Diagnosis of lumbago 9237
Currently, MRI of the lumbosacral spine is the most advanced and progressive procedure for examining all tissues. Magnetic resonance diagnostics allows you to visualize and evaluate the condition of not only bone tissue, as in an x-ray examination, but also ligaments, tendons, muscles, intervertebral discs, radicular nerves, etc.
MRI is prescribed as a reliable way to diagnose the condition of the spinal column. At the initial visit, the doctor prescribes x-rays, from which he can only indirectly assess the condition of the intervertebral discs. If the distance between adjacent vertebral bodies is reduced, then disc protrusion can be assumed. It is impossible to determine the presence of a herniated disc using radiographic examination.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics is the most effective today, since it allows us to detect even minor degenerative and dystrophic changes in the cartilaginous tissues of the intervertebral discs.
The undoubted advantage of the method is the use of a fundamentally new method during the procedure - magnetic radiation, which, as a result of collision with cells, gives a resonant layer-by-layer image of tissue. It does not harm human health.
Meanwhile, layer-by-layer sections, modeled using a computer program into a single image, make it possible to visualize the entire radicular nerve, dura mater of the spinal cord, nerve plexuses, vertebral bodies, arcuate and spinous processes, intervertebral discs, their fibrous rings and pulpous discs. MRI can detect hernias of even minimal size.
Note! Only an experienced vertebrologist or neurologist can evaluate the results of the examination. On your own, even if you have a transcript, you are unlikely to be able to assess the condition of your spinal column and surrounding tissues. Therefore, after the examination, consult a specialist. He will also be able to recommend a suitable treatment method.
What will tomography demonstrate?
MRI of the lower back makes it possible to visualize a clear picture of the corresponding part of the spine, demonstrating it in detail.
The image clearly shows the visualized vertebral bodies that were in the study area, in addition to the intervertebral discs, spinal cord and nearby tissue.
MRI demonstrates visualized symptoms of the following pathological processes in the local area:
- osteoarthritis, osteoporosis and osteochondrosis of the lower back;
- injuries and lesions of the lumbosacral region;
- intervertebral hernia;
- spinal stenosis;
- pathological vertebral fusion;
- cauda equina syndrome;
- tumors (benign and malignant);
- metastases in the local area of the spine;
- myelitis;
- bone infections;
- multiple sclerosis;
- hemangioma;
- abscesses;
- areas of inflammation of bone, soft tissue, etc.
Diagnostics helps to identify pathologies that cannot be determined by other research methods.
Osteochondrosis
Indications
MRI of the lumbar region helps to detect congenital pathologies, tumors, narrowing of the spinal canal, etc. This study is carried out to identify diseases of the spine and surrounding tissues, assess blood flow, and the structure of the vertebrae.
An MRI of the lower segment of the spinal column is necessary in the following cases:
- Restricted mobility, pain in the lower back.
- Painful sensations in the buttocks and legs.
- Impaired sensitivity of the lower extremities, which is manifested by tingling, “crawling”, weakness, nagging pain.
- Disorders of urination and defecation.
- Functional disorders of the pelvic organs.
The latter symptoms indicate poor circulation and damage to the nerves of the lower spine.
MRI is prescribed if the following pathologies of the lumbosacral region are suspected:
How to do an MRI of the thoracic spine
- Osteochondrosis.
- Injuries to a vertebra or several elements.
- Oncological formations.
- Damage to blood vessels of the lumbosacral segment.
- Stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal.
- Tuberculous spondylitis (damage to the vertebrae due to tuberculosis).
- The growth of osteophytes along the edges of the vertebral bodies.
- Spinal infections (infection of the spine).
- Inflammatory processes of the lumbosacral region.
MRI helps clarify the diagnosis after radiography, ultrasound, etc.
What is needed to pass the examination
To undergo magnetic tomography of the lower back, the patient will have to take a referral for the procedure from the attending physician. If you plan to undergo another MRI, the patient must have the results and a transcript of previously taken images with him - specialists will be able to assess the dynamics of the disease and monitor therapy.
If a person is indicated for MRI diagnostics of the lumbosacral spine with contrast, the interval between procedures should be at least three days (with internal contrast) and seven days (with the introduction of contrast into the spinal cord canal).
Progress of the procedure
Not all patients undergoing examination know how an MRI is performed. The procedure differs slightly depending on the type of installation.
The MRI procedure is comfortable for most patients
A standard MRI scan goes like this:
- The patient changes clothes and lies down on a horizontal table, which will then move into the tomograph.
- It is recommended to secure the body with belts so that the patient does not accidentally move. After all, then the results will be distorted.
- The table slides into the tomograph. If the installation is of an open type, then the upper part of the device will be placed above the lumbosacral region, and the upper part of the body will be placed outside.
- Some units make loud noises during operation, so you may want to wear earplugs before the procedure.
- During the examination, the diagnostician will communicate with the patient through a microphone. It is important to follow his recommendations.
MRI does not cause discomfort or pain. After the diagnosis, the patient leaves the office and waits for the results.
Using modern open-type installations, MR scanning with verticalization is carried out. Then the diagnosis occurs in 2 stages:
- At the first stage, the patient is in a horizontal position.
- At the second stage, the table takes a vertical position. This will help the diagnostician see how the vertebrae shift and the shape of the discs between them changes.
Axial load testing helps accurately identify lumbosacral hernias.
The question of how long an MRI lasts is quite relevant. A standard examination takes at least 15 minutes, during which time the table moves inside the tomograph several times. The larger the area that needs to be examined, the longer the MRI takes. The maximum duration of the procedure is 30 minutes.
List of contraindications
All existing restrictions on diagnostics can be divided into two groups: absolute and conditional. The first includes:
- presence of vascular clips;
- the presence of implantable electronic devices in the patient’s body;
- use of a built-in pacemaker.
When it comes to conditional contraindications, you can undergo an MRI of the lower back, but with caution (using devices of a specific design). Conditional restrictions include:
- heart failure;
- the patient’s condition in which he is unable to remain in a stationary position for a long period;
- the presence of metal-ceramic dentures;
- intolerance to confined spaces;
- detection of metal fragments in the patient’s body;
- the body weight of the subject is more than 120 kg.
What does tomography show in women?
MRI of the lower back in women shows lesions of the vertebrae and nearby tissues. Tomography diagnoses oncology of the internal organs of the reproductive system. The same method reveals pathological processes in the bladder and intestines, as well as metastases in the lymph nodes and subcutaneous fat.
In gynecology, MRI is used to determine the cause of a patient’s sterility, inability to bear a child, abdominal pain, and the presence of blood clots in urine and feces. The result of tomography makes it possible to diagnose congenital or acquired diseases of the reproductive organ, ovaries and fallopian tubes.
MRI of the lower back during menstruation
The presence of menstrual bleeding when diagnosing pathologies of the local area can distort the tomography data. Therefore, MRI is performed at the end of menstruation. The seventh day of the cycle is considered preferable for scanning.
MRI of the lower back during pregnancy
At the moment, there is no evidence of the negative impact of MRI on the fetus. However, magnetic tomography is contraindicated during the formation of the child’s internal organs and tissues - this is the first trimester. During the rest of pregnancy, MRI can be performed in cases where the risk to the child can be neglected due to a possible danger to the health of the mother.
When is magnetic resonance imaging indicated?
The procedure can be performed to examine the entire spine, but most often the need for it arises when diagnosing pathologies in the cervical and lumbosacral spinal area.
MRI neck
The occurrence of formations that can be seen on MRI, such as hernias, is observed less frequently in the cervical zone than in the lumbar, and even more so the thoracic. However, MRI of the neck is often performed, since hernias in this area are accompanied by osteophytic formations that deform the edges of the vertebrae.
MRI neck
MRI of the neck is done:
- if cervical osteochondrosis is suspected;
- when there is a possibility of detecting protrusions or hernial formations;
- with abnormal development of the cervical spinal zone;
- after a neck injury;
- if there is a suspicion of tumor formation or metastasis in this area.
MRI of the cervical spine
By the way. An MRI of the neck reveals not only the normal or abnormal functioning of this part of the body, but also determines the performance of the brain, which largely depends on how well the vessels and arteries of the cervical area work.
MRI of neck vessels
Breast MRI
The thoracic area, in which most of the spinal column is located, securely covered by the “armor” of the ribs, can also be susceptible to diseases and pathologies.
Thoracic spine
MRI of the thoracic area is prescribed for the following conditions:
- thoracic osteochondrosis;
- a fracture or injury in a given vertebral area that cannot be seen on an x-ray;
- protrusions and hernial formations;
- tumor-like formations with foci in the thoracic region of the spine and metastases from tumors located in other tissues;
- structural defects, developmental anomalies of congenital and acquired type;
- impaired blood supply to the spinal cord;
- inflammations and diseases associated with them (Bechterew's disease);
- destructive processes causing necrosis;
- vascular and venous anomalies.
MRI of the chest
This study is also used to monitor the spine and determine its condition after surgery or in preparation for surgery.
MRI of the lumbar and sacrum
The lumbosacral area is subjected to magnetic resonance imaging more often than any other area of the spine. This department experiences the heaviest stress and is more susceptible to injuries and infections.
MRI of the spine in the lumbar and sacral area is performed in three projections, concentrating on examining the locations of pain and suspected lesions.
MRI of the lumbosacral region
By the way. Research with this device can also be carried out using a contrast agent. It is used when it is necessary to examine the tumor as clearly as possible or measure the degree of deviation.
What will help identify an MRI of the lower back and sacrum.
- The presence of osteochondrosis and osteoarthrosis.
- Fracture or injury in this area.
- Protrusion or hernia.
- Lumbar spinal stenosis.
- Sacralization of vertebral segments (in which the vertebrae are pathologically fused).
- Osteoporosis at any stage.
- Damage to the spinal nerves, called cauda equina syndrome.
- Benign and non-benign formations and their metastases.
- Hemangiomas.
- Manifestations of multiple sclerosis.
- Myelitis.
- Bone infections.
- Abscesses and inflammations.
MRI of the sacrum
How to prepare for diagnosis
Due to the simplicity of the procedure, there is no need for serious or specific preparation for MRI of the lumbosacral spine. Tomography is carried out at any time of the day without prior use of any means or diet. You can eat and drink before MRI diagnostics of the lower back.
Magnetic resonance imaging has simple step-by-step instructions that must be followed on the eve of the procedure:
- Warn the specialist about the fear of confined spaces. The internal shape of the machine where the patient is located is similar to a tunnel - people suffering from claustrophobia may experience anxiety. As an alternative, you can resort to tomography in open-type equipment.
- Tell your doctor if you have metallic implants or electronic devices in your body that regulate vital organs (for example, a pacemaker), as they may have an adverse effect on the operation of the equipment and distort the results of the examination.
- The patient should inform the doctor about the general state of health, as well as the presence of chronic diseases, since some of them may be contraindications to magnetic tomography. For example, if you have diabetes or kidney failure, an MRI scan should not be performed.
- It is worth maintaining your usual lifestyle without stopping taking medications.
Open type
MRI
During the procedure, specialists try to relieve phobia of confined spaces by prescribing sedatives, so for this group of people it is advisable to constantly have a relative or friend nearby.
Advantages
Magnetic resonance imaging is a breakthrough in the discovery of methods for studying the structure of the human skeleton and organs. The invention of the tomograph provided world medicine with the following opportunities:
- obtain clear images of the spinal column in all projections;
- detect the presence of a tumor at an early stage;
- identify pathogenic changes in bone tissue;
- give timely recommendations to prevent the development of spinal pathologies;
- conduct examinations of the spine and joints without the use of ionization radiation.
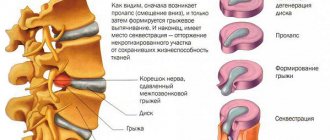
Using the magnetic resonance method, it became possible to visualize the condition of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. The difference between MRI and other diagnostic methods is the ability to detect prolapse (the initial stage of the formation of an intervertebral hernia), which simplifies the process of preventing the disease from becoming chronic. Before the discovery of MRI, such problems were identified at the stage of obvious manifestation of the disease.
- Signs of HIV in men
- Irish crochet lace - patterns with videos, techniques for knitting Irish lace
- Vegetovascular dystonia: symptoms and treatment of VSD in adults and children
The price of the MRI procedure is completely justified due to the fact that after diagnosis using magnetic resonance imaging there is no need to conduct other types of examination. The high information content of the results obtained helps to avoid the costs of additional methods. According to reviews from patients examined using MRI, diagnostic techniques that are cheaper do not always justify the cost savings obtained.
How is an MRI of the spine performed?
MRI of the local spine is performed according to the following scheme:
- the patient assumes a horizontal position;
- to reduce the likelihood of data distortion, the patient’s head, arms, and legs are fixed in a stationary position using special fasteners;
- the couch with the person moves inside the tomograph;
- during diagnostics, a person can hear faint noises that accompany the rotational movements of the wheels of the device;
- in addition to maintaining a motionless state, it is required to follow the instructions of the diagnostician, who from the next room gives the patient the necessary instructions through a special microphone;
- During the tomography process, the patient usually does not experience pain;
- At the end of the MRI, you should leave the office and wait for the doctor’s report.
When performing an MRI with contrast, before moving the patient into the magnetic tunnel, the patient is injected with a contrast agent and waits for some time.
Duration of MRI diagnostics
Typically, magnetic tomography of this part of the back lasts from 15 to 30 minutes. If a contrast agent is used to improve the effectiveness of the examination, the MRI scanning time is slightly extended.
Preparation for the procedure and its implementation
If an MRI of the lumbar spine with a contrast agent is prescribed, it is administered before immersion in the machine. Normally, no preparation is needed, but if the patient is allergic, it is necessary to test the substance itself for tolerance. Most clinics do not do this, relying on the hypoallergenic nature of the components. However, an allergy sufferer should not take the risk.
When a person is fixed on the table, its upper, movable part slowly moves into the chamber itself. The ring part lowers its sensor to the level of the lumbar region and the device turns on. The patient sees the process as actively moving red lights. At this point, you can simply close your eyes if the process makes you nervous. The study does not last long: up to 10 minutes. Then the moving part moves out, the clamps loosen and you can stand up.
The result takes time to process, so it is impossible to get it right away. Only inpatients receive the fastest MRI results: within a few hours on the same day. For other people, receipt is possible only the next day: at the reception or from your specialist who gave the referral.
Research results
After the tomography is completed, the data obtained is processed - after some time, the MRI diagnostic conclusion and a series of attached images of the local area are handed over to the patient. Tomography results are saved to a memory card or external storage device.
This approach helps specialists in other fields quickly make a diagnosis, assess the dynamics of the disease, and plan treatment.
How to interpret the results of an MRI study
Interpretation of MRI is the prerogative of a specialist. Attempting to analyze data on your own will not lead to success. Usually the doctor completes the task in an hour. In rare cases (for cancer, metastases), decoding may take a day.
Based on the MRI results, the specialist refers the patient to a doctor of a certain profile. Among them:
- neurologist (for diseases of the spine, spinal cord);
- neurosurgeon (if surgery is prescribed);
- oncologist (when diagnosing an oncological neoplasm);
- traumatologist (in case of injury in a local area).
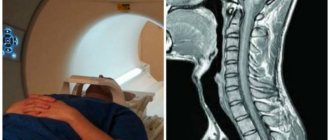
Intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine on an MRI image
Intervertebral hernia is a pathology in which displacement of discs between vertebrae is diagnosed as a result of a violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring.
What does the pathology look like on a successful MRI image? The radiologist notices a small protrusion from the intervertebral space. The more advanced the disease, the larger the protrusion.
There are cases when the hernia is so small that it is practically not visualized on the image. Under such circumstances, the source of pathology is detected by indirect symptoms.
For what pathologies is diagnostics recommended?
MRI of the lumbar and sacral vertebrae is prescribed for such pathologies.
- Osteochondrosis in the specified department.
- Vertebral injuries, in particular their fractures. Magnetic resonance imaging can show changes in the organ that are not visualized or are barely noticeable on an x-ray, etc.
- Intervertebral disc herniation, as well as protrusion.
- Tumor formations in the spine, including malignant ones.
- Abnormalities in the structure of the spine, its curvature, etc.
- Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating processes.
- Disorders in the blood supply to the spinal cord.
- Inflammatory diseases of the spine, in particular ankylosing spondylitis.
- Osteomyelitis, tuberculosis and other destructive phenomena in the spine.
- Deviations in the structure of blood vessels.
- Monitoring health status after surgical interventions.
Magnetic tomography of the lower back with contrast
MRI with contrast is indicated when it is necessary to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the upcoming procedure. Often, scanning with the introduction of a contrast agent is resorted to in cases of suspected tumor development.
Before starting MRI diagnostics, the subject is injected with a contrast component intravenously or into the spinal cord canal. Before using the drug, it is necessary to conduct an allergy test.
MRI of the sacroiliac joints
The SIJ (sacroiliac joint) is quite inactive; it connects the pelvic bones to the spinal column. When problems arise in this area, pain appears that spreads to the legs and groin. It is difficult to diagnose intervertebral hernias and radiculitis in this area. In such cases, MRI of the sacroiliac joints will help; this study will help determine the nature of the pain.
The procedure is prescribed for suspected rheumatism, if it is impossible to take x-rays or if there are symptoms of diseases of the sacroiliac joints, after injuries to the lower back. Diagnosis is also necessary for inflammation of this joint or joints of the legs, osteochondrosis of the lower segment of the spine.
X-ray, CT or MRI - what to choose
It is impossible to answer the question posed unambiguously, since each of the given methods is strong in its own field. The decision to prescribe a specific study is made by the doctor, who analyzes a number of factors, including the location of the suspected pathology, the patient’s condition, the degree of progression of the disease, and characteristics of the symptoms.
To conduct a comparative analysis of the procedures, we provide a table of key selection criteria. First let's compare MRI and X-ray:
| MRI | X-ray |
| Special medical centers are equipped with the device | All healthcare institutions are equipped with the device |
| No radiation exposure | Based on X-ray radiation |
| Duration - 15-30 minutes | Duration: a few seconds |
| Expensive procedure | Low cost |
| Can be performed on pregnant women (2nd, 3rd trimester) | The study is contraindicated for pregnant women |
| The examination is applicable in the diagnosis of soft tissues, ligaments, discs between vertebrae, etc. | The procedure is informative in diagnosing bone tissue |
In terms of information content, it is comparable to magnetic tomography, however, it is based on X-ray radiation. This option is cheaper (compared to MRI), but is not suitable for examining pregnant women and young children.
The most harmful diagnostic method
Where and at what price can you get an MRI of the lower back?
Magnetic tomography of the lumbosacral spine can be performed in specialized medical centers for a fee or free of charge. In the first case, an MRI will cost the patient an average of 3,000 rubles (without contrast) and 4,500 (with contrast). The price depends on the region in which the center is located, the qualifications of the staff and the level of the clinic. You can be examined free of charge if this tomography is included in the list of services under the policy.
Magnetic tomography of the lower back is performed to diagnose local pathologies, injuries and monitor treatment. MRI of the local area is short in time, painless and safe for human health.
The risk of adverse reactions is minimized, especially in the absence of contrast. MRI of the local area has a number of advantages over computed tomography and traditional x-rays, however, it is applicable if it is impossible to diagnose anomalies using alternative methods.
Cost of MRI
If literally 10 years ago, getting an MRI for the lumbar spine was problematic, you had to travel to large cities or sign up for an examination months in advance, but today tomography is an affordable examination. Moreover, the cost of diagnostics has become significantly lower.
Meanwhile, the prestige factor remained in the price gradation. In elite clinics, diagnostics will be significantly more expensive than in a regular clinic.
The cost also reflects the type of equipment used and its functionality. The price will be an order of magnitude more expensive if the diagnostics are carried out on a modern open-type device. An additional fee will be charged for contrast examinations.
The average cost of such an examination in Moscow is:
- 3,000 – 4,800 rubles when performed without contrast;
- 6,200 – 12,500 rubles – with contrast.
There are options for getting an MRI done for free. To do this, the patient needs to visit his therapist and undergo a preliminary examination. After making a preliminary diagnosis, receive a referral signed by the hospital’s medical commission. If you have a medical insurance policy and a referral in hand, the patient has the right to undergo an MRI within 30 days free of charge. But usually the offices of institutions providing such services are too busy. Therefore, if urgent diagnosis is necessary, it is better to give preference to a paid examination.