diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- loss of appetite;
- weaknesses;
- rapid weight loss;
- increased cancer markers in tests;
- changes in the leukocyte blood count.
How is it carried out?
Before the procedure begins, the person will be offered one of the following techniques to reduce pain:
- Sedation. It is carried out using special drugs that introduce the patient into a state of superficial sleep. He does not feel pain or discomfort, but is conscious.
- Local anesthesia. Allows you to reduce discomfort with the help of special gels with lidocaine, which are used to lubricate the tip of the endoscope. Sometimes the substance is administered through a vein.
- General anesthesia. More often used when examining children, people with a low pain threshold or mental disorders.
During the examination (15-30 minutes), the patient takes a lying position and presses his knees to his chest. When all the preparatory stages are completed, the specialist inserts a flexible probe (endoscope) equipped with a tip with a video camera through the patient’s anus. Due to the supply of air, the intestinal walls move apart and allow the device to carefully move forward.
If the examination was carried out successfully, then no complaints should be observed, except for slight discomfort in the anus area.
In this case, you will need to consult a doctor, sometimes hospitalization
SOURCES: https://proskopiyu.ru/kolonoskopiya/mozhno-li-delat-kolonoskopiyu-pri-beremennosti.html https://vospaleniekishechnika.life/diagnostika/mozhno-li-pri-beremennosti-delat-kolonoskopiyu.html https: //diagnostinfo.ru/skopiya/colonoscopy/kolonoskopiya-pri-beremennosti.html
Source: https://uzibook.ru/kolonoskopiya/mozhno-li-delat-kolonoskopiyu-pri-beremennosti.html
Goals
The main goal is to study the condition of the epithelium of the mucous membranes that line the cavity of the intestinal tube. The main goals of this examination method:
- study of the characteristics of the mucous membrane;
- individual anatomical features;
- diagnosing adhesive processes in the lumens;
- detection of tumor neoplasms of both benign and malignant nature.
Colonoscopy is usually prescribed for those who already have a history of chronic bowel disease. Examination of a woman can be either planned or emergency. This depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the well-being of the pregnant woman.
Colonoscopy during pregnancy
As a rule, pregnant women rarely need a colonoscopy. This study is carried out only when necessary, especially in pregnant women and while breastfeeding. But sometimes there is a need to perform a colonoscopy in such patients.
Often, the basis for a colonoscopy is a suspicion of colon cancer. There is an opinion that this disease is typical only for males, but this is not so. According to statistics, among the cancers that occur in women, about 40% are colorectal cancer. Based on this, colonoscopy becomes a necessary measure for the fair half.
Colonoscopy in a pregnant woman
It must be understood that there must be compelling reasons to conduct such a study. Pregnancy is not an absolute contraindication.
An indication for colonoscopy may be, for example, if the expectant mother has a history of nonspecific ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. In this case, a study must be carried out so that a specialist can differentiate a disruption of normal intestinal function from an exacerbation of a chronic disease.
For various lesions of the large intestine, the doctor may prescribe diagnostic methods such as x-rays with a contrast agent (irrigoscopy), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and diagnostic laparoscopy. In this case, it is worth understanding that none of these methods are allowed to be prescribed to pregnant women.
The contrast agent, in fact, has a radioactive effect, albeit small. When it is introduced into the intestines, it is located as close as possible to the fetus, not to mention the fact that X-ray exposure in itself is harmful to the baby. MRI is also contraindicated in pregnant women due to the strong magnetic field.
Laparoscopy, after all, is a type of surgical intervention, which is also harmful in the case of pregnancy.
However, it does not follow from the above that it is better to prescribe a colonoscopy than any other research method. Any procedure is prescribed only if its usefulness greatly exceeds the possible risks to the body.
The question of whether a pregnant woman needs a colonoscopy is decided individually
Colonoscopy in pregnant women is performed only under strict indications!
In the case of colonoscopy in pregnant women, it must be done under local anesthesia, eliminating systemic effects on the body of the expectant mother and fetus.
It must be said that pregnant patients are allowed to undergo colonoscopy, especially if they have a history of chronic intestinal diseases. Patients should always remember this.
The study itself does not pose a significant danger to the woman’s body and the developing fetus.
Anesthesia can be a threat, but it was already said above that in the case of pregnant women, a local type of anesthetic is used, which is less harmful.
The necessity of life forces us to take extreme measures. For your future health, it is extremely important to undergo a timely examination so that there are no sad consequences in the future.
Preparation for colonoscopy
If a colonoscopy has been scheduled, it is important to prepare for it properly. When this procedure is prescribed in a hospital setting, there is no need to worry about any preparatory operations. You need to rely on all the manipulations that the doctors will carry out.
Your doctor will tell you about your diet before a colonoscopy.
Preparation for a colonoscopy begins long before the procedure - with an appropriate diet.
A pregnant woman's diet will most likely already exclude citrus fruits, strong coffee and tea, as well as some other foods that may interfere with the study.
You should also refrain from eating foods that cause fermentation (beans, nuts, raisins, carbonated drinks, brown bread, carrots, beets, etc.).
The next stage of preparing the body is cleansing the intestines. This can be done either with an enema or with laxatives. Both options carry both advantages and possible contraindications.
A cleansing enema is usually not prescribed in late pregnancy due to the risk of causing premature labor. Laxatives are also dangerous because they stimulate bowel activity, which can cause miscarriage.
The choice of a specific cleansing method should not be made independently.
After the procedure, you can almost immediately return to your usual rhythm of life and normal diet. If any unpleasant sensations suddenly arise, they should not linger for long.
Whether it is possible to have a colonoscopy during pregnancy is a rather controversial and debatable issue. It is best to do it when there are no other diagnostic methods and the benefits outweigh the possible risks for both mother and child.
Source: https://diagnostinfo.ru/skopiya/colonoscopy/kolonoskopiya-pri-beremennosti.html
When is it appointed?
There are a number of indications for the examination. These include:
- the appearance of bleeding from the anus;
- detection of blood impurities in the stool of a pregnant woman;
- various stool disorders that do not normalize while taking medications;
- chronic feeling of fatigue and constant weakness;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- diagnosed anemia;
- pain in the abdominal cavity;
- constant feeling of bloating;
- chronic diseases that were diagnosed before pregnancy;
- suspicion of a malignant neoplasm;
- hereditary predisposition to diffuse polyposis.
How to prepare
To obtain reliable research results, it is very important to properly prepare for the procedure.
Preliminary preparation for examination during the perinatal period first of all includes a very thorough cleansing of the intestines from feces. It includes:
- following a special diet 3 days before the event;
- cleaning with enemas and laxatives.
Before the endoscope examination begins, the pregnant woman is administered approved anesthetic drugs. They reduce discomfort. In addition, doctors use special agents that reduce muscle spasms.
It is recommended that expectant mothers, a few days before a colonoscopy, exclude from their diet foods that cause excessive gas formation and stool disorders. On the day when the study will be carried out, it is possible to consume only low-fat broths and still water.
If the intestinal lumen is not cleared, it will be impossible to obtain an objective picture of its condition.
How is it carried out?
A woman must undress completely from the waist down, lie on her side and bend her knees. The doctor inserts an endoscope into the intestinal lumen through the anal sphincter. At this point, she may feel discomfort or slight pain.
If necessary, during the examination the patient may be asked to change position and turn to the other side. If discomfort persists after the procedure, the doctor may suggest No-shpa. As a rule, the entire study takes no more than 20 minutes.
Possible complications
Colonoscopy during pregnancy, especially in the early stages, can cause complications. These include:
- the occurrence of individual allergic reactions to anesthetic drugs;
- increased bleeding;
- violation of the integrity of the wall.
For a woman who is carrying a child, this list can be expanded with the following points:
- increased uterine tone;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina;
- general malaise.
If during the manipulations a woman feels sharp pain or deterioration in her health, then she should immediately tell the doctor who is conducting the examination about this.
Features of colonoscopy in pregnant women
During pregnancy, women may develop or worsen intestinal diseases. Colonoscopy, despite its unpleasantness for the patient, is one of the safest examination methods provided that the following criteria are met:
- Correct assessment of possible risks and indications for diagnostics.
- Necessary preparation of the patient for endoscopy.
- Compliance with the examination methodology.
During pregnancy, computed tomography (CT) scans and contrast-enhanced x-rays to examine the bowel are highly undesirable due to exposure to radiation during imaging and the toxicity of the injected barium.
However, colonoscopy during pregnancy is also not an absolutely safe procedure. During the examination, it is necessary to administer anesthesia or even anesthesia, which may adversely affect the child.
Sedatives that put the patient to sleep during the diagnostic procedure can cause a lack of oxygen for the fetus (hypoxia) and reduce its blood pressure. This is also caused by the woman's prolonged position on her back, which is necessary for inserting a colonoscope. In this case, the uterus, under the influence of gravity, will be pressed against the back wall of the pelvis and compress the blood vessels, in particular the inferior vena cava, which nourishes the abdominal organs and is involved in the blood supply to the developing child.
In the early stages (in the first trimester), when the main organs and systems of the fetus begin to develop, unjustified intervention can lead to internal bleeding or miscarriage. In this regard, the study is postponed to the second trimester, when there is practically no danger to the child. However, this does not apply to emergency colonoscopy, which is necessary if there is a significant threat to the life and health of the mother.
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the introduction of a colonoscope can provoke premature contractions, so if possible, the procedure is postponed until the postpartum period.
Contraindications
Research is not for everyone. It has a whole list of contraindications. These include:
- the presence of pathologies and diseases of the respiratory tract, in particular the lungs, in the expectant mother;
- diagnosed cardiac ischemia;
- heart disease of varying severity;
- heart rhythm disturbances.
As a rule, the very presence of pregnancy is a contraindication to colonoscopy. However, if the risk to a woman’s life and health is higher than the possible risk from the study, then a colonoscopy is performed even during pregnancy.
If a pregnant woman has the above pathologies and diseases, then it is imperative to inform the doctor about them. He will be able to choose an alternative diagnostic method.
What the results say
During the examination using the procedure, the doctor can diagnose many serious pathologies. These include:
- tumor processes;
- ulcers;
- cystic processes;
- adhesions;
- inflammatory diseases.
Based on the data obtained, the specialist can draw up a detailed picture of the disease. Accurate and timely diagnosis significantly reduces the risk of negative consequences and increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Colonoscopy during pregnancy is performed only for serious medical reasons. Many pathologies of the intestinal tube are dangerous not only due to unpleasant sensations, but also to a high risk of death. Correct and timely diagnosis reduces the likelihood of negative consequences.
Inserting an endoscope into the intestines during pregnancy requires extreme caution and attention from the doctor.
The procedure has a number of contraindications, which you must familiarize yourself with before starting it. If a woman has at least one of the limitations, then it is better to give preference to an alternative diagnostic method.
Progress of manipulation
On the day of the diagnostic and treatment procedure, it is important to decide on anesthesia for the pregnant woman. Unfortunately, there are no absolutely safe means for sedation during pregnancy, but doctors resort only to those that significantly reduce the risks of intoxication and teratogenic effects on the growing fetus.
The following drugs are commonly used:
- Diazepam - can only be used in the second trimester of pregnancy;
- Midazolam - used in the first trimester of the gestational period;
- Propofol is used most often at all stages of pregnancy, but under the supervision of an anesthesiologist.
The latter drug is preferable for pregnant women, as it has undergone numerous clinical studies. A nurse and an anesthesiologist-resuscitator must be present in the office during the study.
The clinic where the manipulation is performed must be equipped with intensive care wards and wards for temporary stay.
After all the preparatory manipulations, the procedure begins:
- The woman lies down on her side on the couch;
- The doctor administers anesthesia;
- The anus is treated with an antiseptic;
- Using a colonoscope, a little air is pumped in to expand the intestines;
- The doctor inserts a probe and conducts a study.
During the procedure, doctors continuously monitor the patient’s hemodynamics and breathing. Additionally, a sensor can be connected to assess the fetal heartbeat. Medical management of the woman is carried out from the beginning of the manipulation until she is completely removed from the state of anesthesia.
If necessary during the study:
- polyps are removed
- stop bleeding,
- A biopsy is taken for histological examination.
At the end of the procedure, the woman is moved to a temporary ward, where she is regularly monitored until she is fully conscious.