Today, medicine has made high-tech progress in the field of examining the human body. Thanks to this, various techniques have been created that allow a complete examination of the entire body without surgical manipulation.
This makes it possible to distinguish any disease, even at an early stage of development, which greatly simplifies treatment.
Such diagnostics include:
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
In what cases is it advisable to use RCT?
Before you familiarize yourself in more detail with the question of what RCT is, you need to understand that in some cases the benefits of its use significantly outweigh the harm. The speed of obtaining information allows you to quickly establish a diagnosis and save lives when there is no time for lengthy laboratory tests.
Using the instrumental method, the following is revealed:
- Pathologies of the peritoneal organs, hypertrophy of the lymph nodes, inflammatory foci, proliferation of neoplasms. In a short time, the computer will process the information and determine the scope of the problem and its location.
- Bleeding in the liver, tumors, cysts, degenerative phenomena, a factor that provoked the formation of jaundice.
- Assessment of tissue density by performing an X-ray CT scan of the brain, which identifies aneurysms, tumors, predisposition and consequences of stroke.
- Diseases of the chest organs (pneumonia, cancer, life processes of Koch's bacillus), the state of blood flow, heart muscle, stenosis of the esophagus, destructive changes in the thoracic spine can be detected. CT scanning of the lungs detects any abnormalities in the alveoli, which makes it possible to stop the processes in the initial stages.
- Changes in the spine, hernias, cracks, fractures, areas of infection. Diseases of bones, joints, and muscle fibers of the extremities are determined.
- The condition of the kidneys and ureters is assessed. The device detects stones, neoplasms, and congenital anomalies.
- Intestinal diseases are used as a control method to prevent cancer after 50 years.
- Pathological changes in the reproductive organs.
It is worth noting that initially doctors resort to simpler and safer diagnostic methods. If the cause of symptoms can be determined using laboratory research methods or other instrumental methods, then they are used. In order to clarify the result, an RCT diagnosis may be indicated.
The doctor may prescribe an RCT if necessary:
- conduct a screening test (chronic diseases, suspected cancer);
- urgently diagnose the cause of seizures and bleeding, see a clear picture of the consequences of injuries;
- additional examinations due to uninformativeness of previously conducted ones;
- to clarify the location of the pathological focus before surgery.
The method is quite expensive; the attending physician prescribes it only when it is not possible.
MSCT of the chest organs
This is a highly informative modern diagnostic method, widely used to identify a large number of chest pathologies. Often it becomes the final examination confirming the diagnosis. MSCT of the chest (CHC) is also used to adjust the treatment plan. Thanks to this technique, it is possible to accurately visualize all bone structures, cartilage, nerves, soft tissues, blood vessels, lymphatic systems and mammary glands in women. Indications for MSCT of the chest:
- pulmonary infarction;
- suspected cancer, cysts or metastases;
- lung adenocarcinoma;
- diseases of the aorta or large vessels;
- suspicion of abscess, tuberculosis, pneumonia, pleurisy and other infections;
- diseases of the esophagus;
- aortic pathology.
- Ham salad: delicious recipes
- Banana pancakes: recipes
- How to knit booties with knitting needles
Advantages of the diagnostic method
Compared to radiography, RCT is superior. The main advantages of the modern method are:
- expansion capacity is 20 times greater than that of x-rays;
- no blurred image;
- obtaining an image in three dimensions.
The similarity with X-rays is that both are sources of radiation. The average radiation dose is 2-11 m3v (this figure may change for various reasons).
Preparing the patient for examination
If a doctor prescribes an X-ray computed tomography examination of the skull, brain, nose, temples, neck, thyroid gland, larynx, sternum, spinal column, scapular bones, large articular surfaces, there is no need for preparation. But it’s definitely worth studying the topic and understanding what it is—an RCT study.
RCT of the peritoneal organs without the use of contrast is done on an empty stomach. If the study is carried out using an intravenous injection of contrast, then first familiarize yourself with the patient’s allergic history and determine the absence of contraindications to the components of the injected substance. RCT with an amplifier is performed on an empty stomach. In addition to the daily water intake, you should drink up to two liters of liquid the day before the procedure.
CT colonography requires bowel cleansing. If coronary angiography is planned, you cannot do without monitoring the following indicators:
- heart contraction in a calm state - 65 beats/min.;
- no heart rhythm disturbances;
- ability to hold your breath for 25 seconds.
When examining the liver, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys, the examination is performed on an empty stomach. The day before the procedure, you should avoid raw vegetables, fruits, juices, carbonated water, black bread and milk. Enzyme preparations and antioxidants are not taken.
How the procedure works
Knowing all the advantages and disadvantages of the research method, what RCT is and how it is possible to obtain images in several projections, the whole world continues to use the medical instrumental approach to diagnose serious pathologies.
X-ray rays, penetrating into tissues, are reflected on the sensors with varying strengths. The intensity may differ, since the organs have different structures. The density of the reverse flow forms an image - a tomogram.
Important! The presence of implants and metal objects is not an obstacle to diagnosis, unlike MRI.
X-ray computed tomography is performed using x-rays. A modern research method allows you to obtain a two-dimensional three-dimensional image. There is a feature in the design of the device that distinguishes X-ray CT from conventional x-ray. The source of the rays is a ring-like contour. There is a couch built inside. The position of the patient allows you to obtain images from various points at convenient angles. The computer collects information, carries out processing and produces a model of the organ in a three-dimensional image.
Doctors use one of three existing types of RCT examination:
- The rotation of the X-ray tube around the patient and the simultaneous movement of the patient is helical. Due to the fact that the procedure is carried out quickly, it is possible to obtain a minimal dose of radiation.
- RCT system that allows scanning up to 500 layers. The multilayer technique receives radiation from sensors located in several rows. In this way, you can examine the organ during operation.
- Multispiral X-ray CT of organs uses accelerated technology: the equipment scans quickly and is capable of increasing resolution. The device is used to examine small vessels. The diagnostic method is used by patients with cardiac problems.
Contraindications to the use of the method
Since the medical referral procedure uses X-rays, which have an effect on all systems and organs, not everyone is recommended for this diagnostic research technique. Contraindications include:
- kidney dysfunction;
- obesity (150+);
- plaster or metal splints;
- fear of confined spaces;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- disturbance of psycho-emotional state.
Important! The presence of concomitant diseases and treatment features should be reported to the leading specialist. In case of a possible pregnancy, you should also not hold back information so as not to harm yourself and the fetus.
Is there any harm from RCT to health?
What is RCT? It is an effective and informative medical tool. The capabilities of the device cover all its shortcomings. Harm primarily comes from x-ray exposure. The rays negatively affect the structure of the blood, as a result of which pathological foci develop, provided that the permissible dose is exceeded.
It should be noted that doctors do not prescribe this examination method unless less dangerous ones have been tried (laboratory tests, ultrasound).
The minimum interval between CT scans should be at least six months. Thus, the annual norm is almost impossible to exceed.
Disadvantages of CT and MRI
There are contraindications for MRI or CT scanning of the brain, which becomes a disadvantage for the chosen examination method.
There are absolute contraindications, which mean that the examination cannot be performed under any circumstances, and relative contraindications, when the examination is possible only if certain conditions are met.
Contraindications for CT scan of the brain:
- Absolute. Pregnancy; The patient’s body weight is too high (usually over 150 kg), the working space of the device is limited.
- Relative. Unconscious or severe condition of the subject (decompensated cardiovascular failure, etc.); fear of closed spaces; inadequate condition of the patient.
Complications
If the radiation dose is exceeded, in an adult patient this may cause:
- suppressed immunity due to a decrease in the number of leukocytes (leukemia);
- poor blood clotting due to a decrease in the number of platelets (thrombocytopenia);
- breakdown of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood (hemolytic disorders);
- disturbances in the respiratory function of tissues due to the breakdown of red blood cells (erythrocytopenia).
Adverse deviations occur only when there is an overdose of X-ray radiation. After isolated cases of undergoing radiation examinations, the body recovers within a few days.
For one adult, a dose of 150 m3v per year is not dangerous. For an infant, the rate is significantly lower, as is the case for people suffering from acute and chronic pathologies.
Drugs
As already emphasized, almost all preparations used for computed tomography contain iodine salts. However, they differ from each other in the following important indicators:
- Concentration of the active substance. On the one hand, the more contrast molecules in the preparation, the better, since this should improve image quality. But an interesting paradox was discovered - with increasing concentration, the viscosity of the drug also increased, which negatively affects its distribution in the vascular bed. Therefore, in all modern contrasts this figure does not exceed 350 mg/ml.
- Hydrophilicity (ability to absorb water). Contrasts with high hydrophilicity do not penetrate cell walls well, but are less likely to cause adverse reactions, and therefore are ideal for CT angiography (Urografin, Telebrix). Drugs with low hydrophilicity (Omnipak, Ultravist, Vizipak, Imagopak) penetrate well into the middle of the cells, so they are used if it is necessary to examine individual organs of the abdominal cavity.
- Osmolarity (an indicator that shows the concentration of active molecules in the drug). The toxicity of contrast is directly related to it. The highest osmolarity is in Urografina, the lowest in Vizipak.
"Urografin"
The drug of choice for CT angiography is a study in which the vessels of the abdominal cavity are visualized. Contrast does not penetrate well from the vascular bed into tissues and organs. The recommended dose of Urografin for adult patients for oral administration before CT is 20-50 ml, but in certain situations it can be further increased. The dosage of Urografin for children is presented in the following table:
| Age | Contrast volume, ml |
| Up to a year | 7-10 |
| 1-2 years | 10-12 |
| 2-6 years | 12-15 |
| 6-12 years | 15-20 |
| Over 12 years old | 20 |
The drug is administered intravenously slowly so that the procedure lasts 5-10 minutes. The only exception to this rule is patients with uncompensated pathologies of the cardiovascular system (20-30 minutes).
The study begins a minute before the end of the administration of Urografin. The diagnostic window lasts 20 minutes in patients without kidney pathologies.
The drug "Urografin"
"Omnipak"
The drug is used both for angiography and for contrast enhancement in CT. Its particles penetrate well through the cell membrane and accumulate in peripheral tissues. Therefore, with its help it is easier to detect areas of inflammation or oncological processes . For adult patients, 100-200 ml of the drug is administered intravenously, and for children, an individual dosage is calculated based on the ratio of 2-3 ml per 1 kg of body weight.
The drug "Omnipak"
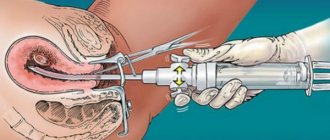
Why is contrast administered during RCT?
A contrast agent is usually used during a secondary examination, when the primary examination did not provide a clear picture, and the doctor still has doubts about the correctness of the diagnosis. The contrast is presented by iodine preparations; accordingly, it is important to make sure that the patient does not suffer from intolerance to the components.
Not all people are allowed the diagnostic method using contrast, since the substance overloads the heart, kidneys, and liver.
The drug is administered intravenously or suggested to be inhaled through the nose. It should be noted that this research method is justified if it is necessary to clearly examine the focus of the pathology, since small details are not lost from view.
Important! Patients who do not have a predisposition to allergies usually tolerate the administration of a contrast agent well. If the drug is administered quickly into a vein, the likelihood of an allergic reaction is significantly reduced.
What does it show?
MSCT clearly displays solid structures and hollow organs, which provide clear boundaries in the images. A contrast agent is used to examine soft tissues and blood vessels. The scan can reveal the following pathologies:
- developmental anomalies;
- ulcerative lesions;
- liver cirrhosis and hepatitis;
- pancreatitis;
- kidney , gall bladder and duct stones;
- atherosclerosis and thrombosis of abdominal vessels;
- consequences of injuries;
- polyps and oncology.
Previously, some of these diseases could be detected using x-rays. But with such a study, a two-dimensional picture was obtained, sometimes the images were superimposed on each other.
With MSCT, it is possible to obtain images with a large number of sections along three axes: transverse, vertical and sagittal. This allows you to assess the depth of the lesion in an ulcer or determine the size and shape of gallstones. When diagnosing oncology, MSCT is an indispensable method , thanks to which it is possible to distinguish cancer from a benign tumor.
Is it possible to do RCT for pregnant women?
Before deciding to conceive a child, the expectant mother must be vigilant. This rule is also relevant when a happy moment has happened. If the doctor recommends undergoing any tests or instrumental diagnostic methods, you should clarify the interpretation of the RCT study, what it is and what the possible consequences are.
Humans are sensitive to radiation emissions. There is no organ that does not respond to rays. During gestation, the embryo is at risk. X-ray flows can negatively affect the processes of restructuring of the body:
- change hormonal levels;
- psycho-emotional state;
- metabolic processes.
If RCT was prescribed to a woman who did not know about her pregnancy, the further development of the fetus cannot be predicted. Before 12 weeks, termination of pregnancy may be recommended. There is a high probability of fetal death or spontaneous abortion.
If the fetus can be saved, there may be defects of the maxillofacial area, sensory organs, thyroid gland and further developmental anomalies.
The doctor determines the viability of the fetus and the likelihood of a successful pregnancy based on:
- gestation period;
- places that were exposed to radiation;
- genetic consultations;
- ultrasound results.
After the diagnostic method, there are no contraindications to conception.
Harm of computed tomography with an enhancing agent
Computed tomography is an x-ray diagnostic method, therefore, the patient is susceptible to radiation. In this case, the radiation exposure is much higher than with radiography. Typically, with an abdominal CT scan, the patient receives 5-14 mSv (depending on the type of machine). Although this dose exceeds the recommended dose for an ordinary healthy person (1-2 mSv), it remains safe.
Without emergency indications, it is recommended to conduct the next study no earlier than 6 months after the previous one. If you do CT scans frequently, you can increase the risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
Important The contrast used for the procedure is not radioactive. But during its administration and 30 minutes after, medical monitoring of the patient’s condition is required. It is during this period that undesirable reactions most often develop.
Side effects
The vast majority of patients tolerate the procedure well. But in a small number of cases the following side effects may occur:
- Allergic reactions (rash, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, disturbances in heartbeat and breathing).
- Increased body temperature.
- Dyspeptic disorders (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting).
- Pain in the head or peripheral muscles.
- Systemic fibrosis (skin, muscles, liver, heart, lungs).
- Nephrotoxicity and acute renal failure.
- Thyroid dysfunction (hyperthyroidism).
Principle of radiation protection
Having an idea of the procedure, knowing a clear definition of an RCT examination, what it is and how important it is to resort to it in a timely manner, few people were interested in the possibilities of avoiding the danger of radiation.
You can reduce the amount of radiation exposure:
- Reducing research time.
- By refusing to take pictures in several projections.
- By reducing the current on the X-ray tube.
- Carry out the procedure through bismuth screens.
- Use lead protection.
In order to obtain good quality images the first time when examining children, children are prescribed sedatives before the procedure.
If the question is relevant: where can RCT be done, then the answer is obvious. It is important that this is a medical institution that meets standards and sanitary norms. The clinic’s specialists are qualified and have all the skills to work with equipment and patients.
RCT is a research method that has significantly facilitated the work of doctors in all areas, as well as saving the lives of many patients. Reasonable use of the resource and the professionalism of doctors allow us to evaluate only the benefits of fast and high-quality diagnostics.