How to treat sutures after surgery, because the rapid and successful healing of the wound depends on how properly the postoperative wound is cared for. Modern medicine is trying to perform laparoscopic interventions instead of conventional open abdominal operations due to their less traumatic nature and easier postoperative period. However, even these minor incisions must be properly cared for.
How long does it take for sutures to heal after ovarian laparoscopy?
The duration of healing of sutures is largely determined by the individual characteristics of the body and the regularity of their treatment. In many patients, they heal completely within a month after surgery. After 2-3 months, the remaining whitish scars disappear and become almost invisible. Sometimes any traces on the abdomen from the operation are completely absent.
The more carefully the doctor applied the suture, the greater the chance of complete healing without the formation of scars.
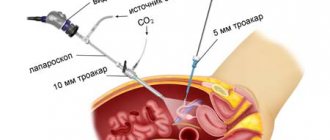
What is laparoscopy and its features
The priority of this type of surgical intervention is a low degree of trauma, which leads to the following favorable factors:
- a few hours after the operation the patient can get up;
- minimal pain during and after surgery;
- complications are rare;
- no scars visible.
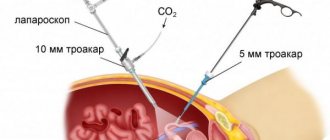
The operation is performed by a surgeon in a medical facility. The examination of internal organs takes place using a telescopic tube equipped with a digital video camera - a laparoscope. The instrument has halogen or xenon lighting and is also synchronized with the monitor.
The procedure is performed under general or, in rare cases, local anesthesia using medical instruments through small punctures in the peritoneum.
The operation is prescribed in the following situations:
- infertility;
- endometriosis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- benign tumor of the uterus (leiomyoma);
- fibroma;
- adhesions in the intestines;
- appendicitis;
- for restoration of fallopian tubes;
- ovarian cyst;
- removal of gallstones.
Laparoscopy is a highly effective and safe method of surgical intervention on the pelvic and abdominal organs.
We recommend reading:
- Methods for treating scars after pneumonia
- What to apply to the skin after blepharoplasty
- How to get rid of cut marks
When and how are sutures removed after ovarian laparoscopy?
Sutures after ovarian laparoscopy are removed after 7-14 days. At the end of this period, the tissues no longer require additional support and are able to completely regenerate on their own. After the stitches are removed, the healing process accelerates.
The procedure is carried out when visiting a doctor. It does not require the use of local anesthetics. The stitches are removed in a few minutes. A woman may experience discomfort, but there should not be any acute pain. After the procedure, the wound is additionally treated with an antiseptic.
Removal of sutures is not required when using self-absorbable sutures during their application.
Means "Kontraktubeks"
“Contractubex” for scars and scars has a large number of indications for use. The drug has a corresponding effect for each scar. Doctors recommend using the product if you have:
- scars after burns, amputations;
- keloid or hypertrophic scars after injury;
- scars after laparoscopy.
The drug can be used to eliminate stretch marks during pregnancy or after birth, as well as for ankylosis. This remedy has no special contraindications or restrictions for use.
Prohibited use:
- should not be used by patients who are allergic to the components of the product;
- limit use if the patient has increased sensitivity to parabens.
Normal healing process
During the process of soft tissue restoration, unpleasant symptoms may appear. Some of them are considered normal:
- pain in the suture area;
- increased pain when changing body position;
- wound moisture;
- itching;
- slight redness of the adjacent skin;
- seal under the puncture.
All these signs should not alarm the patient - their presence indicates the correct course of the healing process. You should consult a doctor if there is no decrease in their intensity for a week and a half or more.
Inflammatory process of postoperative sutures
If the laparoscopic operation was successful and without complications, then the patient will not be kept in the hospital for long, and upon discharge he will receive detailed recommendations on how to remove the sutures after the operation, how to treat them at home and when the patient should see specialists.
Symptoms of the development of a postoperative inflammatory process will be the following manifestations:
- every day the tissue around the stitches becomes more and more painful and the feeling of discomfort in this area does not decrease;
- the skin becomes more and more red, swelling forms on it;
- the sterile dressing becomes wet, various kinds of discharge in the form of blood, mucus or even pus may appear on it;
- the patient’s general well-being worsens with the occurrence of a feverish state, increased temperature, headache and muscle pain and weakness.
When such symptoms first appear, you should immediately see a doctor, as the resulting inflammatory process can lead to very serious complications. Depending on how dangerous the condition of the sewn tissue is, the doctor will select the necessary methods to eliminate the infection and properly treat the sutures. If the processes are not started, then inflammation can be eliminated by thorough disinfection of wounds and physiotherapy methods; in other cases, it will be necessary to remove the suture and install drainage, and the use of antibiotics may also be required. To prevent this from happening, the patient in the postoperative period must realize how important competent care of the wound surface is at this time.
The day on which the sutures are removed after laparoscopy depends on how many days the damage takes to heal. If the patient’s sutures were removed later than usual, after two weeks or more, this means that healing occurred with disturbances, but the doctors managed to cope with the inflammatory process. Often threads are used for wounds, which can dissolve on their own, which makes wound care easier and, in most cases, accelerates the healing process. If no unforeseen complications arise, ordinary suture materials are disposed of after a week, as they can provoke further inflammation.
Why do scars form?
The longer a wound takes to heal, the greater the risk of scarring. The following factors negatively affect the regeneration process:
- obesity;
- hormonal disbalance;
- non-compliance with diet during the postoperative recovery period;
- low level of immunity;
- dehydration;
- elderly age.
The following symptoms indicate abnormal tissue healing after ovarian laparoscopy:
| Type of symptom | Reason for appearance |
| Severe, persistent itching | Consequence of wound infection. |
| Swelling of the suture that does not subside for more than a week | Occurs due to irregular processing or improper application of threads. |
| Increasing seal size | A sign of accumulation of pus or fluid. |
| Blood clots on the surface of the wound | Appear when the seam diverges. |
These signs require urgent medical attention.
Otherwise, there is a risk of infection spreading inside the wound and complete rupture of the seam. This may be accompanied by increased body temperature, general weakness, dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen. Long-term and complicated healing wounds after ovarian laparoscopy turn into scars that are difficult to hide.
Complications of the regeneration process and an increase in its duration are possible if the sutures are not removed in a timely manner. Performing this procedure too early may result in the tissues damaged during the operation becoming separated.
What is it processed with?
The seams need to be treated with antiseptic solutions, which are sold in pharmacies: hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, alcohol-based liquid. During processing, it is better not to use cotton wool, as it can leave pieces along the edges of the seam, which can cause an inflammatory process. A gauze swab is better suited for these purposes. The ichor oozing from the wound should be a cause for concern.
The procedure for processing postoperative sutures is as follows:
- Roll up a small part of the sterile bandage, then dip it in the treatment solution and wipe the seam. Moreover, it is necessary to ensure that all the dimples are wetted. Next, let the skin dry.
- If you experience a burning sensation or pain, apply a sterile gauze bandage.
- If there is no pain, then a cotton swab dipped in brilliant green should be used to smear the seam. After which a sterile bandage is applied.
With the doctor's permission, for better healing, the wound can be left unsealed. In this case, it is important to wear loose, natural underwear that will not catch or damage the scar. After removing the stitches in this way, it is necessary to carry out treatment within a week. Many people worry whether it hurts to remove stitches. They usually don't hurt to take them off. Most often, pain is present in the presence of inflammation.
While processing seams, you should not take a bath or sauna. For hygiene procedures, it is allowed to use a shower, during which it is better to seal the scar areas with cellophane to prevent them from getting wet. Next, carry out processing in the usual way. It is necessary to carefully approach the treatment of sutures after laparoscopy. Since even minor scars can become inflamed and cause serious complications. Most often this occurs in the navel.
When to see a doctor
After the operation, the patient must visit the doctor several times. If complications arise, a meeting with a specialist should be arranged as soon as possible. This is necessary for the following symptoms and conditions:
- long-term healing of sutures;
- severe itching and burning of the wound;
- increase in the focus of inflammation;
- persistent redness of the skin;
- increase in seal size;
- bloody discharge from the wound;
- discharge of pus or brownish fluid;
- persistent pain syndrome;
- increased swelling of the suture.
These signs may be more pronounced in the umbilical wound. This is due to the difficulty of tissue healing in this area.
Pain relief in the postoperative period
After laparoscopy, there is pain throughout the abdomen; often the patient cannot pinpoint the location of the greatest pain.
In case of severe pain in the first 24 hours after laparoscopy, opiate narcotic drugs ( Tramadol ) are prescribed, which reduce the synthesis of pain mediators and block the conduction of pain impulses in the central nervous system. Narcotic analgesics quickly relieve pain, but have a number of side effects on the heart and nervous system.
Then they switch to the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( Xecofam, Lornoxicam ), the mechanism of action of which is to block the synthesis of prostaglandins.
No-shpa, Drotaverine are prescribed as auxiliary therapy , which relieve spasm of the smooth muscles of the internal organs, especially after gall bladder surgery.
Types of Scars
After tissue healing, scars form, which degenerate into scars. The latter have two main types. They differ in appearance and cause of appearance.
Keloid
The most common type of scar after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst or other pathologies. The result of an accumulation of collagen cells at the wound site. To prevent its occurrence, the following manipulations are used:
- injection of corticosteroids into the wound area;
- wearing silicone plates;
- use of tight bandages;
- exposure of a fresh scar to laser or liquid nitrogen.
A woman can reduce or completely remove an old scar in salons that specialize in eliminating skin defects.
Atrophic
With a small number of collagen cells, atrophic scars appear. They look like small depressions in the skin. To remove them you need:
- biorevitalization – subcutaneous injection of gel with hyaluronic acid;
- mesotherapy - the use of local injections with substances that stimulate regeneration;
- dermabrasion – mechanical peeling of the skin.
This type of scar is most noticeable if a woman is overweight. It is much more difficult to detect in slender and young patients.
Reasons for long recovery
If scars after laparoscopy take too long to heal and cause discomfort to the patient, then it is important to determine the cause of this deviation.
A slow recovery process may occur in the following cases:
- Reduced immunity. In this case, tissue regeneration deteriorates, which provokes prolonged wound healing.
- Chronic diseases of the endocrine system, as well as problems with the production of hormones.
- Not following the doctor's recommendations for postoperative nutrition. Eating puts stress on your abdominal muscles.
- Obesity or physical fitness problems. Due to the large fat layer, it is difficult for the tissues to carry out the required regeneration for complete restoration of the sutures.
- Elderly patient. The functions of muscle tissue in this case are greatly weakened.
- Lack of fluid in the body. When dehydrated, muscle tissue is not saturated with oxygen, which also leads to problems with regenerative function.
In all the described cases, the process of patient recovery and scar healing can occur simultaneously with severe but tolerable pain.
Preventing complications
If punctures are treated incorrectly or take too long to heal, complications may occur. They usually manifest themselves in the form of suture dehiscence or suppuration.
Suppuration
The presence of pus is accompanied by an increase in the size of the compaction under the wound, the spread of the inflammatory process, and persistent pain. The best way to prevent this complication is to regularly clean the sutures. If damaged tissue comes into contact with dirty clothing, dust, etc., you should immediately wipe the wound with antiseptics.
Divergence
Most often, sutures after ovarian laparoscopy come apart due to too intense physical activity. Doctors recommend avoiding sports for a month after the intervention. Additionally, you should wear a postoperative bandage - it will speed up the healing process and prevent the sutures from coming apart.
Another cause of complications is flatulence in the intestines. It can occur if the diet is not followed during the rehabilitation period. In case of gas formation, you should adjust your diet and take a drug that reduces peristalsis of the organ.
How to avoid complications of suture healing?
The most common complications during healing are:
- Suppuration.
- Seams coming apart.
Suppuration
If a tumor, hard nodule or lump appears in the area of the sutures, this indicates possible purulent inflammation. It is often accompanied by pain. If leukocytosis is detected (an increase in the number of leukocytes to more than 9 million in 1 ml of blood), it is worth talking with a high degree of confidence about the development of a purulent complication. To eliminate this dangerous complication, you need to examine the wound area daily for swelling and pain.
Postoperative sutures must be properly processed
Seam divergence
The first reason for this is non-compliance with the recommended physical activity regimen. In order for the suture to heal on time, it is necessary to avoid heavy static and dynamic loads for at least a month. The best means of prevention is wearing special bandages. They are sold in regular pharmacies or orthopedic salons.
It is necessary to monitor the food consumed and water intake. Coarse fiber, fatty foods and excess carbohydrates should be excluded during the postoperative recovery period. These products enhance peristalsis and promote the development of flatulence.
If you follow dietary recommendations, the risk of postoperative sutures coming apart is minimized.
A special group of patients are diabetics. If a patient has diabetes mellitus, all reparative and regenerative abilities are reduced. Therefore, any wounds heal worse. This is why diabetics are given special attention during surgical interventions, including laparoscopy. Compensation of glycemia using oral hypoglycemic therapy or insulin therapy in adequate doses is the key to the normal course of the postoperative period and rapid wound healing.
If the sutures come apart, the wound should be considered infected. Therefore, it is treated with antiseptic solutions every day. In this case, systemic antibiotic therapy is carried out in parallel. The stitches are reapplied. If eventration occurs, laparotomy is possible.
Self-processing of seams
From the first days after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst, a woman must take care of the punctures on her own. Seam care rules:
- daily personal hygiene;
- avoiding contact of wounds with water in the first week after the intervention;
- use of medical plasters and special bandages;
- treatment with antiseptics 1-2 times a day;
- use of wound healing drugs;
- restriction of physical activity - 1-2 weeks after surgery, light exercise is allowed.
To prevent suppuration of the sutures and speed up their healing, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, which should be used from 1 day after surgery.
Caring for seams
The postoperative period is the most vulnerable time when a variety of problems with the surgical wound may arise. If recommendations on diet and physical activity are not followed, tissue divergence may occur under the suture. This is fraught with separation of the sutures and eventration of the intestine - a dangerous complication in which the loops of the organ are visible through the incision of the surgical wound. This happens especially often during operations on the navel (after laparoscopy).
Therefore, on the day of the procedure, the patient is recommended to rest in bed. For the first 5 hours after the intervention, you should lie down, but at the same time make active movements of your limbs, turn over from one side to the other.
The patient's stay in the department under observation can last from 3 days to a week, depending on the condition. If there are no indications for monitoring, a patient with stitches may be sent home.
The mode of physical activity is gradually expanding. The same applies to eating behavior. For the first day, the patient is advised to refrain from eating at all. Only mineral water is allowed. After a day, you can use enveloping and fermented milk products: jelly (oatmeal or berry), kefir, fermented baked milk. Gradually switch to low-fat broths and soups. Fried, spicy foods are excluded.
Medicines that accelerate healing
Additional means to accelerate tissue regeneration after ovarian laparoscopy can be used after the sutures are removed. The most popular of them:
| Name of the drug | Effect of the drug |
| Contractubex | Softens scars after laparoscopy, has antibacterial properties. |
| Mederma | Smoothes the skin, makes wound marks less noticeable. |
| Levosin | Relieves inflammation and pain, has an antibacterial effect. |
| Dermatix | Softens and smoothes the skin, relieves itching, and prevents pigmentation. |
These drugs are used after treating the wound with antiseptic solutions. To enhance their effectiveness, patches or bandages soaked in the gel or ointment chosen for healing are used.
Gels and ointments
To quickly heal scars, it is recommended to use the following products:
- "Levosin" is a budget anti-inflammatory ointment with an antibacterial effect. The product is used externally. Helps speed up the process of tissue regeneration, has an anesthetic and antibacterial effect. The ointment is applied to gauze, and then applied to the area of skin treated with hydrogen peroxide.
- "Mederma" is a product that is a gel for eliminating scars for up to a year. This drug cannot cope with old scars on the skin; for this you should use cosmetic devices and a laser. Due to the special components in the composition, the gel helps soften the skin and make it smoother. The ointment can be applied to scars on the face, neck, and abdomen. The product is sold in a pharmacy and does not require a prescription from a doctor.
- "Dermatix" is a silicone-based gel that helps moisturize the skin, improve the appearance of scars, and smooth out damaged areas. This product also eliminates discomfort in sore areas, relieves itching, and improves skin pigmentation. Most often, the drug is prescribed for the care of hypertrophic and keloid scars.
Prevention of scars and scars
Prevention is full compliance with the rules of postoperative rehabilitation. To prevent scar formation, you should:
- limit physical activity;
- do not allow dirt to get into the wound;
- wear loose clothing that does not compress the seam and does not cause itching;
- carry out regular care of sutures after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst;
- stop taking baths, visiting baths and saunas for a month;
- do not sunbathe in the sun without means that reduce the effect of ultraviolet radiation on the skin;
- follow nutrition rules.
If you need to wear thick, rough clothing, protect the wound with a medical plaster. It is recommended to do this during sunbathing or contact with dust.
The formation of scars and cicatrices after ovarian laparoscopy can be minimized. To do this, it is enough to follow all the recommendations prescribed by the doctor. Punctures should be regularly treated with antiseptics. If pain persists for a long time or the sutures become suppurated, you should seek medical help.
Effective healing products
How to reduce scars after laparoscopy? After the stitches are removed, gauze soaked in special ointments and creams is regularly applied to the damaged area, which help quickly restore tissue, improve the condition of the skin and make the stitches smaller. The most popular remedy is the drug “Curiosin”, which contains the active ingredient – zinc hyaluronate. Its deficiency leads to the appearance of pronounced scars.
After some time has passed after the operation and the scars no longer hurt very much, experts recommend applying the Contractubex patch to the scars. This product helps soften scars on the skin, speed up the process of growing new tissue and cell formation. The Contractubex patch is distinguished by its mild effect and antibacterial effect.
Scars after gunshot wounds
A wound received by a bullet is very dangerous to human life and health. It is very important, when removing a bullet, to check for bullet fragments. Bullets come in different sizes and shapes, which determines the shape and depth of the wound.
There are several types of bullet wounds:
- a through wound, when the bullet leaves the body without leaving any fragments in the wound area;
- a blind wound, when the bullet is in the human body, having the ability to move there;
- a tangential wound, when the bullet does not hit the body, but only damages the skin.
The scar from a bullet wound is usually oval or round in shape, no matter whether it is on the face or body. The entry wound initially has uneven contours, and then an irregularly rounded scar forms at the bullet entry site.
Scar after a bullet wound
The wound suddenly began to ooze, what should I do?
If the surgeon has not stitched the edges of the wound well enough, or they have separated, then the wound on the skin begins to ooze. If measures are not taken in time, then after healing, a very noticeable scar will remain on the skin. To avoid this, you need to treat the skin around the wound with an alcohol solution and the wound with hydrogen peroxide. After treatment, a bandage with syntomycin ointment is applied to the wound. Until the wound stops oozing, it should not be wetted.
Another postoperative complication is the formation of a ligature fistula. This is an inflammatory process at the site of wound suturing, which appears as a result of pathogenic bacteria getting on the ligature thread. A ligature thread is used to stitch the edges of a wound. If measures are not taken in time, this will lead to the development of an abscess.
A few days after the appearance of the ligature fistula, it opens and the contents come out. Over a long period of time, the fistula can open and close on its own, but surgical assistance is required to completely eliminate it.
More often, a long-healing fistula appears when the wound is sutured with silk threads. At the first symptoms of a fistula, you need to go for an examination either to a therapist or to your surgeon. Many patients do not know that if the fistula is not removed in time, it can lead to disability. There are cases when people lived with a fistula for five or even ten years, and then a large-scale inflammatory process began around the source, up to blood poisoning.
Important! Ligature fistula is a dangerous postoperative complication that can result in sepsis.
Fistula after surgery