There are currently enough methods for examining the large intestine - they all have certain differences and are prescribed according to the indications present. Some commonly recommended diagnostic methods include sigmoidoscopy or rectoscopy (examination of the rectum and part of the sigmoid colon) and colonoscopy (examination of the entire lumen of the large intestine).
Of course, these two types of diagnostic procedures have many similarities, which manifest themselves both during preparation and in the examination technique, but there are also a certain number of differences. Patients, when receiving a referral for these types of examinations, are often perplexed and interested in what is the difference between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy?
Features and Differences
Despite the fact that both of these methods involve direct examination of the intestines and have some similarities, there are still certain differences. Distinctive aspects are present in almost all aspects of the preparation and conduct of procedures.
Method capabilities
The main difference is considered to be the difference in diagnostic capabilities, which are determined by the medical instruments used for research. For sigmoidoscopy, a rigid (inflexible) rigid device is used - a sigmoidoscope, approximately 35 cm long. Its length determines the distance of the intestinal section from the anus, and, accordingly, allows you to examine that part, which is the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Therefore, the capabilities of sigmoidoscopy are limited to 30-35 cm, and because of this, the method is generally considered less informative than colonoscopy.
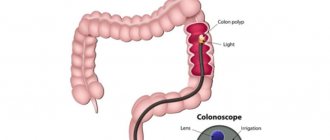
Sigmoidoscope and colonoscope - instruments for examining the large intestine
Colonoscopy has free access to all parts of the intestine, thanks to a flexible and long colonoscope that gradually moves into the lumen of the organ and transmits information to a specialist using a built-in mini-camera. Using a colonoscope, it is possible to examine 1.5–2 m of the large intestine and even the small part of the small intestine adjacent to it.
A significant difference between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy is the ability of the latter to immediately treat the affected area during examination and identification of pathologies in the organ, such as polyps, stenoses and others. Using a colonoscope, you can not only coagulate blood vessels if bleeding is detected or treat ulcerative lesions, but also collect tissue material for further laboratory study.
Indications for prescribing methods
The shape, length and flexibility of devices for performing these procedures are directly related to the indications for the purpose of one or another technique. So, in most cases, a patient will be recommended to have a rectoscopy if the following symptoms brought him to the doctor:
Colon cleansing before colonoscopy
- regular bowel dysfunction – constipation or diarrhea;
- violation of the act of defecation (decreased amount of stool);
- mucous or purulent discharge from the anus;
- painful manifestations of chronic hemorrhoids.
The specialist will definitely send the patient for this procedure if a tumor is suspected in the rectum. A colonoscopy will be prescribed for manifestations such as:
- pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the rectum;
- sudden weight loss for unknown reasons;
- bleeding from the anus;
- the presence of general weakness, anemia.
And also if you suspect the occurrence of neoplasms of various types in the large intestine or Crohn's disease. Due to the wide capabilities of colonoscopy, which allows you to examine the entire surface of the organ, it is recommended as a screening method for all patients over 55 years of age.
Scattered distribution of inflammatory foci in Crohn's disease and their specific localization in colitis
This is associated with an increase in coloral cancer and other oncological processes in the large intestine. Sigmoidoscopy in most cases is prescribed as a diagnostic method when there is a suspicion of pathological changes in the rectum or sigmoid colon.
Indications for FCS and sigmoidoscopy
There are a number of general indications for both diagnostic methods:
- chronic diarrhea and constipation;
- constant pain of unknown nature;
- blood and mucus in the stool;
- polyps;
- Crohn's disease;
- peptic ulcer;
- suspicion of cancer;
- inflammatory processes;
- anemia,
- weight loss.
FCS is also performed for intestinal obstruction and ulcerative colitis, and sigmoidoscopy for chronic hemorrhoids to identify hemorrhoids.
Differences in contraindications
Considering the difference in indications, of course, we cannot remain silent about the differences in contraindications for these diagnostic methods. Of course, prohibitions on undergoing procedures cannot differ greatly due to their considerable similarity, but still there is a certain difference.
Sigmoidoscopy
There are much fewer contraindications to undergoing sigmoidoscopy than to colonoscopy, which is due to less access to the study, and, accordingly, the likelihood of aggravating the patient’s already pathological condition is reduced. Rectoscopy can be prescribed even in situations where the patient has minor unpleasant or painful symptoms.
This procedure is absolutely painless, and even if there is slight discomfort in the organs being examined, the patient should be patient for a while so that the doctor can determine the disease and prescribe the necessary therapy. There are few contraindications for undergoing rectoscopy, but they still exist.
These include:
- inflammatory processes of the rectum or sigmoid colon (acute form);
- exacerbation of mental disorders associated with increased activity;
- pulmonary and cardiovascular failure;
- traumatic injuries to the anus;
- thermal or chemical burns of the intestines;
- hemorrhoids (enlargement of the veins of the rectum);
- peritonitis (inflammatory process of the abdominal cavity).
But even these pathologies are not absolute contraindications - the doctor can always prescribe sigmoidoscopy if it is necessary to take emergency measures when a threat to the patient’s life arises.
Colonoscopy
This procedure is quite unpleasant for the patient, and therefore, if it is possible to postpone its completion for a while, then you should not conduct an examination for any acute diseases or even colds. It is better to be examined when your health status returns to normal. Colonoscopy, due to its deep penetration throughout the intestine, has a much wider range of contraindications than sigmoidoscopy, including:
- acute stages of heart disease (coronary disease, heart attack and others);
- violation of the integrity of the walls of the large intestine (perforation);
- large hernias of the abdominal cavity or small pelvis;
- ulcerative colitis (inflammation of the intestinal mucosa);
- peritonitis (inflammatory process of the abdominal cavity);
- blood clotting disorder;
- heavy bleeding in the intestines;
- anemia (decreased hemoglobin in the blood);
- severe general condition of the patient;
- pregnancy.
Hernias of the abdominal cavity and pelvis are a good reason for prohibiting colonoscopy
The listed pathologies during colonoscopy can lead to a deterioration in the condition of the patient, which forces doctors to abandon them in favor of less dangerous, but also less informative diagnostics.
Contraindications to intestinal endoscopy
Fibercolonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy cannot be performed in the presence of the following diseases:
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- stage 3 hypertension;
- peritonitis;
- respiratory failure
- acute forms of inflammation;
- acute inflammation of anal fissure;
- acute infectious diseases;
- hemorrhoidal thrombophlebitis.
Our clinic is equipped with modern endoscopic equipment, which makes it possible to accurately and quickly diagnose gastrointestinal diseases, as well as perform surgical operations to remove benign tumors.
Difference in preparation
Since sigmoidoscopy is the study of only two sections of the intestine - the rectum and the sigmoid colon, the patient is not required to perfectly cleanse the entire organ. It will be enough to refrain from dinner the day before and breakfast on the day of the examination, and do a cleansing enema a few hours before the examination.
For colonoscopy, it is necessary to thoroughly cleanse all parts of the intestine, and be sure to adhere to a slag-free diet in order to minimize the process of gas formation. Therefore, preparation for the procedure will take at least 3-4 days - to maintain proper nutrition, and about a day to get rid of feces with enemas or medications.
Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy, what is the difference and which is better?
Sigmoidoscopy
For many patients, it is not clear until recently what the difference between the two types of examinations is and which is better. Both of them provide important diagnostic information by examining the inner walls of the intestine. But choosing what exactly to prescribe is the prerogative of the attending physician.
Both studies will be effective only with proper preparation, the main part of which is following a strict diet and cleansing the intestines before conducting. The patient’s behavior after the examination is also important. There are no strict restrictions, but reasonable caution is required when switching to a normal diet. Overeating and abuse of heavy foods is not recommended.
Use of painkillers
It's no secret that most people try to avoid even a routine examination by a proctologist, during which no medical instruments are used. The mere understanding that the doctor will insert a finger to diagnose possible nearby diseases in the rectum or anus is disturbing long before the examination begins.
And when receiving a referral for any examination of the intestine with direct intervention in its lumen, many will be horrified by the upcoming procedures. But often this is mostly panic - pain can only be felt during a colonoscopy due to the introduction of air used to stretch the walls and folds of the intestine. This is done to study them more thoroughly.
Therefore, in certain cases, with a high pain threshold of the patient, the presence of inflammatory processes and adhesions in the intestines or cracks in the anus, medicated sleep (sedation) is used or anesthesia is administered. To relieve children from the fear of these manipulations, anesthetics must also be used, and they are necessary for the procedure for patients with mental disorders.
Sigmoidoscopy is carried out without the introduction of anesthetic drugs - the doctor, before inserting the sigmoidoscope, widens the anus with an anoscope. This reduces the possibility of pain, but if the patient feels severe discomfort, then the procedure must be continued after injection of a drug that reduces sensitivity.
What is the difference between colonoscopy and endoscopy?
Home / News / What is the difference between colonoscopy and endoscopy? November 14, 2014
Colonoscopy and endoscopy are similar procedures, the only difference being the organ being examined. Colonoscopy is a specialized type of endoscopy. Both methods are performed using a small tube called an endoscope, while colonoscopy is aimed at examining the large intestine. Both during colonoscopy and endoscopy, a rigid or flexible tube is used - an endoscope. An endoscope may have a camera at the end and may be equipped with a light to view internal organs. In addition, it has a built-in image transmission facility that helps the doctor to conduct an adequate examination.
The goal of colonoscopy and endoscopy is to obtain as much information as possible while using the least invasive method.
In many cases, surgery can be avoided in favor of one of these testing methods, or the procedures can reveal valuable information regarding the need for surgery to cure the patient. Minor risks associated with colonoscopy and endoscopy do exist. These include soreness at the endoscope insertion site, internal or external infections, and occasional side effects of sedation.
To examine the large intestine and small intestine using colonoscopy, an endoscope is inserted through the anus.
The endoscope illuminates the inside of the intestine and allows you to diagnose ulcers or polyps within the colon. The procedure also allows for biopsy of suspicious lesions in the colon. In some cases, the damage can even be completely removed. Endoscopy can have many different purposes. One of the most common is endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Gastrointestinal endoscopy helps examine the stomach, esophagus, duodenum, small intestine, large intestine (colonoscopy), and bile duct. The anus and rectum can also be examined in a magnified view using an endoscope.
Endoscopy can also examine the respiratory tract, ear canals, urinary tract, and reproductive system of women. During pregnancy, an endoscope can be used to examine the amnion (amnioscopy) and the fetus itself (fetoscopy). These procedures generally do not require any incision, but examination of some organs or closed cavities may require a small surgical incision. An examination of the pelvic or abdominal organs (laparoscopy), joints (arthroscopy), or chest organs (mediastinoscopy or thoracoscopy) is also performed.
Photo: nnoble.com
Further on topic:
- Smart toilet diagnoses diseases by analyzing stool and urine
- Magnetic stimulation relieves depression
- A universal flu vaccine has been created
- Acupuncture may reduce migraines
- Researchers have found a gut enzyme that helps prevent aging and frailty
- What is a cannula?
- Symptoms of gallbladder inflammation
- How to relieve sciatic nerve pain?
- What affects bone health?
- What are antacids?
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy are used to diagnose pathology of the large intestine. Endoscopic examinations can identify inflammatory and degenerative diseases, polyps, tumors, erosions and other conditions.
Possible complications
From a medical point of view and diagnostic value, of course, colonoscopy is considered the best option, since with its help you can carefully examine the entire intestinal mucosa and identify many pathologies in the initial stages. But due to the immersion of the patient in drug-induced sleep and dulling of his sensitivity, there is a possibility of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane by the colonoscope.
Severe pain when examining the intestines is a long-recognized myth
With sigmoidoscopy, the likelihood that this could happen is reduced to zero. Firstly, the device is not inserted deeply and the doctor can better control its movements, and secondly, the subject is fully conscious and in case of the slightest discomfort he will immediately notify the diagnostician.
Colonoscopy
A diagnostic research method carried out to identify intestinal diseases using a special endoscope (colonoscope) is called “colonoscopy”. The main functions are to examine the inner surface of the intestine and diagnose possible pathologies.
When is it prescribed?
Indications for examination using colonoscopy are:
- discomfort and pain in the anus and abdominal cavity;
- purulent discharge from the rectum;
- the presence of mucus in the stool;
- difficult bowel movements alternating with loose stools;
- sudden weight loss of unknown nature while maintaining nutrition;
- presence of cancer in a family history;
- anemia of unknown etiology;
- elevated temperature;
- intestinal bleeding;
- traces of blood in the contents of the distal colon.
The procedure is also prescribed if there is suspicion of:
- disruption of the movement of contents through the intestinal tract;
- Crohn's disease;
- the presence of various neoplasms;
- UC (nonspecific ulcerative colitis).
During the inspection, the following actions are possible:
- tissue sampling for analysis when neoplasms of various etiologies are detected;
- removal of a foreign body;
- removal of abnormal tissue growths (polyps) and small benign tumors;
- restoration of patency during intestinal narrowing.
How is it carried out?
Pre-cleaning includes two important stages:
- Following a special slag-free diet.
- Medicinal cleansing of the intestinal tract.
The study takes place in a specialized room. The examination is usually performed by an endoscopist surgeon.
Step-by-step colonoscopy:
- The patient, who first undresses to the waist, is placed on the couch on his left side with his knees bent and his legs pressed to his stomach.
- Anesthesia is administered.
- The specialist slowly and carefully moves the colonoscope deep into the colon, filling it with air to straighten the folds.
- The doctor, by palpating the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, controls the passage of the device through the bends of the rectum.
- During the entire procedure, a video is shown on the screen, which is carefully studied by the endoscopist.
- At the end of the study, gas is removed from the intestine, the endoscopic device is carefully removed and disinfected.
Patients who have undergone local anesthesia or sedation leave the clinic on the same day. The person being examined under general anesthesia is moved to a ward until the anesthesia wears off or left in a medical facility for several days under the supervision of specialists.
Videos of the procedure or photos of individual areas of the colon can be recorded on digital media. At the end of the examination, the doctor enters the data into a special document, gives the necessary instructions and writes a referral to a specialist for further treatment.
Contraindications
- acute myocardial infarction;
- diseases of the bronchial system;
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- severe circulatory disorders;
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy;
- penetrating damage to the walls of the colon;
- diverticulitis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- inguinal or umbilical hernia;
- general serious condition of the patient.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of colonoscopy include the following factors:
- this is one of the most accurate and informative ways to assess the condition of the intestine available to modern medicine;
- high visualization allows a specialist to detect even minor changes;
- Along with the examination, it is possible to carry out a number of therapeutic manipulations.
The advantage of colonoscopy is also considered that the examination allows:
- assess the condition of the mucous membrane and walls;
- determine the spread of pathologies;
- differentiate inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- takes a little time.
The disadvantages include:
- the complexity of the preparatory stage, the accuracy of which determines the reliability of the information obtained during the study;
- fear of the procedure, which usually causes anxiety and requires the patient’s psychological attitude;
- the need for anesthesia due to pain;
- the risk of a condition that aggravates the underlying disease.
The disadvantages of the procedure include the risk of the following complications:
- end-to-end violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls;
- bleeding;
- reaction to sedatives;
- nausea;
- gagging;
- temperature increase;
- feverish condition;
- pain in the abdominal cavity.
The video explains the colonoscopy procedure. Filmed by the channel Live great!
Conducting a survey
Differences between procedural methods are based on differences in the structure and length of the devices, as well as the areas of the intestine being diagnosed. These differences include the position of the patient during the examination - during rectoscopy he is asked to stand in the knee-elbow position, and during colonoscopy the subject is placed on his left side.
Only in certain cases, when it is possible to use a flexible device during sigmoidoscopy, can the patient be placed on his side to increase his comfort. Due to the size of the colon surface being examined, colonoscopy takes approximately 30 minutes to 1 hour, while rectoscopy takes only 5–10 minutes.
Preparing for the study
Preparing for a colonoscopy examination of the rectum consists of strictly following the doctor's instructions. The main condition for obtaining an informative result is a clean intestine without feces. If the feces are not completely eliminated, the proctologist may postpone the diagnosis to the next day, since fecal plugs will not give a complete picture of the condition of the organ. An erroneous diagnosis will not lead to the patient’s recovery, but will only worsen the problem.
48 hours before the session, the patient goes on the recommended diet. Products that contribute to excessive gas formation are excluded. You cannot eat fresh fruits and vegetables, pearl barley, rolled oats, millet, black bread, sunflower seeds, fatty fish and meat, milk, kvass.
You can consume lean meat and boiled fish, fermented milk products, biscuits, jelly, teas (green varieties, not strong). Some medications should not be taken. For example, medications containing iron, activated carbon. The day before testing the condition of the colon, a thorough cleansing is required. To do this, they resort to enemas, medicinal laxatives, oral and local use.
Patients who have shyness, a feeling of discomfort and inconvenience in front of a specialist conducting an examination in the anorectal area are recommended to purchase special panties for colonoscopy. Then the psychological state will be more predisposed to the procedure.
After the procedure
At the end of the rectoscopy, the patient can get dressed, and if he does not need the results of the examination very urgently, go about his business. Whereas after a colonoscopy performed under anesthesia, he needs to spend two hours under the supervision of an anesthesiologist, and only when the specialist is convinced that everything is in order can he leave the diagnostic room.
For a patient planning a colonoscopy with the use of anesthetic drugs, the best option would be to ask someone close or familiar to accompany him to the procedure and back. This will help avoid unexpected reactions associated with the administration of sedatives.
Rectoscopy
An endoscopic examination aimed at studying the condition of the intestine using a sigmoidoscope (rectoscope) is called sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy). Inflammatory processes, all types of neoplasms in these organs are diagnosed and, if necessary, removed using this procedure.
Diagnostic rectosigmocolonoscopy is performed for the purpose of a thorough examination of the intestinal mucosa. This procedure is prescribed to determine the correct treatment tactics.
With the help of such an examination it is possible to diagnose:
- rupture of the mucous membrane of the final part of the digestive tract;
- chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane with the formation of ulcerative processes;
- congenital malformations of the distal intestine.
In addition, sigmoidoscopy is indicated when symptoms occur:
- cutting, pain in the anorectal area;
- purulent inclusions and mucous discharge from the anus;
- bleeding;
- constipation;
- IBS (irritable bowel syndrome);
- hemorrhoids;
- pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood due to iron deficiency of unknown etiology;
- chronic colitis, enterocolitis;
- severe symptoms of intestinal microflora disturbances for no apparent reason;
- causeless weight loss;
- alternation of loose stools and difficult bowel movements;
- uncontrollable urge to defecate;
- preparation for further intestinal examination;
- suspicion of polyps;
- possible pathological growth of the endometrium;
- presumptive oncopathology.
Therapeutic indications for the procedure include:
- removal of abnormal tissue growth (polyps);
- removal of foreign objects;
- stopping bleeding from blood vessels, ulcers, tumors.
Before performing rectoscopy, it is necessary to collect information about the presence of diseases and allergic reactions in the patient, as well as medications taken. The examination is possible only 5-7 days after an X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract using barium, since it interferes with the examination of the mucous membrane.
The sigmoidoscopy procedure, like colonoscopy, requires preliminary preparation:
- 2-3 days before the procedure, you must begin following a certain diet;
- the night before and on the day of the study, you should avoid eating any food;
- to empty the intestines of contents, cleansing enemas are performed, which can be replaced by taking laxatives;
- Half an hour to an hour before the diagnosis, the patient is given a microenema.
The inspection includes the following steps:
- The patient is asked to undress to the waist and is placed on the examination table with his back or left side, with his legs bent at the knees. It is possible to use the knee-elbow position.
- The specialist examines the patient’s anus, assesses its condition and palpably examines the mucous membrane for the presence of feces, mucous and blood discharge.
- The sigmoidoscope is lubricated with Vaseline and carefully inserted into the anus to a depth of about 5 cm.
- Air is pumped into the intestines to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane. When moving the sigmoidoscope to a depth of 10–15 cm, the problematic area is reached – the natural curvature of the intestine. To prevent discomfort, the patient should relax as much as possible.
- The sigmoidoscope is removed using gentle rotational movements. In this case, the specialist carefully examines the rectal mucosa.
- Pathological areas found during examination are removed, or tissue is collected for further histological examination.
After the procedure is completed, the patient is left alone in the office for a short period of time, so as not to embarrass him during the period of gas leaving the intestines. The duration of the recovery process depends on the general condition of the patient and, as a rule, varies from 5 minutes to half an hour. If the patient feels well, he can immediately leave the clinic.
Sigmoidoscopy is characterized by the following advantages:
- the procedure is relatively easy to perform and takes little time;
- the study is well tolerated and, as a rule, does not cause complications;
- examination allows you to study the condition of the objects under study with the possibility of conducting an accurate biopsy;
- The examination may be accompanied by therapeutic procedures, if necessary.
- the procedure makes it possible to study a short section of the colon and examine only the mucous membrane;
- in rare cases, perforation of the intestinal walls is possible.
Cost of research
If we take into account the capacity, duration of colonoscopy and the need for the most expensive equipment to perform it, it becomes clear that this method is several times more expensive than rectoscopy. And if you add the cost of anesthetic drugs, the price will at least double, but the doctor will have the opportunity to examine in detail the entire surface of the organ.
The price of a colonoscopy is mainly determined by the need for expensive equipment and the high information content of the study
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: areas of examination
Sigmoidoscopy of the intestine is a method based on visual inspection of certain parts of the intestine. This is mainly the mucous membrane of the rectum; less often, this method is used for the distal parts of the sigmoid colon (on average, up to a distance of 20-25 cm from the injection site - through the anus). This diagnostic method is considered one of the most informative in modern medicine.
It allows you to visually assess the condition of the intestine in the area it covers. Such diagnostics are often used to check for the presence of various neoplasms, since the technique allows not only to examine the surface of the intestine, but also to immediately perform a biopsy if something suspicious is noticed.
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination in which the entire large intestine is examined using a special instrument. That is, the instrument penetrates 120-150 cm of the total length of the intestine. This makes the technique more informative compared to sigmoidoscopy. And this is the main difference between these two methods - in the areas of research coverage.
There is another research method - irrigoscopy . What kind of diagnosis is this? This method is an x-ray examination of the colon using a special x-ray contrast agent.
Often the doctor is faced with a choice - sigmoidoscopy or irrigoscopy. Since the second method is considered more gentle (only a substance is injected, and not a rigid instrument), then if there are contraindications to sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, this particular X-ray examination is chosen. But since it is more suitable for contour diagnostics and not all changes are visible on it, it can be considered a kind of compromise.
Both sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy help assess the condition of the intestinal walls according to several basic characteristics, changes in which may indicate the presence of a serious disease - the color of the walls, vascular pattern, elasticity, tone, and, to identify tumors, relief.
How to choose the optimal examination option?
Knowledge of all the features of diagnostic tests allows the patient to avoid complications in unforeseen circumstances, properly prepare for procedures and choose the best conditions for the procedure. But this is where the powers of the patients end, and everything else should be decided by a specialist with the appropriate education.
Only he or a medical council can make decisions regarding the choice of the optimal type of diagnostics to establish a diagnosis for certain symptoms. Therefore, the question is not raised which examination is better for any reason, but its feasibility for a given pathology is taken into account.
Which research method is better?
Despite a number of differences between colonoscopy and rectoscopy, these research methods are not usually opposed to each other. The doctor prescribes the examination that is most appropriate. In some cases, both procedures are carried out to obtain maximum information.
You can evaluate the difference between colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy and which research method is better based on several factors:
- Information content. When it comes to diagnostic value, colonoscopy wins. This procedure is intended for a thorough diagnosis of the mucous membrane from beginning to end of the colon.
- Soreness. From the point of view of the patient’s subjective feelings, colonoscopy is more painful. Sigmoidoscopy is accompanied by less discomfort. Sigmoidoscopy does not require anesthesia; anesthesia is administered only in some cases or, at the patient’s insistence, sedatives are used.
- Simplicity and ease of implementation. Colonoscopy takes two to three times longer than a sigmoidoscopy examination and requires more thorough preparation before it is performed.
What is the difference between the methods?
To answer the question of how colonoscopy differs from sigmoidoscopy, you need to delve a little deeper into the structure of the large intestine. It consists of several sections - the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid and rectum.
The main difference between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy is the depth of the examination:
- Sigmoidoscopy allows you to examine the rectum and the final section of the sigmoid colon to a depth of 25-30 cm from the anal passage.
- Colonoscopy makes it possible to examine the entire large intestine.
Accordingly, various tools are used for these purposes:
- A sigmoidoscope is a rigid metal instrument that is inserted into the rectum.
- A colonoscope is a flexible fiberoptic instrument that can be passed throughout the large intestine.
Since sigmoidoscopy is practically not accompanied by discomfort or pain, it is much easier to tolerate by patients and does not require anesthesia. Its duration rarely exceeds 5-10 minutes. Preparation for sigmoidoscopy is not as thorough as for colonoscopy.
How much does research cost?
A sample of the cost of colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy services is presented in the table:
| Region | Cost of colonoscopy | Firm | Cost of sigmoidoscopy | Firm |
| Moscow | from 2900 rub. | "Trustmed Medical Center on Taganka" | from 1000 rub. | "Medical On Group - Balashikha" |
| Chelyabinsk | from 1000 rub. | "City Hospital No. 8" | from 400 rub. | "Polyclinic of Hospital No. 2" |
| Krasnodar | from 1600 rub. | "Railway Hospital" | from 700 rub. | "Family Health Clinic "City Clinic"" |