Cells that fight cancer
In the body of every person there are atypical cells that the immune system normally fights. If there is a failure in the protective function, or the rate of destruction of mutated cells is much lower than the rate of their division, tumor neoplasms are formed: benign or malignant.
The former are characterized by slow growth and a low likelihood of relapse. Moreover, the cells of benign formations are tightly connected to each other and do not grow into neighboring tissues, therefore, do not destroy them. The same cannot be said about malignant (cancerous) tumors, the cells of which are characterized by uncontrolled growth, do not have their own membrane, and therefore easily penetrate into neighboring tissues, affecting and destroying them. They are also characterized by metastasis - the spread of cancer cells throughout the body through connective tissue (lymph or blood), fixation and further growth in individual organs.
The diagnosis of “oncology” has long been in second place in terms of morbidity and mortality after cardiovascular diseases. And no matter how advanced modern medicine is, a cure for cancer has not yet been invented. The causes of this pathology have not been fully identified.
The only method of stopping the development of the disease (in some cases, completely defeating it) is early diagnosis of the disease. Only at the initial stage is cancer treated.
Do blood tests indicate cancer?
The results of a blood test for oncology allow us to suspect the presence of the disease. However, this analysis does not allow us to determine in which particular system the pathological focus is located. A referral for blood sampling is issued by a physician, and in case of suspicion of a malignant neoplasm, follow-up observation and additional diagnostics are carried out by an oncologist. A general blood test can be performed in a private or public medical laboratory. The execution time does not exceed 1 day.
In most cases, a person affected by cancer experiences an increase in the level of leukocytes, a sharp increase in ESR and a decrease in hemoglobin levels, however, it is unacceptable to make a verdict on the presence of cancer pathology based on one blood test. To make a final diagnosis, additional laboratory methods (analysis for tumor markers) and instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, MRI) are used.
Leukemia results in a decrease in the number of platelets (possibly a decrease in the number of all blood cells) due to bone marrow dysfunction. However, single minor deviations in blood test results are not diagnostically significant. This fact is explained by the fact that all laboratory criteria can vary in a person depending on the time of day and physiological state. These conditions are not life-threatening, much less indicate the presence of a tumor with 100% accuracy.
Read further: What are tumor markers, how much can they be trusted when determining oncology?
Analysis of serum blood material for the presence of antigens
A biochemical blood test for specific substances, tumor waste products or substances produced by normal tissue structures in response to altered newly formed cells (tumor markers) will show the presence of antigenic stimuli in the blood, which determine the presence and localization of the oncological process. By monitoring such changing data, it is possible to find out at what speed the growth occurs with the development of the tumor, what organs are affected by oncology, and whether there is a result from treatment.
The most common antigens (tumor markers) are:
- PSA. It is a prostate-specific antigenic element. This oncological marker characterizes male pathologies. It is secreted in a small amount by the prostate. Indicators change with age. If this cancer marker is excessively elevated, then it is an indicator of the formation of prostate tumors.
- CA 125. This indicator is responsible for the female reproductive system. Often this tumor marker is exceeded in ovarian cancer. Oncology of the inner mucous membrane of the uterine body (endometrium) is also possible. Even if this tumor marker is elevated, the statement indicating cancer is erroneous. Additional diagnostics are needed.
- CA 19-9. These tumor markers determine oncological neoplasms of the pancreas and intestinal tract.
- CA 242. For diagnostic procedures, this tumor marker indicates the specific localization of the oncological process.
- REA. A cancerous embryonic antigenic stimulus will indicate the part of the intestinal tract where there is oncology. But this antigen can also be high in cirrhotic changes in the liver.
Confirmation or refutation of pathological processes of the digestive system should be through a comprehensive study of all oncological markers with additional diagnostic procedures.
Hemoglobin in oncology
Hemoglobin is a specific protein that is part of red blood cells and transports oxygen from the lungs to all organs and tissues, as well as carbon dioxide on the way back.
Low hemoglobin and oncology may be related to each other, since a decrease in the indicator is recorded in more than 60% of patients. This condition has its own definition - anemia (anemia).
Normal levels of hemoglobin in the blood of a healthy person:
- men – from 130 to 174 g/l;
- women – from 110 to 155 g/l.
Deviations of several units in any direction do not have any effect on the general condition of a person. But in the presence of a malignant tumor, anemia, shock, severe infections, etc. the content of this blood component begins to decrease.
Important: in cancer pathology, the hemoglobin value is ten times less than normal values.
A decrease in hemoglobin levels is indicated by a set of symptoms:
- general malaise;
- attacks of acute pain in the chest;
- rapid onset of shortness of breath even when walking calmly;
- dizziness;
- pale skin;
- brittle nails and hair loss;
- cold sweat;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- reduction of the body's natural defenses (immunity).
What does increased hemoglobin mean for the body?
Hemoglobin is studied most often in capillary blood. Its unit of measurement is g/l (grams per liter). The norm of this substance depends on the age, gender of the person, as well as the norm of hemoglobin in women during pregnancy. The highest rates are recorded in newborns (130–225 g/l), which is due to the physiological characteristics of this period of life.
Hemoglobin norm:
- In children older than one year - from 100 to 120;
- For women - from 120 to 140;
- For men - from 140 to 160.
High hemoglobin is said to be when the indicator exceeds the norm by 20 - 25 units. Moreover, a high value is not an independent disease, it serves as a sign of pathology present in the body.
It would seem that this is not bad when there is a lot of hemoglobin. But this condition is of great importance for the human body. When hemoglobin concentration is increased, blood thickening occurs. This, in turn, provokes the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels.
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin in the blood in oncology
Hemoglobin levels can change during cancer for a variety of reasons. It is important to establish the reason for the decrease in protein concentration in each specific case in order to know how to increase hemoglobin and prevent complications of the disease in the future.
The cause may be due to internal bleeding. Oncopathology often causes such a complication, especially with the active progression of a malignant tumor or against the background of an adverse reaction from prescribed therapy. Other reasons that may contribute to a decrease in serum hemoglobin levels are also identified:
- gastrointestinal dysfunction resulting from problems with iron absorption;
- spread of metastases to the bone marrow;
- loss of adequate nutrition (with cancer of the stomach, esophagus or intestines), resulting in iron deficiency in the body;
- the use of potent drugs and procedures (chemotherapy or radiation), the adverse reactions of which are a decrease in the ability to form hematopoiesis;
- acute intoxication of the body, due to the constant growth and disintegration of a malignant tumor in the last stages of oncology.
Why is the level rising?
Whether blood leukocytes will increase in the case of cancer depends on the type of cancer. An increase in WBC occurs mainly in the second stage of cancer.
For some malignant tumors, the analysis in the early stages changes little. Doctors are worried not only by the magnitude of the deviation from the norm, but also by the appearance in the analysis of:
- myeloblasts (precursors of red blood cells, neutrophils, platelets);
- lymphoblasts (precursors of lymphocytes).
In lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoblasts account for up to 20% of all white blood cells, the value of which can reach 300*109/l. Hemoglobin and platelets decrease, and ESR increases.
Myeloblastic leukemia is characterized by accelerated proliferation of myeloblasts, which, without having time to mature in the bone marrow, enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. The disease is more common in adults and is characterized by a decrease in red blood cells, platelets and mature WBC. At the same time, due to the active entry of immature forms into the bloodstream in the analysis, the indicators of total leukocytes will be increased.
At the early stage of stomach cancer, hemoglobin is reduced with normal values of other analysis parameters.
The level of leukocytes increases even at a late stage of oncology.
Changes caused by lung cancer are observed at the advanced stage of the disease. When tumors appear in the lung, they are always detected in a blood test:
- leukocytosis;
- increase in eosinophils;
- increased ESR.
Important information: What is WBC in a child’s blood test (table of interpretation and norms)
Lung cancer is characterized by the appearance of immature forms of leukocytes along with the presence of old platelets in the blood plasma.
Pancreatic cancer is accompanied by blood changes:
- leukocytosis;
- increase in neutrophils;
- increased ESR.
Anemia develops in late stage pancreatic cancer.
WBC values increase in malignant lymphomas, which include Hodgkin's disease and the group of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, which includes about 30 different cancers of the lymphatic system.
Clinical analysis for malignant lymphomas reveals:
- leukocytosis;
- increased neutrophils;
- decreased lymphocytes;
- increased monocytes and eosinophils;
- high ESR.
High hemoglobin in cancer
There are cases when a patient with cancer has a high level of hemoglobin, for example, with:
- kidney or liver cancer;
- Vaquez-Osler disease is a pathological condition during which there is excessive production of red blood cells by the bone marrow.
Thus, an increase in hemoglobin in oncology is no less important an indicator than its decrease. Therefore, the diagnosis of cancer cannot be considered complete without a general blood test.
Symptoms of elevated hemoglobin
It should be noted that this condition does not have a specific clinical picture. Quite often a person does not even notice that there is excess hemoglobin in the body. However, if this condition lasts for quite a long time, general symptoms may appear. But they do not indicate an increase in hemoglobin.
Symptoms of hyperhemoglobinemia:
- Increased fatigue;
- Problems with sleep (insomnia, shallow sleep, difficult and prolonged falling asleep);
- Decreased or lack of appetite;
- They beat me in the head;
- Dizziness;
- Pain syndrome in the abdominal area;
- Hypertension (increased blood pressure);
- Skin itching;
- Joint pain;
- Blood clot formation;
- Diarrhea followed by constipation;
- Loss of body weight;
- The appearance of areas of hyperemia and pallor on the skin.
In infants, this condition manifests itself:
- Lethargy and drowsiness (the baby constantly sleeps, the crying is sluggish);
- Refuses to breastfeed, sucks sluggishly;
- Yellowness of the skin may occur;
- Blueness of the lips, nasolabial triangle and fingertips;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia or arrhythmia).
If these pathological signs are detected in an adult or child, you should consult a therapist or pediatrician (children’s doctor).
If necessary, after the tests the patient will be sent for a consultation with a hematologist, a specialist who diagnoses and treats blood diseases.
How to increase hemoglobin in cancer?
If a blood test shows low hemoglobin due to cancer, it must be increased. For this purpose, special medications are used in combination with diet.
In medical practice, drugs that can increase hemoglobin levels include:
- transfusion of purified red blood cells;
- administration of erythropoietin - a drug to stimulate the functioning of the bone marrow, after which the body experiences increased synthesis of red blood cells and hemoglobin;
- solutions and tablets of iron ion preparations.
A special diet has been developed for cancer patients, which allows you to increase the concentration of hemoglobin and keep it at an optimal level from the very beginning of the disease. It is worth noting that without medicinal preparations of iron ions, this method does not work well, so it must be combined with the above medical procedures.
Products indicated for normalizing hemoglobin levels:
- high in iron (liver, spinach, corn, peas and peanuts);
- oatmeal, wheat, buckwheat and barley porridge;
- fortified food with a high content of vitamins C, B12, folic acid;
- berry infusions, compotes and juices (preferably freshly squeezed). Every day, you should drink 2 liters of liquid;
- sprouted wheat for breakfast.
Read further: What does high hemoglobin signal in women?
When is tumor marker analysis necessary?
Additional reasons are:
- age over 40;
- family history of cancer;
- exceeding the normal range of biochemical analysis and blood test results;
- pain or prolonged dysfunction of any organs or systems, even to a minor extent.
Blood for antigen tests is donated from a vein in the morning. Results are issued within 1-3 days, and in order for them to be reliable, you must follow certain recommendations:
- don't have breakfast;
- do not take any medications or vitamins the day before;
- three days before diagnosing cancer using a blood test, avoid alcohol;
- do not eat fatty or fried foods the day before;
- the day before the study, avoid heavy physical activity;
- on the day of delivery, do not smoke in the morning (smoking increases CEA);
- To prevent third-party factors from distorting the indicators, first cure all infections.
After receiving the results in hand, you should not draw any independent conclusions or make diagnoses. This blood test for cancer is not 100% reliable and requires instrumental confirmation.
Read further: Hemoglobin and leukocytes in oncology - norms, causes of deviations, therapy
Carrying out such a blood test requires compliance with certain rules:
- blood is taken strictly from the finger;
- the analysis is carried out only on an empty stomach; it is not recommended to eat anything before it;
- the day before, it is undesirable to eat fatty and spicy foods, as this can cause an increase in the number of leukocytes;
- the patient must be completely healthy; in case of some ailments, the tests are postponed;
- a depressive state can also have a bad effect on the test results, so in such a situation it is better to consult with your doctor;
- blood is drawn using a sterile needle intended for single use.
Such a procedure is prescribed in cases where:
- early diagnosis of tumors is necessary;
- it is necessary to identify whether a benign tumor is in the body or a malignant one;
- it is necessary to determine how adequate the treatment prescribed for the disease is;
- it is necessary to determine metastases and their number before they become a clinical manifestation, that is, they do not spread throughout the body.
A couple of days before taking such an analysis, it is advisable not to drink alcohol and give up the harmful habit of smoking. If the first analysis reveals the presence of the disease, further examination is carried out every 3-4 months to determine its effectiveness.
Leukocytes in oncology
In most patients, the number of leukocytes in the blood serum during oncology increases significantly (leukocytosis) to fight mutant cells in the body. The number of white blood cells is under the control of the human immune system. When natural defenses are weakened, malignant cells begin to divide so quickly that white blood cells do not have time to destroy them.
If the normal value of the indicator in people over 16 years of age ranges from 4 to 10 * 109 units, then leukocytes in cancer reach critical values. It should be noted that standard values for the value under consideration in cancer have not been established, since they can vary over a fairly wide amplitude (from slight increases to tenfold).
What do low values of leukocytes in the blood indicate in oncology?
In medicine, this condition is called leukopenia. It is noted that most often this condition develops in patients undergoing chemotherapy. This happens because the human body does not accept the prescribed drug, and there is no positive dynamics in the treatment of cancer pathology. Doctors adjust the course of therapy and transfer the patient to more aggressive treatment methods that negatively affect the cellular composition of the blood.
In addition, malfunctions of the kidneys and liver, which lose their ability to remove toxins from the body, can lead to leukopenia.
A low concentration of white blood cells in diseases, including cancer, can also be detected in bone marrow dysfunction. For example, in patients under the age of 30, leukopenia occurs much less frequently than in older patients. This is explained by the fact that the bone marrow of a young organism has a higher reserve of leukocyte synthesis.
It should be noted that the results of a general blood test also depend on the patient’s diet. In a situation where the body receives few nutrients, it begins to become depleted, which means the negative effects of chemotherapy drugs become more pronounced.
Read further: How to quickly increase white blood cells in the blood after chemotherapy at home?
What will the white blood cell level tell you?
Leukocytes are a group of white cells of the circulatory system, responsible for the protective function of the body, and have antimicrobial and antitoxic properties. They produce antibodies that attack pathogenic cells, thereby preventing their development and spread. The normal level of leukocyte concentration includes the range from 4.0* to 9*.
To the question: “How many leukocytes are there in the blood with cancer?” There is no clear answer, since this indicator has a significant amplitude relative to the norm (healthy person).
Consultation with an Israeli specialist
In cancer, white blood cells may be elevated or decreased. Over time, the doctor will be able to determine the onset of tumor formation and make an accurate diagnosis by conducting a number of additional studies.
The main sign characterizing the progress of a malignant tumor is considered to be a high level of white blood cells, the vast majority of which are young cells. This phenomenon is called leukocytosis.
An increased level of white cells is observed in leukemia, which comes in several types, so the analysis can detect both lymphoblasts and myeloblasts.
To normalize the level of leukocytes in blood cancer, hormonal agents are used in therapy. Corticosteroid drugs reduce the symptoms of the disease and increase the reserve capacity of the bone marrow. Treatment of acute leukemia with hormones, suppressing mitotic processes in blasts, creates the effect of reducing the tumor.
Treatment begins with small doses of the drug. In the absence of positive dynamics, the amount of hormones is increased. If resistance to the steroid used is determined, another medicine is prescribed. Timely change of the drug allows you to achieve positive results in the fight against tumor formations.
Treatment is prescribed by a specialist
Hormonal therapy is carried out continuously until the cancer patient’s stable condition is established. Then the amount of drugs used is gradually reduced. Corticosteroid drugs are prescribed not only as monotherapy for leukemia, but also in complex treatment. To check whether leukocytes are elevated in cancer after the course, blood is taken for subsequent analysis.
A process characterized by a reduced content of white cells is called leukopenia. This pathology in oncology is much less common than leukocytosis. The reasons for its occurrence may be:
- Chemotherapy;
- Diseases of the kidneys and liver, leading to a decrease in the rate of elimination of toxins;
- Small bone marrow reserve for the formation of white cells (in older people);
- Individual intolerance to the drug used for treatment;
- Incorrect dosage of medication;
- Incorrect medication use;
- Poor nutrition, as a result of which the cancer patient’s body is depleted and becomes more vulnerable to “chemistry”, recovery from which in this case occurs very slowly.
The number of leukocytes in the blood of cancer always decreases after chemotherapy. If a week after completion of the course their concentration exceeds 2500, then there is no need to prescribe special drugs. If a week before a new course of “chemistry” the number of white cells has not returned to normal, then medications are added to stimulate the growth of these cells. If during this period the level of white cells has not risen to the required level, then the use of these drugs is extended for several more days, with the addition of hormones.
In the case of IV degree leukopenia, a system of therapeutic measures is carried out to raise leukocytes to the required level, where the following is prescribed:
- antibiotics;
- stimulators of white cell maturation;
- hormones;
- hematopoietic stimulants;
- leukocyte transfusion.
Correction of high white blood cell counts in cancer
The level of leukocytes in oncology increases in many types of leukemia, during which hormonal therapy is prescribed. Taking corticosteroids reduces symptoms and increases bone marrow reserve.
Hormone therapy for severe leukemia can suppress mitotic processes in the lesions, while providing additional resistance to the tumor.
Initially, treatment is carried out in small doses, but if the patient experiences negative dynamics, the administered doses are gradually increased. In severe stages of the disease, as well as in severe hemorrhagic syndrome, treatment is carried out with the maximum permissible doses of steroids.
Why is it important to increase the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and neutrophils
A low number of different forms of leukocytes in the hemogram indicates the patient's immunosuppression. Suppression of the immune system is accompanied by an increase in the body's susceptibility to viral, fungal and bacterial diseases. A decrease in the level of lymphocytes (especially NK cells) increases the risk of tumor relapse, since these cells are responsible for the destruction of atypical (malignant) tumors.
Pancytopenia is also accompanied by impaired blood clotting, frequent spontaneous bleeding, fever, polylymphoadenopathy, anemia, hypoxia and ischemia of organs and tissues, an increased risk of generalization of infections and the development of sepsis.
Why are blood cells needed?
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, contain the iron-containing pigment hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. Red blood cells ensure adequate delivery of oxygen to the tissues of the body, maintaining full metabolism and energy metabolism in cells. When there is a shortage of red blood cells, changes in tissues are observed due to hypoxia - insufficient oxygen supply to them. Dystrophic and necrotic processes are observed that disrupt the functioning of organs.
Platelets are responsible for blood coagulation processes. If a patient's platelet count is less than 180x109/l, he or she experiences increased bleeding - hemorrhagic syndrome.
The function of leukocytes is to protect the body from what is genetically foreign to it
Actually, this is the answer to the question of why it is important to raise the level of leukocytes - without leukocytes, the patient’s immune system will not function, which will make his body accessible to various infections, as well as tumor processes
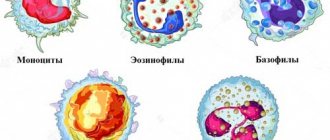
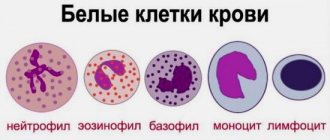
Leukocytes themselves are divided into the following groups according to their microscopic characteristics:
Granulocytes:
- eosinophils,
- neutrophils,
- basophils;
Agranulocytes:
- monocytes,
- lymphocytes.
Eosinophils are directly involved in antiparasitic immunity and also modulate some types of hypersensitivity reactions. Eosinophilic granulocytes can both contribute to the development of an allergic reaction and act as its inhibitors.
The function of neutrophils is antifungal and antibacterial protection. The granules that the neutrophil contains in its cytoplasm contain strong proteolytic enzymes, the release of which leads to the death of pathogenic microorganisms.
Basophils take part in the inflammatory process and allergic reactions. In their cytoplasm they contain granules with the mediator histamine. Histamine leads to dilation of capillaries, a decrease in blood pressure, and contraction of bronchial smooth muscle.
Lymphocytes are divided into several types. B lymphocytes produce immunoglobulins, or antibodies. T-lymphocytes take part in the regulation of the immune response: T-killers have a cytotoxic effect on viral and tumor cells, T-suppressors prevent autoimmunization and suppress the immune response, T-helpers activate and regulate T- and B-lymphocytes. Natural or natural killer cells help destroy viral and atypical cells.
Monocytes are the precursors of macrophages that perform regulatory and phagocytic functions.
What happens if the leukocyte level does not increase?
An increase in white blood cells after chemotherapy is necessary to prevent the effects of immunosuppression. If a patient has leukopenia, particularly neutropenia, he will be susceptible to infectious diseases.
Clinical manifestations of neutropenia may include:
- low-grade fever (temperature in the armpit within 37.1-38.0 °C);
- recurrent pustular rashes, boils, carbuncles, abscesses;
- odynophagia - pain when swallowing;
- swelling and pain of the gums;
- swelling and soreness of the tongue;
- ulcerative stomatitis - the formation of lesions of the oral mucosa;
- recurrent sinusitis and otitis - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and middle ear;
- symptoms of pneumonia - cough, shortness of breath;
- perirectal pain, itching;
- fungal infections of the skin and mucous membranes;
- constant weakness;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- pain in the abdomen and behind the sternum.
Most often, patients are admitted with:
- sudden illness;
- sudden fever;
- painful stomatitis or periodontitis;
- pharyngitis.
In severe cases, sepsis develops like septicopyemia or chroniosepsis, which can lead to septic shock and death.
Correction of low leukocyte levels in oncology
Leukocytes in cancer most often decrease while taking chemotherapy drugs. For this reason, the condition of leukopenia requires special attention.
If a week before the expected date of a new course of chemotherapy in a patient, the level of leukocytes does not return to normal, then in addition to therapeutic measures, drugs are prescribed that can cause their additional synthesis. In a situation where blood tests do not return to normal before the start of the main anti-cancer treatment, the drug intake is extended for some time by adding hormones.
Increased white blood cells and antibiotics
By the way, from what I just wrote, paradoxically, one very important thesis follows.
In case of uncomplicated acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI), there is no need to take a general blood test “just in case.”
You will definitely see lymphocytosis there and will worry where it came from! You will rush to search the Internet for the causes of leukocytosis, you will definitely find horror stories about leukemia there, you will not sleep for two nights, you will make an appointment with a hematologist... And leukocytosis in this case was simply a “witness” of a viral infection. Moreover, it can remain in the blood for up to a month after a cold.
And the second very important idea: leukocytosis is not a disease, but only a symptom of a wide variety of conditions. Hence the conclusion, which is useful to remind not only patients, but also many doctors.
You cannot simply prescribe antibiotic treatment based on the detection of leukocytosis without making a diagnosis and identifying the source of infection.
The fact is that there is no universal “broad-spectrum” antibiotic; For different infectious diseases, completely different drugs and their dosages are used. As a rule, trying to prescribe treatment in a situation where the disease has not been found, but the doctor says: “You have an infection somewhere in your body...” only leads to further diagnostic confusion.
The fact is that pathogens of infectious diseases do not just float in circles in the blood; they always strive to “settle” somewhere, causing a picture of a specific disease. Not to mention the fact that not every fever and not every leukocytosis are signs of a bacterial infection, which, in fact, should be affected by antibiotics.
So, I repeat, with rare exceptions, there is no need to take antibiotics until there is an answer to the question of the name of the disease that we are treating.
Reduced hemoglobin, increased red blood cells and lymphocytes causes. Decreased leukocyte hemoglobin
In some situations (overeating, severe physical fatigue, exercise, stress), the number of white blood cells increases. This is a normal reaction of the body, much worse if the leukocytes in the blood are low. This condition is called “leukopenia” and is asymptomatic.
Low white blood cells in most cases indicate problems in the body. After all, their main task is immunity. If it is low, the body will be easily attacked by dangerous microorganisms.
Causes of low white blood cells
Reduced leukocytes in the blood, what does this mean? Leukopenia indicates the development of a disease. Its presence provokes the fall of white cells. There are several reasons that cause this condition.
Lack of substances responsible for the production of leukocytes
this is the most common cause of low white blood cell counts. At the same time, the number of white cells decreases slightly and depends on other blood parameters (hemoglobin and red blood cell levels). After all, their reproduction requires the same substances:
- vitamins: thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), folic acid (B9), ascorbic acid (C);
- trace elements: iodine, cobalt, copper, manganese, zinc, iron;
- arachidonic acid, selenium, proteins.
Conditions in which leukocytes are below normal are determined by the doctor, based on the results of duplicate tests. They are carried out several times over a short period of time.
Such situations are easily corrected by diet and taking additional vitamins. When white blood cells are low in an adult and the body cannot absorb nutrients, drug treatment is used.
Death of leukocytes in the body
. Sometimes there are situations when the body actively creates new white cells, but they die in the blood. There may be several explanations:
- Immune response
. When a virus enters the body, white blood cells rush towards it, leaving their usual places (vessels). In this case, the analysis determines a low level of leukocytes in the blood, although they are present in normal quantities in the body itself. - Destruction of leukocytes
. Leukocytes, protecting the body from damage by bacteria and viruses, sacrifice themselves - they die. Their number decreases sharply during this period, which may affect the research results. - Intoxication
. When poisons enter the body for a long time. These could be toxins from the air, heavy metals from water, fungal spores in food (if vegetables are not stored properly). There are few leukocytes in the body - they die, saving the host from toxins.
Diseases and medicines
. Leukopenia can develop as a result of many serious illnesses, as well as with long-term use of certain medications.
Diseases:
- Liver cirrhosis, tuberculosis, diseases that cause an increase in the functional activity of the spleen (hypersplenism), lymphogranulomatosis.
- Syphilis, trichinosis, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, myelofibrosis.
- Infectious diseases: typhoid fever, viral hepatitis, brucellosis, malaria, influenza.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarthrosis, rheumatism.
Taking medications:
- antibacterial (chloramphenicol, sulfonamides, syntomycin);
- anti-inflammatory (analgin, amidopyrine, reopirin, pyrabutol, amidopyrine);
- depressing thyroid activity (potassium perchlorate, propicyl, mercazolil);
- for oncology (cyclophosphate, vincristine, methotrexate).
Bone marrow disorders
. The homeland of white blood cells is the bone marrow, where they are born and mature before entering the blood.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vwq9FAO9C04
When the bone marrow is damaged or diseased, the level of white cell production drops sharply, and there is a decrease in leukocytes in the blood.
The normal functioning of the bone marrow can be affected by:
- Congenital diseases
. The occurrence of leukopenia is provoked by certain genetic diseases that affect the normal functioning of the bone marrow and the production of leukocytes (myelocathexys, Kostmann's syndrome). - Poisoning
. Poisons that systematically enter the body have an active effect on the bone marrow. Such conditions are caused by poisoning with food, alcohol, drugs, and chemical compounds. - Treatments provided
. A low white blood cell count can be caused by the treatment of certain serious diseases (cancer tumors, viral hepatitis). - Chemotherapy
, taking interferon - all this is necessary for severe damage to the body, but it affects the functioning of the bone marrow. - Autoimmune damage
. This situation occurs when the immune system, which has reacted to bacteria that have entered the body in large quantities, “goes crazy.” The destruction of your own bone marrow cells begins. - Oncology
. When a cancerous tumor grows, it can penetrate the bone marrow. Its metastases actively destroy brain tissue responsible for the production of leukocytes, which immediately affects their number.
Low white blood cells in children
In children, the concentration of leukocytes is higher compared to adults. The younger the baby, the higher his level of white cells. At the same time, the overall level of leukocytes is within normal limits, and some of the varieties go beyond the limits.
A child is diagnosed with leukopenia when the number of leukocytes in the blood is 2 units less than the normal age level. Situations when leukocytes are low in a child’s blood are an alarming signal. This bell may indicate the development of serious illnesses:
- anemia;
- radiation sickness;
- acute form of leukemia;
- autoimmune diseases;
- bone marrow damage;
- acute allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock);
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism);
- viral or bacterial infections (chickenpox, hepatitis, rubella, brucellosis, measles).
If such diseases are not identified, then the reasons for the decrease in leukocytes should be sought in low blood pressure, loss of strength, serious physical or psycho-emotional exhaustion, and decreased body tone.
Long-term use of antispasmodics, sulfonamides, and antibiotics also leads to the occurrence of leukopenia.
Low white blood cells, accompanying some diseases, can cause a number of additional symptoms. These include rapid pulse, high temperature, severe chills, dizziness, and rapid heartbeat. With prolonged leukopenia, increased anxiety, severe weakness and prolonged headaches are often observed.
Doctors include enlarged lymph nodes and spleen as relative signs of a low level of leukocytes.
Leukopenia is a symptom of the disease. But based on such signs, it is impossible to identify the true cause of leukopenia (the disease that provokes it). This requires a number of additional measures:
Treatment of childhood leukopenia is carried out in complex therapy, the main goal of which is to get rid of the underlying disease. With prompt diagnosis and proper treatment, this condition goes away without any consequences.
Many, seeing the results of an analysis where there are few leukocytes in the blood, do not attach much importance to this and think that leukopenia itself does not harm the body in any way, but only accompanies current diseases. This opinion is wrong. A low level of white blood cells seriously weakens the body's protective functions.
According to statistics, when white blood cells are below normal, the risk of developing cancer increases by 2-3 times. The possibility of serious illnesses that can lead to death increases. With leukopenia lasting 2-3 weeks, severe infectious diseases occur in 25% of cases, more than 6 weeks in 100%.
Extreme manifestations of leukopenia are situations when the body completely stops producing white blood cells. This can lead to the development of aleukia (severe blood pathologies).
Asks: Ksenia, Queen
Female gender
Age: 30
Chronic diseases: not specified
Source: https://zdornation.ru/zabolevaniya/reduced-hemoglobin-elevated-red-blood-cells-and-lymphocytes-cause-reduced-leukocyte-hemoglobin/
Let's talk about elevated lymphocytes in the blood of an adult
Every person should know that his blood contains special cells that can provide information about the presence of various diseases in the body. These cells are called lymphocytes.
Lymphocytes are components of white blood (leukocytes) that form part of the immune system . Lymphocytes perform one main and important function. They provide an immune response to the body if any foreign body is detected in the body. Alien invasions refer to various viruses, bacteria, etc.
Visually about lymphocytes
Analysis for determination
Lymphocytes in the blood and their number can be determined using the simplest test - a blood test. This clinical analysis allows us to identify the overall total lymphocyte count .
A blood test is used as the main method for diagnosing elevated lymphocyte levels. Therefore, for early diagnosis of any serious disease in the body, it is important to donate blood for testing at least once every six months .
In order for the analysis result to be more accurate, you need to prepare for it.
Recommendations before donating blood for lymphocytes are as follows:
- The test must be taken on an empty stomach, that is, more than 8 hours must have passed after the last meal. As a rule, it is carried out in the morning.
- The dinner before the test should not be heavy, but light.
- Doctors also advise not to eat fried foods, fatty foods, or drink alcohol 1 or 2 days before a blood test, but most people neglect this rule.
- You should stop smoking an hour or two before the test.
By following these recommendations, your blood test will be more accurate.
The meaning of the analysis results and acceptable standards
A screening blood test will allow you to find out whether lymphocytes in the blood are increased or decreased. There are acceptable standards for the presence of lymphocytes, which indicate that everything is in order with the body.
When assessing the norm of indicators, they rely on their absolute and relative value to white blood cells - lymphocytes.
For an adult, the following are considered normal indicators:
- Relative amount – 19-37%.
- Absolute quantity – 1.0-4.8 * 109 l. *
Increased values
An increased number of lymphocytes in a person's blood is called lymphocytosis. It is determined by two indicators - relative and absolute.
Absolute lymphocytosis means that the total number of lymphocytes in the blood has increased.
Relative shows that only the proportion of lymphocytes in the total amount of white blood , that is, in leukocytes, has increased. For example, 45.7% is relative lymphocytosis.
Interesting information about elevated white blood cells
We can talk about the presence of elevated lymphocytes in the blood only if these values are much higher than normal values.
Absolute and relative lymphocytosis
Relative lymphocytosis is much more common than absolute lymphocytosis. Relative lymphocytosis is determined in all diseases that are accompanied by a decrease in other types of leukocytes, for example, in viral infections, etc.
Absolute lymphocytosis is characteristic mainly of acute infections, for example, rubella, mumps, whooping cough, etc.
Reasons for the increase
There are many reasons for the increase in lymphocytes in the adult body. But one of the main reasons is illness of varying severity. Let's analyze them.
Reasons for enlargement in men:
- various inflammations in the pelvic organs, bladder and kidneys;
- excessive physical activity;
- improper diet;
- taking any medications.
Reasons for enlargement in women:
- premenstrual period;
- poor nutrition;
- various infections, viruses, bacteria;
- burns;
- malignant tumors;
- arthritis;
- large blood loss, for example, during menstruation;
- diabetes.