Diagnosis of typhoid fever is difficult due to the difficult differentiation of the disease from intestinal disorders, tuberculosis or cholera, which are similar in symptoms. Tests for the presence of typhoid fever and other studies are usually prescribed at the stage of consolidation of a constant febrile (38-390C) temperature and stable characteristic signs. In addition to determining the diagnosis of the disease, testing for typhoid fever is mandatory for catering workers, employees of children's and medical institutions, and representatives of the hotel or sanatorium services sector.
Causes
The causative agent of the disease is the Salmonella typhoid bacillus. When it enters the human body, it releases endotoxin, which is a very dangerous substance.
The pathogen enters the environment through the patient’s urine and feces. Particles of feces on the paws are carried by flies, so the peak of the disease occurs in the summer-autumn period.
Children are most susceptible to the infectious disease, but in adults typhus is more severe and is characterized by an acute onset.
Since this infectious disease is common in third world countries, people who visit epidemic sites, as well as patients with weakened immune systems, are at risk.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of typhoid fever is based on clinical manifestations, results of bacteriological and serological examination. The disease is differentiated from typhus, malaria, sepsis, tuberculosis and other infectious diseases.
Laboratory tests include a general blood test, bacterial culture, biochemical and serological examination.
In the early stages, you can identify the causative agent of typhoid fever by donating blood for bacterial culture. After 4-5 days, the results are ready.
The pathogen is detected by a biochemical blood test for Salmonella typhoid.
An analysis for typhoid fever can be done faster if you determine the titer of antibodies to the Salmonella bacillus in the blood. In addition to blood, in the 2nd week of the disease, feces, urine and even the contents of the duodenum are examined. In the latter case, the material is taken during duodenal intubation.
Serological diagnosis of typhoid fever is an auxiliary method. Conducted with the help of RNGA. A serological test for typhoid fever can detect antigens to the pathogen within 4-5 days after infection. Also highly sensitive and fast diagnostic methods are the immune fluorescence reaction (RIF) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
If the test for typhoid fever gives positive results, then antibacterial treatment should be started immediately.
What tests are performed
To confirm typhoid fever, laboratory tests are prescribed, which must be carried out before starting antibiotic therapy (taking antibacterial drugs may affect the accuracy of the diagnosis).
For examination, blood, feces, urine, bile, and cerebrospinal fluid can be taken (if a complication is suspected). Depending on the stage of the disease and symptoms, the following tests for typhoid fever may be prescribed.
Serological study
It examines blood plasma. Necessary for the detection of specific antibodies produced by the human immune system. The analysis can be carried out only 4–5 days after infection with typhoid fever, since the body does not synthesize antibodies earlier.
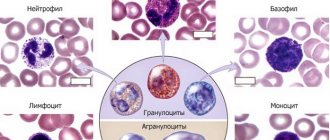
General blood analysis
Diagnostics of salmonellosis
It is prescribed to determine the quantitative characteristics of all blood cells. When infected with typhoid fever, normal blood counts change.
Leukopenia occurs (the number of leukocytes decreases), aneosinophilia (eosinophils are absent), and the number of lymphocytes increases, which indicates the presence of infection in the blood.
Also, during typhoid fever, the level of neutrophils, leukocytes synthesized by the body during inflammation, increases, and the number of platelets, which are responsible for blood clotting, decreases.
A detailed blood test is required upon admission to hospital treatment and during therapy in order to monitor the dynamics. For the study, a blood test is taken from a vein or finger.
Blood biochemistry
Detects acute phase proteins and should be carried out before taking an antibiotic. The test requires 5–10 ml of blood from a vein, the results of the study can be found out within 24 hours.
Bacterial culture
There are few bacteria in the blood sample taken, so it is transferred to a nutrient medium (meat peptone broth) and placed in a thermostatic apparatus. Under favorable conditions, the microorganism will begin to form a large colony, which will be suitable for research.
Afterwards, chemical reagents are used and the type of bacteria is determined. A similar test is performed on all patients with hyperthermia, as well as when checking for typhoid fever. Results can be obtained 4-5 days after the analysis, a preliminary answer will be given after 2 days. Tank culture is the most accurate laboratory diagnosis of typhoid fever.
To detect antibodies to typhoid fever, a radioimmune or enzyme immunoassay method is used
RNGA and RPGA
To detect a person who is a carrier of the typhoid bacillus, as well as to monitor the effect of vaccination against typhoid fever, IRHA (indirect hemagglutination reaction) or passive hemagglutination (RPHA) is used. This method helps detect antigens and antibodies using red blood cells that precipitate when they come into contact with the antigen.
Red blood cells on which antigens are adsorbed stick together upon contact with the antibody. An immunological study determines the level of these antibodies. In a person suffering from typhoid fever, it can be at a level of 1:40, and in someone who has defeated the infection it is 1:2000, so diagnostics are carried out at intervals of 5 days to monitor the dynamics.
Bacteriological examination of stool
This test is rarely prescribed, since the typhoid bacillus leaves the body only 8–10 days after infection. This method is used to identify people who are carriers of the infection, but are not sick themselves.
Analysis of urine
Typhoid bacteria are detected in urine only 1–1.5 weeks after infection. A urine test can indicate such indirect evidence of typhoid fever as leukocytosis (at the initial stage of the disease, the number of white blood cells increases, and within 7 days it drops sharply), leukopenia, increased ESR, aneosinophilia, relative lymphocytosis.
Before collecting urine, the patient must perform hygiene of the external genitalia, then collect the material for analysis in a sterile jar. For diagnosis, 40–50 ml of urine will be sufficient. To test for infection, a sediment is used, which is transferred to a solid nutrient medium.
The ability to detect the causative agent of typhoid fever by microbiological methods is directly related to the number of bacteria in biological fluid and the use of antibacterial therapy. A week after infection with Salmonella S. Typhi, serological agglutination tests (RPGA for typhoid fever) give a positive response.
Serological tests are less specific than bacteriological methods, since a positive response may indicate a past infection caused by another species of Salmonella. An additional study after five days helps to monitor the increase in titer, which is characteristic of an acute infection.
Bacteria in the blood are found only in sick people; in the urine and feces, the bacteria can be found in both the sick person and the bacteria carrier
Treatment
Patients are subject to hospitalization in the infectious diseases department. The course of treatment is at least 23 days. During this period, patients are not allowed visitors and they cannot go outside.
Patients are prescribed bed rest. They are allowed to sit only on the 6th day and walk on the 10th day after body temperature normalizes. Be sure to follow a diet. Products should be high in calories, but easily digestible. To prevent dehydration, you need to drink plenty of fluids
The main treatment is antibiotics. Levomecitin, Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Ampicillin are effective. Detoxification therapy is carried out together with antibacterial therapy. In case of severe intoxication, colloidal and crystalloid solutions are indicated.
Complications
The most dangerous consequence of the disease is the death of the patient. The likelihood of death increases in children and people with weakened immune systems.
Typhoid fever was a deadly disease until antibiotics were invented.
Complications:
- Re-infection. The causative agent of typhus is resistant to antibiotics, so it can live in the bile ducts of the liver and manifest itself when the immune system is weakened.
- Intestinal bleeding, perforation of the intestinal wall and the development of peritonitis.
- Meningoencephalitis.
- Pneumonia, otitis.
- Myocarditis, thrombophlebitis
- Cholecystitis.
- Ostemiolitis.
Complications often develop during the acute course of the disease. They may appear after the patient has recovered.
Prevention
The most effective method of protection against typhoid fever is vaccination. It is necessary to be vaccinated if you are planning a trip to a country where typhus is endemic.
The effectiveness of the vaccine is 50-80%.
Other preventive measures:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, wash your hands before eating;
- prepare food in compliance with sanitary standards;
- do not drink tap water, use bottled water for cooking and washing vegetables;
- do not use other people’s personal hygiene products;
- Consume vegetables only after heat treatment and cook until tender.
The prevention of typhoid fever should be carried out not only by the population, but also by the Ministry of Health and the authorities responsible for compliance with sanitary standards. It is especially important to monitor the condition of tap water and promptly disinfect foci of infection.
The prognosis for recovery is favorable. If you go to the hospital in a timely manner and there are no complications, treatment is successful, otherwise severe symptoms of intoxication can cause the death of the patient.
Author: Oksana Belokur, doctor specially for Moizhivot.ru
zhkt.ru
Indications
The causative agent of typhoid fever is transmitted through household contact, most often through contaminated water. Without treatment, the disease is life-threatening due to the development of complications such as intestinal bleeding and intestinal perforation.
The causative agent of typhoid fever
Of the laboratory tests for diagnosing the abdominal type, the most valuable is the isolation of the pathogen from the patient’s blood. Additionally, hematological studies are carried out and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the number of leukocytes and the ratio of their formed elements are determined.
When and how to take a blood test for typhoid fever? Legislation requires that workers in specific professions, as well as organizations operating in certain areas, have health certificates. Employees of food industry enterprises, public catering, educational institutions, organizations and consumer service enterprises, swimming pools, baths, hydropathic clinics, hairdressers, hotels are required to have sanitary certificates. This also applies to medical staff, pharmacy chain and medical industry workers, and drivers transporting products.
Holders of health certificates are required to periodically undergo certain tests, including an annual blood test for typhoid fever for the health certificate.
About typhoid fever
Do not confuse typhoid and typhus. Translated from Greek, the word “typhoid” (τῦφος) means something similar to fog, smoke, and with this term old doctors called a kind of clouding of consciousness, lethargy of the patient, which can occur both with acute intestinal infection and with typhus. Typhus has nothing to do with typhoid fever other than this symptom. It is a blood infection and is transmitted by lice and fleas - blood-sucking ectoparasites.
Where does typhoid fever come from? This is a disease of “dirty hands” and contaminated water. The causative agent of typhoid fever is a large microorganism called Salmonella from the genus Enterobacteriaceae, and the causative agent of typhus is extremely small rickettsia.
Usually, when people talk about typhus, the harsh years of the Civil War come to mind. But then there were epidemics, mainly of typhus. And today, every year more than 20 million people, or the population of two cities like Moscow, become infected with typhus. Almost 900 thousand of them die every year. Such outbreaks occur in hot African countries, India, Colombia and Malaysia, Indonesia and Afghanistan. Therefore, great danger awaits those travelers who underestimate the likelihood of infection.
It is very easy to contract typhoid fever, and the severity of this disease lies, first of all, in the fact that it begins as a mild ailment with ordinary food poisoning. Such features of this infection have led to the fact that all so-called decreed persons working in the food industry, educational institutions and medical organizations must be tested annually for typhoid fever and checked for carriage of typhoid bacilli. Persons working in the food trade should undergo the same examination.
Symptoms
But the indications for such an analysis are not limited to the need to obtain a health certificate.
If a person gets sick and has symptoms for donating blood for typhoid fever, such as:
Severe discomfort due to abdominal infection
- Malaise;
- Headache;
- Delirium, clouding of consciousness;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Gradual increase in body temperature;
- Intoxication;
- Lack of appetite;
- Red rash on the abdomen;
- Symptoms of dehydration:
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea alternating with constipation;
A test for typhoid fever is also necessary if the diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis, evidence of contact with sick people and other laboratory blood tests.
Rash on the stomach
When to test for typhoid fever
A blood test for typhoid fever can be taken in two cases:
- when a clinical manifestation characteristic of an intestinal infection appears;
- to prevent epidemics (is a mandatory analysis when renewing a health certificate).
If a patient goes to the doctor with a complaint about digestive problems and hyperthermia, the doctor, based on the manifestations of the disease, will make an assumption about the development of an intestinal infection. The presence of typhoid fever is indicated by the following patient complaints:
- abdominal pain;
- signs of poisoning (nausea, vomiting, weakness, loss of appetite, hyperthermia);
- problems with stool (constipation, somewhat less commonly diarrhea);
- dehydration (extreme thirst, tongue covered with a white coating, peeling skin);
- formation of roseola is possible (a skin rash appears a week after infection. When you press it, it disappears and then appears again. The number of rashes is from 4 to 25 elements).
Typhoid fever usually occurs as follows. Acute onset of the disease in 30% of cases. Symptoms of poisoning, deterioration of sleep, headache, weakness increase gradually. Body temperature increases over several days and reaches febrile values. Reaction inhibition appears, the stomach is swollen, flatulence and rumbling appear.
After a person has had typhoid fever, he develops a strong immunity to the typhoid bacillus.
The causative agent of typhus in fresh water can remain viable for up to a month, and in agricultural products for up to 10 days; in dairy products it multiplies and accumulates. Houseflies can also transfer the bacteria to food.
The first signs of the disease appear 7–23 days after infection, so it is extremely difficult to determine the exact source. Typhoid fever must be differentiated from tuberculosis, brucellosis, typhus, cholera, plague and other diseases in which the patient experiences fever and intoxication.
Preparation and delivery of analysis
To achieve correct blood test results, you must stop taking medications three days before the procedure. Two days before the typhus test, you should not drink alcohol. On the day of donating blood for typhoid fever analysis, you must avoid foods such as eggs, dairy products, smoked foods, spicy seasonings and fried foods. Do not smoke an hour before donating blood.
For diagnostic purposes, a blood test for typhoid fever is performed according to the following indicators:
- Hemogram, or general blood test. Carried out when infectious diseases are suspected. The detection of typhoid fever can be indicated indirectly by leukopenia, absence of eosinophils and increased ESR;
- Bacterial culture. It may take up to five days for microflora growth to appear and to be identified;
- A biochemical blood test can detect the presence of proteins indicating an acute course of the disease;
- Serological blood test for typhus, which allows detection of antibodies on the fourth day of illness;
- Enzyme immunoassay for typhus;
- RNHA is a reaction of mediated (indirect) hemagglutination.
Positive results confirm the presence of antibodies to the pathogen. This indicates either the presence of the disease in the acute phase, or a past infection.
If the test result for typhoid is negative, this indicates either that the disease has just begun, or that it has been suffered for a long time, or that the person is healthy and has never had typhoid fever.
Sometimes tests give a false positive result. The cause may be other Salmonella infections, hemolysis of the blood sample, or antibiotic use.
What tests are prescribed to diagnose typhoid fever?
If there are signs of illness, a blood test for typhus should be taken before taking antibiotics. This condition is explained by the fact that after 2-4 days from the start of treatment, a blood test may give a negative result. In general, a number of the following tests are usually prescribed for such a study:
- Serological blood test (Vidal reaction). With its help, you can detect antibodies to the causative agent of typhoid fever on the 4-5th day of illness.
- General blood analysis . Such an examination is usually prescribed in the first days of the disease, but it only indirectly indicates the presence of typhoid fever.
- Biochemical blood test - detects acute phase proteins.
- Bacterial culture - the results of such a blood test can be obtained only after 4-5 days.
To detect antibodies to typhoid, radioimmunoassay and enzyme immunoassay blood tests are used. The most common method of analysis, which is used to detect carriers of infection among employees in the food industry and to assess the effectiveness of vaccination against typhoid fever, is the research method using IRHA (indirect hemagglutination reaction). The material for this analysis is venous blood. To obtain the most accurate data, smoking is prohibited 30 minutes before taking the RNGA analysis.
If the blood test for typhus is positive, we can talk about an acute course of the disease, or about a previous infection. In addition, a positive result may indicate that the person is a carrier of the causative agent of typhoid fever. If the test results are negative, the doctor can conclude that a long time has passed after recovery, an early form of the disease (in the presence of appropriate clinical manifestations), or even the absence of infection in the body. A false-positive test for typhus is possible in the presence of cross-reactions with other pathogens of infectious diseases such as Salmonella.
Typhoid fever is a dangerous infectious disease caused by Salmonella S.typhi. You can catch typhoid fever through food, contaminated water, failure to follow simple hygiene rules (through unwashed hands), as well as from a carrier of the infection.
The initial signs of typhoid fever are in many ways very similar to various other infectious diseases, so if you suspect the presence of this infection in the body, it is necessary to do a test for typhoid fever for an accurate diagnosis. Only in this way can the fact of infection be confirmed and effective treatment be prescribed in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of the disease
Differential diagnosis of typhoid fever can be complicated. The independent laboratory Invitro came to the aid of public medical institutions. The Invitro laboratory network uses the latest test systems from the leaders of the global pharmaceutical industry in Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Russia.
Invitro successfully diagnoses a variety of diseases, including typhoid fever. The basis for confirming the diagnosis is the isolation of Salmonella typhi from the patient's blood.
The pathogen is detected in the blood by bacteriological (blood culture on nutrient media) and serological methods (RPHA rapid test for antibodies). Rapid tests are inferior to bacteriological methods in specificity, since they detect antibodies to other microbes of the genus Salmonella. In addition, the test also reacts positively to antibodies indicating a previous illness. Therefore, a repeat test is indicated after five days. If the antibody titer increases, then the disease is in the acute phase.
No special preparation is required for taking blood for analysis in Invitro. Blood must be taken on an empty stomach, or four hours after breakfast or lunch.
The interpretation of a blood test for typhoid fever is information for the doctor, who makes the final diagnosis.
Testing blood for typhoid fever
Differential diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of typhoid fever are in many ways similar to other infectious diseases. And it is very important to distinguish it in a timely manner from influenza, meningococcus, brucellosis and rash type.
- only in a third of cases the disease begins acutely;
- sleep is disturbed, weakness appears, as well as pain in the head;
- the reaction is inhibited;
- the skin turns pale;
- intoxication develops very slowly;
- the temperature does not rise quickly either, people do not sweat;
- heart rate slows down;
- blood pressure decreases, a wet cough appears;
- Abdominal bloating and rumbling occur.
Diagnostics of the abdominal type consists of general clinical methods, as well as specific reactions. Serological testing for typhoid fever is widely used. As a result, it becomes possible to understand the severity of the disease, as well as identify the characteristics of the bacterium and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. The necessary tests are carried out at the very beginning of the disease and before leaving the hospital. If necessary, the test is repeated many times.
It is very important to conduct a specific examination in the laboratory to distinguish typhoid fever from the so-called paratyphoid fever.
Treatment and prevention
Patient care is of great importance in the treatment of typhoid fever. Patients are hospitalized, and during the critical stage of typhoid fever they are prescribed bed rest, which is extended after the temperature drops for another week. Then, the recovering person will be allowed to sit down, and after another week get up.
During hospitalization, the patient should drink as much as possible, preferably sweet tea. Food should be semi-liquid and high in calories
Treatment of typhoid fever is carried out in two directions:
- combating the pathogen and measures against intoxication and dehydration. The fight against the causative agent of typhus comes down to the use of antimicrobial agents. Measures against dehydration and intoxication are carried out using parenteral administration of appropriate drugs.
Depending on the situation, symptomatic drugs are used, cardiac, restorative and others. Patients with typhus are discharged from the hospital no earlier than three weeks after the temperature drops, subject to negative results of bacteriological tests.
Treatment and prevention of typhoid fever involves vaccination to prevent the person recovering from becoming a carrier of the bacilli. Prevention of typhus, excluding vaccination, consists of observing sanitary hygiene standards, monitoring the sanitary condition of food industry enterprises, catering and trade.
Personal prevention is washing hands, vegetables and fruits before eating and heat treatment of raw animal products.
sostavkrovi.ru
When is it necessary to get tested?
When a mild illness occurs, most people treat themselves on their own and see a doctor only if absolutely necessary. As a result, the doctor can begin treatment only after the disease has developed and seriously affected the body. Failure to go to the hospital in a timely manner increases the chances of developing complications and serious pathologies, and also complicates treatment. You should undergo a medical examination and donate blood for analysis annually, and consult a doctor immediately after the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. In this case, doctors can detect the development of diseases in the early stages.
Indications for the study of typhoid fever are:
- General weakness, nausea, impotence, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, initially slight. After 3-5 days, the temperature rises strongly and can exceed 38 degrees.
- Signs of dehydration and extreme thirst.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal symptoms include constipation, diarrhea and vomiting. Symptoms may appear sequentially.
- Lack of appetite and even aversion to food.
- Red spots appear on the stomach.
- With the development of typhoid fever, a person's weight decreases.
- Due to the toxic effect of the infection, the spleen and liver become enlarged, which is especially noticeable in patients who have lost weight.
- Workers in the food industry and some other professions are regularly tested for typhoid fever as a preventive measure.
The symptoms of typhoid fever at the onset of the disease are very similar to ordinary food poisoning, which may subside in a couple of days. However, the same signs accompany the development of sepsis, brucellosis and other serious diseases. If you feel seriously unwell, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo the necessary tests.
What research are we doing?
In our center you can get tested for typhoid fever, brucellosis, dysentery, measles, rubella, yersiniosis, pseudotuberculosis, as well as syphilis and other diseases.
Typhoid fever is a severe acute intestinal infection that affects the lymphatic system of the lower small intestine. Symptoms of the disease: weakness, pale skin, loss of appetite, constipation, high fever, characteristic pale pink rash. After treatment, the disease can attack a person again, as it is cyclical in nature.
Brucellosis is an infection that enters the human body through sick animals. It affects many organs and systems of the human body. Symptoms: loss of strength and weakness, bone pain, high body temperature, increased sweating, abdominal pain, sleep disturbance.
Rubella is a viral disease that mainly occurs in children. It is very dangerous during pregnancy. If infected with rubella, serious birth defects can occur. The fetus's cardiovascular system, eyes and hearing are affected.
Types of studies
- A general examination of the patient's blood sample is carried out when the first signs of typhoid fever appear. This is not a completely diagnostic research method, since it cannot confirm the presence of the disease. The analysis is aimed at identifying an inflammatory process that may explain the high temperature.
- A typhoid blood culture test is done to detect a specific type of bacteria. In a patient's blood sample, the number of microorganisms that cause intestinal infections is too small to detect them. The patient's biological sample is placed in a nutrient medium in which bacteria begin to actively multiply. The sample is then examined again under a microscope and the bacteria are identified using chemical reagents.
- Serological diagnosis of typhoid fever is used to look for antibody cells to the infection. Immediately after an alleged infection with a bacterium that causes typhoid fever, it is pointless to conduct this type of research, since the body has not yet begun to fight the foreign microorganism and produce specific antibodies. Serodiagnosis is effective only on days 4-5 of the disease.
- Typhoid fever is detected by urine analysis.
- Biochemistry can confirm the diagnosis, but this requires a blood sample to be taken before starting treatment, provided that the patient is not taking any medications.
There are other types of tests, for example, the indirect hemagglutination reaction, which can be referred to as RNGA or RPGA. Hemagglutination is based on the special properties of red blood cells to stick together over time. The passive indirect approach involves the adhesion of red blood cells through immune serum. This test is not prescribed to patients with suspected typhoid fever; it is intended to assess the effectiveness of vaccination.
Characteristics and features of the causative agent of typhoid fever
The infection is caused by a pathogen from the genus Salmonella – Salmonella typhi . This is a mobile gram-negative rod that lives in conditions of oxygen access. It is not capable of forming spores, but is very stable in environmental conditions. While in water, the typhoid bacillus remains viable for 1 to 5 months. It is active in feces for 25 days.
With moderate cooling, for example, in a refrigerator, the microorganism in dairy products is not only preserved, but is also capable of multiplying within a month. High temperatures have a detrimental effect on the pathogen. When boiled, the typhoid bacillus dies instantly. If you heat water to 60°C, the microorganism will die in 4-5 minutes. When exposed to direct sunlight, it also loses its viability.
Typhoid bacillus is very sensitive to chemical disinfectants. When exposed to chloramine, sublimate, or Lysol, it is disinfected in a few minutes .
Typhoid bacillus has a complex antigenic structure. But for diagnostic purposes, only two antigen complexes are used: O-antigen (thermostable somatic) and Vi-antigen (heat-labile flagella). The pathogenic microorganism is capable of forming L-forms, which contribute to the development of bacterial carriage and relapse of typhoid fever.
Preparation for analysis and interpretation of results
Serological testing is carried out on an empty stomach. The day before, it is not recommended to eat heavy food, which can have a negative impact on health. The use of alcohol, medications and other substances that affect the blood is strictly prohibited.
A negative test result indicates that the person is healthy. If the laboratory test result is negative, but the patient has characteristic symptoms of typhoid fever, the disease may be at an early stage.
The body has not yet started producing antibodies, and the number of bacteria is not large enough to be detected.
A positive result indicates that the patient has typhoid fever. If there are no symptoms of the disease, but the test is positive, the person may be a carrier of the disease. At the same time, the person himself may not have typhus, but it is contagious to other people.
Treatment of the patient involves taking medications prescribed by the doctor, as well as special nutrition, drinking plenty of fluids and bed rest. In cases of severe disease, the typhoid patient is hospitalized. To prevent infection with typhoid fever, it is necessary to observe sanitary hygiene standards. Before traveling to hot countries, it is better to get vaccinated.
krov.expert
Do you need to prepare for the test?
A blood test for typhoid fever should be taken not only by patients with characteristic signs of the disease, but also by those who come into contact with a large number of people or food products when working. This is done to prevent the spread of typhoid fever, since an infected person can be a carrier of infection for a long time.
The patient excretes the greatest number of bacteria in feces during the period from the first to the fifth week of the disease, and in urine for 2–4 weeks. Every tenth person who has had an infection releases the typhoid bacillus into the external environment for 3 months, and 3–5% of the total number of typhoid patients are chronic carriers of the infection, spreading the bacillus for several years.
When passing and renewing a health certificate, a test for typhoid fever is mandatory. Many people do not know where the blood is taken for testing. To carry out diagnostics, venous blood is taken from the patient from the area of the elbow.
The study is carried out in vitro, which literally means “in vitro”. How long the test takes depends on the workload of the laboratory; at a minimum, the result will be ready in two days. The doctor issuing the referral will clarify how to properly take a test for typhoid fever.
If there are no clarifications, then the following recommendations should be followed:
- You need to donate blood on an empty stomach;
- the day before the event, you should not eat too spicy, salty, fatty or smoked foods;
- it is necessary to exclude the intake of weak and strong alcoholic drinks, medications at least three days before donating blood;
- There is no need to change your drinking regime, but it is still better to give up coffee;
- Smoking is not allowed an hour before the test.
If antibodies to typhoid fever are not detected, then this is confirmation that the person is not a carrier of the infection. If symptoms of the disease are present, and the test does not show the presence of a specific protein, then it is possible that the immune response has not yet been formed, since the pathology is at an early stage.
A false positive test result is possible if a bacteria from the genus Salmonella is present in the body, but causes another disease, that is, the microorganism is present and the immune system reacts by producing antibodies. The doctor will indicate what tests to take if you suspect typhoid fever or when checking for bacteria carriers, as well as where it is best to donate biological material.
If typhoid fever occurs in an acute form, the patient will be hospitalized in an infectious diseases hospital. The patient is prescribed antibiotics, diet and bed rest. It is recommended to avoid any overexertion, even when visiting the restroom. Typhoid fever, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to toxic shock and perforation of the intestinal mucosa. Therapy lasts from 2 to 4 weeks.
jktguru.ru