Decoding the results
When performing a blood test, the number of red blood cells that have stuck together and precipitated is calculated. The result of the study is presented as the level of antibody titer and is defined as:
- positive;
- false positive;
- negative.
When the titer is from 1:2 to 1:800, a suspicion of syphilis is established, which means the presence of antibodies to treponema in the patient’s body. However, this does not indicate the presence of the disease in a person. At the first stage of syphilis development, rates rarely reach a level of 1:320. The second stage of the disease is determined by titers slightly higher than 1:320. In the third, latent stage of the disease, the indicators may again fall below 1:320. A high titer level exceeding 1:640 is usually detected with high infection activity.
False positives are usually values greater than 1:800. Values less than 1:640 may also be nonspecific or false positive. Such situations are possible if the following factors are present:
- post-vaccination period;
- menses;
- pregnancy;
- autoimmune diseases;
- eating fatty foods on the eve of the test;
- oncology;
- myocardial infarction suffered over the past 6–8 months;
- any infectious diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs.
In the event that the patient has ever previously suffered syphilis, the RPGA test will be positive for life, even if the person is healthy. Therefore, to clarify false-positive and positive results, an additional study is prescribed in the form of blood tests for RMP or RPR. If the RPR or RMP is negative, then the patient does not have the disease.
In a negative reaction, red blood cells do not stick together into a structure. This result of the research is possible if the patient does not have the disease. However, a negative reaction can also occur when the blood for the test is taken incorrectly, or no more than 4 weeks have passed since the infection and the body has not had time to start producing antibodies.
Quite often, test results are written with the following symbols:
- 2+;
- 3+;
- 4+.
In this case, 2+ means that a mild test reaction is observed. A value of 3+ is a positive reaction, and a value of 4+ corresponds to titers with high results.
The causative agent of syphilis, determined using the RPGA blood test
Importance in the earliest stages and during recovery
Since antibodies belonging to the immunoglobulin G class remain in the blood serum, as a rule, for life, even after active and successful treatment of syphilis with subsequent recovery, these antibodies remain positive.
Only in the case when syphilis was suspected and treated in the “very embryo”, a few days after infection, at the stage of formation of chancre and regional lymphadenitis, then RPGA can be negative. The fact that in both secondary syphilis and tertiary syphilis the RPGA will be equally positive means that such a study cannot be used for differential diagnosis of the stages of the disease. Using RPGA it is also impossible to assess the effectiveness of treatment, since antibodies will still circulate in the blood. The effectiveness of therapy must be assessed using other laboratory tests. Particularly high rates and significant dilution of the patient’s blood serum during RPGA occur in secondary syphilis, as well as in the early and latent form of this disease.
How is the analysis carried out?
In order for the examination data to be reliable after the analysis, it is necessary to follow a number of recommendations:
- The blood sampling procedure is carried out in the morning from 8 am, but no later than 10 am.
- You should not pre-eat breakfast before the test. This may affect the results of the examination. Therefore, it is necessary to donate blood on an empty stomach. It is advisable that the last meal be 11-12 hours before the test.
- Like food, you should not consume any drinks, especially carbonated ones, before the event. The only thing you can drink is plain boiled water, but its volume should not exceed permissible levels. Significant fluid injection negatively affects the examination.
- It is better if the patient does not smoke for 3-6 hours before the examination. But in most situations, such a gap is impossible for a cigarette addict. Therefore, it is advisable to refrain from inhaling nicotine for 30 minutes before collecting the test material.
- Alcoholic drinks and other alcohol-containing substances the day before the RPGA analysis are strictly prohibited.
- If the patient takes certain medications during the examination, it is worth notifying the attending physician or rescheduling the administration of medications to a later time.
- If the patient feels unwell or shows weakness in the morning on the day of blood sampling, then to eliminate negative situations, such as loss of consciousness, the nurse should be notified in advance.
It is necessary to take blood sampling from a vein seriously. The tests obtained determine whether there are pathogenic bacteria in the lymph or whether they are absent. Upon receiving the test results, the doctor makes the correct diagnosis and begins treatment of the patient.
Analysis process
Venous blood is collected for serological testing in the first half of the day. The patient should arrive at the laboratory in advance, taking with him the necessary documents (passport and referral for analysis).
The patient is asked to go to the treatment room and sit comfortably on the chair. Blood is drawn from a vein located in the elbow area, so it is necessary to free the forearm and elbow area from things. A tourniquet is applied to the shoulder and a pillow is placed under the arm. The nurse puts on disposable sterile gloves and treats the puncture site with a cotton swab soaked in a disinfectant.
The algorithm for performing a venous injection includes pumping blood into a vein; for this, the patient is asked to clench and unclench his fist several times. In this case, the vessel is better visualized and palpated, which facilitates the collection of material. The nurse then inserts a syringe needle into the vein, draws 10 milliliters of blood, and applies a bactericidal patch to the injection site. To avoid the formation of a hematoma, after the manipulation you should bend your arm at the elbow for 15-20 minutes.
Decoding the result
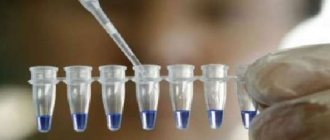
The analysis is carried out by adding a special reagent to the sample. If Treponema pallidum is present in the blood, an agglutination reaction occurs and red blood cells precipitate. Based on the number of red blood cells glued together, one can draw conclusions about how many antibodies are present in the sample.
Test results are assessed using a 4-point system, based on the size of the formed film. When an agglutination reaction occurs, red blood cells remain on the surface of the well, forming an “umbrella”. If the result is negative, they sink down and accumulate at the bottom in the center of the hole.
The test result is deciphered as follows:
- "-" - negative result. With it, red blood cells sink to the bottom, forming a compact sediment;
- “1+” is a mixed reaction. Red blood cells form a loose sediment with fuzzy edges and a gap in the middle;
- “2+” – weakly positive reaction. A film appears at the bottom of the hole, forming a dense ring with pronounced clearing - a positive reaction. Red blood cells almost completely cover the hole, while a clear ring forms around the sediment;
- “4+” – positive reaction. With RPHA 4+, red blood cells form an umbrella and evenly cover the hole.
Here's what RPGA test results might look like
Positive result
If the test gives a positive response, this indicates the presence of a pathogen in the body. In this case, the patient is prescribed additional laboratory and instrumental tests, based on which it will be possible to confirm or refute the presence of the disease.
If the result is positive, the RPHA test must be performed on the person with whom the infected person had sexual contact. It is worth considering that in approximately 5% of cases, the RPGA analysis gives a false positive result. Most often this is due to ignoring the preparation rules.
Also, a false positive reaction may occur in the following cases:
- formation of oncological tumors;
- hepatitis of various forms;
- HIV.
In rare cases, a false positive reaction is a sign of pregnancy. A distinctive feature of a false-positive response is that it is accompanied by a low titer. It is also worth considering that the test may be positive if the patient was already sick with syphilis, but underwent successful treatment.
Negative result
A negative RPGA reaction indicates that:
- the causative agent of syphilis is absent in the body;
- less than 3 weeks have passed since infection. At this early stage, the immune system does not begin to produce antibodies;
- improper blood sampling.
If the doctor suspected syphilis in the patient, but testing showed a negative result. After some time, it is recommended to take the test again to ensure the absence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood serum.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method
PCR, developed in 1991 to detect the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule of Treponema pallidum, is highly sensitive and specific, allowing the detection of DNA fragments of the pathogen.
This analysis is based on copying short sections of DNA from the pale spirochete, which meets the specified parameters and is present in the sample. All this is performed under artificial conditions (in vitro). The reaction is carried out in a device - a thermal cycler, which provides periodization of temperature cycles. Cooling occurs followed by heating of the test tubes with an error of 0.1˚C.
The DNA template is heated for 2 minutes at a temperature of 92-98˚C (the maximum temperature is used if the polymerase is thermostable). When heated, DNA strands separate due to the breakdown of hydrogen bonds between them. In the annealing step, the reaction temperature is reduced to bind the primer to the single-stranded template.
Annealing takes about 30 seconds, during which time hundreds of nucleotides are synthesized. Newly synthesized molecules are copied by polymerase, as a result of which specific fragments of deoxyribonucleic acid are multiplied. Subsequent detection of fragments is carried out using agar gel electrophoresis.
PCR diagnosis of syphilis is still experimental in nature, but is justified when detecting a congenital infection, in complex diagnostic cases, or when the content of Treponema pallidum is minimal in the test material.
Decoding the results
The test value can be deciphered by the intensity of bonding, which can be from – to 4+. Understanding these cases gives a clear idea of the presence of antibodies to the infection.
Laboratory screening can be explained as follows:
- 4+, if there is a uniform mat of cells covering the entire hole.
- 3+ if most of the well is covered with a uniform mat of cells.
- A lower density mat surrounded by a small ring (+2) is another positive analysis scenario.
- The intensity of the mat is reduced and surrounded by a denser ring with a distinctly open center.
If there is a small, clear center and the cells are located at the bottom, the result can be considered negative. The indicators are within the normal range and do not require further investigation. But in the case of an intermediate positive test, MHA-TP and FTA-ABS studies are prescribed.
Note!
Normal ranges may vary slightly between laboratories. Some laboratories use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of the test results.
Positive result
If the RPGA result is positive, it is likely, but not certain, that the disease is present. In this case, the doctor will prescribe a more specific test to confirm the results. A treponemic test is often used to confirm a positive test. It tests whether the immune system has produced antibodies in response to Treponema pallidum, which causes syphilis.
After making a final diagnosis, it is imperative to undergo full treatment. It is necessary to complete a full course of antibiotic treatment, even if symptoms go away. Failure to do so may cause relapse.
Negative result
A negative test is normal. This means that no syphilis antibodies were detected in the blood sample. Normal ranges may vary slightly between laboratories. Some medical centers use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of the results.
This test may give a false negative result in early and late stage disease. The test must be confirmed by other screenings to make a definitive diagnosis.
About false positives
Antibodies produced as a result of the infection may remain in the body even after the virus has been treated. In some cases, the body may not produce antibodies even if a person is infected with syphilis. This means that the analysis will be inaccurate.
The following conditions may cause false positive results:
- HIV.
- Lyme disease.
- Malaria.
- Pneumonia (certain types only).
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Intravenous drug use.
- Tuberculosis.
The RPHA test is not perfect, but it is a reliable test that can be the first step in helping determine whether a person is infected. In a blood test, syphilis can be detected as early as 1-2 weeks after infection. The greatest accuracy can be expected within three months, and non-accurate results are possible any time during the first 90 days after infection.
People who have suffered from a syphilis infection in the past may also have a false positive result due to antibodies lingering in the blood. If RPHA testing returns a negative result 90 days or later after exposure, infection is considered absent.
Note!
Other diseases such as yaws and yaws (two other types of skin diseases) can also result in a positive FTA-ABS. Sometimes there can be a false positive result, most often in women with lupus.
Who's at risk
Anyone with signs or symptoms of the disease should be tested for syphilis. Some patients should be screened even if they have no symptoms or know of a sexual partner who is infected. Sexually active people can discuss their risk factors with their doctor and ask about testing for syphilis or other STDs.
Those most at risk include:
- those who have unprotected sex;
- patients with HIV;
- people with multiple sexual partners.
On a note! When a pregnant woman is diagnosed with syphilis, the infection can be passed on to her unborn child. All pregnant women should be tested at their first antenatal visit.
RPGA for syphilis is a method of primary nonspecific laboratory diagnosis. It is the most commonly used screening test worldwide. The test is used because of its simplicity, sensitivity and accessibility. RPGA has quantitative data on antibody titer. This assessment has essential implications for future treatment.
Persons with a positive non-treponemal test, such as RW or the well-known Wassermann reaction, should always undergo a treponemal test to confirm the diagnosis of syphilis. This chain of procedures is considered a classic testing algorithm.
Procedure for conducting the study
A venous blood sample donated by the patient is sent for testing. In order not to receive an erroneous conclusion, the patient should be responsible in preparing for the analysis. In order for the test results to be reliable, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- The test should only be taken on an empty stomach.
- On the day of the analysis, you can drink mineral water without gas in minimal quantities.
- You should not smoke for at least 30 minutes before the analysis, but it is better to increase this time to several hours.
- A direct ban is imposed on the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Patients who need to regularly use any medications must inform the doctor referring them for examination.
- If you feel unwell or feel unwell, you must notify the nurse who is taking the blood or the doctor at the outpatient clinic where you need to take the test.
Be responsible not only about the question of where to get tested, but also about preparing for the examination.
Diagnosis of other infectious diseases
One should not think that a study such as RPGA can be carried out only to identify the causative agent of syphilis in the body.
An analysis with a salmonella diagnosticum allows you to detect the presence of an infection in the digestive system - salmonella. Starting from the fourth day after infection, the body produces antibodies to Salmonella antigens, which the RPGA method helps to identify. A negative result indicates the absence of infection, and a positive titer, increasing from 1:200 to 1:800 in the acute phase, will indicate its presence.
The method of performing RPGA with a diphtheria marker makes it possible to diagnose diphtheria and assess immunity after vaccination. Antibodies begin to be produced by the immune system the very next day after infection, and remain in the body for several weeks. The sensitivity of this analysis is superior to the bacteriological research method. A titer of 1:80 confirms the presence of diphtheria in the body.
The dysentery marker for RPHA most accurately detects shigellosis (bacterial dysentery), even compared to the laboratory diagnostic method through bacterial culture. If the patient does not receive quality treatment, the disease develops into a chronic process, in which relapses often occur. The analysis allows you to diagnose the acute and chronic phases of diarrhea, identify the causative agent of dysentery, distinguish bacterial shigellosis from colorectal cancer, endocrine disorders or inflammation of the colon. A negative reaction indicates the absence of the bacillus, and its presence is confirmed by a titer of 1:80 for children or 1:320 for adults.
Conducting a test with a measles marker allows you to determine measles disease. Such an examination may become an alternative to the RTGA analysis often performed for diagnosing measles.
So, RPGA blood test - what is it? To summarize, we can safely say that this is a modern, highly sensitive and reliable method for diagnosing various diseases of bacteriological etiology.
What diseases will it help identify?
Testing for RPHA is a specific test used to diagnose syphilis. Testing blood using this method makes it possible to detect infection of the body at any stage. As you know, all types of syphilis can be divided into two stages - early and late.
The RPGA test allows you to determine:
- primary seronegative syphilis;
- primary syphilis seropositive;
- secondary fresh syphilis;
- secondary latent syphilis;
- secondary recurrent syphilis;
- tertiary active syphilis;
- tertiary latent syphilis;
- latent syphilis;
- fetal syphilis;
- early congenital syphilis;
- late congenital syphilis;
- latent congenital syphilis;
- visceral syphilis;
- syphilis of the nervous system.
Despite the fact that the RPGA test is primarily associated with testing for syphilis, it is also used to diagnose other internal diseases and other bacteriological pathologies. To diagnose other diseases, the reagent to which blood samples must be added is replaced. So, to detect measles, a study is carried out with a measles marker, and for salmonellosis - with a salmonellosis marker.
The RPGA method is used to detect diphtheria, shigellosis and other intestinal diseases. The sensitivity of this reaction is higher than that of bacterial culture and makes it possible to diagnose disorders in the endocrine system, dysentery and inflammatory processes in the colon.
The test does not allow monitoring of syphilis treatment. The fact is that if the human body was infected with the Treponema pallidum bacterium once, then the test for RGPA will give positive results throughout its life.
Occasionally, a situation occurs that the test results are positive, but there are no syphilis bacteria in the body, and never have been. This is called a false positive, and possible reasons for this phenomenon will be discussed below. But this fact is worth taking into account, and before a diagnosis is made, other laboratory data must be assessed.
How reliable is the analysis?
If RPGA is prescribed, the patient must understand the seriousness of the analysis. Therefore, you should pay very close attention to the results obtained and preparation for the examination.
If a person is afraid of becoming infected with syphilis due to contact with an infected person, then he should wait at least 2-4 weeks. Only then carry out the analysis. Earlier diagnosis will not give a positive result.
In some situations, the incubation period lasts in the patient’s body for more than 4 weeks. In this scenario, the survey can only provide 86% accuracy. The initial stage is the most unpredictable and elusive for determining the diagnosis.
You cannot postpone a visit to a venereologist and an examination if the following signs of the development of a venereal problem are identified:
Symptoms of syphilis
- The skin becomes covered with a rash, with redness present on the skin of the palms and soles.
- Painful ulcers appear on the anus, genitals, as well as on the mucous membranes and mouth.
- Severe pain in the head is constantly recorded, and the ability to work is lost.
- There is a sharp increase in body temperature to significant levels.
- An increase in lymph nodes is recorded.
Even if after the appearance of such signs there is a decline in symptoms, it is necessary to see a specialist. Probably, the inflammatory process has become chronic, and is accompanied by attenuation of symptoms. The latter condition can change dramatically to the acute stage.
VDRL
The method recommended by the World Health Organization for staging a reaction with a lipoid antigen (AG) is rightfully considered the best among other standard non-treponemal tests. Developed in the USA, Georgia in the laboratory of sexually transmitted diseases (Venereal Diseases Research Laboratories).
The institution's abbreviation served as the name for the sample - VDRL. VDRL is a modification of MR. Serum from a patient with syphilis is inactivated and placed on a glass slide. The antigen used consists of cardiolipin, cholesterol and lecithin in varying percentages. The answer is registered almost immediately.
Distinct flocculation occurs in the presence of antibodies in the serum. The serum becomes reactive after 4 weeks of infection. To assess the amount of antibodies, the serum is pre-diluted exponentially.
Advantages of VDRL:
- 1relatively high sensitivity;
- 2 relatively high specificity;
- 3 ease of implementation;
- 4low cost of reagents;
- 5get a quick response.
A disadvantage of VDRL is its relatively high false-positive rate.
Their causes are the same diseases listed above.
Treponemal tests are performed with specific Treponema pallidum antigens. They are necessary and mandatory to establish a final diagnosis. These are immunofluorescence reaction (RIF), indirect hemagglutination reaction (IPHA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), etc.
After a positive result of a non-treponemal test (RPR, MP, VDRL), treponemal tests should always be performed (usually a combination - RPGA, ELISA, RIF).
Treponemal tests are more complex to perform than rapid tests and require more money.
What can affect the result
Test results can be false positive for many reasons. The results of the analysis are affected by some diseases. These include rickettsial infections such as typhus or Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Results may be inaccurate if screening is done too early after infection. 14–21 days after infection, the body's immune response is detected using a test. Drinking alcohol within 24 hours before the test may also give a false negative result.
Factors influencing the result of the analysis:
- pregnancy;
- intravenous drug use;
- tuberculosis;
- chronic liver diseases;
- recent vaccinations or inflammation of the lining of the heart or valves.
Recommendation!
When reading your blood for RPHA, make sure your doctor knows about all the medications, herbs, vitamins and supplements you are taking. This includes drugs that do not require a prescription and any illegal drugs.
What to do if sexually transmitted diseases are detected
If serological diagnostics confirms the presence of an STI, then it is necessary to immediately proceed to the treatment stage in order to avoid complications and chronicity of the process. The patient should make a second appointment with the attending physician. He will prescribe etiotropic complex treatment and will dynamically monitor the patient’s condition during drug therapy.
Title: Serological tests: what is it, a blood test to determine infections, how to take and decipher it, reaction methods to determine diseases
Description: What are serological tests and what diseases are they used to identify. How is a blood test done to determine infection? How to prepare, submit and decipher the result after receiving it. Methods of carrying out reactions to determine the disease.
Features of the course of infection
Typhoid fever occurs with a gradually increasing high temperature, the appearance of abdominal pain, and general symptoms of intoxication characteristic of all infections. A feature of typhoid fever is the proliferation of pathogens that have penetrated through the intestinal wall into the intestinal immune defense organs - into the lymphatic follicles, into the liver, into immune defense cells. In these follicles, pathogens multiply, and then they penetrate through the thoracic lymphatic duct into the blood and this coincides with the beginning of the acute period of the disease. A characteristic danger of typhoid fever is intestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation or necrosis of lymphatic follicles.
At the same time, typhoid fever is a unique disease that requires the presence of a cavity operating room in an infectious diseases hospital. The fact is that a patient diagnosed with typhoid fever and with intestinal bleeding should under no circumstances be hospitalized in the general surgical department, since it is very contagious. Therefore, in an infectious diseases hospital, a special operating room is equipped for such a case, and, if necessary, surgeons are called in to perform an emergency operation.
Typhus is transmitted only by humans; you cannot get typhus from animals. You can get sick, I communicate not only with the sick person, but also with a healthy carrier. One of the most famous figures in history is the so-called “Typhoid Mary.” While clinically healthy, she worked as a cook in the early 20th century in the United States and, as a result of her food-related work, a total of about 47 people died, whom she personally infected. Typhoid pathogens multiplied in her gall bladder and were released into the environment along with feces. The situation was aggravated by the fact that she refused to be examined and denied the preventive value of hand washing.
But a huge number of victims, which regularly appear to this day in countries with a hot climate and a low standard of living, are associated with the consumption of food and, above all, with infected water and milk, which are contaminated with feces and sewage in the absence of a centralized sewage system.
The outcome of typhoid fever can be either recovery or transformation of the patient into a chronic carrier. No more than 5% of all those who have recovered become chronic carriers, and this causes a certain epidemiological danger.
About false positives
But, despite the high sensitivity and specificity of this test, false positive values are also possible when performing RPGA for syphilis. They occur infrequently, in no more than 2.6% of cases, and appear when antibodies circulate in the patient’s blood that are very similar to syphilitic ones, but are not them. These may be autoantibodies, and most often such “surprises” are thrown up by systemic lupus erythematosus.
Also, those diseases that are caused by other representatives of treponemes, or spirochetes, can lead to false-positive values, for example, Lyme disease, which is caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, a “close relative” of syphilis. You can read about the diagnosis of Lyme disease, or tick-borne borreliosis, here. In some cases, such distortions are caused by oncological pathology, pregnancy, and even sluggish acute myocardial infarction. In the latter case, particles of necrotic cardiac muscle enter the blood, which are similar in structure to cardiolipin antigen; it is used to stage the Wassermann reaction, and is extracted from the heart of cattle.
Also, the cause of false positive results may be cases of intravenous drug addiction, HIV infection and viral hepatitis B and C, leptospirosis and relapsing fever, as well as diseases that occur in hot countries and are caused by treponemes - pinta, yaws, bejel. In rare cases, in patients with low immunity, treponemes, which are saprophytes and live in the oral cavity, may be activated. Also, tuberculosis and infectious mononucleosis can cause such reactions, as in the case of extensive polytrauma and numerous fractures.
Such false-positive reactions must be rechecked after some time; they usually disappear within six months, for example, after resolution of pregnancy or for a longer time.
Decoding the results
The syphilitic RPGA method provides two types of indicators:
- Qualitative. Responsible for the presence of protein bodies in the serum, the appearance of which is caused by the introduction of a pathogenic pathogen into the body.
- Quantitative. Helps assess the intensity of antibody production and determine the nature of the activity of Treponema pallidum.
The analysis may show:
- 4 – results are positive;
- 3 – positive;
- 2 – weakly positive;
- 1 – the result is doubtful;
- – – no infection.
The primary form of syphilis is characterized by reduced rates (less than 1:320). In case of secondary venereal disease, elevated titer values are detected (more than 1:320). In case of latent infection, the indicators are also underestimated.
A negative RPGA test means that the patient is not infected with Treponema pallidum or the disease is in the incubation period, which is 7-14 days. In some cases, this result is obtained due to a laboratory technician’s mistake when taking biological material for research.
The reasons for obtaining a false positive result are:
- Pregnancy.
- Autoimmune processes.
- Hepatitis.
- Bacterial endocarditis.
- Conditions after vaccinations.
Studies using the RPGA method do not allow differentiation of syphilis and other treponematoses, early and late forms of venereal disease. The results must be assessed in conjunction with other indicators obtained using laboratory and instrumental methods.
Positive
The result of the study is indicated by the titer level. A titer is the maximum possible dilution of a blood sample to the extent that antibodies are still detectable (i.e., the titer refers to the amount of antibodies in the blood).
A positive result obtained by the RPGA test indicates the presence of bacteria in the body that cause the disease. According to statistics, false positive reactions occur no more often than 2.5% of the total number of people who have undergone this examination.
In people who are not infected with syphilis, studies can produce a similar result due to the following factors:
- infectious diseases (flu, chickenpox, ARVI, etc.),
- recent myocardial infarction,
- pregnancy,
- extensive injuries,
- oncological diseases,
- HIV infections,
- during menstruation in women,
- presence of narcotic drugs in the blood,
- hepatitis B and C,
- period after vaccination,
- chronic diseases.
Typically, if the reaction is false positive, the titer will be low. Secondary syphilis and manifestations of previously hidden syphilis are characterized by high rates. Also, in patients with oncology, the blood usually contains a large amount of antibodies, and therefore, when conducting an RGPA test, the results will display a high titer, which is a false positive reaction for a test for syphilis.
If the RGPA reaction is positive, then you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. A qualified healthcare professional will definitely prescribe additional tests and conduct a full examination. Treatment of syphilis requires the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. At more severe stages of the disease, intramuscular antibacterial injections are added to therapy.
Not only the patient himself needs treatment, but also all his relatives, as well as people in contact with him. For successful treatment, it is necessary to disinfect the sick person’s home.
Negative
A negative result is also a result! In the case of tests for syphilis, the reaction to this result is often positive. But do not forget that such a response to the RPGA test can be obtained due to various reasons.
- The first and most successful reaction for the person taking the test is a negative reaction, because the person does not have syphilis.
- The second option for obtaining such a result may be a violation of blood collection technology and other errors by medical personnel.
- And the third, most unpleasant situation for the patient, is when a person is actually already infected with syphilis, but the body has not yet reacted, and the production of antibodies has not yet begun. In this case, the analysis gives a false negative reaction.
NON-TREPONEMAL TESTS
Wasserman reaction - RW, RW
, on average, becomes positive at 4-6 weeks of illness. As the entry of the syphilis pathogen into the blood increases, the RW titer also increases. It reaches its maximum in the secondary relapse period of syphilis. In late forms of the disease, the Wasserman reaction often becomes negative.
The result of the Wasserman reaction is determined by the presence or absence of hemolysis. RW is sharply positive - ++++, complete delay of hemolysis, RW positive -+++, significant delay of hemolysis, weakly positive rw -++, +- doubtful RW - partial and, accordingly, insignificant delay of hemolysis. Negative RW—complete hemolysis.
The disadvantage of RW is its non-specificity, i.e. The Wasserman reaction becomes positive in the absence of syphilis. This type of analysis is called a false positive.
The Wasserman reaction can be false positive in various diseases and conditions - connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, dermatomyositis), rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, oncology, blood diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular system - myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, pregnancy, use of medications, etc.
Due to the nonspecificity of the Wasserman reaction and its false results, other reactions are also used.
Microprecipitation reaction (RMR)
and its analogues:
the RPR
test - Rapid Plasma Reagins and the
VDRL
(Venereal Diseases Research Laboratory) - these are non-treponemal tests that are widely used as screening tests for syphilis.
Microprecipitation reaction
It is advisable to take it 20-30 days after dangerous contact.
The essence of the RMP reaction is that a few drops of the patient’s blood serum are mixed with cardiolipin antigen, and during the reaction a precipitate forms. The reaction is assessed qualitatively - by quantity +, from 4+ (strongly positive) result, to 1+ (doubtful result). In case of a positive result, a quantitative assessment is carried out - titration - the maximum dilution at which a precipitate is formed. The result is positive starting from a titer of 1:2-1:4. In the vast majority of cases, a positive microreaction result means syphilis. However, the microreaction can be false-positive in case of systemic diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, glomerulonephritis, diabetes mellitus; in oncological processes, heart diseases - acute myocardial infarction, endocarditis, myocarditis; during pregnancy, etc.
A negative microreaction result indicates the absence of syphilis, an early seronegative period of the disease, before the appearance of antibodies in the blood. Also, the microreaction becomes negative or questionable in late forms of syphilis.
Promotion!!!
Blood test for syphilis, HIV, AIDS, hepatitis - 2500 rubles! Phone: 8 985 9230340
RMP
is one of the criteria for the reliability of the treatment of syphilis. Unlike other serological reactions - RIF, RIBT, ELISA, RPGA, after successful treatment of syphilis, RMP becomes negative in more than 90% of cases.
Non-treponemal tests (microprecipitation reaction (MPR) and Wasserman reaction (RW)) are integral methods for diagnosing syphilis. A negative result of these reactions in the vast majority of cases means that the person being examined is healthy. Otherwise, if positive test results are obtained, treponemal tests are prescribed.
Certificate about syphilis
Syphilis is a chronic infectious STD caused by Treponema pallidum. Treponema pallidum is a microorganism from the order of spirochetes, which are bacteria in the form of spirals.
Treponema pallidum, unlike other spirochetes, has from 8 to 15 curls, moves smoothly and slowly
There are several ways of contracting syphilis:
- Direct (sexual), predominant.
- Indirect (household).
- Transplacental (from woman to fetus).
Treponema pallidum can affect almost all tissues of the body
Syphilis is usually divided into several stages:
- Incubation period.
- Primary syphilis.
- Secondary syphilis.
- Tertiary syphilis.
The incubation period lasts about two weeks, and there are no visible signs of infection. Treponema pallidum at this moment is actively mastered in the body and multiplies. As a result, a primary focus is formed on the skin/mucous membrane, in the place through which microorganisms entered.
The primary lesion is a nodule, hard and painless, characterized by redness. This formation, otherwise called chancre, indicates the onset of primary syphilis. After some time (up to 2-3 weeks), the nearest lymph nodes are affected.
In the photo, in the center of the ulcerated chancre there is a red bottom: under it there are many small vessels
During secondary syphilis, multiple rashes are found on the patient’s skin. They can be of different shapes and sizes, called syphilides. Each such syphilide contains a huge number of treponemes, which is why the period is considered the most contagious.
Currently, the last stage is rare, since it develops only years after infection. In addition, the disease can be treated quite successfully if treated in the early stages.
During tertiary syphilis, internal organs and systems are affected, which can lead to death. This period is characterized by gummas - special delimited zones of inflammation that are chronic. This stage poses virtually no danger to others.
In the center of the gumma there are treponemes and a zone of dead cells (necrosis), the immune system cannot cope with their destruction. Immune cells around the center are modified and enlarged
Having analyzed all of the above, we can identify several criteria that affect the severity and location of the lesion:
- the route of penetration of treponema into the body;
- stage of the disease;
- time of initiation of treatment and the approach to therapy itself.
Dark field microscopy of Treponema pallidum
This method is based on the direct detection of treponema pallidum in the test material using a microscope and special devices (most often discharge from erosions and ulcers, less often cerebrospinal fluid and other substrates).
Using scarification, scraping, squeezing, exudate is obtained from erosions and ulcerative defects, then the prepared preparation is examined under a microscope.
Typically, treponema pallidum is detected in a preparation obtained from chancre, from foci of secondary fresh, secondary recurrent syphilis, as well as punctate of lymph nodes and placenta.
Based on the phenomenon of small particles glowing in a dark field when hit by a beam of light (Tyndall’s phenomenon), the method perfectly allows differentiating the causative agent of syphilis from other treponemes based on morphological differences and differences in the modes of movement of the bacterium.
For microscopy, a special dark-field condenser of appropriate optical resolution is used. The drug is obtained by the crushed drop method (a drop of material is applied to a clean, grease-free glass slide and covered with a very thin coverslip).
Immersion oil is dropped onto the cover glass. By turning the tube and turning the magnifying lens, the desired lighting is adjusted.
In the dark field of the microscope, blood cells, epithelial cells and the causative agent of syphilis are detected. Treponema pallidum looks like a spiral, very thin, emitting a silvery color, with smooth movements.
Figure 2 - Dark-field microscopy as a way to visualize Treponema pallidum in the material under study. Illustration source: CDC
Treponema pallidum must be distinguished from other treponemes, including Tr. refringens, which can be found in the oropharynx and on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. This bacterium makes chaotic movements, has wide and asymmetrical, rather rough curls. In addition, Treponema pallidum is distinguished from Tr. Microdentium, Tr. Buccalis and Tr. vincenti.
Visualization of bacteria in a dark field is sometimes supplemented by a fluorescence reaction. For this purpose, antitreponemal antibodies labeled with a fluorescent dye are added to the native material. In this case, a complex called antigen-antibody (abbreviated AG-AT) is formed, which is the object for study using a fluorescent microscope.
Types of blood tests for syphilis
A number of methods have been developed to diagnose syphilis, but none of them gives a 100% accurate result. The material for research is most often blood plasma; discharge from skin rashes is also used; in some cases, lymph node puncture is performed. The main types of research include serological tests, which are used for initial diagnosis and to monitor the results of therapy.
Serological tests for syphilis are based on the mechanism of formation in the body, when the causative agent of the disease enters it, antibodies that interact with special antigens. The main serological blood tests for syphilis are as follows:
- Wasserman reaction - during this test, syphilitic antigens are added to the patient's blood serum to determine antilipid antibodies (reagins). Antigens form an immune complex with reagins, which adsorbs and binds complement. When such a complex is formed, the red blood cells are not destroyed, but precipitate, which indicates a positive reaction. If there are no reagins in the blood serum, hemolysis occurs (destruction of red blood cells), in which case the reaction is negative.
- The microprecipitation reaction with cardiolipin antigen (RPR or RMP) is a screening method for diagnosing syphilis, which can be considered as a more modern modification of the Wassermann reaction. The main indications for taking a blood test for syphilis using this method are initial examination, medical examinations, and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy. If a positive result is obtained from a blood test for syphilis using this method, other more accurate tests are prescribed to confirm it.
- Blood test for syphilis ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is one of the advanced and promising methods of laboratory diagnosis of this disease. The principle of the study is to identify a specific antigen-antibody complex, which is formed by combining syphilitic antigens absorbed on a solid carrier with antibodies from the patient’s blood serum. In modern medical practice, an indirect version of the blood test for syphilis, ELISA, is common, which uses antibodies to human immunoglobulins combined with enzyme markers. Depending on the amount of bound antibodies, the final products of this reaction are stained, the degree of which is used to evaluate the results of the analysis.
- Passive hemagglutination reaction test (RPHA) - during this study, the combination of syphilis pathogens in blood serum with sheep red blood cells processed by special methods is studied. If treponema pallidum is present in the blood serum, agglutination of red blood cells occurs, that is, gluing with subsequent sedimentation. To decipher a blood test for syphilis using the RPHA method, the staining of the sample is assessed, since erythrocyte agglutinate is dark red.
- Immunofluorescence reaction study (RIF) - during this analysis, the intensity of the glow of Treponema pallidum in the preparation is determined, which occurs only if anti-treponema antibodies are present in the blood serum.
- The immobilization test for treponema pallidum (TIRT) is the most specific diagnostic test for syphilis, in which the presence of video-specific antibodies (immobilisins) is determined in the blood serum, which immobilize pallidum treponema in the presence of complement. Under a microscope, the proportion of treponemas that have lost mobility (immobilized) is calculated. This blood test for syphilis is carried out no earlier than 2 weeks after finishing taking antibiotics and other medications.
The RPR test can give a false positive reaction, since antibodies to it can be released not only by syphilis, but also as a result of some other diseases. According to statistics, the Wasserman reaction test gives one false positive result per 10,000 tests. To exclude erroneous diagnosis of syphilis, the result is further clarified using other studies. The most accurate methods are considered to be RIF, RIBT and ELISA, which make it possible to detect syphilis already in the incubation period and at all subsequent stages.
Alternatives
Since we have already found out that not a single technique, including RPGA, gives one hundred percent confidence in the result, it is not surprising that doctors prescribe extensive examinations. In such complex studies, both specific and nonspecific testing methods are successfully combined, which makes it possible to almost completely eliminate the possibility of erroneous diagnosis.
So, in combination with RPGA or instead of it, nonspecific tests such as the Wasserman reaction and microprecipitation reaction are used. Both the first and second methods require the use of blood from a finger and are not used in the initial stages of the disease.
Of the specific tests that can replace RPGA, it is worth noting:
- ELISA or enzyme immunoassay . This is one of the most accurate diagnostic methods, which is usually prescribed after undergoing nonspecific studies.
- RIF or MFA . Fluorescent antibody method. Suitable for early diagnosis.
- TPI - Treponema pallidum immobilization test. An exact method, but it is used only after the fourth month of illness.
- IB . Immunoblotting or Western blotting. New method. Very accurate and very expensive.
- Laboratory analysis . Fast and inexpensive.
Summarizing everything that has been written, we can conclude that checking blood for RPHA is a modern and fairly accurate method for checking health. Due to the fact that RPGA is a relatively simple and inexpensive analysis, it is used everywhere.
What is RPGA
Conventionally, laboratory diagnostic methods can be divided into two types: they look for either the pathogen itself, or the antigens that the immune system has developed for the “stranger.” RPGA for syphilis is a specific serological test that allows you to detect antibodies to the pale spirochete. If they are detected, then the test result is positive; if antibodies are not detected, the test result is negative.
To conduct the study, red blood cell diagnostics is required, or, more simply, red blood cells treated with a special solution. They are obtained by separating blood plasma from formed elements in a centrifuge. If a person is sick, then his red blood cells will carry antibodies to the antigen (pale spirochete) and attach to it, “stick together.” Accordingly, in order to detect them, you need to introduce an antigen into the blood serum and observe the reaction, which can be:
- Weak intensity (there are no antibodies on the surface of red blood cells, the causative agent of syphilis is absent in the body or is present in an undetectable amount).
- Moderate intensity (red blood cells have combined with the antigen, but in an insufficient quantity to clearly diagnose the disease).
- Intense (there are a lot of antibodies on the surface of red blood cells, clusters of sticky cells have formed).
- Sharply intense (a large number of red blood cells combine with the antigen, forming a characteristic precipitate).
In the last two cases, we can confidently assert the presence of the disease. A reaction of medium intensity requires clarifying analyzes, since two options are possible. Either the infection occurred recently and a sufficient number of antibodies have not yet developed, or the blood preparation was performed incorrectly, and the study needs to be repeated.
Is it possible to have a false positive result for syphilis? Yes, despite the high accuracy of the RPGA method (99-100%), this can happen. This is due to the fact that the immune system produces antibodies to all pathogens, and some of them are similar in structure to Treponema pallidum, for example:
A false positive result is also possible in the presence of autoimmune diseases, myocardial infarction and pregnancy. And if the clinical picture does not indicate syphilis and there are doubts, you need to take another test that clearly confirms or excludes the disease.
Treponema
DNA hybridization
DNA hybridization is performed in vitro and is based on the complete or partial joining of two single-stranded DNA molecules into one molecule. In the case of complete correspondence of complementary fragments, merging occurs easily. If the complementary match is partial, then the joining of DNA strands occurs slowly. Based on the time of chain fusion, the degree of complementarity can be assessed.
When DNA is heated in a buffer solution, hydrogen bonds are broken by nitrogenous bases that are complementary, causing the DNA chains to diverge. Next, a drug is obtained from two denatured deoxyribonucleic acids. When cooled, the single-stranded regions become renatured. A so-called DNA hybrid is formed.
The method allows you to estimate and analyze the annealing rate, taking into account the characteristics (similarities and differences) of DNA between species or within a species.
The use of a DNA probe involves hybridizing a labeled DNA fragment with a specific DNA region to identify complementary nucleotide sequences. A group of unsaturated atoms (chromophores) or radioactive isotopes are used to label the probe.
The DNA probe is used for heterogeneous and homogeneous detection of nucleic acids. The role of the probe is to identify areas where target-probe fusion has occurred. Detection in a homogeneous system has the advantage of allowing one to monitor the hybridization of DNA molecules in real time.
The essence of the method is DNA denaturation and renaturation (reunification of DNA chains). The process of renaturation of the nucleic acid and DNA probe ends with the formation of a “hybrid”.
Specific nucleic acid sequences hybridize with the DNA probe and, thus, are detected and allow one to estimate the amount of DNA in the material under study.
Preparation and indications for RPGA
No preparation for the analysis is required, the only exception is made for smokers. The last cigarette should be smoked no earlier than 30 minutes before donating blood, and it is better to stop smoking altogether on that day. Venous blood is taken from the ulnar vein, and this study is indicated for four groups of patients:
- persons who have symptoms and signs of syphilis (these include probable chancre, enlarged regional inguinal lymph nodes, an unclear skin rash against the background of a suspicious history, sluggish meningitis, diffuse baldness, symptoms of syphilitic leukoderma in the second period, or suspected formation of gummas, signs of spinal tabes, star-shaped scars, indicating advanced tertiary syphilis;
- persons who have sexual and household contact with patients;
- donors;
- registration of a health record, preventive medical examinations, planned hospitalization in a medical institution.
The fifth category of persons are those patients who have had a positive reaction to syphilis obtained by other diagnostic methods, most often the Wasserman reaction.
How do you submit material for research?
An analysis for syphilis RPHA can be carried out using venous, capillary blood, as well as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), taken if there is a suspicion of damage to the nervous system by Treponema pallidum (neurosyphilis).
Many laboratories use venous blood to perform the test.
It is collected in clean, dry tubes or vacutainers without the use of anticoagulant substances. The biomaterial is placed in a thermostat for an hour (T=37), after which it is transferred to a cold place for 60-90 minutes. Centrifugation of the resulting clot is carried out for ¼ hour at 1000 rpm.