The success of treatment largely depends on the correct diagnosis. For this purpose, various studies of internal organs are carried out, including blood tests. In this case, special attention is paid to the main element of the circulatory system - hemoglobin. It has an important function - to ensure the delivery of oxygen to all organs and tissues in the body. How to donate blood for hemoglobin?
The role of hemoglobin
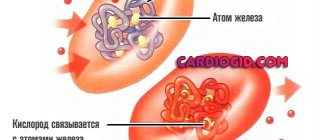
In its structure, hemoglobin is a protein of complex structure with the inclusion of iron. In addition to its main responsibility for transporting oxygen, it also helps bind carbon dioxide or CO2 in tissues and release it from the lungs. But there is also another useful task that hemoglobin performs - ensuring normal metabolism between blood cells.
Now it is unlikely that anyone can overestimate or underestimate the importance of this protein. This is another sign that Mother Nature has planned for everything. Typically, hemoglobin can be of two types:
- Pathological - it is formed as a result of some defect in the structure of the protein, which is caused by its combination with carbon monoxide and chemicals.
- Physiological - this form, in turn, is divided into several more varieties. One type of protein is found in the blood of adults. Another type of hemoglobin (called fetal) is present only in children under two years of age and over the years it completely disappears.
Where can you donate blood for hemoglobin? Usually, when there are complaints, the doctor himself writes out the appropriate referral, which is part of the diagnostic study. But if you wish, it makes sense to contact a laboratory that is present in every city.
The study of this protein allows you to detect the presence of any disease or make sure that all body systems are functioning normally. A deviation in the amount of hemoglobin in one direction or another already indicates that a disorder is present.
But at the same time, it is worth considering that some natural factors can also cause discrepancies with the norm. But if we talk about disorders, a low hemoglobin level indicates anemia. Exceeding the norm indicates the presence of a disease caused by thickening of blood plasma.
What is hemoglobin and what is its role?
Hemoglobin, which is part of erythrocytes (red blood cells), has a special role in capturing oxygen in the lungs and distributing it throughout all tissues of the body. In this case, hemoglobin captures carbon dioxide molecules along the way, exchanging them for oxygen. The correctness and sufficiency of internal respiration of the whole organism depends on the level of hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is a complex protein formed around iron molecules.
Each red blood cell contains many such compounds, which ensures the normal functioning of the entire body.
All metabolic processes inside cells depend precisely on the sufficiency of this protein.
The production of red blood cells occurs in the bone marrow, a continuous process as red blood cells only live for about 120 days. So that their death is not noticeable, they must be constantly compensated. And in order for the production process to proceed without failures, you should monitor your daily iron intake.
An adult needs from 5 – 7 to 10 – 18 mg of iron per day, which depends on gender, the person’s condition and the existing loads. For example, pregnant women and athletes require more iron than other people.
Glycated hemoglobin
There is another concept - glycated hemoglobin or glycohemoglobin (HbA1C). How to donate blood for glycated hemoglobin? Its presence is detected during a biochemical blood test. Thanks to this, you can find out the average blood sugar level of the human body, but over a long period (3 months). This is the main difference from glucose measurement, which shows the sugar level at a specific point in the study.
All this is directly related to a disease such as diabetes. Unfortunately, the number of people with this diagnosis increases every year. Hemoglobin analysis allows you to determine how much protein is combined with glucose molecules. And a deviation from the norm in this case indicates the development of diabetes mellitus.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that the processes occurring in the body can lead to irreversible consequences. With an increase in blood glucose levels, the risk of serious pathologies and complications associated with them increases. Therefore, you should not only know whether it is possible to donate blood with low hemoglobin, but also understand the importance of this study. Although with a small amount of protein, the patient will simply be refused testing for his own good. Probably due to anemia.
Red blood cells with hemoglobin live on average 120-125 days, for this reason the study indicates glucose levels in relation to 3 months. Moreover, the analysis must be carried out not only for preventive purposes. It is mandatory for those patients who are undergoing a therapeutic course or have already completed treatment for diabetes mellitus. In this way, the doctor can evaluate how effective the therapy was during the last quarter.
Functions of hemoglobin
Red blood cells are important because they enable the “respiration” of cells and tissues of the body. But they only serve as a kind of transport that helps carry vital oxygen; in fact, the main respiratory function is performed by protein - hemoglobin, which red blood cells are saturated with. It is he who gives them their color and interacts with oxygen, attaching it to itself and delivering it to the tissues, and then taking carbon dioxide from the cells. It also plays a significant role in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body. It is noteworthy that immediately after their creation, red blood cells are not yet saturated with hemoglobin; this happens after they enter the blood. Normally, a mature red blood cell contains about 400 million hemoglobin molecules.
Since hemoglobin is responsible for one of the most important functions - respiratory, its indicators are very important; in case of deviations, hypoxia begins - oxygen starvation, which has a very negative effect on the body as a whole. At the same time, it must be remembered that the deviation of its indicators beyond the norm is not an independent disease, but at the same time serves as its consequence; this always prompts a more in-depth study of the state of health to identify the real cause of such a deviation and prevent possible consequences.
Separate studies of hemoglobin are not carried out; its quantity is studied as part of a general (clinical) blood test, where other blood components - red blood cells, leukocytes and platelets - are analyzed in combination with hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin and pregnancy
Monitoring hemoglobin levels in pregnant women is especially important, since deviations to a lesser or greater extent can have serious consequences. Moreover, this applies not only to the course of the pregnancy itself, but also to the child. Normally, the protein level is between 12-14 units.
Those who want to know how to properly donate blood for glycated hemoglobin should consider one important point. Deviations may be insignificant, which can also be regarded as the norm, since in most cases they are short-lived. In the female body of a pregnant woman, hemoglobin, in addition to normalizing blood flow between internal organs, forms a connection with the placenta, through which the child receives the necessary amount of oxygen.
When blood protein levels are low, graying symptoms are felt:
In most cases, hemoglobin levels in pregnant women decrease after the 20th week. At the same time, this negatively affects the development of the child - first of all, his growth slows down, even in the womb his immunity is greatly undermined, and the metabolic process worsens. Therefore, many women are concerned about how to properly donate blood for hemoglobin.
It is more likely that the child will subsequently be born with low birth weight, and will also be seriously behind his peers in development. In addition, complications cannot be avoided during the birth of a child. Due to the low hemoglobin content, labor activity slows down significantly. There may also be heavy bleeding.
Hemoglobin norm
Newborns have the highest rate - 135-240 g/l. This happens because the fetus takes hemoglobin from the mother to accumulate its reserves. Then he gradually consumes them. In a baby by six months, the norm drops to 120 g/l (option 105-140). This indicator is considered normal up to 6 years. Further, the norm should increase slightly. In children seven to twelve years old it is 110-160 g/l.
In adult men, normal hemoglobin is about 160 (140-180 g/l). If it is higher than normal, then this is also not good, you also need to see a doctor about this.
The indicator for women is 120-160 g/l. In case of heavy regular blood loss, the hemoglobin level should be checked at least once every 6 months. It is during this period that the reserves accumulated by the body are consumed. It is also good to sometimes donate blood from a vein for serum iron testing. To prevent iron deficiency anemia, you need to take medications. Of course, this is all prescribed by the doctor.
Hemoglobin function
Transport. Everyone knows that it delivers oxygen to every cell of the body. Takes in unnecessary carbon dioxide in order to remove it. Some will say that this is done by erythrocytes - red blood cells. This is of course correct. But hemoglobin is part of the red blood cell. It is he who attaches O2 or CO2 molecules to himself.
What needs to be done to have good blood
For a healthy body, there are two options. Or eating well means regularly eating meat, fish, vegetables, and fruits. Heme iron, which is found in meat, is absorbed much better. This promotes the production of high-quality hemoglobin.
The trace element iron from plant foods is absorbed much less. But fresh vegetables, fruits, and berries contain ascorbic acid, which help absorb Fe from the intestines. Therefore, it is ideal to eat well-cooked meat with salad. In addition to plant foods, lactic acid, as well as fish or poultry dishes, are also useful.
There are foods that interfere with the absorption of iron. If you eat them often, then your hemoglobin will also not be normal. These are products based on soy protein, nuts, beans, tea, coffee. Calcium also prevents iron from being absorbed well. Therefore, there is no need to drink meat with milk.
You need to know that if your hemoglobin is below normal, then you will not raise it with food alone. You'll have to take medicine. Good, nutritious nutrition can only support quality blood. This is only if there are no problems with the bone marrow, small intestine, red blood cells or other chronic diseases.
If for some reason you do not eat meat products that contain highly absorbable iron, then you absolutely need to take iron supplements 2 times a year.
If you don't eat meat
I don't understand vegetarianism at all. For what reasons do people refuse to eat meat to such an extent that they then have low hemoglobin, leading to iron deficiency anemia? Maybe you feel sorry for the animals? I also love cows and rams. But, in my opinion, we need to understand: a cow is a domestic animal. And beef is a product necessary for health. This is how nature works, you can’t argue with it. Low hemoglobin is especially common in pregnant women and children. Therefore, vegetarianism is not acceptable for them.
I tried to write clearly about hemoglobin and its norm. If you have any questions, write. How do you feel about vegetarianism? Maybe you are affected by the problem of hemoglobin levels? How did you solve it - share by writing a comment.
Rules for taking a hemoglobin test
As we have now found out, a hemoglobin test allows us to find out the amount of iron-containing protein in the circulatory system over the past three months. No special preliminary preparation is required. However, it is important to perform this procedure early in the morning and preferably on an empty stomach. Moreover, the last meal should be at least eight hours ago.
Do you donate blood for hemoglobin on an empty stomach or not? This question worries many pregnant women, who may simply faint on an empty stomach. In this case, you can and even need to take something to eat with you after the procedure. Chocolate will be the best option so that your health does not deteriorate and strength is not lost.
At the same time, a week before the procedure, you must stop taking medications. However, if this is not possible, you should discuss this issue with your doctor. Also, on the eve of the analysis, it is imperative to refrain from eating fatty foods and junk food. Also, try to avoid strenuous physical activity and remain calm.
Procedure for collecting total hemoglobin
The level of regular hemoglobin can be found by performing a complete blood count. To do this, material is taken from capillaries, that is, from a finger. The nurse pre-disinfects it. Now the process itself, how to donate blood for hemoglobin.
The puncture itself is made using a disposable instrument, which a medical professional opens in the presence of the patient. Then, armed with a special device (a glass tube connected to a small bulb through an elastic transparent thin hose, but sometimes it is immediately located at the end of this tube), he collects the released blood from the finger. After this, the seized material is placed in test tubes, which are sent to the laboratory for testing.
It was mentioned above that the physiological form of hemoglobin has several varieties, but it is worth dwelling on this in a little more detail. There are three of them:
We are already familiar with the pathological form. When conducting the study, attention is paid specifically to physiological hemoglobin. The obtained data are compared with a table containing normal indicators, depending on the patient’s gender and age. Possible deviations that are caused by the individual characteristics of the human body are also taken into account.
Why is hemoglobin so important?
Blood tests must be taken regularly for preventive purposes. This will help to detect deviations from the norm in time and correct them. To obtain accurate results, you must follow some rules.
Everyone should know what hemoglobin is, since hemoprotein is indispensable for the normal functioning of all organs and systems. It saturates the body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. It also takes part in metabolism. With its deficiency, many diseases develop.
Hemoglobin is part of red blood cells. This protein contains iron, which the body needs.
There are two types of hemoprotein:
- Physiological. This is the one found in the blood of an adult, as well as fetal hemoglobin. The latter is contained in the baby’s blood and disappears when the child reaches two years of age.
- Pathological hemoglobin differs in chemical composition and occurs with birth defects associated with the formation of this protein.
The level of physiological hemoprotein can be determined by taking a complete blood test (CBC). It is taken from the finger. To determine pathological hemoglobin, venous blood and biochemical analysis may be needed.
What type of analysis the patient needs to undergo is determined by the attending physician.
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin
Where can I donate blood for glycated hemoglobin? Actually, in the same place where the procedure is carried out in relation to total protein - clinic, laboratory. But how is biological material collected in this case? No special preliminary preparation is required here either. In this case, you can donate blood on an empty stomach or on a full stomach - this will in no way affect the final result.
It is enough to follow the general rules for preparing for research. Before the procedure, do not drink alcohol or energy drinks for 6-12 days, and avoid physical and nervous stress. Also refrain from smoking. The same applies to taking medications. They can distort the results, and therefore it is worth temporarily stopping their use.
However, if therapy cannot be interrupted for any reason, you should notify your doctor in advance. In this case, he will assess all the risks of stopping the medication, and also determine whether it is worth conducting such an analysis at all. Also, the question should not arise: is blood tested for hemoglobin taken on an empty stomach or not?
The only difference lies in the method of collecting biological material. The level of total hemoglobin is determined by taking blood from a finger, while for glycated protein - from a vein.
Increased iron levels in the blood
A condition in which the level of ferrum in the blood is elevated is more rare compared to iron deficiency. An excess of this element is diagnosed when its intake into the body exceeds its consumption and excretion. The critical value is considered to be 30.4 µmol/l. If this number is exceeded, the patient is diagnosed with an excess of ferrum. This is possible with some diseases and an overdose of iron-containing drugs. Symptoms of this deviation are:
- pain and swelling of the joints;
- loss of appetite;
- arthritis;
- nausea, vomiting, heartburn;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- hair loss;
- muscle soreness;
- decreased libido.
Causes
A less dangerous cause of excess of this microelement is an overdose of iron-containing drugs. In this case, they are canceled, after which the iron level should return to normal within a couple of days. Overdose occurs when consuming up to 200 mg of ferrum per day. Causes of excess include some diseases and special cases:
- hemochromatosis;
- different types of anemia (hemolytic, aplastic, sideroblastic, hypoplastic)
- hemosiderosis;
- thalassemia;
- premenstrual period;
- frequent blood transfusions;
- viral and acute hepatitis;
- iron metabolism disorders;
- acute liver necrosis;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- hepatopathy.
How to reduce
Unlike the treatment of iron deficiency, to reduce ferrum levels it is necessary to eliminate foods with high ferrum content, which were listed above. These are meat, beans, mushrooms, seafood, apples, pears, etc. You should also avoid drugs that improve the absorption of this element in the intestines. This applies to vitamins B and C, folic acid. Medications that help lower ferrum levels include:
- heptapeptides;
- hepatoprotectors;
- zinc preparations;
- complexing agents.
Iron-binding drugs, such as Thetacine calcium, Deferoxamine, Desferal, can also be used. In addition to medications, special procedures are carried out:
- Phlebotomy is periodic bloodletting. About 350 ml of blood is taken from a person every week.
- Hirudotherapy. This is a treatment with leeches that feed on human blood. Due to this process, iron levels decrease. This is due to the fact that the blood loses hemoglobin.
- Donor blood transfusion. This type of donation is also called exchange donation. It involves taking blood from the bloodstream and simultaneously infusing donor blood.
Venous blood collection procedure
As we now know, to determine the hemoglobin level in relation to diabetes mellitus, venous blood is needed. To do this, the procedure is performed according to the standard algorithm. The patient takes a comfortable sitting position in a chair, puts his hand on a special cushion, slightly bending it at the elbow.
After this, the nurse tightens the arm with a tourniquet just above the elbow, placing a napkin in advance (to protect against damage). Now you can proceed directly to the procedure:
However, in a number of medical institutions, this procedure, like donating blood for hemoglobin, may differ from the established standard. A special vacuum tube is used there, which minimizes trauma to the skin and increases the reliability of the data.
How to test hemoglobin at home?
At home, hemoglobin levels are not checked.
However, some symptoms may suggest reduced hemoglobin in the blood.
Symptoms of decreased performance may include:
- feeling of constant drowsiness, muscle weakness, weakness, causeless fatigue;
- yellowish, sallow or grayish skin tone;
- peeling, dry skin;
- jams in the corners of the lips;
- dry mucous membranes;
- dry and cracked lips;
- brittle nails;
- alopecia;
- dry, split and dull hair;
- desire to eat crayons, raw meat products, soil;
- perverted sense of smell (unpleasant odors seem pleasant);
- muscle pain, etc.
Interpretation of results
If the test results show an increased level of hemoglobin in the blood, this does not indicate the development of diabetes mellitus. But with a greater degree of probability, one thing can be said - the process of carbohydrate metabolism is definitely disrupted.
Only the attending physician can detect the presence of a particular disease. However, in some cases, additional research will be required to exclude other variants of the body’s reaction.
For example, low levels of glycated protein (hypoglycemia) can indicate many diseases, including the development of a pancreatic tumor. This pathological condition in the body leads to increased production of insulin. Due to this, sugar levels drop, which causes hypoglycemia.
In this regard, it is important for patients not only to understand when it is better to donate blood for hemoglobin, they are not recommended to try to independently interpret the test results. It must be remembered that they are not always true. And here, in many respects, everything depends not only on the actions of medical workers, but also on the preparation of the patient for the analysis. Therefore, there are certain rules that are not difficult to follow; they allow you to avoid distortion of the results.
Does hemoglobin drop during menstruation?
The hemoglobin content in the blood after heavy menstruation may decrease slightly. However, hemoglobin during menstruation still remains within normal limits.
If a patient’s Hb drops below the normal range after menstruation, she needs to undergo a comprehensive examination by a gynecologist.
A common gynecological cause of decreased Hb is dysfunctional uterine bleeding and inter-cycle bleeding.
Chronic light blood loss often leads to moderate and severe anemia, which is difficult to treat.
Read further: About the causes and consequences of low hemoglobin in women
Normal indicators
What should be the normal level of total hemoglobin? It all depends on many factors. Representatives of the stronger half of humanity have slightly more protein in their circulatory system than women. This is due to the characteristics of the body and the influence of the hormone testosterone. The average value also depends not only on the gender, but also on the age of the person. The normal parameters are given in the table below.
| Patient age | Norm for men, g/l | Norm for women, g/l |
| From 12 to 15 years | 120-160 | 112-152 |
| From 15 to 18 years old | 117-160 | 115-153 |
| From 18 to 65 years old | 130-160 | 120-155 |
| Persons over 65 years of age | 125-165 | 120-157 |
As for children under 12 years of age, the amount of hemoglobin in boys is the same as in girls. Its level varies according to age. It is advisable for anyone who is interested in how to properly take a blood test for hemoglobin to know this. The average protein value is below:
At the same time, the average value of the norm, regardless of the patient’s age, in a healthy person can be in the range of 110-160 g/l. Over the years, the blood begins to thicken, and accordingly, the hemoglobin level, from a theoretical point of view, should increase. But in reality everything happens differently. And this is mainly due to the fact that most older people have various diseases. As a result, hemoglobin levels drop, leading to anemia.
In pregnant women, the level of total protein also decreases, but only in the second half of the term. This can also be considered the norm. This is due to the fact that the blood volume in the body increases, and the bone marrow does not have time to produce the required amount of red blood cells and hemoglobin. For this reason, the normal limit for pregnant women is 110 g/l.
Hemoglobin Hb, blood
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein in red blood cells that gives blood its red color. The main function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen molecules to organs and tissues and remove carbon dioxide from the body. With a lack of hemoglobin in the blood, the transfer of oxygen is difficult, as a result of which the cells do not receive enough of it. This leads to disruption of metabolism and cell function. The condition of the body in which there is a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood is called anemia.
According to the degree of decrease in hemoglobin, iron deficiency anemia is divided into: - anemia of the 1st degree (mild) - hemoglobin 100-120 g/l in men and 90-110 g/l in women. A person usually does not feel particularly pronounced symptoms at this stage of the disease. In some cases, weakness, malaise, and increased fatigue may appear.
- anemia of the 2nd degree (moderate) - hemoglobin 80-100 g/l in men and 70-90 g/l in women. In this case, the symptoms of anemia begin to manifest themselves more strongly. The person feels constant headaches associated with insufficient oxygen supply to the brain, and dizziness. The heart rate usually increases, shortness of breath and pain in the heart area appear. In some cases, however, even this degree of anemia is asymptomatic. - anemia of the 3rd degree (severe) - hemoglobin below 70 hl. This stage of the disease is considered quite severe. When the hemoglobin level is below 70 g/l, there is a danger to human life. The symptoms that are observed at this stage are manifested by changes in the structure of nails and hair, hair loss, increased dryness of the skin and its flaking, coldness and numbness of the extremities, perversion of taste and smell (many patients feel the desire to eat chalk, clay or smell glue, gasoline, kerosene ).
When examining patients with 3rd degree of anemia, blood thinning is observed, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This degree of anemia requires mandatory medical intervention.
An increased level of hemoglobin in the blood can also be a symptom of various diseases (blood thickening, congenital heart defects, etc.). Based on the results of only one blood test for hemoglobin, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, but determining hemoglobin will reveal possible disturbances in the body’s functioning and indicate the need for additional examination.
The test detects the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood (in g/liter).
The main methods for determining hemoglobin in blood are colorimetric. One of the most common methods in laboratory practice is the hemiglobin cyanide method using acetone cyanohydrin. The essence of the method is that hemoglobin, interacting with acetone cyanohydrin, in the presence of potassium iron sulfide (red blood salt) forms a red substance - cyanmethemoglobin (hemiglobin cyanide). The color intensity of this substance is proportional to the hemoglobin content in the test sample.
Reference values - normal (Hemoglobin (Hb), blood)
Information regarding the reference values of indicators, as well as the composition of the indicators included in the analysis, may differ slightly depending on the laboratory!
Men - 135-160 g/l, women - 120-140 g/l, children of the first year of life and pregnant women - 110 g/l.
Source:
Norm for glycated protein
As for the question “how to donate blood for glycosylated hemoglobin,” its value is determined as a percentage. Again, everything depends on the age, gender and health status of the person. The normal indicators are presented in the table below.
| Standard | Persons under 45 years old, % | After 45 years, % | People over 65 years old, % |
| Normal indicator | Less than 6.5 | Less than 7 | Less than 7.5 |
| Satisfactory result | From 6.5 to 7 | From 7 to 7.5 | From 7.5 to 8 |
| Increased value | More than 7 | More than 7.5 | More than 8 |
If the analysis shows the result within normal limits, then there is no reason to worry - the person is completely healthy. If the readings are satisfactory, you should think about your own health. And the sooner the better. As you can understand, elevated values should already force any person to immediately seek medical help - the development of diabetes mellitus is quite likely.
Pregnant women also have their own norm:
In this regard, every expectant mother also needs to know how to take a blood test for glycated hemoglobin. At the same time, even if a person feels completely healthy, he should still undergo periodic tests to determine whether he has diabetes. This is especially true for those who have a family history of people suffering from this disease. In addition, all pregnant women should also be on guard, since gestational diabetes is not uncommon.
Norms and deviations of hemoglobin in a blood test
A general blood test allows you to accurately determine hemoglobin. The content of this protein in the blood is calculated in the laboratory using several modern methods.
The most complete picture can be obtained using the following methods:
- colorimetric study;
- gasometric;
- determination of iron content in the hemoprotein molecule.
The last two options are the most accurate, but they take a long time, so the first method is used most often, since it is simpler and faster. There are clearly defined norms for representatives of different genders and ages. Deviations in any direction can cause harm to the body.
A person is considered healthy if:
- Representatives of the stronger half have hemoglobin from 135 to 160 g/l.
- In women, indicators are not lower than 120 and not higher than 140 g/l.
- The highest rates are in newborns. In the first days of life, hemoglobin is from 180 to 240 g/l and gradually decreases. When a child reaches one year of age, indicators of no less than 110 and no more than 135 g/l are considered normal.
Correcting low hemoglobin levels
Adjusting hemoglobin levels can be done not only by taking medications. In addition, you should adhere to a certain diet depending on the situation.
It’s clear how to take a blood test for hemoglobin, now it’s worth touching on what can be done to adjust its amount. If your hemoglobin level is low, you can increase it by consuming foods rich in protein and iron. Beef or chicken meat and liver are especially valuable in this regard. It is worth considering that iron is absorbed much better from animal products. Pomegranate, buckwheat and apples also contain a lot of this essential element.
Eating other equally healthy foods will help bring your hemoglobin level back to normal:
In addition, a balanced diet should be supplemented with physical activity (of moderate intensity) and a nightly routine. You should also spend time in the fresh air whenever possible - the benefits of oxygen should not be discounted either.
How to increase hemoglobin
First you need to find out what led to the decrease in hemoglobin and eliminate this cause. In most cases (if the decrease in the indicator is not catastrophic), it is possible to raise the level to normal with the help of food.
You should enrich your diet with foods high in iron, remembering that iron is absorbed better from foods of animal origin than from fruits and vegetables.
Animal products that increase iron levels include: liver, especially chicken and beef, rabbit meat, veal, beef tongue, beef and pork heart, chicken egg yolks, turkey meat.
Plant products containing iron include: various types of legumes, dried and fresh mushrooms, cocoa, bananas, seaweed, broccoli, peaches, baked potatoes, raspberries, carrots, fresh tomatoes, natural honey, molasses, wheat bran .
It is important to remember that iron absorption occurs faster and better with additional consumption of foods rich in vitamin C. And dairy products and black tea significantly reduce the level of absorption of this element.
In severe forms of anemia, in addition to special nutrition, medications containing divalent iron are also prescribed to more quickly replenish it in the body.
Diet for high hemoglobin levels
Those who are interested in how to donate blood for hemoglobin correctly may be wondering what can be done if its level increases? First of all, it is necessary to exclude all red foods from the diet:
You should also be careful with berries. As for meat products, it is better to replace them with fish and other seafood during the diet period. The consumption of oats and barley should be significantly limited, but legumes and dairy products should be included in the diet. In addition, patients with high hemoglobin levels need to arrange fasting days at least once a week.
Fish oil, which can be found in capsule form at almost any pharmacy, is an excellent dietary supplement. Shilajit will also help cope with increased protein levels.
Causes and dangers of increased hemoglobin
Reasons for increasing hemoglobin levels include:
- Living in unfavorable areas, for example, high in the mountains, where the air is thin and there is a lack of oxygen, as well as in regions with poor ecology, in large cities.
- Constant physical strain, serious physical activity, hard physical work. Lack of proper rest.
- Dehydration due to insufficient fluid intake, especially during the hot season.
- Presence of heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Taking diuretics.
- Various gastrointestinal diseases or food poisoning, accompanied by vomiting or severe diarrhea.
A high level of hemoglobin is usually manifested by severe weakness of the whole body, loss of appetite, and pain in the joints and muscles. Some people may experience severe hearing or vision loss. Severe redness of the skin, dizziness, insomnia, abdominal pain, and constipation may occur.
It is important to remember that an increase in hemoglobin always indicates blood thickening, and this disrupts its flow through the vessels, which also leads to oxygen starvation due to untimely supply of oxygen to the tissues.
How often do you donate blood for hemoglobin?
Completely healthy people, upon reaching the age of 35, should be tested for hemoglobin at least once every three years. But some people should carry out this procedure more often - once a year. In particular, this applies to the following cases:
In addition, the risk group includes women who have had gestational diabetes and women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Monitoring hemoglobin levels is also necessary in young children and adolescents. As a result, you can promptly identify the presence of any problems in the body and prevent possible complications in the case of diabetes.
But older people should be especially careful. As a rule, after reaching the age of 65, most of them are diagnosed with increased sugar levels in the circulatory system.
However, many are not only not interested in how to donate blood for hemoglobin, but are also in no hurry to see a doctor and do this after their health has seriously deteriorated. But eliminating complications in old age is much more difficult. Therefore, the importance of regular blood testing should not be underestimated!
Critical level of hemoglobin in the blood in women and men
Main article: Hemoglobin norms in women and men with decoding
A decrease in Hb is called anemia. This condition is fraught with complications such as:
- oxygen starvation in tissue and organ structures;
- development of cardiomyopathies;
- arrhythmias and extrasystoles;
- decreased immunity;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- memory loss;
- decreased visual acuity;
- menstrual irregularities;
- the appearance of hormonal imbalance;
- decreased libido;
- the appearance of erectile dysfunction, etc.
In children, chronic anemia can cause developmental delays.
For children under 5 years of age, as well as for women carrying a child, the minimum threshold value is 110 g/l.
Children from five to twelve years old - 115. For children from twelve to fifteen years old - 120.
For patients over fifteen years of age:
- 120 for women;
- 130 for men.
In patients with anemia, there are three degrees of Hb reduction:
- light (from one hundred ten to ninety);
- average (from ninety to seventy);
- severe (less than seventy).
Read further: What does increased hemoglobin mean in men, and what should be done?