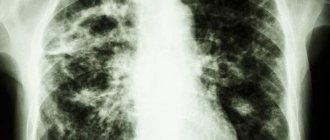
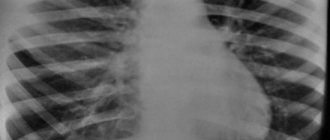
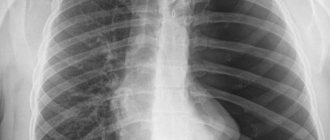
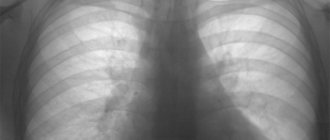
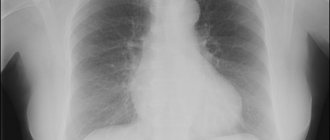
Respiratory diseases are a fairly common problem in the modern world, since the air is highly polluted by humans, especially in cities, where most of the population lives. For this reason, it is important to monitor this as closely as the condition of all other organs and systems of the body. One of the most serious diseases associated with the lungs is tuberculosis, from which they try to protect people of all ages, because even schoolchildren are given the Mantoux test, which makes it possible to identify this disease in its early manifestations. And adults must have an x-ray every year for the same purpose; its other name is fluorography. Below you can see what pulmonary tuberculosis looks like on an X-ray and its photo.
X-ray is the cheapest and most commonly used diagnostic method.
What is a chest x-ray?
Radiography is the most accessible and cheapest research method. A radiograph is obtained by exposing film to x-rays and producing a projection of the shadow of the human body. As X-rays pass through the human body, they tend to be attenuated depending on the density of the tissue, and when the image is taken, dark and light spots are obtained. X-ray film contains a special substance that changes its properties when an inhomogeneous beam of rays passes through it. This substance is silver bromide, and when the film is developed, the silver begins to be restored and the places where it is completely restored become darker, and where it is not completely restored, they become lighter.
There are several methods of X-ray examination - radiography, tomography, fluorography. The display of tuberculous changes on an x-ray is projected by shadows of varying shading densities. Shadows can have different structures, shapes, and localizations, and this must be taken into account when describing them.
Radiography
Chest X-ray is a research method that allows you to assess the condition of the bone skeleton of the chest and the organs contained in it. The image is obtained in real scale by projecting the shadows of body parts onto x-ray film. Electronic radiography, which allows image editing for better visualization, is becoming increasingly popular.
There are several mandatory rules for performing chest x-rays:
- the photograph must be taken in two projections (frontal and lateral);
- the frame should capture the apexes of the lungs and costophrenic sinuses.
Following these simple rules will prevent diagnostic errors and allow tuberculosis to be visualized on an x-ray.
The correct description of the radiograph of the lungs is of great importance; for this you need to adhere to the developed algorithm:
- assessing the quality and completeness of the image;
- condition of bone structures;
- comparison of pulmonary fields by pattern, shape;
- study of pathological changes (if any);
- assessment of the condition of the roots of the lungs;
- mediastinal shadow.
If the algorithm is followed, the analysis is as complete and consistent as possible, however, even if all the rules are followed, it is not always clear what pulmonary tuberculosis looks like on an X-ray. Such cases are rare, but they do occur. It is important to remember this and not rely entirely on this diagnostic method, especially if there are clinical signs of the disease.
There are many types of tuberculosis, and each of them has its own special x-ray picture:
Primary tuberculosis complex. A dense focal shadow in the right lung, a “path to the root” is observed. The pulmonary pattern is enhanced.
This x-ray shows tuberculosis of the hilar lymph nodes. Homogeneous focal shadows in the roots of both lungs, strong intensity, with a clear edge.
Disseminated lung disease. Multiple lesions in the upper lobes of the right and left lungs. The changes affect the roots and are accompanied by infiltration of lung tissue in the affected area.
Miliary tuberculosis. A huge number of small millet-like foci in all lung fields, with signs of fusion.
Focal tuberculosis. A small focal change in the left lung, 1-1.5 cm in size, with an uneven and unclear contour, the structure is heterogeneous.
Infiltrative TBC of the right lung. Severe infiltration of the upper lobe of the right lung with involvement of the root, as well as the lower lobe of the left lung. The pulmonary pattern is enhanced.
Caseous pneumonia. Severe disseminated infiltration of both lungs.
Tuberculoma of the right lung. Heterogeneous large-focal formation in the right lung with an unclear double contour.
Cavernous tuberculosis of the left lung. Ring-shaped shadow in the upper lobe of the left lung (indicates the presence of a decay cavity).
X-ray of fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis. A ring-shaped shadow at the apex of the left lung with a clear, dense contour. Finely focal seeding of the left lung.
Cirrhotic pulmonary tuberculosis. Total darkening of the left and upper lobes of the right lungs (indicates severe sclerosis of the lung tissue).
Left-sided exudative tuberculous pleurisy. Darkening in the lower parts of the left half of the chest. The pulmonary pattern on the left is weakened.
An X-ray of the lungs may not show bronchial tuberculosis in isolation, since it occurs only in conjunction with other forms. Infiltration along the large bronchus of the right lung. The pulmonary pattern is strengthened, the root is deformed.
Silicotuberculosis. Disseminated infiltration of both lungs.
An X-ray examination is mandatory if a patient is suspected of having tuberculosis; it corresponds to the GPP level of evidence, i.e. current clinical practice.
We also recommend reading the article about tests for tuberculosis.
Milliary form
It has small lesions of the same size with clear contours and in large numbers. Their sizes range from 2.5 – 3 mm. They have a medium darkening intensity and are located on both lungs.
Post Views: 3,122
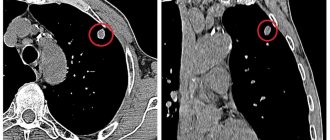
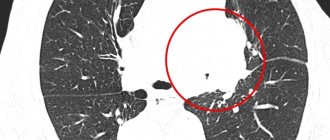
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography is the most informative diagnostic method in comparison with other x-ray examinations. But due to high cost and low availability, the method is not used very often.
Indications for computed tomography of the lungs for tuberculosis:
- clarification of the diagnosis;
- determining the location and volume of the lesion;
- differential diagnosis with other lung diseases;
- assessment of the dynamics of the process under the influence of therapy.
Expert opinion
Anna Sandalova
Pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Ask a Question
CT for this disease is performed only when necessary, in cases where other methods are ineffective or ineffective.
CT images for pulmonary tuberculosis look like this:
Cavernous tuberculosis. A cavity with dense thick walls is observed.
Primary tuberculosis complex. A focus of compaction of the lung tissue and enlarged lymph nodes of the mediastinum and root of the lung.
Focal tuberculosis. Small focal compactions in the upper lobe of the left lung.
Infiltrative lung damage. Focal infiltration of lung tissue. Some images show decay cavities.
Tuberculoma. A heterogeneous formation on the periphery of the right lung, with a clear calcified contour and less dense contents.
Fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis. Multiple cavities (cavities) with a thick dense contour and areas of compaction around.
Tuberculous pleurisy. The presence of fluid in the pleural cavity.
Conclusion
Will an X-ray show pulmonary tuberculosis? Typically, this pathology is diagnosed using this method. Qualified medical workers will be able to identify the disease even at the initial stage. To identify the form and stage of tuberculosis, you need to have certain knowledge and skills. Before you start examining yourself or your baby, make sure the device is working properly and the specialist is experienced.
X-ray examination in children is somewhat different from examination in an adult. Such a serious act is done only in extreme cases, when no other examination can be used.
Treatment
Hematogenously disseminated tuberculosis is treated with chemotherapy drugs. The patient is prescribed medications:
- Rifampicin;
- Isoniazid;
- Ethambutol;
- Streptomycin;
- Pyrazinamide.
Each case history contains information about the prescription of anti-tuberculosis antibiotics (Isoniazid + Ethambutol, Isoniazid + Pyrazinamide). Consumption is treated with corticosteroid medications and immunomodulators. Treatment of disseminated tuberculosis in adults is carried out in a hospital.
Stage 1 of therapy is intended for patients who release mycobacteria into the environment. The course of treatment for consumption consists of an intensive phase, which lasts 2-4 months. The maintenance stage of therapy lasts 7 months. The clinical and radiological dynamics of the disease, the value of ESR, and the massiveness of bacterial excretion are studied in the patient.
The patient is prescribed complex therapy with Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol in a dose corresponding to his weight. Ethambutol is often replaced with Streptomycin, which is used intramuscularly for 2 months.
In case of focal pneumonia, broad-spectrum antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, vitamins, and immunomodulators are prescribed. The patient takes Tsiprolet, Isoniazid, Rifampicin.
For the treatment of caseous pneumonia the following is prescribed:
- antioxidants;
- antihypoxants;
- immunomodulators;
- hormonal drugs.
AB is used only after bacterial culture of sputum. In the second phase of therapy, the following regimen is prescribed: Isoniazid (H), Rifampicin (R) + Pyrazinamide (Z) + Ethambutol (E) + Streptomycin (S) for 2 months.
Indications for fluorography
This diagnostic method is used both for preventive purposes (once a year) and for certain ailments:
- determining the cause of cough, chest pain, shortness of breath;
- suspicion of pneumonia (pneumonia);
- the presence of pathology of the heart and blood vessels (atherosclerosis, aortic aneurysm, pathology of the heart valves);
- contact with a patient with tuberculosis;
- suspected HIV infection;
- search for foreign bodies in the respiratory tract and upper gastrointestinal tract.
Differences between fluorography and x-rays
If it is necessary to examine the organs of the respiratory system, many people have a question about what to choose: fluorography or x-ray of the lungs.
Fluorography is a cheaper method, since it requires less film. In addition, you don’t need to use special devices to develop it; the pictures appear immediately on the film. Due to its high availability, fluorography has become widespread during preventive examinations.
However, it is not as accurate and informative as x-rays. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis and control the disease over time, it is necessary to conduct a chest x-ray. Another advantage of X-rays is lower radiation exposure, so if X-ray diagnostics are necessary, this method is prescribed for pregnant women and children.
Differential diagnosis of tuberculosis
Typically, when diagnosing tuberculosis using x-ray, it is necessary to be able to distinguish it from lung cancer and pneumonia. Often there is practically no difference in the images of pneumonia and tuberculosis, especially with the infiltrative form. However, there are some differences. Pneumonia is usually a unilateral lesion, while tuberculosis in most cases affects the lung tissue on both sides.
In addition, in case of pneumonia, the infiltrate is localized in the lower parts, and in case of tuberculosis - in the upper parts. The infiltrate is more pronounced in tuberculosis; there are often foci of destruction and dissemination.
It should also be noted whether the images show cancer different from tuberculosis. Sometimes this is quite difficult to do, especially with focal forms of tuberculosis. A number of the following signs will help with this:
- the cancer shadow is intense, with more blurred contours;
- the shadow of cancer in most cases has a homogeneous structure;
- the growth of the tuberculosis process, if there is no dissemination, is limited to the pleura, and therefore does not grow into the adjacent lobes of the lung;
- Cancer can spread to adjacent lobes.
Diagnosing tuberculosis using x-rays is quite difficult, and only a doctor can make a final diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. After all, tuberculosis is not a death sentence!
Contraindications to fluorography and x-rays
Although identifying foci of tuberculosis on an x-ray is the most informative way to diagnose this disease, x-ray examination is associated with radiation exposure, and therefore there are a number of contraindications to its implementation:
- child's age under 15 years;
- the patient’s serious condition, in which it is impossible to transport him to the X-ray room;
- pregnant women, especially during the first trimester, since this is when the child’s organs are formed;
- women during lactation;
- respiratory failure with severe course.