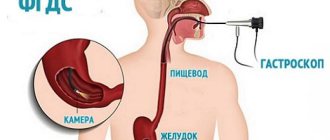
Fibrogastroscopy (FGDS) is a method of instrumental diagnostics, which is carried out using endoscopic equipment. In this case, the esophagus, stomach and duodenum are examined. This procedure is also called gastroscopy.
In this case, the probe is inserted through the oral cavity. Since it is equipped with a video camera and a light source, the doctor can assess the condition of the mucous membranes of these organs. Also, using instruments inserted through the channel of the device, he can perform some surgical interventions.
Endoscopist
Duration of the procedure
The duration of FGDS may vary. How long the procedure lasts depends on its type and goals. If gastroscopy is performed only for diagnostic purposes, then its duration does not exceed 15 minutes. If this study is carried out for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes, the procedure time increases to 40 minutes.
Quite often, the doctor cannot say exactly how long this study will take, since it is during the process that he evaluates the lesion and decides what scale of medical intervention will be required.
The duration of the procedure also depends on how psychologically positive the person is. Since if the patient is relaxed, the probe will pass through the esophagus easily. But if the patient is tense, the tube may stop in the esophagus and even injure its walls. In this case, the procedure will be significantly delayed, since it will need to be repeated all over again.
The endoscope moves easier in the stomach. Therefore, examination of the stomach and duodenum is much faster.
What does the procedure look like from the outside?
Probably, having become familiar with the most likely sensations of gastroscopy of the stomach, many want to know how FGDS will occur:
- first, the patient is given a subcutaneous injection of Atropine to reduce hypersalivation and the pharynx is irrigated with an anesthetic solution;
- after the injection and irrigation with anesthetic, the person is placed on the table (on his left side) and allowed to clamp a mouth guard with his teeth, which prevents the reflex closure of the jaws;
- a gastroscopic probe lubricated with gel to improve sliding is inserted through the hole in the mouthguard, placed on the root of the tongue and pushed into the opening of the esophagus;
- After the esophagus is passed, the probe enters the stomach cavity. If necessary, the organ can be filled with air to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane and study the walls in more detail;
- after the stomach, the duodenum is examined in the same way;
- at the end of a detailed examination of all accessible digestive organs, the gastroscope is smoothly removed, the person is asked to remove the mouth guard from the mouth and spit out excess saliva into a special tray.
All data on the examination is displayed on a large monitor in the office, and if necessary, the gastroscopist can take photos and videos of individual moments of the examination for a more detailed study.
On average, a typical examination procedure along with patient preparation takes about 10 minutes, but in some cases, gastroscopy of the stomach can take longer.
FGDS diagnostics
Most often, gastroscopy is performed to determine the presence of inflammation of the gastric walls. That is, for acute and chronic gastritis. Also, using this study, you can diagnose the duodenum. In this case, its inflammation, which arose for various reasons, is determined. You can also additionally diagnose:
- Esophagitis and reflux esophagitis.
- Peptic ulcer localized in the stomach and duodenum.
- Tumor processes.
- Duodenitis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
In the standard diagnosis of the above cases, the probe is gradually passed through the esophagus, stomach to the duodenum. How long does the FGDS procedure last in different situations? It takes no more than 15 minutes to assess the condition of the mucous membranes.
As for varicose veins, obstruction of the esophagus and stomach, diagnosis will take no more than 5 minutes.
It will not take much time to carry out FGDS of the stomach in such cases as determining the acidity in the stomach, cauterizing a vessel that is bleeding, collecting biological material to determine the presence of Helicobacter, taking material for a biopsy. Thus, important data for diagnosing serious diseases can be obtained in just a few minutes.
Thanks to different attachments during the examination, you can quickly take biological material for analysis, remove polyps or a foreign body, and cauterize the vessel in a few minutes.
Diagnosis of the stomach without gastroscopy: alternatives
Gastric endoscopy is a standard diagnostic test to examine the upper digestive tract. In some cases, an alternative to gastroscopy without swallowing the tube is necessary.
- scoliosis 4 degrees with displacement of internal organs;
- previous hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- pathological formations of the mediastinal organs, which are accompanied by a violation of the anatomical position of the esophagus - aneurysm, tumors, congenital anomalies;
- blood clotting disorder;
- severe hyperplasia of the thyroid gland;
- mental illness;
- an epileptic condition that is difficult to correct with medication;
- cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus;
- persistent arterial hypertension;
- a person’s categorical refusal of this type of diagnosis.
It is possible to check the stomach without gastroscopy. The doctor decides which method is best to replace the examination. In addition to general clinical tests, non-invasive diagnostic methods are used to check the condition of the stomach, which are presented in Table 3.
| Study | Features of the methods |
| Capsule endoscopy | It is produced by swallowing a special light-weight capsule. The device is equipped with a light diode and a camera that shoots video and takes pictures several times per second for 5-8 hours. After output, the obtained result is analyzed by connecting the mechanism to a computer. A significant disadvantage is the high cost of the study, the lack of the possibility of biopsy and collection of material to determine Helicobacter pylori |
| CT scan | Sections are made using X-ray radiation. Determine space-occupying formations, ulcerative defects, developmental anomalies of the abdominal organs |
| MRI | A layer-by-layer study is performed using nuclear magnetic resonance. Differentiate the degrees of the malignant process, the presence of metastatic foci |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | A special sensor is used to look at the size and structure of the organ, determine the presence of ECHO-positive formations and defects, and the functional characteristics of the stomach |
| X-ray with barium | Before the examination, the patient drinks a contrast agent - barium suspension. After this, fluoroscopy is performed and the movement of the substance through the esophagus and stomach is observed. If a specialist observes pathological areas, additional radiographs are taken |
| Electrogastroenterography | In the projection of the stomach and intestines, electrodes are attached to the skin, which pick up impulses and transmit them to a computer monitor. Thus, the functional ability of the digestive organs is determined |
None of the listed methods can fully replace standard gastroscopy of the stomach. Gastroscopy is an important multifunctional study that allows you to differentiate a number of gastric diseases, and also helps to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and the dynamics of the disease.
Duration of preparation
Gastroscopy is a medical procedure for which you need to carefully prepare. The timing is also important, since gastroscopy is performed only on an empty stomach. 24 hours before the procedure, you should eat only light food. And dinner before gastroscopy should take place no later than 19.00, it should not include a large amount of food. In the morning, eating is already prohibited. Water is allowed to be drunk in small sips no later than 2 hours before FGS. In view of this, a planned gastroscopy of the stomach is often scheduled for the morning. 3 hours before the procedure, the person is prohibited from smoking. It is very important to comply with these conditions.
Smoking before FGS may distort the results of the study
Sometimes the patient is prescribed drugs to speed up the digestion process, namely enzyme agents. This is justified if a short time has passed since the last meal. For example, if gastroscopy is prescribed on an emergency basis.
If the procedure is performed without anesthesia, local anesthesia is used. This may be a special spray that is used to irrigate the throat, or the patient will need to gargle with an anesthetic solution. After 5 minutes, the probe can be inserted. But if therapeutic measures are carried out using gastroscopy, that is, the procedure lasts more than 20 minutes, then local anesthesia will not be effective. Since during any surgical operations using an endoscope, the patient will feel pain.
If anesthesia or sedation (medicated sleep) is required, then the preparation is increased by another 10-30 minutes, since anesthesia is administered intravenously. After artificial sleep and general anesthesia, 1-2 hours after waking up, the person can go home. Only doctors do not recommend driving a vehicle for 24 hours after this procedure.
After gastroscopy, a person may feel temporarily unwell. Usually there may still be vomiting for 30 minutes.
What can you eat after gastroscopy of the stomach?
After the study, many patients abstain from eating. However, experts recommend eating when the procedure is completed, or drinking some water. Allowed dishes and food products after gastroscopy:
You can drink sweet tea, fruit decoction or still mineral water. If no discomfort is noted after endoscopy, return to your normal diet. In the first days, limit foods that irritate the gastric mucosa - strong broths, fresh cabbage salads, legumes, fried and fatty foods.
Equipment
Endoscopy room
The time for gastroscopy also depends on the quality of gastroscopic equipment. Many modern clinics already have a device that is additionally equipped with an ultrasound sensor. Thanks to this, it is possible to determine parameters such as the thickness of the gastric walls and determine whether there are seals. Gastroscopy with the help of such modern equipment lasts as long as a standard examination, but it costs much more.
Quite rarely, a diagnostic study lasted more than 10 minutes. This is usually done in 7-8 minutes. Many patients note that they only feel discomfort.
Feelings during FGS
Often the diagnosis is painless, and the procedure does not last long. However, the patient may experience slight discomfort due to the aspirator, a tube through which the contents of the gastrointestinal tract are removed. The doctor carries out the procedure slowly, having previously discussed with the patient the need to remain motionless, as well as a symbol when the slightest pain appears. All the patient must do to survive the procedure as quickly and pain-free as possible is to prepare correctly and relax.
PAY ATTENTION! Do not prolong gastritis or an ulcer until stomach cancer, it is better to be on the safe side, but this will be necessary. read the story of Galina Savina >>
Conducting and price of FGS
You need to come to the clinic in the morning and undergo an FGS of the stomach. The procedure looks like this:
- Carrying out FGS of the stomach
Initially, the tongue will be treated with Lidocaine as an anesthetic. Why is this necessary? To make the procedure easier, and the patient does not feel discomfort and there are no strong contractions. Pain relief occurs not with an injection, but through a spray. - How soon can I start? After about 5-10 minutes, the remedy will take effect and the doctor begins FGS. The patient is placed on his side, his head on the pillow and a towel should be placed on it, since strong salivation is possible.
- To prevent the jaw from hurting and closing on its own, a special dilator is inserted into the mouth. This will preserve the endoscope itself during operation.
- Next, the patient will need to swallow the endoscope. To do this, the hose is inserted into his oral cavity, and the patient needs to pass the tube through swallowing movements. This is necessary to make the research faster and easier. As a rule, the procedure is not pleasant, but the amount of time will be spent is minimal.
- After this, the endoscope can show the patient's internal cavity. Using a camera at the end of the tube, the doctor examines the organs and mucous membranes. The procedure is unpleasant, but nothing should hurt you. Much depends on the patient; if you breathe through your mouth and try not to swallow drool, the discomfort will be reduced.
- When the examination is completed, the doctor may do a biopsy, if such an analysis is needed. The tissue sampling is felt, but does not hurt.
- The tube is removed from the mouth and stomach in a matter of seconds, after which there may be a urge to vomit, but vomiting itself will not happen.
Cost of performing FGS of the stomach
The photo on the side shows FGS. Veliky Novgorod, Moscow, as well as the Penza clinic offer a more modern device that uses a fiber optic endoscope. After the studies, the device can show the doctor a video of the FGS of the stomach, due to which it will be possible to better assess the condition and prepare the necessary treatment. After the examination, the doctor prescribes treatment, but if necessary, prepares for surgery.
The price for such an examination is not high, from 1100 rubles in Moscow. Many people are interested in the questions, how often can FGS be done and how often should it be done? When answering the question of how many times a year an examination should be carried out, only a doctor can say. For prevention, it is allowed from 2 to 4 times a year, but it is possible even for several days if the patient has serious pathologies and it is necessary to monitor their changes.
pozheludku.ru
How to prepare for research
It is necessary to prepare for the study in advance (except in emergency situations). Otherwise, it is difficult or impossible to carry out the procedure, and there is a high probability of obtaining questionable or false-positive results. The patient is warned about the need to prepare 1-2 days before EGD. There are early (24-18 hours before) and late preparation (8-12 hours).
Early preparation
Here's how to prepare for gastroscopy:
- Avoid seeds, nuts, mushrooms, chocolate-containing products, spicy, smoked, pickled foods, and pickles. Drinking alcohol in any form and any strength is contraindicated 72 hours before the examination;
- It is extremely undesirable to smoke 10-12 hours before fibrogastroscopy (especially during intranasal examination);
- The last time you can eat is 10-12 hours before gastroscopy. Eating should be sieve, but exclude coarse and difficult-to-digest food that disrupts the motility (rhythmic contractions) of the stomach and intestines;
- Avoid foods rich in fiber (cucumbers, pumpkin, apples, cabbage, etc.), seasoned with mayonnaise, whole grain bread, fatty and stringy meats, fatty fish, sharp and blue cheeses, fermented milk products;
- It is not recommended to eat pearl barley, buckwheat (kernels), millet porridge, beans;
- Food should not be too hot or cold (optimally t⁰ no more than 45-50 ⁰С and no less than 37 ⁰С);
- It is best to eat a green salad with a small amount of chicken fillet or breast, steamed chicken cutlets, low-fat soft cottage cheese, semolina or oatmeal with milk. You can eat potato, vegetable, fruit puree or steamed broccoli, baby food, boiled rice;
- During a capsule study, it is recommended to use a “mild” laxative or perform a cleansing enema 12 hours before the procedure. In the morning, it is advisable to empty your bowels.
- Before any examination, you must empty your bladder;
- In case of allergies, the entry of potential allergens into the body and contact with them are excluded. Otherwise, it is necessary to stabilize the patient’s condition in advance (medication, physiotherapeutic procedures, etc.);
- Stop taking medications that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (if this is not possible, you must notify the doctor about this);
- It is advisable for the patient to find out what medications he is taking and has taken previously, especially for chronic diseases and pathologies;
- It is recommended to sleep at least 8-9 hours;
- It is better to wake up at least 1.5-2 hours before the procedure;
- It is contraindicated to be nervous 3-4 hours before the examination; it is necessary to avoid stressful situations the day before;
- It is not recommended to undergo strong physical activity 72 hours before gastroscopy.
Useful tips
Gastroscopic examination allows you to obtain biological material, which can be further examined in more detail. A procedure such as FGDS allows you to cauterize injured vessels, as well as remove foreign objects from the stomach.
It is important to know! 2-3 days before the examination you are required to stop drinking alcohol.
In addition to alcohol, it is not recommended to include the following foods in your food for several days:
Smoking is also prohibited, as this may lead to inaccurate results. A timely examination of the gastrointestinal tract allows you to identify diseases of the stomach, as well as the duodenum. A timely diagnosed disease can be cured if proper treatment is carried out. During the procedure, or more precisely at the time of insertion of the endoscope, the patient is required to unquestioningly comply with the doctor’s requirements. But often, all the requirements come down to one thing - open your mouth and wait for the procedure to end. The cost of FGDS depends on the type; if this is an ordinary study, then it will cost 500-700 rubles. If it is necessary to carry out medical procedures, the cost will depend on the complexity of these actions.
Important! A remedy for heartburn, gastritis and ulcers, which has helped a huge number of our readers. Read more >>>
Diseases of the digestive system occupy one of the leading places among all diseases of the human body. Some of them are difficult to diagnose using “external” research methods. Then gastroscopy comes to the rescue. Many people have a question: how long does FGD last? Let's look at this issue in detail.
Gastroenterologist Mikhail Vasilievich:
“It is known that for the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, etc.) there are special drugs that are prescribed by doctors. But we will not talk about them, but about those medicines that you can use yourself and at home. » Read more >>>
Factors that increase the duration of gastroscopy
A routine examination, during which only an examination of the internal state of organs is carried out, is always short-lived, but FGS is carried out not only for diagnostic purposes.
The procedure can be done in the following cases:
- Removing a foreign object from the esophagus or stomach. The duration of FGDS is difficult to calculate: it will depend on the structure of the foreign body (smooth or too hard objects are more difficult to remove) and on its location. In some cases, the object that has gotten inside is first crushed, and then gradually removed from the digestive organs.
- Removal of polyps. This procedure is done after a detailed clarification of the location of the polyposis, and the doctor can almost always calculate how long the therapeutic gastroscopy will last.
- Irrigation of certain areas of the gastric wall with medicine. This type of FGS is performed quickly and takes 3-5 minutes more than diagnostic gastroscopy.
- Elimination of certain types of bleeding. Minor erosive bleeding or ulcer bleeding is not always a reason for surgical intervention. In some cases, bleeding can be stopped using more gentle methods during gastroscopy.
But even in therapeutic cases, FGDS lasts no more than half an hour.
The duration of gastroscopy is not very long; if the patient behaves correctly during the examination, it causes almost no discomfort. Then only a slight numbness in the throat after the anesthetic reminds of the examination completed. Probably, this information will help many people to have a positive attitude towards the research necessary for diagnosis and treatment, because every person can endure 10-20 minutes of unpleasant sensations.
zheludoc.ru
Feelings during FGS
Often the diagnosis is painless, and the procedure does not last long. However, the patient may experience slight discomfort due to the aspirator, a tube through which the contents of the gastrointestinal tract are removed. The doctor carries out the procedure slowly, having previously discussed with the patient the need to remain motionless, as well as a symbol when the slightest pain appears. All the patient must do to survive the procedure as quickly and pain-free as possible is to prepare correctly and relax.
Indications and contraindications
FGS of the stomach is prescribed when there are suspicions of serious abnormalities in patients, for example, with ulcers, gastritis or other abnormalities. As for all indications and contraindications, they are presented in the table:
| Indications: | Contraindications: |
| My stomach hurts for 2 days. For unknown reasons. | Heart attack. |
| Discomfort of the esophagus and stomach. | Obvious curvature of the spine. |
| Constant heartburn. | Stroke. |
| Constant vomiting. | Heart diseases. |
| Failure of swallowing function. | Esophageal stenosis. |
| Rapid weight loss. | Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. |
| Anemia. | Hypertension. |
| Pathologies of other internal organs. | Angina pectoris. |
| The patient always undergoes FGS of the stomach before surgery. | Mental disorders. |
| For gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcers). | During pregnancy |
| After removal of polyps. | |
| As a preventive measure or to monitor the course of the disease. |
Important! In some cases, contraindications can be ignored if urgent diagnostics are required. In this case, the doctor will assess the possible risks, after which it will be necessary to take measures. It is worth noting how dangerous FGS can be during pregnancy. The baby can be easily harmed, so during pregnancy the doctor should use other diagnostic methods, for example, ultrasound.
Why gastroscopy and not ultrasound
Patients often wonder, why not make a safer type of gastrointestinal examination through ultrasound? Today, medicine has reached unprecedented proportions. Ultrasound examination is the best way to determine processes and identify various types of pathologies of internal organs.
Ultrasound examination is possible only for those organs that are not filled with air. To examine the kidneys, it is necessary to fill them with fluid as much as possible. You can also examine the liver, spleen, and other organs with ultrasound. The stomach is filled with air, so to be able to conduct an ultrasound examination, it is necessary to fill it with liquid. This is impossible to do, so gastroscopy is performed. For gastroscopy to be successful, it is important for the patient to properly prepare for the procedure.
I’ll tell you how long it lasts, whether it hurts or not, and give advice on how to behave!
Hi all! If you are reading this review, then most likely you will soon have this procedure. And I immediately want to reassure you! It lasts no more than a minute! I've done it 3 times already and they all lasted so quickly! They looked at me both through the monitor screen and through the peephole, there was no significant difference in time.
But let's figure out how it goes:
- so first they spray an anesthetic into your throat, if I’m not mistaken it’s lidocaine. It tastes very nasty, bitter.
-then you will be asked to lay a towel on the couch, a towel under your head (this is necessary because you will drool) and lie on your left side.
- you will be asked to open your mouth and they will insert a special thing there so that it does not close; you will hold it with your teeth.
-then the doctor will begin to push the hose through and you will involuntarily swallow it and you will begin to vomit - the main thing here is to calm down!
I usually lie down, cross my arms to control them, close my eyes and think to myself that now everything will end soon)
How will you feel when the hose is inside:
While it is going through the esophagus, you will have a strong urge to vomit, this is a normal reaction of your body to a foreign object and you should not be ashamed of the doctor, he sees this 1000 times a day.
then, when the hose goes into your stomach, you will feel a little better, the urge to vomit will subside a little, and the most important thing here is to calm down and breathe again, I noticed that if you breathe through your mouth, it’s easier. It is better to take a deep breath, it lasts longer, because when you exhale you will again gag.
then the doctor will insert it into the duodenum, here I already had pain during the last study, before that it was not painful, but there was no gastritis either. But this pain quickly passed when the doctor moved a little further. Here you feel that something hard is crawling inside you, it looks like a hard big worm, for some reason it seemed to me that they would pierce me now, but I tried to mentally calm down and kept repeating - now it will all be over, now it will all be over!
Subjective feelings of a person
What does it feel like when a gastric tube is inserted?
First of all, discomfort from the presence of a foreign body, and other sensations depend on the stage of FGDS:
- Vomiting. The gag reflex is most pronounced at the moment when the probe enters the esophagus, irritating the root of the tongue. Then, as the gastroscope passes through the esophagus, the gag reflex decreases. At this moment, the person experiences a feeling of awkwardness due to profuse salivation and vomiting spasms, which seem to continue for an unbearably long time. But if you put aside false shame and, on the doctor’s advice, breathe deeply and evenly, then examining the esophagus will take a few seconds.
- Then, when the probe is inserted into the stomach, the urge to vomit almost subsides if you breathe deeply and evenly. This stage of FGS of the stomach, if there is no pronounced pathology of the organ, is also short-lived and takes about a minute. During the examination of the stomach, the main cause of discomfort in patients is awkwardness from excessive salivation, some even try to swallow saliva. But attempts to swallow cause spasm of the esophagus and increase discomfort.
- Afterwards, the gastroscope is inserted into the duodenum, and many people feel as if there is a hard and unpleasant foreign body in the stomach. Perhaps the most unpleasant moment when examining the duodenum is often at this stage a reflex muscle tension in the patient may occur, which makes it difficult to pass the gastroscope and can provoke pain. But it doesn’t last long either.
- After examining all accessible parts of the digestive tract, the doctor carefully pulls out the gastroscope. As a rule, the last stage of gastroscopy of the stomach in most people is accompanied by a feeling of relief from the removal of the foreign object.
After removing the probe, the procedure can be considered complete.
Thus, the duration of each stage is related to human behavior. If the patient follows all the specialist’s instructions, FGS will not last long.
How often do you need to undergo an examination of the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract?
Patients suffering from diseases of the digestive system are often interested in how often gastroscopy should be done and whether this diagnosis will do any harm if prescribed regularly? Of course, given the unpleasant moments that accompany the research process, many patients want to avoid it and try to find ways to cancel the procedure.
But in fact, this examination does not have any negative consequences, even if performed frequently, and the doctor does not need to prescribe it without reason. If the patient visited a specialist for the first time with complaints of pain in the stomach or esophagus, then a gastroscopy is performed and, based on the results obtained, appropriate therapy is prescribed. After treatment, the procedure is repeated to check the effectiveness of the therapy.
If a patient is diagnosed with cancer or a peptic ulcer, and the patient has undergone surgery, then examinations can be scheduled several times a year for observation and timely detection of relapses of the disease. The question of how long it will take to do the next check of the gastrointestinal mucosa can only be answered unequivocally by the attending physician. As a rule, such patients undergo gastroscopy 4 or more times per year.
Indications for gastroscopy (FGDS)
Tests and x-rays do not always make it possible to make a diagnosis, but performing an FGDS of the stomach allows you to see the picture of the disease from the inside, clarify or make a final diagnosis. The examination is mainly carried out to diagnose diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially its upper part.
When is FGDS performed:
- in the presence of nausea, heartburn, belching;
- cough for no apparent reason;
- pain when swallowing;
- swallowing dysfunction;
- bloating, gas formation;
- noticeable weight loss;
- abdominal pain, especially in the epigastric region;
- blood in stool;
- vomiting, blood in vomit;
- B12 deficiency anemia;
- with stomach bleeding;
- to deliver a medicinal product;
- remove polyps;
- take tissues, gastric juice for analysis, samples for gastrobacteria, for example, they often jointly perform a urease test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter pylori);
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
FGDS reveals the following diseases: gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, stomach and esophageal cancer, inflammatory processes in the esophagus, reflux disease, polyps, duodenitis and other diseases.
A timely EGD of the stomach will help diagnose the disease at an early stage, which makes it possible to start treatment on time.
For chronic diseases, FGDS is performed once a year, in other cases - according to the indications and direction of the attending physician.
The main difference between FGS and FGDS
What is FGS of the stomach
? What does FGS show? This procedure allows you to examine the condition of the stomach, its walls and mucous membrane. If you prepare for fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS), then the doctor will be able to diagnose not only the stomach with this method; the duodenum will also be examined. One study and the other are very similar to each other, not only in how to prepare for the procedure, but also in how the procedure is done.
Many people are interested in what FGS is and how it is diagnosed. If you read reviews or listen to people who have previously undergone such diagnostics, you can get very scared, since not so long ago a device was used that was quite large in diameter. Due to this, examination of the stomach was problematic, and the procedure itself was very unpleasant and sometimes traumatic. Therefore, today many are interested in whether it hurts to make such a diagnosis.
Today, after FGS of the stomach, there is no stomach pain, and the examination itself is carried out without unnecessary discomfort. In addition, people can use alternative research methods that already exist in Penza, Nizhny Tagil, Moscow and other cities, where the method of diagnosing the stomach without swallowing a tube or gastroscope is used. Additionally, people can use a method where the doctor puts his patient into a medicated sleep; the person is not under anesthesia, but under a sleeping pill.
How long does such an inspection take? Typically 40-45 minutes. After this, the person who was under anesthesia, or rather in a dream, does not feel any discomfort or side effects. At the same time, the doctor himself can normally analyze and examine the person, since he does not move or feel discomfort; patients simply sleep under anesthesia. This alternative makes it possible to diagnose children, which is impossible, or rather difficult, to do FGS without anesthesia. Knowing what can replace diagnosis, you will need to additionally know who is undergoing FGS and who is contraindicated for FGS of the stomach.
How long does a gastroscopy take?
The time for fibrogastroscopy depends on the plan of the proposed measures (urease test, biopsy, etc.), the general condition of the patient, individual tolerance of sedation drugs, the severity of the gag reflex, the progress of the study, and the presence of obstacles to the advancement of the tube in the gastrointestinal tract. The duration is also affected by the mental state of the patient and the development of complications. A simple planned uncomplicated examination takes 10-15 minutes.
If general anesthesia is necessary, the procedure lasts according to the duration of action of the administered drugs. If additional studies are carried out or organic lesions of the digestive tract are discovered, psychomotor agitation develops, chronic pathologies worsen or complications develop, the time increases. On average, in the presence of complications or the development of pathological conditions, the examination is extended to 30-40 minutes. FGDS can be transferred from diagnostic to therapeutic - the time is extended until the end of the operation (on average up to 1-1.5 hours). The transition from diagnostic to therapeutic gastroscopy occurs when:
- Detection of foreign bodies;
- Development of bleeding from the upper digestive tract;
- The presence of small benign neoplasms;
- The need for urgent low-traumatic surgical intervention with the consent of the patient;
- Suspicion of the presence of an unspecified tumor - therapeutic manipulation is carried out after confirmation of the results of a microscopic examination.
Description of the procedure, what FGDS shows
FGDS is carried out in special diagnostic rooms as planned or urgently, strictly on an empty stomach.
Before the procedure, the patient is introduced to the examination technique, and written permission to conduct it is taken.
FGDS procedure
A nurse or doctor irrigates the patient’s throat with lidocaine spray, if there is no allergy to it (this issue must be clarified in advance).
The patient is placed on the couch on his left side. The position should be convenient and comfortable for the patient, otherwise he will be tense, and this interferes with the insertion of the probe.
A mouthpiece is inserted into the mouth for ease of insertion of the endoscope (sometimes the device for FGS is called a gastroscope) and so as not to injure the mucous membranes of the lips and mouth.
The doctor begins to insert the endoscope, the patient, at the doctor’s command, performs a swallowing movement. At the time of administration, a gag reflex may appear, but if you breathe deeply and calmly, this condition goes away. After insertion of the endoscope, you should not swallow; saliva is collected by suction.
When the probe is inserted, air is introduced into the stomach (to straighten the folds) so that the mucous membrane can be better examined.
The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes and, if the doctor’s requirements are met, does not cause much discomfort to the patient.
If any therapeutic measures are carried out, then the time of its implementation reaches 30 minutes.
In some cases, the study is performed under general anesthesia (children, the patient’s agitated state, complete pain intolerance).
With FGDS you can see:
- what is the condition of the mucous membrane and walls of the stomach and esophagus;
- scar formation;
- narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus;
- degree of reflux (reflux - stomach contents enter the esophagus);
- various neoplasms.
After the procedure, the endoscopist issues an FGDS conclusion - the result of the examination, a description of the consistently seen picture of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach, pylorus, and duodenal bulb. The presence of free patency, peristalsis, the amount of gastric secretion/bile reflux, varicose veins, plaque, closure/insufficiency of the cardiac rosette, inflammation (hyperemia, swelling), folds, and damage are indicated.
Quite often, a biopsy is taken - a microscopic piece of the mucosa to check for the presence of malignant cells.