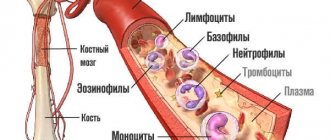
Vitamin D (calciferols) plays a huge role in human life, having a pleiotropic (multiple) effect on the body. The most significant representatives are D2 and D3. The first comes with food, the second is synthesized by the epidermis under the influence of the ultraviolet spectrum and is also replenished when eating.
The largest amount of the nutrient is found in fatty fish (cod, halibut), dairy products, chicken eggs, chanterelle mushrooms and beef liver. Calciferol is also present in citrus fruits and fresh spring greens (nettle, parsley), but in small concentrations.
Vitamin D is converted in the body into a steroid hormone and has the following effects:
- regulates phosphorus-calcium metabolism;
- affects certain genes;
- protects blood vessels from the development of atherosclerosis, prevents cardiovascular diseases;
- plays a key role in the development of the immune response;
- reduces the amount of parathyroid hormone, enhances the synthesis of sex hormones and serotonin;
- protects brain cells and nerve structures;
- reduces the concentration of mediators of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress;
- prevents the development of malignant tumors, diabetes, obesity and other pathologies;
- slows down the aging of the body;
- reduces the risk of organ rejection during transplantation.
With a lack of calciferol in children, changes in the skeletal system become the most noticeable. Bone growth slows down and they lack strength. In severe cases of vitamin deficiency, deformation of the chest, spine, arms and legs is observed. Therefore, throughout the civilized world, pediatricians from the first days of life are engaged in the prevention of rickets.
In adults, with calciferol deficiency, osteoporosis develops. Bones become brittle and break easily, leading to systematic fractures. General weakness, insomnia, joint pain, muscle cramps, cephalalgia and other symptoms may also cause concern. A person is susceptible to frequent colds and infectious diseases, chronic inflammatory processes.
It is not difficult to check the concentration of the active substance in the body. To do this, you need to donate blood from a vein.
Indications for taking a vitamin D test
A study of calciferol (vitamin D) levels in the blood is indicated in the following cases:
- in the complex diagnosis of mineral metabolism disorders;
- with hypocalcemia;
- during pregnancy;
- for eating and digestive disorders;
- with symptoms of rickets - curvature of the leg bones, growth retardation;
- if osteoporosis is suspected, increased fragility and fragility of bones;
- with neoplasms of the parathyroid glands;
- during therapy with vitamin D-containing medications;
- to monitor the treatment of vitamin deficiency conditions.
- As part of a comprehensive examination, a blood test can determine the cause of vitamin D deficiency or excess.
- When treated with appropriate medications, the dosage of the medications is adjusted based on the results of a blood test for vitamin D.
Reasons for decreased and increased vitamin D levels
Calciferol levels decrease in the following situations:
- with insufficient insolation, lack of sunlight;
- for eating disorders;
- with a deficiency of foods containing ergocalciferol in the diet;
- with malabsorption syndrome, due to which the absorption of all substances from the intestines is impaired;
- against the background of liver diseases, vitamin D is metabolized in this organ;
- in connection with taking certain medications, for example, phenytoin, rifampicin.
An increase in vitamin D concentration in a blood test occurs if:
- Foods with excess vitamin D.
- Intense solar radiation.
- Taking etidronic acid, orally.
- With excessive use of medications containing calciferol.
Additional tests for examination
Blood tests for vitamin D are prescribed by doctors of several specialties: rheumatologists, orthopedic traumatologists, and therapists.
- Often, in addition to this analysis, other examinations are prescribed, the purpose of which is to facilitate diagnosis.
- Recommended tests and examinations include:
- Study of serum calcium and phosphorus levels.
- Determination of the amount of magnesium in blood serum.
- Determination of parathyroid hormone levels in the blood.
- Ultrasound of the parathyroid glands.
The levels of calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone and vitamin D correlate with each other - an excess of vitamin is accompanied by a drop in parathyroid hormone levels and a change in the concentration of these microelements.
Decoding the results
There is special laboratory equipment that allows you to perform not only a hemotest, but also a comprehensive study of tissue mineral density, and accurately calculate the concentration of vitamin D and the calcium-phosphorus system in the body.
This procedure is called densitometry and refers to x-ray diagnostic methods. It is prescribed to postmenopausal women with diabetes and taking medications that remove calcium from the body.
In other cases, traditional laboratory microscopy methods are used. The results of such diagnostics do not differentiate by gender and age of the patient. Laboratory assessment of the collected biological material takes 1-2 days.
The reference value is considered to be at least 30 ng/ml of blood.
Table of serum vitamin D content:
| Body status | Calciferol concentration, ng/ml |
| Norm | 30-100 |
| Insufficient content | 10-29 |
| Acute shortage | less than 10 |
| Hypervitaminosis | over 150 |
In clinical practice, vitamin D deficiency is more common than excess.
Calciferol deficiency factors:
- digestive dysfunction;
- inhibition of metabolic processes;
- hepatobiliary disorders;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- insufficient amount of solar ultraviolet radiation received.
This condition may occur due to the inability of hepatocyte cells to process vitamin compounds supplied with food. Calciferol deficiency is often due to poor absorption of nutrients by the intestinal and gastric walls.
In such cases, an additional blood test is prescribed for the content of enzymes secreted by the liver and a general ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is performed.
If the cause of hypovitaminosis is insufficient consumption of nutrients containing ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol, the diet is adjusted to increase the specific gravity of fatty acids that improve the absorption of vitamin D.
Chronic alcoholism inhibits the functions of the liver and gastrointestinal tract. This is a common cause of hypovitaminosis. With constant alcohol intoxication, the body experiences an acute deficiency of all vitamins and nutrients.
An increased concentration of calciferol in the blood serum indicates abuse of fatty foods, uncontrolled use of vitamin and mineral medications and dietary supplements.
A slight increase in reference values is considered normal during pregnancy, the premenopausal period, and menopause.
Hypervitaminosis in the initial stage manifests itself:
- lack of appetite;
- dyspeptic effects;
- dizziness;
- migraine;
- irritability;
- spontaneous pain in muscles and joints;
- sleep disturbance.
Laboratory diagnostics demonstrate an increased vitamin D content against the background of a decrease in concentration:
- phosphorus;
- gland;
- magnesium;
- potassium;
- thyroid hormone.
The metabolism of calciferol is worsened by antiepileptic, hypnotic and sedative medications. Therefore, hypovitaminosis is often recorded in older people and patients with severe autoimmune pathologies - multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and others.
It is advisable for them to be tested for vitamin D regularly, as well as for those who take anti-tuberculosis drugs or anticoagulants, which impair the metabolism of calciferol. In obesity, the nutrient accumulates in lipid deposits and does not participate in mineral metabolism.
Vitamin D and autoimmune diseases
A number of studies have proven that calciferol is involved in the regulation of the formation of immunocompetent cells (T-lymphocytes).
- It was noted that against the background of long-term hypovitaminosis D, the likelihood of developing autoimmune diseases significantly increases.
- Due to this fact, doctors recommend taking a blood test for vitamin D regularly in order to begin replenishing its deficiency as early as possible.
- This will reduce the risk of autoimmune pathology.
Preparing and conducting analysis
For laboratory testing, venous blood is collected. It must be taken on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning. No special preparations are required.
To obtain the most reliable result, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Avoid drinking alcohol for a week before visiting the laboratory.
- 3 days before collecting biomaterial, exclude fatty foods and fish from the diet.
- The time interval between food intake and blood sampling should be at least 8 hours.
- For 30 minutes. You should not smoke before the diagnostic procedure.
It is not advisable for women to donate blood during the menstrual cycle, which significantly distorts the test results. Venipuncture in the laboratory is performed in compliance with antiseptic rules. The resulting biological material is placed in a test tube with EDTA.
This is a special acid preservative that prevents blood clotting and changes in its rheological properties. The puncture point is pressed with cotton wool to quickly stop the bleeding. When collecting biomaterial, it is not frozen, but immediately placed in a laboratory centrifuge.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes a urine test, in which the level of calciferol is determined using special reagents. For such a study, the Sulkovich test is used, which allows one to determine the calcium content in the obtained biological material.
Based on it, the concentration of vitamin D is determined, which affects the metabolism and absorption of this chemical element. A laboratory test detects only the presence of calcium in the urine. It is impossible to determine its quantitative value in this way.
Venipuncture is considered a more informative analysis. Donating urine for testing is often prescribed for preschool children. This is a less traumatic analysis. For children, it is especially important due to the increased risk of deviations in physical development, the formation of rickets pathology and curvature of the spinal column.
They occur against the background of vitamin D deficiency and calcium metabolism disorders. For children born in the autumn-winter period, the risk increases due to a lack of solar ultraviolet radiation, which stimulates the synthesis of this physiologically important compound in the skin cells.
If the test result shows a deficiency of calciferol, it is added artificially by adjusting the diet or taking a vitamin complex with careful dosage control. An excess of vitamin D is no less dangerous than its deficiency. Children develop convulsive syndrome.
Excess physiological compounds accumulate in bone fibers. As a result, there is a slowdown in the growth of skeletal structures and their aesthetic deformation. Urinalysis is an extremely simple and comfortable procedure for the child.
In the laboratory, the resulting biomaterial is combined with Sulkovich's reagent. This is a mixture of oxalic acid with calcium salts in precisely calculated proportions. As a result, the liquid becomes cloudy.
Based on the volume and severity of the sediment, a conclusion is drawn about the content of vitamin D in the body. In adults, venous blood is collected for research. The content of calciferol affects the functioning of the heart, liver, and kidneys.
Therefore, such an analysis is considered important, although not mandatory during a routine annual medical examination. A key biological role of vitamin D is the regulation of cell division. Their uncontrolled reproduction leads to the formation of malignant and benign hyperplasias.
It is necessary to take a vitamin D test regularly to prevent cancer pathologies, enhance immune activity, and control blood pressure. A gynecologist must prescribe such a test for women when planning a pregnancy.
Calciferol is involved in the cellular differentiation of the embryo. It is involved in hormonal synthesis in the mother and is responsible for the formation of the child’s skeleton, teeth and nails.
Therefore, pregnant women are often prescribed vitamin D, and the exact dosage is calculated based on the test results. It is adjusted over time, so the study is carried out at different trimesters.
Vitamin D and tumors
In the search for a cure for tumors, scientists noticed that against the background of vitamin D deficiency, the incidence of various malignant neoplasms increases significantly.
- Studies have shown that normalization of vitamin D (ergocalciferol) levels is accompanied by a decrease in the likelihood of cancer.
- Vitamin D supplements are now included in adjunctive therapy regimens for some forms of cancer.
Vitamin D and parathyroid adenomas
Vitamin D deficiency causes the parathyroid gland to produce more parathyroid hormone.
- More intensive work of the glandular cells of the parathyroid glands is accompanied by increased cell proliferation - reproduction.
- The result of this process is the appearance of tumors of the parathyroid glands - adenomas.
- An increased level of parathyroid hormone in the blood causes calcium to be “leaked” from the bones, which leads to osteoporosis.
Vitamin D oil solution
The most common dosage form of vitamin D (calciferol) is its oil solution. This is explained by the fact that the vitamin itself belongs to the class of fat-soluble compounds, so it is absorbed from the intestines much more easily if it enters it in combination with oil. The main compounds of this group are:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is formed in human skin under the influence of sunlight.
- Vitamin D4 (dihydrergocalciferol).
- Of the provitamins D, ergosterol is the most common in nature.
Calcium with vitamin d
Since vitamin D is responsible for the absorption of calcium from the intestines, it is advisable to prescribe it simultaneously with calcium supplements.
- This allows you to eliminate both the deficiency of the vitamin itself and the deficiency of calcium in the body.
- Special preparations have been developed containing both calciferol and calcium in an easily digestible form as active components.
- The use of such combination drugs is recommended for children during periods of intensive growth, the elderly, and pregnant women.
- Only a doctor can prescribe medications with vitamin D based on a blood test.
Vitamin D standards for women and men by age
The daily requirement of vitamin D is the same for men and women. Before 70 years of age, it is 600-800 IU (15-20 mcg) per day, after 70 years - 800-1000 IU (20-25 mcg). In children under 1 year of age, the daily normal value is lower – 400 IU (10 mcg).
For pregnant women, the need for calciferol increases. The daily norm should not be less than 800-1200 IU (20-30 µg). A constant adequate concentration of the active substance in the blood is important to prevent congenital defects and diseases of the nervous system in the unborn child.
Practice shows that the above-mentioned preventive doses do not ensure that the level of vitamin D3 in the blood is adequate to modern views. Therefore, both therapeutic and prophylactic doses in therapeutic practice are many times higher. Specific dosages are selected by the attending physician based on laboratory tests.
The 25(OH)D indicator reflects the state of vitamin D in the body as follows:
- less than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/l) – deficiency (with a value of less than 12 ng/ml (30 nmol/l) they speak of an acute deficiency of the substance; rickets appears in children);
- from 21 to 29 ng/ml (51-74 nmol/l) – deficiency;
- from 30 to 100 ng/ml (75-250 nmol/l) is normal. Moreover, depending on the goals, the level in the blood should be different: more than 30 - prevention of rickets in children, ensuring phosphorus-calcium metabolism in adults, more than 50 - modulation of immunity, 70-90 - prevention of oncopathology;
- more than 100 ng/ml (250 nmol/l) – excess.
It should be noted that these values were recommended by endocrinologists based on how much they affect the condition of the skeletal system. Oncologists insist that the minimum acceptable level of 25-hydroxycalciferol should not be below 70 ng/ml (>150 nmol/l). It is this concentration of vitamin D that minimizes the risk of the formation of malignant tumors of any location.
The table shows how much the possibility of developing diseases decreases with a stable level of 25(OH)D in the blood above 50 ng/ml:
| Name of pathology | Percent |
| rickets | 100% |
| osteomalacia | 100% |
| cancer in general | 75% |
| mammary cancer | 50% |
| ovarian cancer | 25% |
| colon cancer | 67% |
| non-Hodgkin's lymphoma | 30% |
| kidney cancer | 67% |
| endometrial cancer | 35% |
| type 1 diabetes mellitus | 80% |
| diabetes mellitus type 2 | 50% |
| fractures in general | 50% |
| falls in women | 72% |
| multiple sclerosis | 50% |
| myocardial infarction in men | 50% |
| vascular atherosclerosis | 80% |
| preeclampsia | 50% |
| C-section | 75% |
Source: Holicfc, Michael F., PhD., MD, Boston University School of Medicine, textbooic - Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications (2nd Ed 2010 Humana Press). Page 12.
Also, an optimally high level of vitamin D in the body prevents the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease, dementia, mental disorders, depression and autoimmune processes.
Vitamin D ointment or cream
There are not only enteral forms (taken by mouth) of vitamin D, but also topical preparations.
- Ointments or creams enriched with vitamin D are prescribed for psoriasis.
- Psoriatic rashes are thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction and vitamin D deficiency.
- Topical application of cholecalciferol (vitamin D) as part of a cream or ointment leads to a reduction in psoriatic rashes.
Other indications for the use of such ointments are:
- skin aging;
- burns in the healing stage;
- uninfected sores on the skin;
- ichthyosis;
- allergic dermatosis.
- Topical application of creams and ointments with vitamin D stimulates the processes of regeneration and renewal of the skin.
Symptoms of vitamin D3 overdose in children
Signs will not appear if the child is given the drug in the amount prescribed by the doctor. An overdose is possible when using drops in a larger volume. Symptoms:
- long time to fall asleep;
- regurgitation or vomiting;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- slow hair growth;
- hyperactivity;
- increased thirst;
- polyuria;
- diarrhea or constipation.
If a child receives vitamin D in excess, bones grow faster and joints become stronger. This leads to curvature of the spine, frequent fractures and dislocations.
Attention! If signs of overdose appear, consult a doctor immediately.
When taken in increased quantities for 2-3 months, hypervitaminosis develops. The disease is manifested by a sharp decrease in weight, up to anorexia, alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Vitamin D supplements for those planning pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body's need for calcium increases several times - this microelement is required for the normal development of the fetus.
- To improve calcium absorption, pregnant women and women planning pregnancy require vitamin D in combination with calcium. Vitamin D preparations for pregnant women:
- “Vitrum prenatal.”
- “Elevit pronatal.”
- “Complimentary Mom.”
These drugs are necessary to prevent rickets in a newborn. But in addition to medications, proper nutrition and rational exposure to sunlight are necessary.
Indications for the procedure
In order to take a test for 25-OH vitamin D, it is enough to show symptoms of a deficiency of element D in the body, manifested by increased fatigue, decreased appetite, irritability, tearfulness and poor sleep in the child.
In particular, the analysis is carried out if the concentration of element D is increased, which occurs due to prolonged exposure to sunlight on the body and due to intoxication. Signs of vitamin D toxicity include anorexia, polyuria, bone demineralization, vomiting, hypercalcemia, muscle weakness and pain.
Main indications for testing:
- Hypovitaminosis D.
- Chronic pancreatitis, which is accompanied by secretory insufficiency.
- Vitamin deficiency D.
- Radiation enteritis.
- Renal osteodystrophy.
- Crohn's disease.
- Hypophosphatemia.
- Hypoparathyroidism and hyperparathyroidism with osteomalacia.
- Whipple's disease.
- Senile osteoporosis due to corticosteroid use.
- Chronic gastritis with achlorhydria.
- Hypocalcemia.
- Lupus erythematosus, which primarily affects the skin.