What is a colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is a painless method of examining the large intestine from the inside. The study is carried out using a flexible, thin and long hose, which is equipped with light and optics. This device is called an endoscope.
Advanced models are equipped with built-in mini-cameras at the end and a device for taking biopsies. With their help, images of the insides of the large intestine are recorded and tissue is taken for analysis. Then the pictures are displayed on the screen, studied in detail and deciphered. Photos can be saved on digital media. Before performing a diagnosis, preparation is required.
Advantages of the method using anesthesia
Previously, the examination took place without anesthesia and was very painful. Now these sensations are warned in advance and the person does not experience negative sensations. After the procedure, he doesn’t even have any unpleasant memories.
This method is especially relevant for children, people with diseases of the large intestine or a low sensitivity threshold. Diagnostics can detect cancer in its early stages. During the study, polyps are removed, eliminating the need for surgery for the patient.
During the procedure, the doctor can stop minor bleeding and take tumor tissue for analysis. The examination also helps prescribe optimal treatment without surgery.
Colonoscopy in a dream: pros and cons
Colonoscopy is an internal examination of the large intestine using a special probe with a video camera.
This approach makes it possible to identify serious pathologies at the initial stage of development. It is carried out for the purpose of visual inspection, qualitative examination of tissues; during the procedure, biological material is taken from the sites of damage for examination (biopsy). The procedure allows you to remove benign neoplasms - polyps, which create a risk of malignant tissue degeneration. Internal examination of the intestine using a colonoscope due to the mechanical effect on the intestine is associated with unpleasant sensations for the patient. Opening of the intestinal lumen is achieved using a small stream of air. The degree of discomfort depends on a number of factors:
- individual manifestations of pain syndrome associated with the characteristics of the nervous system;
- psychological tension and emotional state of the patient;
- the presence of intestinal diseases that contribute to increased pain.
Taking into account the features, colonoscopy is done with varying degrees of anesthesia, using:
- gel anesthetics, which are applied locally to the intestinal epithelium during the movement of the probe;
- sedation, introducing the patient into a controlled state of superficial sleep, in which painful sensations do not cause physical discomfort;
- general anesthesia, is often used when complex endoscopic procedures are necessary and when large areas of the intestine are damaged, if there is a possibility of insufficient pain relief during sedation.
Sedation is considered the best option for colonoscopy. Young patients easily tolerate the examination under local anesthesia and report minimal discomfort.
If, according to the diagnostician, the procedure will be accompanied by anxiety of the patient, anesthesia is definitely recommended. It is necessary to ensure not only the patient’s comfortable condition, but also calm conditions for one’s own work, during which there will be no need to be distracted by complaints. With sedation and general anesthesia, complete relaxation of the muscular layer of the intestine is achieved, and the risk of mechanical traumatic damage and perforation of its walls is much less.
If the center strongly recommended sedation during your examination, you should agree to this procedure option, despite the increased cost of the service. As a rule, people with a low pain sensitivity threshold are immersed in a state of shallow sleep.
What types of anesthesia are used?
Colonoscopy can be performed using three methods. First, it is determined whether or not there are allergic reactions to certain drugs, and the type of anesthetic drugs is selected.
Sedation method
General or local anesthesia is not necessary for colonoscopy. A sedation method can be used, which uses the drugs Metazolam or Propofol. They act the same as anesthesia. The person falls into a medicated sleep and feels nothing. However, the sedation method has polar sides. The advantages of the method include:
- The patient does not fall asleep completely, but finds himself in a state of half-asleep. The body is so relaxed that it does not feel pain. However, a person hears everything and can even respond to the doctor’s requests to change position.
- "Metazolam" erases any memories of the procedure from the memory, but the person then wakes up for a very long time.
- After Propofol, the patient, on the contrary, remembers everything. At the same time, he wakes up very quickly.
- The person does not connect to the machines and breathes on his own.
The disadvantages include possible allergic reactions to the drug, and the risk of side effects increases. The doctor has difficulty determining the patient’s sensations, since pain is completely absent.
Local anesthesia
If local anesthesia is used, pain relief occurs as the probe advances, onto the tip of which a special drug is applied that reduces the excitability of nerve endings. However, it does not completely suppress them, so the painful sensations are only partially eliminated. The person experiences some degree of inconvenience. Despite the unpleasant moments, the procedure as a whole is much easier to tolerate than without anesthetics at all.
General anesthesia
With the help of general anesthesia, a person’s consciousness is completely switched off. The patient falls into deep sleep, sees, hears and feels nothing. This is the perfect barrier against pain. However, general anesthesia is not suitable for everyone.
Pros of colonoscopy under sedation
In addition to the fact that the patient is completely free from pain and discomfort, as well as shame and fear, he is not exposed to the risks of general anesthesia. But there are also factors for the diagnostician and the patient being examined, the better the procedure under anesthesia:
- Young children may become very frightened and behave in such a way that they may forget about the examination. In addition, the painful procedure is too stressful for the child. Therefore, for them, colonoscopy is only performed with sedation;
- Patients of any age, due to a complex of negative sensations (fear, shame, pain, etc.), are very pinched. This leads to difficulties when inserting the device and negative sensations;
- Sometimes, due to severe pain, the colonoscopy has to be stopped halfway;
- When using sedation, a person understands everything; the doctor may ask him to turn over several times in order to freely pass difficult parts of the intestine. In a state of stress due to negative emotions, the patient ceases to adequately perceive the doctor’s requests, and work becomes very difficult;
- Many intestinal pathologies progress under the influence of stress. Therefore, the lack of pain relief leads to exacerbation of chronic problems;
- Uncontrollable flinching from pain is dangerous due to injury to the wall by the tip of the colonoscope; when using anesthesia, the risk of injury is negligible;
- Under anesthesia, the diagnosis takes less time, since the coloproctologist does not have to be distracted by the person’s reactions.
To put it simply, colonoscopy under sedation does not hurt the patient, and it is convenient for the doctor to work. Therefore, anesthesia helps to obtain a reliable diagnostic result with minimal complications.
Despite the undeniable advantages of sedation, colonoscopy without anesthesia, according to reviews from patients and doctors, in 8 out of 10 cases passes without problems or complications. Therefore, you should not exclude this option altogether.
Indications
Colonoscopy is indicated for people over 45 years of age and in the presence of intestinal cancer. Routine diagnostics are carried out for patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn's pathology. The examination should be done for people whose relatives were found to have polyps or colon cancer. Diagnostics is also indicated for:
- anemia;
- bloating;
- excessive fatigue and sudden weight loss;
- general weakness and lack of appetite;
- diarrhea;
- pain in the abdomen and intestines;
- mucus discharge from the anus;
- constant constipation;
- bleeding;
- polyps on the intestinal walls;
- genetic predisposition to cancer.
For the listed indications, diagnosis can be carried out both with and without anesthesia. Anesthesia is necessary if the examination is performed on young children under 12 years of age, as well as for:
- Patients with intestinal adhesions. They appear after surgical operations, during peritonitis, which was caused by gynecological pathologies or as a complication after surgery. Adhesions interfere with the advancement of the probe. As a result, the pain syndrome increases significantly.
- People with destructive intestinal changes.
- Patients who have very low sensitivity. In them, even mild pain can provoke loss of consciousness and disrupt the functioning of the body.
Anesthesia is indicated for a number of diseases or the appearance of neoplasms, the localization of which is near the intestines. In this case, the patient may experience severe pain without anesthesia. Diagnosis is mandatory for people whose tumor has been excised.
The examination is done to prevent relapse. After 50 years, colonoscopy is carried out as planned. At this age, the risk of various diseases increases significantly.
Important!
Diagnosis is carried out for hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and all women who are scheduled for surgery in the pelvic area (in particular on the uterus, ovaries).
Alternative laboratory methods
Colonoscopy with sedation is not the only way to examine the condition of the inner walls of the intestine. Therefore, if you do not want interference in your body or are afraid to plunge into a state of sleep, then there are alternative options. These are:
- Capsule endoscopy. An innovative method that is highly effective. It is based on the introduction into the colon of a special small device equipped with a camera. Carrying out such a procedure does not cause the patient any discomfort or pain. Also, the likelihood of injury to the mucous membrane is minimized. A few hours after insertion, the probe is removed from the body naturally. After this, the recorded information is removed from the integrated drive and the results are decrypted. However, capsule endoscopy is not available in all medical institutions, and its cost is prohibitive.
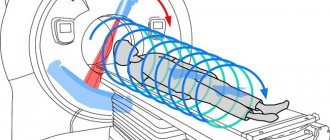
- Magnetic resonance imaging. This type of research is considered one of the best. It allows doctors not only to diagnose various diseases at the primary stage of development, but also to determine their etiology, as well as get a complete picture of the patient’s health status. During the examination, a special device is fixed on the body and takes detailed, high-quality images in three projections. Any pathologies are clearly visible in the photographs. In this case, the examination is carried out as comfortably and safely as possible. Therefore, if for some reason a patient cannot be sedated during a colonoscopy, for example due to the presence of certain contraindications, then doctors in the vast majority of cases prescribe an MRI. However, magnetic resonance imaging has one significant drawback. This method cannot detect cancerous tumors smaller than 10 millimeters in size. In addition, the body receives a certain dose of radiation.
According to experts, colonoscopy is still preferable. This is due to the fact that alternative diagnostic methods are only informative. Therapeutic measures cannot be carried out with their help.
Contraindications
Contraindications are divided depending on the diagnostic method. Colonoscopy under general anesthesia cannot be performed on people with obvious heart failure, mental or neurotic diseases (including lungs and bronchi) in an acute stage. For children, the list of contraindications expands:
- high temperature with no known cause;
- pustular skin lesions;
- light weight;
- respiratory tract diseases in the acute stage;
- severe stage of rickets.
Contraindications for any type of colonoscopy under anesthesia include colds or intestinal exacerbations, severe valve stenosis. The procedure is not performed if the patient has any serious conditions that could worsen the situation or contribute to the introduction of infection into the intestines or its spread.
When is a colonoscopy with anesthesia indicated?
The patient’s desire to fall asleep and not feel anything is not enough to carry out a full-fledged manipulation.
Indications for prescribing colonoscopy with general anesthesia include the following conditions, features and diseases:
- Children's age up to 12-14 years;
- The presence of adhesions in the intestine in any location along its length;
- Strictures or pronounced narrowing of the intestinal lumen of any location and nature;
- Exacerbation of hemorrhoidal disease, acute inflammatory reactions, focal ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane (including emergency colonoscopy);
- Mental disorders, spontaneous attacks of psycho-emotional instability, epilepsy;
- Low pain threshold, when patients experience shock even with the usual drawing of blood from a finger, at the sight of “white coats”.
General anesthesia or sedation may also be indicated at the discretion of the attending physician if the patient is not psychologically ready for the procedure or expects unexpected reactions from him that may interfere with the procedure.
Restrictions on holding
Considering that sedatives and general anesthesia place a tremendous burden on the body, such methods of pain relief may have a number of contraindications:
- Severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- Insufficient function of vital organs;
- Adhesive processes with a tendency to grow into the membranes of the colon;
- Acute peritonitis;
- Ascites or loose fluid in the abdomen;
- Pregnancy (colonoscopy is not usually performed for pregnant women except in emergency situations);
- Post-stroke condition;
- Ulcerative colitis with severe course.
If the patient’s condition does not require emergency intervention, then wait for a more favorable period to perform a colonoscopy with anesthesia, or prescribe the most informative analogue of a colonoscopy.
Preparation for the procedure
We wrote in more detail about preparing for a colonoscopy in our other article - “Colonoscopy under anesthesia: complete instructions”
Before performing a colonoscopy, mandatory preparation is required. If its rules were not followed or the person did not follow medical recommendations at all, then the diagnosis may not give the correct results.
Three days before the examination, bowel cleansing begins. All foods and dishes that cause increased gas formation should be excluded from the diet:
- juices;
- black bread;
- carbonated drinks;
- vegetables and fruits in any form;
- any berries;
- legumes;
- any nuts;
- dairy products.
You should avoid fatty, spicy, smoked and salty foods. You are allowed to eat steamed (or boiled) fish and dietary meat, light broths, and porridges cooked in water. The last time you can eat is 17 hours before the scheduled diagnostic time.
In the evening, on the eve of the study, a cleansing enema is performed. The procedure is repeated twice more after the morning bowel movement. To calm down and as a breakfast, you can drink a cup of weak tea.
Before the study, you must notify your doctor about the presence of diseases. Especially diabetes, problems with the heart and blood vessels, and pathologies of internal organs. Sometimes the patient needs to be tested for hepatitis and AIDS.
Carrying out colonoscopy of the intestines
Colonoscopy is considered the main instrumental diagnostic measure for female and male patients. The procedure is carried out using the classical and capsule method. A classic examination involves inserting a flexible fibercolonoscope instrument into the anorectal canal.
The procedure is prescribed for:
- taking a biopsy;
- removing a foreign object;
- restoration of intestinal patency;
- elimination of neoplasms;
- preventing blood loss.
Most often, colonoscopy is performed while you sleep, in other words, under general anesthesia. How long does a diagnostic colonoscopy take? On average, the procedure takes from 25 to 50 minutes. To conduct a research event, high-quality preparation is necessary. To do this, proctologists recommend thoroughly cleansing the intestines with enemas or laxatives. If a person often experiences constipation, he is additionally prescribed to drink castor oil; enemas are necessary for rare bowel movements. A special Esmarch circle device is used as an enema.
A slag-free diet is prescribed three days before a diagnostic colonoscopy. You cannot eat raw vegetables or fruits, herbs, smoked, salted, pickled foods, or black bread. Chocolate, sunflower seeds, coffee, milk, flour, sweets, and nuts are excluded. In the evening before the appointment of the session, proctologists recommend cleansing yourself of toxins and fecal accumulations with the medications Lavacol, Fortrans or Endofalk.
Organ testing begins with the insertion of a bendable probe with a microcamera through the anorectal canal, which causes some inconvenience and discomfort for the patient. To relieve psychological stress, patients are recommended to buy special panties for colonoscopy. The examination begins with the rectum, moving step by step through all areas and parts of the organ. To improve visibility, air is pumped into the patient’s intestines through special equipment (straightening folds and pockets).
If the diagnosis is carried out correctly, people do not experience complications, however, in some cases, patients came with complaints after the session about:
- blood loss;
- intestinal perforation;
- bloating;
- fever;
- pain.
If after examination the condition worsens, urgent medical attention is needed. When there are no diseases in the organ, the mucous tissues have a pinkish color with a shine, without ulcers, tumors, or protrusions. The pattern of blood vessels is smooth, there are no compactions, polyps, pus, fibrin deposits or necrotic masses. In case of peritonitis, severe respiratory and heart diseases, heart attack, ischemic stroke, the study is not carried out.
Technique
During a colonoscopy using anesthesia, an anesthesiologist must be present next to the patient during the entire duration of the procedure. It is necessary to provide quick assistance in emergency situations.
Immediately before the colonoscopy, the person takes the position required by the doctors. Basically, this is a position lying on your side. In this case, the legs should be pulled up to the chin. The patient is given anesthesia or the end of the probe is lubricated with an anesthetic. First, the intestine expands slightly with air flow. This helps to straighten the organ and facilitate the sliding of the probe.
Then it begins to be inserted slowly through the anus. Due to its elasticity, the tube easily follows the curves of the intestine, moving along it. While driving, the camera transmits an image to the monitor. If necessary, the doctor takes pictures of the desired areas for more detailed study.
If polyps are detected as the endoscope moves, they are easily removed using a small surgical loop, which is brought to the desired location through the probe tube. When tumors are detected, pieces of their tissue are taken for analysis. This will help establish the nature of the tumors and their danger. If, during the removal of polyps, a vessel was accidentally touched and it began to bleed, it is immediately cauterized.
The duration of the entire procedure is up to 40 minutes. This depends on the need to take tissue for analysis, remove polyps, and cauterize blood vessels. If this is not required, the procedure takes approximately 10 minutes. After completing the examination of the intestine, the endoscope is slowly removed from the intestine.
Attention!
After a colonoscopy, which was performed under anesthesia, a person may experience a temporary headache, dry mouth, weakness and abdominal distension. These manifestations are normal and quickly go away on their own.
If polyps were excised during the examination, the patient may experience pain in the intestines. They can be easily eliminated with simple analgesics. If gastroscopy is performed at the same time, then if anesthesia is used, the duration of the procedure will be about an hour.
Data decoding is carried out immediately after the completion of the colonoscopy. The doctor explains what changes, neoplasms were identified, and the general condition of the intestines. The conclusion is given to the person immediately. When biopsy samples are taken, a day is designated when the patient can come back to receive the test results. In this case, the final conclusion will be ready in a few days.
Colonoscopy without anesthesia
Colonoscopy is performed without anesthesia if it is impossible to perform any drug pain relief due to acute allergic reactions or a burdened clinical history in relation to vital organs and systems.
The following indications for the need for diagnostic manipulation without anesthesia are identified::
- Blood diseases, including clotting disorders;
- Mental disorders requiring the use of serious medications;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Epileptic seizures;
- Acute allergic reactions, up to anaphylactic shock;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (especially heart failure, stroke, myocardial infarction).
For such patients, discomfort and pain can be relieved with local anesthesia, which consists of treating the tip of the colonoscope with lidocaine.
Note : the patient himself can refuse anesthesia due to concerns for the general condition of the body, fear of side effects and unwanted complications.
Is it painful to have a colonoscopy without anesthesia?
Fear of severe pain often provokes subconscious fear in patients, even when using anesthesia.
To minimize pain and facilitate manipulation, there is a whole research scheme:
- Preliminary preparation, bowel cleansing, diet;
- A special position during manipulation (position on the side with legs bent to the stomach);
- Liberally lubricate the probe tip with Vaseline or special gel.
The colonoscope has a small shape, the tip itself has a small diameter. The main discomfort is caused by the injection of air and manipulation of the tip into the intestinal lumens. In the presence of adhesions, inflammation, or a sharp narrowing of the intestinal lumen, pain may intensify so much that the procedure is postponed to another day or general anesthesia is offered.
An important aspect of a painless colonoscopy is the psychological preparedness of the patient. If necessary, the doctor can always interrupt the examination and apply a local anesthetic.
Why is research dangerous?
Modern drugs practically eliminate the negative effects of anesthesia on the body unless the patient has any special contraindications.
The main danger is associated with the following features:
- Possibility of damage to the intestinal walls;
- Prolonged awakening from anesthesia;
- Prolonged depression of consciousness;
- Development of unpredictable allergic reactions;
- Preservation of symptoms of intoxication.
Intestinal damage is caused by the absence of absolutely any sensations during anesthesia and contact with a diagnostician. Otherwise, complications during anesthesia are rather rare. Usually the patient is carefully examined, the clinical history is studied, and the potential risks of complications during the administration of anesthesia are assessed.
Possible complications
The mildest possible side effect is urticaria. In severe cases, the patient may experience anaphylactic shock, which puts human life at risk. Side effects also include:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- disruption of the heart;
- drop in blood pressure.
In addition to the above, intestinal perforation may occur. This largely depends on the qualifications of the doctor. After tissue collection for analysis or removal of polyps, bleeding may occur.
A person may experience pain for several days after a colonoscopy. This is accompanied by an increase in temperature. Sometimes breathing problems appear as a complication.
According to numerous reviews, thanks to anesthesia, patients really do not feel pain or discomfort. A colonoscopy with anesthetic is the preferred option for many people. The technique allows you to detect intestinal cancer in the early stages or prevent the development of oncology.
- Gastroscopy of the stomach and alternative methods...
- Pregnancy after hysteroscopy
- How to check your colon without a colonoscopy
- Laparoscopy is a new method of diagnosis and surgery
- PET CT
Types of procedure
There are several methods for performing a colonoscopy.
- Virtual - information is collected using CT and MRI. Both laboratory research methods are innovative and are highly accurate and informative. This option is the most preferable because it is completely painless and has almost no contraindications or side effects.
- Using an endoscope, a special device is inserted into the intestines through the anus, which is a two-meter long tube, at one end of which there is a video camera that displays the image on the display.
In the latter case, the patient is sedated before the colonoscopy. This is a mandatory condition, since the procedure causes severe discomfort and pain to the person, so it is simply impossible to endure it without anesthesia.
How the research is carried out
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is carried out in several stages. First, the patient must remove dentures (if any), remove underwear and put on special shorts. After the preparatory stage, the anus is disinfected, the end of the endoscope is lubricated with a soap solution or Vaseline. The patient lies on his left side, squeezing his knees. In this position, they begin to insert the probe.
To insert the device into the colon, the intestinal walls are straightened with air. The endoscope's video camera transmits images to the monitor. Excess air is aspirated, and some of it is also removed independently after completion of the examination. During the procedure, there is always a doctor present who performs the manipulations, a nurse who helps him take a biopsy, and an anesthesiologist who monitors the patient’s condition. When the device passes beyond the sigmoid colon, the patient is turned onto his back, because otherwise there is a risk of intestinal perforation.
- Losing weight with herbs - recipes and applications. Effective ways to lose weight
- Personal hygiene rules that are important for your health
- How to remove stretch marks on your stomach
Types of colonoscopy
There are two main types of colonoscopy. The first examination method, called fibrocolonoscopy, is carried out using a special device - an endoscope. This device is a thin tube (1.5 cm in diameter) equipped with a lighting device, having at one end a device for biopsy (sampling cells and tissue fragments), and at the other a clamp for fixing the position of the device. An examination with an endoscope allows you to see the slightest changes in the walls of the intestine, remove polyps and cells that can turn into cancer.
Another examination method is called virtual colonoscopy. This is a method of reconstructing the surface of the intestine based on the results of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Using a computer program, the doctor displays three-dimensional images of the intestines on the screen. The undoubted advantage of virtual colonoscopy is that it helps to notice a tumor not only on the inner, but also on the outer surface of the intestine.
Virtual colonoscopy does not involve the use of anesthesia, and this diagnosis itself is completely painless, but it is considered not very effective because it cannot be used to examine malignant formations with a diameter of less than 5 mm, and the accuracy of the results depends on the quality of the image on the tomograph. Fibercolonoscopy is performed under anesthesia - this is a painful procedure, but it remains the most effective method for examining the intestinal walls.
A private type of fibrocolonoscopy is video colonoscopy under anesthesia. This is a more expensive diagnosis, but it takes less time (from 10 to 20 minutes), and the entire intestinal mucosa is recorded on images that are available for further study. Video colonoscopy is performed under anesthesia, but due to the fact that the procedure is carried out quickly, it can be performed without anesthesia.
- Eye patches - how to use. Rating of the best collagen, hydrogel and gold eyelid patches
- How to find out a mobile operator by phone number
- Hormonal gymnastics of Tibetan monks - reviews and videos
Indications and contraindications for colonoscopy under anesthesia
The main arguments in favor of using pain relief are:
- chronic constipation;
- sensation of foreign inclusion in the anus;
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- the presence of blood in the patient’s stool;
- severe weakness;
- cachexia;
- suspected cancer;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- the presence of a genetic predisposition to neoplasms;
- undergone treatment for cancer.
There are a number of contraindications to the use of anesthesia. These include an infectious process, the risk of developing peritonitis, thrombocytopenia or adhesions.
You should not use anesthesia, or even better, refrain from performing the procedure altogether in patients who have had a heart attack or stroke, or who suffer from cardiac pathologies.
Anesthesia during intestinal colonoscopy cannot be used if you are intolerant to anesthetic agents. It is not advisable to conduct the study for persons suffering from mental disorders, convulsive readiness or pregnant women. In any case, before deciding to use anesthesia, it is necessary to do allergy tests to avoid the development of severe complications.
The decision to use anesthesia is made by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the type of intestinal pathology he has. An accurate diagnosis plays an important role, which sometimes does not allow the use of pain relief.
Possible risks and complications
Developed anesthesia methods help avoid pain during endoscopy, but this does not mean that the patient cannot experience complications after the examination. Some clinics offer patients to spend 2 to 5 days under inpatient observation after endoscopy. In older people, the risk of complications increases due to the fact that any anesthesia affects the functioning of vital organs.
To avoid side effects, you need to carefully choose a clinic, consult with several proctologists, consult with a therapist, and follow the recommendations of a specialist. Possible complications during colonoscopy under anesthesia include:
- nausea, vomiting that occurs during or after eating;
- problems with bowel movements, bleeding;
- allergies, red spots on the skin;
- respiratory arrest during or immediately after diagnosis;
- increase in temperature, pressure;
- blood poisoning;
- damage to the intestinal walls, spleen;
- pain in the abdomen, side, back;
- exacerbation of heart and lung diseases;
- Hepatitis B;
- infectious diseases.