Published 04/09/2019 · Comments: · Reading time: 7 min · Views: Post Views: 13,773
Highly accurate studies allow diagnosis at an early stage of the disease. The discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) significantly expanded the diagnostic capabilities of the physician. A modern device detects the smallest changes in cellular structure, even when the patient is unaware of the disease. Another name for NMR is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI of any part of the body is performed, including MRI of the intestines and stomach.
The principle of operation of magnetic resonance imaging
The human body consists of countless cells. Cells are made up of atoms, the largest number being hydrogen atoms (water is the main component of cells, the formula of water is H2O, H is hydrogen). The nuclei of hydrogen atoms have their own charge. Magnetic tomographs contain powerful magnets that create an intense electromagnetic field. Once in the field, the nuclei of atoms are arranged in linear chains. At the same time, they emit a radio signal that is detected by the tomograph sensors. Sophisticated programs convert radio frequency signals into images. The image is displayed in three planes on the screen.
Features of preparation
Magnetic resonance imaging of the intestines does not involve any pitfalls for which you should prepare with special care. The most important condition is cleaning the gastrointestinal tract from elements that impede visualization during tomography. It is worth 12–24 hours before “day X” to completely eliminate or limit the use of products that are a kind of catalyst for the manifestation of bloating and the fermentation process.
We are talking about foods such as vegetables and fruits, which contain coarse fiber, legumes (beans, peas, etc.), confectionery and bakery products, especially white bread, dairy products, and fast food. The list continues with fried and smoked food, spices, coffee, carbonated drinks, energy drinks, etc.
At 9–10 pm, on the eve of the diagnosis, you can take the last portion of food.
Before the study, it is highly advisable to take a laxative and do a cleansing enema: the intestines should be as clean as possible at the time of the procedure
If a person suffers from flatulence, he is recommended to take special tablets. Among the most effective are:
- Mezim forte;
- Activated carbon;
- Cerucal;
- Espumisan;
- Motilium;
- Linux;
- Rennie;
- Meteospasmil;
- Infacol;
- Festal, etc.
What can be seen during the study
MRI is more often used to visualize dense organs - liver, kidneys, brain. Hollow organs - the stomach, intestines - are not so clearly visible without additional contrast. But when contrast is used, the wall of the intestinal tube becomes visible and accessible for high-quality diagnostics. What does an MRI of the intestine show? The doctor will give you a referral for an MRI of the abdominal cavity, in which, in addition to the intestines, all organs will be visible in the images. A separate intestinal tomogram is not performed. The images will show layered images of the entire abdomen. Slice by slice, the device will give a picture of the liver, pancreas, kidneys, blood vessels, adipose tissue, lymphatic system, stomach, small and large intestines. If necessary, the internal genital organs and bladder will be checked.
Bone tissue is not examined using MRI because bones contain little water and hydrogen atoms, respectively.
What is an MRI examination?
This examination method is not considered informative for all organs of the digestive chain. While the stomach and esophagus are clearly visible on MRI, the intestinal system, due to its physiological structure, is not always accessible for detailed study. But visualization of the pelvis and terminal sections of the large intestine is excellent on tomography. To examine the middle part as accurately as possible, hydro MRI is used. In this case, the intestines can only be examined with double contrast.
From the inside, the intestine is filled with fluid, and a contrast agent is injected into the vein. This allows the doctor to examine both the walls and the internal filling of the intestine. The visualization process becomes clearer. You can detect polyps, inflamed areas, and the presence of neoplasms. This method is highly valued when viewing the small intestine, which is inaccessible to standard fiber equipment.
Diagnosis of the intestine using MRI is prescribed:
- after endoscopic procedures (examination of the stomach and intestines from the inside using miniature video cameras), when the doctor wants to get a more complete picture of the detected changes;
- when contraindicated to other procedures. For example, a patient cannot undergo an X-ray examination because the permissible dose of radiation is exceeded. Or you can’t do a colonoscopy if your general condition is severe;
- as a method of monitoring therapy. MRI can be done frequently due to the lack of negative effects on health;
- if there is a suspicion of a tumor, especially one that is inaccessible to other diagnostic methods;
- if bleeding is suspected in any part of the intestines and stomach;
- with abnormalities of intestinal development.
MRI of the intestine or colonoscopy, which is better?
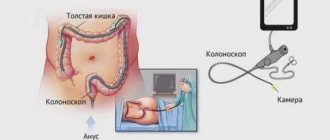
Today, intestinal examination is carried out using ultrasound, CT, X-ray, various endoscopic techniques (colonoscopy, rectoscopy, etc.), MRI and some other techniques. But the most commonly used are colonoscopy and MRI. Let's figure out which is better: colonoscopy or MRI of the intestine, and consider the differences between these two procedures:
- The MRI method is based on the effect of a magnetic field on a person while he is completely immobile. Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination method in which the intestine is examined using a special tube with a camera installed on it.
- MRI is painless and non-traumatic, but colonoscopy brings pain and discomfort to the patient, causes spasms and in some cases even requires anesthesia.
- MRI does not have the risk of side effects, but with colonoscopy, a decrease in pressure, damage to the intestinal walls, bleeding and dehydration, deterioration of microflora and other negative consequences are possible.
- During a colonoscopy, the doctor can examine every centimeter of the mucosa and take material for a biopsy and remove polyps. And with MRI, difficulties are caused by overlapping intestinal loops.
- Colonoscopy will give more accurate results in cases where intestinal motility is too active and areas of inflammation are small in size and area.
Thus, each of these studies has both disadvantages and advantages. The choice of type of diagnosis is made by a specialist depending on the individual characteristics and nature of the expected problem.
If it is possible to carry out both procedures, then MRI is used for the study as a safer and painless technique.
Pathologies detected on abdominal MRI
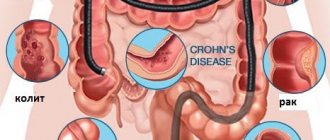
Tomographic images give an idea of all layers of the intestinal wall, the location of loops in the abdominal cavity, lymphatic and blood vessels, and nerve plexuses. Diseases such as:
- anomalies in the development of the intestinal tube: elongation of the large intestine - dolichocolon, or its part - dolichosigma, lateral protrusion of the area - diverticulum;
- inflammatory processes of the entire intestine or some segment: ulcerative and non-ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease;
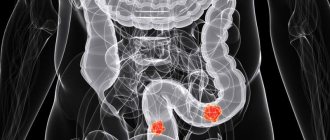
- tumors of any part of the intestine. In addition to localization, it is possible to determine the condition of the surrounding tissues around the tumor, whether there is growth into neighboring organs. The lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity are assessed, the presence or absence of metastases is revealed;
- polyps, and even the smallest growths of the mucous membrane are noticeable;
- bleeding from intestinal vessels;
- intestinal obstruction, including blockage caused by a foreign object;
- the condition of the bile ducts, including the common bile duct, which opens into the duodenum.
MRI of the small intestine with contrast is especially important, since other methods do not always provide a reliable assessment of the condition of the organ. MRI of the large intestine also shows the presence of pathologies, but there is another method in stock - colonoscopy, which shows the condition of the intestine from the inside.
The fundamental difference between MRI and CT
The intestine is considered one of the most problematic organs for diagnosis. But in recent years, the number of gastrointestinal diseases that can provoke dangerous consequences for the patient has increased significantly.
A sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work and poor nutrition increase the risk of cancer, bleeding and colon ulcers, which are difficult to treat. A large number of techniques are used for early diagnosis. They must be combined to make a correct diagnosis.
Among the latest developments, the most informative and high-quality are MRI or CT of the intestine. Both methods have a number of advantages:
- no pain or discomfort;
- the ability to complete a full scan in 30–60 minutes;
- high degree of information content with the ability to highlight blood flow, erosions and polyps;
- high probability of diagnosing a neoplasm without a biopsy.
Despite the similarity of the equipment, the methods differ in the principle of their effect on the patient’s body:
- or CT scan works by producing high-power X-rays. It penetrates and accumulates in organs and bone tissue, showing inflamed areas and the outlines of a tumor on photographs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, involves applying an electromagnetic field to the patient's body. The signal causes hydrogen molecules to move, indicating the condition of the patient’s internal organs, areas of inflammation, internal bleeding and any neoplasms.
Among the advantages of MRI over other methods:
- qualitatively shows the stage and size of the formation, allowing you to determine a cyst, polyp, or tumor without surgery;
- with high accuracy identifies blood vessels, places of blockage by blood clots, aneurysms;
- shows on photographs tumors and metastases growing into the mucous membrane, digestive organs, and pancreas;
- safety of electromagnetic radiation;
- the possibility of carrying out the procedure several times a year.
The disadvantages of MRI are:
- low information content when examining bone tissue;
- sometimes gives erroneous data for inflammation, ulcers and erosions on the intestinal wall.
CT examination of the intestines is prescribed due to many positive aspects for the patient:
- shows malignant tumors at an early stage;
- detects ulcers and internal damage highlighting the edge of erosion;
- shows inflamed areas with colitis, gastritis, Crohn's disease;
- determines pathological changes in neighboring organs, the stomach.
But computed tomography CT also has a number of disadvantages:
- during one examination the patient receives a high dose of radiation;
- many contraindications to the technique;
- does not provide clear visualization of soft tissues and blood vessels.
But the most important thing is the information content of the CT or MRI method for a particular patient. In the first place when choosing, the doctor puts the expected diagnosis and risks for the patient.
Contrast MRI
Two methods of contrast are used: intravenous and intracavitary. With the intravenous method, a special substance is injected into the patient’s vascular bed. The drug is distributed throughout the vessels, including those supplying the intestines. The vascular network of intestinal tumors is clearly visualized on tomographic images.
The intracavitary method involves taking about 1.5 liters of liquid orally. Use plain water with mannitol or sorbitol, which ensures long-term retention in the intestinal cavity. The fluid stretches the intestinal loops from the inside. Hydro MRI of the intestine clearly demonstrates the condition of the intestinal wall, irregularities, and mucosal defects.
What can an MRI show?
During the examination, the doctor examines in detail the general condition of the entire intestine and more carefully examines suspicious sections. The problematic area, shown in enlarged form, allows you to obtain information about the prevalence of the pathology and its localization.
MRI reveals:
- abnormal structure;
- tumors;
- ailments of the rectum and intestines;
- polyps;
- metastases;
- foreign objects;
- diverticula.
Note! MRI allows not only to detect oncological tumors. This study characterizes the stage of cancer progression, the presence of metastases, and during therapy allows us to evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen treatment tactics.
MRI is a simple procedure that takes about 40 minutes
Depending on the expected diagnosis, examination of the intestine can be carried out for different sections.
Contraindications for MRI
Since the device creates a strong electromagnetic field, the study cannot be carried out if there are metals or devices in the patient’s body that would be damaged by the magnetic field.
The main leads for MRI are
- pacemakers of any type. The operation of the tomograph will cause disruption of activity;
- an insulin pump that delivers medicine. MRI requires temporary removal of the device;
- metal inner ear implants;
- metal fragments in the body of any location;
- some types of artificial heart valves, stents, vascular clips;
- installed Ilizarov apparatus for fractures;
- dental metal prostheses.
Use MRI with caution in the presence of such factors
- the presence of tattoos with metallic inks, this includes permanent makeup;
- first trimester of pregnancy. Assess possible risks, since MRI is safer than radiography and endoscopy in pregnant women;
- fear of closed spaces;
- severe obesity.
Children's age is not a limitation for MRI. The only condition is the child’s complete immobility. If persuasion cannot be achieved, then an MRI is performed under light anesthesia.
Contrast MRI is contraindicated in patients intolerant to contrast agents.
What does Hydro-MRI show in women?
To examine the small intestine, which is a hollow internal object, medical specialists use a double contrast technique. During scanning, a pharmacological solution is used to stretch the walls. Hydro-MRI helps to identify:
- Obstruction.
- Crohn's disease.
- Abnormal localization of the mesentery.
- Tumors.
Hydro-examination belongs to the contrast category of tomography. It is based on intravenous water or oral administration of a drug that brightly colors the inflamed areas.
On the search portal you can make an appointment at any local clinic, without waiting in line! When using the services of our service, you can take advantage of promotional offers and get a discount of 1000 rubles!
Preparing for an MRI
The intestines are examined using hydro-MRI - the patient must drink a solution before starting the procedure. Preparation for an MRI of the intestine begins a few days before the examination. First of all, a slag-free diet is prescribed. Products that irritate the mucous membrane and cause gas formation are excluded.
Be sure to take medications that eliminate bloating (espumisan). There is no dinner the evening before the MRI. Be sure to cleanse the intestines using saline solutions. Drink 2-4 liters of special laxatives based on macrogol (Fortrans, Lavacol). After taking the solutions, the intestines are freed from feces. The MRI is performed on an empty stomach, so there is no breakfast in the morning.
In what cases is an MRI of the rectum performed?
Using MRI, it is difficult to examine genital organs that are filled with gas rather than blood. These include, for example, the lungs and intestines. Therefore, MRI is not included in the standard set of methods for their study; doctors often prefer X-ray methods or colonoscopy. MRI is an indispensable method for studying the condition of the intestine when the doctor needs to decide on the need for surgical intervention.
Intestinal obstruction is the reason for the procedure.
So is it possible to do an MRI of the intestine? Of course, the results of the study are extremely valuable for the attending physician. MRI of the intestine is done without contrast agent if the patient is properly prepared and does not move during the scan.
Many intestinal diseases cannot be diagnosed using standard methods due to inaccessibility due to the anatomical structure of the organ. Performing a colonoscopy is not difficult for an experienced doctor, but it does not answer questions about the condition of the intestines under the mucous membrane.
One of the most common diseases that doctors miss when examining a patient is rectal adenocarcinoma. This is one of the subtypes of cancer, the occurrence and development of which is genetically determined. External factors accelerate the onset of the disease and its development.
Often genetic diseases lead to the formation of rectal fistula. This is an extremely unpleasant disease, during the development of which additional channels (fistulas) are formed between the rectum and the skin. In other words, a through tunnel runs from the rectum to the outside. If you pour liquid through the anus, it will begin to come out through this tunnel.
Less commonly, rectal adenocarcinoma develops as a result of chronic diseases of the colon (colitis, hemorrhoids, rectal fissures, fistulas, polyps) or rectal fistula. Rectal cancer can occur due to a combination of the following factors:
- alcohol abuse and smoking, taking drugs;
- regular anal sex;
- unbalanced diet (lack of fresh vegetables and fruits, a lot of baked goods and red meat);
- sedentary lifestyle and excess weight;
- haemorrhoids;
- exposure to harmful chemicals (eg asbestos).
It is noteworthy that rectal adenocarcinoma is more common in men than in women. And residents of countries whose culture does not regularly consume meat (for example, as they do in India) do not know what colorectal cancer is.
The reasons for visiting a doctor should be:
- frequent urge to defecate (up to 20 times a day);
- the appearance of blood and pus in the stool;
- change in the smell of stool to fetid;
- alternating constipation with diarrhea, prolonged constipation or diarrhea;
In addition to the discomfort from constipation or diarrhea, patients become more tired than usual, feel constant weakness in the body, have problems sleeping, lack of appetite and exhaustion. MRI of the rectum is an effective and painless research method; it will allow the doctor to understand what is causing the patient’s discomfort.
If the disease is detected at an early stage, then in 90% of cases it can be defeated
But in most cases, patients do not realize that they are sick at the onset of the disease; its symptoms become noticeable when treatment may no longer be effective, which shows how important it is to monitor your health and undergo regular examinations with a doctor
Indications for intestinal MRI:
- suspicion of a neoplasm;
- control over neoplasms and metastases;
- a foreign body in the intestine that does not contain magnetic components;
How does the procedure work?
NMR machines are installed in radiology centers or departments. The patient is assigned a time when he must appear prepared. When conducting a contrast MRI, you must arrive for the study in advance to drink the solution. A 2% solution of Mannitol or Sorbitol is used - 1.5-2 l. The doctor will warn you in advance whether the solution is taken in the clinic or at home (pre-ordered at the pharmacy or issued by the medical staff of the center). You also need to take with you a 2-liter container of still water and diapers for adults. In the preparation room, the patient leaves a watch, mobile phone, jewelry, magnetic cards - anything that can interfere with the operation of the magnet. It is advisable to wear a diaper, since you cannot move during the MRI, and the liquid you drink will make itself felt. An intravenous catheter is installed to administer contrast. The patient is placed stomach down on the movable couch of the device. Headphones or earplugs are provided, as the tomograph is quite loud. Throughout the entire study, communication with the doctor is maintained; in case of fear or poor health, the tomography will immediately stop. The study lasts about 40 minutes.
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a reliable, high-precision, safe method.
Carrying out the procedure
MRI is a fairly simple procedure. After the procedure, the patient immediately returns to his normal life. The procedure does not harm the person and does not affect his well-being. The patient receives the results of the study a few minutes after the procedure.
The patient is fixed motionless on a retractable platform
Preparatory stage
To get the most informative results, you need to properly prepare for the event. The doctor prescribing the examination will definitely inform the patient about this.
Important! Proper preparation of the intestine for MRI will enable the doctor to more carefully and in detail study the anatomy of the intestine, identify pathologies and make the correct diagnosis.
The preparatory stage consists of the following activities:
- 3 days before the proposed study, it is necessary to review the diet. Foods that increase intestinal motility and cause fermentation and bloating should be excluded from the menu. Doctors recommend avoiding eating beans, radishes, cabbage, peas, and apples. In addition, dairy products, various sweets, and baked goods should be excluded from the diet on the eve of the study.
- Normalization of intestinal function. People suffering from constipation should definitely resolve this problem before the study. Cleansing enemas or laxatives are carried out in advance. It is prohibited to carry out these activities immediately before the study, as they can distort the MRI results.
- Reduced gas formation. Will the intestines be fully examined if gas production is increased in the body? Unfortunately, it will not be possible to obtain reliable results. To reduce bloating and flatulence in the intestines, you can take the appropriate drug. The use of the medicine must be agreed with the doctor. Activated carbon, Espumisan, is most often recommended.
- Refusal to eat before the study. MRI should be performed on an empty stomach. In this case, it is necessary to ensure a “clean” intestine if possible. To do this, it is recommended that if the procedure is carried out in the morning, you have your last meal no later than 6 pm. But dinner should be quite hearty. So that by the time of the study the body does not experience excessive hunger. Otherwise, peristalsis will increase. Diagnosis will become impossible.
- Reducing spasms. To reduce the severity of intestinal spasms, the patient can take an antispasmodic drug. Of course, after discussing this point with the doctor. The most effective remedies for spasms are: “No-shpa”, “Papaverine”, “Drotaverine”.
Progress of the event
After the preparation described above, they begin to conduct an MRI of the intestine, as many do this procedure.
The platform with the patient is fed into the device
The event is carried out as follows:
- Initially, a person must remove all metal objects (watch, bracelet, earrings, hairpins).
- The patient then lies down on a special retractable platform.
- To prevent accidental movements during the procedure, the person’s limbs are secured with special belts. Body immobility is achieved using special rollers.
- If an MRI of the stomach and intestines involves a study with a contrast agent, then a catheter is installed for the patient through which the necessary solution will be supplied.
- The platform is fed into the tomograph. The doctor installs it in such a way that the area to be examined is located in the ring of the device.
- Pictures are taken in different projections, while holding your breath. The magnetic field, together with the scanning device, moves freely around the patient's peritoneum.
- The event lasts about 40 minutes. At this time, the person does not experience any pain or negative sensations.
Alternative
Currently, the doctor has an extensive list of bowel examination techniques at his disposal. The most informative are MRI and colonoscopy of the intestine. But, unfortunately, the “ideal” method still does not exist. They all have their advantages, disadvantages and contraindications. In the case of each patient, the choice of study is selected individually.
What is the best way to check your intestines - MRI or colonoscopy?
Patients often ask: is it possible to do an MRI of the intestines instead of an unpleasant colonoscopy? In the case of examining the large intestine, colonoscopy has been and remains the most informative research method, during which the endoscopist will notice the smallest changes in the intestinal mucosa (which makes it possible to recognize the disease at a very early stage, MRI cannot “do this”), and, if necessary, will take tissue samples for analysis will remove polyps immediately during the procedure. If malignant tumors are detected, the colonoscope will not provide complete information about the size of the formation. In this case, MRI will act as a method of additional diagnostics and will show the full picture: how much the tumor has spread inside the tissues, whether there are metastases. We can conclude that in the case of screening the large intestine, MRI cannot fully replace colonoscopy. If we are talking about examining the small intestine, then colonoscopy is completely powerless here; the colonoscope tube only reaches the final sections of the large intestine. Here the choice in favor of MRI is obvious.
Advantages and disadvantages of methods
Both types of surveys have their strengths and weaknesses. They are taken into account by doctors when choosing a study for each patient individually.
| Methodology | Advantages | Flaws |
| MRI of the intestines |
|
|
| Colonoscopy |
|
|
Be sure to read:
Preparation and performance of computed tomography (CT) of the intestine
In addition, MRI is not performed on patients with high body weight (more than 120 kg), metal implants, pacemakers or dentures.
Contraindications
Despite the information content and effectiveness of diagnostic methods, each of them has a number of contraindications:
- MRI. Presence of insulin pumps, pacemaker, metal implants, prostheses and implants, pregnancy, claustrophobia.
- CT. It has no obvious contraindications, with the exception of an allergy to the contrast agent.
MRI is not recommended for children. A CT scan can only be performed if indicated by a doctor. The fact is that the negative effects of radiation exposure have not yet been fully studied. During pregnancy, MRI and CT scans can only be performed if prescribed by a doctor. The specialist takes into account the benefits for the mother and the expected harm to the fetus.
Tomography of different parts of the gastrointestinal tract
Examination of the stomach and esophagus
Tomography of the stomach is performed if the doctor cannot make a clear diagnosis based on either gastroscopy or radiography. MRI of the stomach and intestines is prescribed only in extreme cases, since it is a very expensive and complex research method. In addition, at the initial appointment, it is enough for a specialist to conduct an x-ray or gastroscopy.
Examination of the stomach and intestines MRI is prescribed only in difficult situations, provided that:
- the clinical picture of the disease is poorly expressed;
- X-ray and gastroscopy did not show the desired results.
- MRI of the esophagus and stomach can show the presence of a diaphragmatic hernia, esophagospasm in the esophagus, internal bleeding, etc.
Tomography of the large and small intestines
MRI of the large intestine is performed both with and without a contrast agent. Experts rarely prescribe magnetic resonance imaging of the colon as the only diagnostic method. The location of this organ does not allow a normal study of the condition of the walls, because it has many folds.
The advantage of magnetic tomography of the large intestine, in contrast to colonoscopy, is that it is an absolutely painless research method.
Most often, magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose diseases of the small intestine. The fact is that it is very difficult to get to this section using an endoscope or gastroscope, so many doctors are helped by examining the intestines using a tomograph. To conduct a quality examination, specialists resort to hydro MRI of the intestine.
What does intestinal tomography show? Such a study can show the doctor the presence of polyps, scars, neoplasms, ulcers, erosions, inflammatory processes in the organ, thinning of the ducts, etc. A study using this method can be prescribed as an additional research method if problems such as are suspected:
- tumors;
- polyps, diverticula;
- presence of foreign bodies, etc.
Often, with the help of MRI, doctors are able to monitor the process of recovery of a diseased organ after surgery, determine the stage of cancer, assess the size of the tumor, as well as the effect of medications on the condition of the organ being studied.
Tomography of the rectum
MRI of the rectum is usually not used to detect any diseases of this organ. Most often, colonoscopy is used to diagnose the rectum. Magnetic tomography is more often used to monitor the quality of prescribed treatment.
Tomography of the rectum will definitely show:
- the presence of malignant or benign tumors, metastases;
- bleeding of unknown origin;
- disturbances in the movement of contents through the digestive tract, etc.
Using magnetic tomography, doctors examine and evaluate the condition of the gastrointestinal tract, easily identify pathologies, and make an accurate diagnosis. This is a convenient, safe, non-invasive study.