The main task of parents is to create all the conditions so that a small child grows up healthy, physically and mentally developed. An important place is given to a diet containing the necessary microelements for development. These include iron, the lack of which causes a dangerous condition for the baby - anemia. Anemia occurs when the level of red blood cells in cells, that is, hemoglobin, decreases. WHO studies have shown that in modern conditions, about 47 percent of children suffer from a lack of hemoglobin.
A small child may experience anemia - a symptom of a lack of hemoglobin in the blood
To make it clear to parents what process we are talking about, doctors explain that hemoglobin is a protein. It contains iron and carries oxygen from the lungs to all other organs. Therefore, when hemoglobin levels fall below normal, a painful condition called anemia occurs. Anemia is usually accompanied by weakness, headaches, tinnitus, decreased appetite and sleep disturbances.
Traditional treatment
If the mother monitors the child’s health, controls his diet, and uses folk remedies that maintain hemoglobin concentration within acceptable limits, he will not develop anemia.
It is possible to raise a child’s hemoglobin level without medications. It is enough to use folk recipes that have stood the test of time. Simple remedies can help increase iron concentration. Children use many of them with pleasure. They increase hemoglobin in infants aged 7 months and older children.
A particular home remedy should not be used if it causes an allergic reaction or other side effect. If undesirable manifestations occur (rash, itching, etc.), the drug is discontinued.
It is possible to increase the concentration of iron-containing protein using:
- Decoction of rose hips. Take 5 tablespoons of berries and infuse them in 1 liter of boiling water. The product is given to the baby in the morning. Add 0.5 teaspoon of honey and a little lemon juice to 0.5 cups of extract.
- A mixture of buckwheat and walnuts helps raise the level of iron-containing protein. The ingredients are ground to a powder and combined with honey. All components are taken in equal quantities, 1 glass each. The dose for a one-year-old baby is 1 tablespoon per day.
- Fruit and honey mixture. Walnut kernels, raisins, dried apricots are ground in a blender and combined with honey in equal quantities. Take a teaspoon 2-3 times a day.
- If hemoglobin is low, use fresh fruit and vegetables. Give children apple juice mixed with carrot and beetroot in proportions 2:1:1. Daily dose – 200–250 ml.
- Fruit-honey mixture with aloe. Grind walnuts, dried apricots, prunes, raisins, honey and juice obtained from aloe leaves are mixed. The ingredients are taken in equal quantities. Use 2-3 teaspoons daily.
- To quickly replenish iron deficiency, use a simple folk recipe. Thanks to him, anemia is treated even in tiny children. Oat grains are simmered in milk for an hour. For 500 ml of milk take ½ cup of oats. Babies are given a teaspoon. Older children drink the decoction as tea.
- Herbal collection. Boil 750 ml of water and pour into a thermos. Add 3 tablespoons of St. John's wort, blackberry and chamomile, 2 tablespoons of nettle, leave. Drink 250 ml warm three times a day.
It is strictly forbidden to treat anemia in a child without consulting a doctor. Self-medication leads to the development of complications. Without tests, it is impossible to track hemoglobin levels. Folk remedies and medications will not help if the baby suffers from another type of anemia rather than iron deficiency. Only a doctor can understand the reasons for low hemoglobin.
Acceptable standards
Hemoglobin concentration in childhood varies:
- in a newborn in the first three days it reaches 180–240 g/l;
- in infants up to a month – 115–175 g/l;
- in a baby 2–12 months – 110–135 g/l;
- from one year to 12 years of age – 110–145 g/l;
- in adolescents – 120–155 g/l.
When a baby’s hemoglobin is low, its level is quickly raised with iron-containing medications. There are medications for children aged 1 year. However, in the early stages of anemia development, pediatricians insist on correcting the nutrition of the infant and mother. They are advised to eat foods rich in iron.
Methods for increasing hemoglobin
When a baby develops hemoglobin deficiency, comprehensive measures are required to eliminate the problem.
A nursing mother is able to independently predict the occurrence of such a pathology. If during pregnancy a woman lived in a student dormitory and ate mostly “dry crust” and instant noodles, then the likelihood of anemia in the newborn is high.
When a woman has lost a lot of blood during childbirth, the likelihood of anemia in the baby increases. With regular and careful monitoring of the baby, you can easily notice signs of low hemoglobin.
It should be emphasized that the hemoglobin level in each infant has its own individual value. During the first year of life, extreme values fluctuate between 100 and 220 g/l.
At values below 100, anemia is diagnosed and an increase in hemoglobin is required
Pediatricians focus the attention of parents and guardians on the fact that it is very important to provide appropriate conditions for the synthesis of hemoglobin in the body
The main condition is breastfeeding. If possible, you should breastfeed your baby for as long as possible, at least up to a year.
In order for food to be fully absorbed, it is necessary to ensure the uninterrupted functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The condition of the infant's digestive system requires regular monitoring.
Animal proteins must be included in a baby's diet. Complementary feeding of infants begins at 4 months, although some pediatricians recommend doing this from six months.
For mild anemia, apple or Brussels sprouts puree helps raise hemoglobin.
Currently, a large number of ways to increase hemoglobin in infants have been developed and tested in practice.
When choosing certain products that stimulate the formation of hemoglobin in the child’s body, you need to carefully monitor the consequences.
The specificity of the situation is that modern babies are increasingly suffering from allergies. There is a lot of talk about the causes and dangers of allergies, and this is not just empty talk.
Formulas for a child suffering from anemia should be prepared in small quantities, gradually increasing the portion to the optimal volume.
Iron supplements
It often happens that all diets to increase hemoglobin in infants do not bring the desired result. This situation cannot be tolerated under any circumstances. In this kind of situation, the pediatrician prescribes special iron-containing drugs.
It must be emphasized that giving such medications to a child of his own choice is strictly prohibited: only a specialist can write a prescription and explain the rules for taking the drug. Medicines are available in liquid form and added to complementary foods.
When raising the hemoglobin level in a baby with the help of medications, you need to be aware that the baby’s stomach has difficulty digesting such additives.
Video:
Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the baby’s reaction and, in case of severe consequences, simply replace the medicine.
A negative sign is loose, black stools or prolonged constipation. The course of treatment is prescribed for a period of up to 3 months.
In a month you need to donate blood for testing for control. Sometimes you have to use another drug.
Nutrition rules for children
First of all, it is necessary to point out that hemoglobin deficiency is often associated not with a lack of certain micronutrients, but with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hormonal, and cardiovascular systems.
Therefore, you should definitely consult your children’s doctor (pediatrician) about this. He will also direct you to all the necessary studies and tests that will help establish the exact cause of anemia.
Up to 1 year
To increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood of children under one year old, breast milk is the optimal diet. And it is more important during this period to follow a healthy diet for the young mother , including iron-containing foods in the diet, as well as those rich in B-group vitamins. These include:
- beef;
- lean pork;
- liver (beef or pork);
- apples;
- grenades;
- carrot;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- legumes;
- cereal porridge
And the most important thing is to eat a varied diet. That is, regularly prepare different dishes to normalize the biochemical composition of blood and breast milk.
If the child is bottle-fed (formula), then preference should be given to those that contain iron and B-group vitamins . You should consult your pediatrician about this. Formulas are always selected individually, depending on how well the child’s body assimilates them.
If the child is more than 9 months old, then complementary feeding is allowed. In this case, be sure to add ground grain porridge, meat puree, vegetable oil, natural compotes or juices to the diet (must be diluted with water).
From 1 to 3 years
During this period, preference should be given to vegetables, fruits, herbs, and meat purees. If you have low hemoglobin, you should not overuse dairy products, especially cottage cheese, yogurt, dairy desserts, kefir - they contain calcium, which makes it difficult to absorb iron.
Also, the diet must include applesauce (or dried apples), carrot juice or puree (with sugar), buckwheat porridge, and legumes (not earlier than 18 months). You should also give up wheat bread in favor of bran bread - this is a good prevention of constipation (and at the same time, bran has a high iron content, almost 20 mg per 100 grams).
And, if possible, the child should be breastfed up to 2–3 years of age . Mother's milk is a concentrated mixture of vitamins, easily digestible proteins, iron, which best helps increase hemoglobin, as well as comprehensively strengthen the immune system.
From 3 to 6 years
In addition to recommendations for children under 3 years of age (with the exception of breast milk), it is recommended to gradually add to the diet:
- chocolate (and other cocoa-based products, with the exception of white chocolate, as it has a high milk content);
- liver (can be in the form of puree or pate with vegetables, it is recommended to cook at home);
- berries;
- fruit juices;
- prunes, raisins, dried apricots;
- eggs (chicken eggs are also suitable, but quail eggs are much healthier and easier for the stomach to digest);
- pumpkin, potatoes (boiled or baked, without frying).
You can also give small amounts of table flaxseed oil - it is rich in omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids, which accelerate intercellular metabolic processes, including those involving iron molecules.
Not recommended foods at this age include fatty cheeses, sour cream, fermented baked milk, as well as various types of desserts.
From 6 to 12 years
At this age, you can quickly increase hemoglobin using the following foods and drinks:
- greens (including parsley, turmeric, basil);
- pomegranate juice (not recommended in concentrated form, must be diluted);
- fresh and baked apples;
- nuts;
- wheat or rice bran;
- seafood (preference should be given to fatty fish, as well as red and black caviar).
Also, many pediatricians recommend making tea at this age based on rose hips - this helps not only raise hemoglobin, but also strengthen the immune system.
But non-recommended foods at this age include soda in any form, dairy yoghurts, fried potatoes, and fast food - it’s best to avoid all of this .
You should also definitely avoid black tea, coffee and any other drinks that contain caffeine - they all significantly slow down the absorption of iron and increase the concentration of tannins in the blood (which interfere with biochemical reactions with amino acids).
Symptoms
With anemia, a child experiences:
- poor appetite;
- fatigue, weakness;
- drowsiness;
- decreased activity;
- apathy;
- dizziness;
- cracks in the corners of the lips.
The child’s nails break, hair loses its shine, becomes dull, falls out, the skin turns pale and acquires a yellowish tint. The epithelium is dry, flaky. There are dark circles under the eyes, the heart rate is increased. Immunity is low, the baby is constantly sick. Diseases are difficult and cause complications. If iron deficiency is not corrected, children experience delayed physical and mental development.
Symptoms and diagnosis
It is possible to accurately detect low hemoglobin in a child 1 year of age or more only by taking a blood test. But there are symptoms that may warrant a visit to the doctor:
- pale, dry skin of the baby, circles under the eyes are possible;
- drowsiness and fatigue;
- irritability, the child is constantly capricious for no reason;
- frequent viral diseases;
- frequent regurgitation;
- lack of weight gain;
- thrush, stomatitis;
- developmental delay.
It is customary to distinguish three degrees of anemia. If it is low, having found the cause, for example, in nutrition, it can be easily eliminated.
With a moderate degree, the baby may have a slight developmental delay, tachycardia, dryness and pallor of the skin. Severe degree is characterized by impaired psychomotor development, enlargement of internal organs (spleen and liver).
To diagnose anemia, a complete blood test is performed. But there are small nuances - the hemoglobin content in the blood may be normal, but its reserves in the body may be running low, so it is recommended to additionally conduct a biochemical study.
When conducting the study, pay attention to the color indicator and the number of red blood cells.
Important! Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach. After diagnosing the disease, the child is referred to a hematologist and gastroenterologist for additional tests.
Causes of iron deficiency anemia in children
The reasons for the development of iron deficiency anemia in children are different. They can be divided into two large groups: external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous)
Exogenous causes include:
1. Reduced intake of iron into the child’s body. The 5% of iron that is excreted from the body in feces must be replaced. If iron does not come from the environment through diet (meat, eggs, liver, fish, vegetables, fruits) or it is bound by other foods and converted into indigestible complexes (when consuming milk, legumes, tea, coffee, nuts), then this percentage is not replenished, and the body borrows it from the liver. When liver reserves are depleted, iron deficiency anemia develops.
2. With increased iron consumption. Girls begin menstruation during puberty. This entails a loss of blood, and therefore hemoglobin, so at this time girls need additional iron supplies to the body.
3. Bleeding. Bleeding entails the consumption of iron from the body, which requires its correction.
4. Artificial feeding. Breastfeeding a child protects him from the development of anemia, since the child receives iron from the mother's milk, and breast milk proteins do not bind it into insoluble complexes, unlike cow's milk proteins, on the basis of which all formulas are made. Therefore, transferring a child to artificial feeding too early can lead to the development of anemia.
Endogenous causes include:
1. Diseases of the stomach and intestines. These can be gastritis, enteritis, colitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. With all these diseases, the integrity of the mucous wall of the stomach and intestines is compromised. Because of this, the absorption surface decreases, and iron from the intestines does not return to the body. Also, with peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, periodic bleeding from ulcers is observed, which is a chronic loss of iron in the body.
2. Reduced concentration of vitamin B12 in the body. Vitamin B12 is involved in the transfer of iron from the intestinal lumen into the bloodstream. When its concentration decreases, the process of iron capture occurs less actively, and a large amount of iron is released into the environment.
3. Reduced iron reserves in the “depot” (liver). As mentioned earlier, the iron “depot” is formed in the child during pregnancy. If the mother had colds during pregnancy, did not eat well, or if it was a multiple pregnancy (two or more children), the deposition of iron in the liver is disrupted and the child is born without an additional supply. Usually after birth there are no manifestations of this, since the amount of hemoglobin and iron content in the blood is normal, but after 3-4 months these reserves are depleted and signs of anemia appear.
4. Anemia can occur with increased destruction of red blood cells. This can occur when:
a) ingestion of toxic substances into the body, in particular arsenic, the poison of some mushrooms; b) diseases associated with a decrease in the lifespan of erythrocytes (sickle cell anemia, macrocytosis of erythrocytes); c) diseases of the spleen (splenomegaly).
Reasons for the decline
A decrease in hemoglobin levels occurs for many reasons. The most obvious and common causes of low hemoglobin in children:
- Intrauterine anemia. Every second pregnant woman has low HGB. The body does not supply iron to the child. Anemia affects children born prematurely, since their organs are not fully developed, as well as children born as a result of multiple pregnancies.
- Improper nutrition of the mother while breastfeeding her baby. The diet must contain vitamins and microelements, sources of iron, such as cereals and meat. Nutrition should be balanced. The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding until age 2. This is the best prevention of anemia. The bioavailability of iron from breast milk is several times higher than in formula.
- Introducing complementary foods too early. An immature gastrointestinal system cannot fully process food. The recommended age for introducing complementary foods is six months, taking into account the infant's nutritional interest.
- Lack of balanced nutrition for the child. Meat products (turkey, rabbit, veal, beef) must be given with fiber (any green vegetables). You cannot prepare dairy products for your child together with meat products, as in this case calcium will act as an iron antagonist.
- Lack of vitamins B9 and B12. In this case, the production of red blood cells is disrupted.
- Genetic predisposition. Violation of the structure of the protein molecule can be inherited.
Important! In children 2 years of age and older, the main causes are poor diet, gastrointestinal diseases, poisoning with toxic substances and blood loss.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia in children
The main sign of the development of iron deficiency anemia is pallor of the mucous membranes and skin. However, the range of symptoms for this disease can be much wider.
So, for example, with a lack of iron, a child, in addition to pallor, may experience:
excessive dryness of the skin, peeling and cracking; disturbance of taste and smell; brittleness and curvature of nail plates; hair loss and weak hair growth; decreased appetite; development of caries; diseases of the digestive organs; excessive fatigue. The child often experiences headaches, he is emotionally unbalanced, and complains of tinnitus. In some cases, delayed psychomotor development is possible; delayed physical development. May present with urinary incontinence or sphincter weakness; decreased blood pressure and shortness of breath. Listening to the child's heart often ends with the identification of functional systolic murmurs; frequent respiratory diseases that are quite acute. This is due to damage to barrier tissues.
There are a lot of characteristic symptoms, but diagnosing iron deficiency anemia can only be done after a general blood test, which will determine the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin, as well as a change in the color indicator.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin in the blood of a child
Which doctors should a child see at 6 months?
Signs of low hemoglobin levels manifest themselves in different ways. They can be divided into the following groups of symptoms:
- Asthenic – manifested by increased fatigue, irritability, poor sleep and lack of appetite;
- Epithelial – pallor of the face, ears and oral mucosa. The skin is dry and often flakes, the hair becomes brittle;
- Cardiovascular – increased heart rate, complaints of pain in the heart area;
- Muscular – rapid fatigue, involuntary bowel movements due to weakness of the sphincter muscles;
- Secondary immunodeficiency syndrome - manifested by frequent colds. Otitis, pneumonia and intestinal infections often occur.
Drug therapy
Iron deficiency anemia usually occurs in children. If hemoglobin levels are low, both the one-year-old baby and the older child need urgent treatment. A pediatrician determines the cause of anemia and prescribes treatment.
If you have iron deficiency anemia, you need to adjust your diet and take medications prescribed by your doctor. Medicines are prescribed for three months. An increase in hemoglobin occurs if the child takes:
- long-acting medications: Ferograd, Ferrum-lek, Irovit;
- short-term agents: Ferrous fumarate, Ferrous sulfate.
If an infant or young child is sick, the doctor will prescribe drops or syrup. Children with fears are given chewable lozenges; the active substances from them are gradually absorbed into the blood from the intestines.
Positive dynamics should occur after 30 days of treatment. It is determined by blood tests. The lack of therapeutic effect is due to:
- wrong dose;
- misdiagnosis (non-iron deficiency anemia);
- Irregular use of medications.
Reasons for low hemoglobin
How to donate blood for sugar in a child under one year old, normal result
In order to timely track the problem of iron deficiency in the body, you need to know what the reasons for its decrease in infants are. Pediatricians consider the most significant of them:
- Blood loss, for example, during injuries, the hemoglobin level decreases over several hours, which leads to iron deficiency anemia;
- Lack of blood in the bone marrow, that is, erythropoiesis, which is caused by infections, deficiency of copper and folic acid, vitamin B1;
- Increased destruction of red blood cells, which manifests itself in Epstein-Barr viral infection, congenital heart defects, and insufficient levels of phosphates in the blood.
Among the reasons that are more understandable in everyday life for a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, pediatricians identify:
- inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- prematurity of the child;
- lack of iron in the diet of a pregnant woman;
- lack of iron intake during guarding or IV.
There are other risk factors that lead to the most common type of anemia, iron deficiency, such as allergies or a deficiency of vitamin C and folic acid, which are necessary for iron to be absorbed into the blood.
Infectious diseases can cause a decrease in hemoglobin levels in children
For your information! A decrease in hemoglobin levels is not always regarded as a pathology. A child's body needs a lot of iron to develop, so due to rapid growth, it may be temporarily insufficient, leading to a known problem.
General information about hemoglobin
Low hemoglobin
(in medicine - anemia, iron deficiency anemia) is a low content of red blood cells in the blood. The main task of red cells is to transport and distribute oxygen molecules to organs and tissues to obtain energy and ensure the vital functions of the body. A low hemoglobin level will negatively affect the overall development and physical condition of the infant.
In babies under one year of age, the hemoglobin level in the blood should not be lower than 105 g/l.
In children in the second year of life, anemia is indicated by an indicator
of less than 100 g/l.
Causes of hemoglobin loss in the body
There are many reasons for the decrease in red blood cells in the blood of an infant. Factors that may contribute to this include:
- External (surgeries, unbalanced diet, anemia of the pregnant mother);
- Internal (hereditary pathology, immune, infectious diseases);
- Features of intrauterine development.
The intrauterine period of development and formation of the child’s body depends entirely on the health of the mother
, organizing her proper nutrition, the presence/absence of bad habits, hereditary diseases, etc. The supply of iron accumulated by a newborn during intrauterine development will be enough for about the first six months. After this time, a decrease in hemoglobin occurs. In the future, normal hemoglobin levels can be maintained through continued breastfeeding and.
When artificially feeding a baby, the level of red blood cells should be maintained using special fortified baby food with the addition of complementary foods (meat, fish, fruits, vegetables, vitamins) in subsequent months, which can correct the hemoglobin level.
It is necessary to take into account the intensive development and growth of the child in the first year of life, when significant changes occur in height and body weight. Accordingly, the consumption in energy production increases, and therefore in the production of red blood cells, which the body may not be able to cope with for various reasons.
Conditions for normal hemoglobin formation
- Breastfeeding should continue for as long as possible.
- The diet of a nursing mother and a bottle-fed infant must be balanced.
- Normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and hematopoietic system.
- No acquired or hereditary blood diseases.
- The presence of animal protein in food.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia
Symptoms of low hemoglobin in an infant can be divided into primary and secondary.
Unfortunately, parents do not always pay attention to such primary signs as: decreased appetite, constant weakness, increased fatigue, and the general unsatisfactory condition of the child. The progression of the disease in the future can be expressed in the following external signs:
The progression of the disease in the future can be expressed in the following external signs:
- pale skin (up to a jaundiced tint);
- unreasonable increase in temperature to 37.5º;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- dry skin.
Prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemia
It is necessary to treat anemia in infants, as it will lead to oxygen starvation of the whole body, will depress the functioning of the nervous system, create the preconditions for a lag in general and mental development, and will worsen the general condition of the baby. Iron deficiency anemia can be easily prevented by balancing your child's diet.
When breastfeeding, the baby's need for iron will be fully satisfied until almost 6 months due to the good digestibility of iron in milk (up to 50%), which is significantly higher than in other products. By the end of the first year of life, the child’s diet has been significantly expanded, thus it is possible to adjust the amount of iron entering the body.
Buckwheat, apples, beets, meat, liver, apple and pomegranate juices
contain high iron content However, pomegranate juice must be diluted with water (1:1) to avoid problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, in order to increase the hemoglobin level in an infant, you need to eat:
- Lots of fruits: blueberries, apricots, dried apricots, apples, strawberries, pomegranate;
- Lots of meat: beef, turkey, liver, veal;
- Any products made from wheat flour;
Treatment of anemia (low hemoglobin) with drugs should be carried out as prescribed by a pediatrician.
Why is low hemoglobin dangerous in a child?
According to statistical data, the incidence of low hemoglobin is significantly higher than high hemoglobin. According to the World Health Organization, 47.5% of children under 7 years of age have a lack of hemoglobin; in schoolchildren, the incidence is 25.5%.
A prolonged lack of hemoglobin leads to insufficient oxygen supply to organs and tissues, especially the brain. As a result, the baby may begin to lag behind his peers in development. In addition, low hemoglobin is a factor that stimulates the development of pathologies of the heart and kidneys, as well as the immune system and skin.
Patients may be concerned about frequent infectious diseases, constant weakness, dizziness, fainting, muscle pain, heart rhythm disturbances, itching and dry skin, brittle nails, hair loss, etc.
In the absence of competent methods for correcting the condition, the child may have cardiomyopathy, extrasystole, persistent tachyarrhythmia, etc.
How to increase hemoglobin in children using natural products
Young children in the first year of life are often susceptible to anemia, which is the result of insufficient hemoglobin levels in the blood. Anemia is quite dangerous for a child, as it leads to a decrease in the body’s immunity and resistance and slows down the child’s development. Its level can usually be determined by the results of routine blood tests. A pediatrician who detects a low level of hemoglobin in the blood is often advised to start taking special medications in order to increase hemoglobin in children's blood.
However, in many cases, this measure is an extreme measure, and not every mother wants to drug her child from an early age. Very often, it is possible to increase hemoglobin in children’s blood by adding natural products to the children’s diet that stimulate its production.
Foods that can increase hemoglobin in children.
When choosing foods high in iron and vitamins for your child, it is worth remembering that you cannot offer him those that cause allergies.
How to increase hemoglobin in a child using folk remedies:
Recipe 1: take 1 cup (250 ml) of rosehip infusion, add a couple of drops of lemon juice and 1 teaspoon of natural honey (if there are no allergies). This healthy vitamin drink contains a huge amount of hemoglobin and vitamin C. You need to drink it on an empty stomach; half a glass is enough for a child;
Recipe 2: Take walnuts, dried apricots, natural honey, large sweet raisins (in a ratio of 1:1:1:1) grind in a blender, mix into porridge and give the child a few spoons of the mixture every day. In addition to increasing the level of hemoglobin in the blood, such a cocktail of dried fruits also saturates the baby’s body with all the necessary vitamins.
Recipe 3: 1/2 cup freshly squeezed apple juice (preferably red apples), 1/4 cup beet juice and 1/4 cup carrot juice. Mix the juices and give it to the baby to drink half an hour before feeding. Before this, you need to give the child a spoonful of sour cream or baby cream, since fat is necessary for proper absorption. This juice cannot be stored, so the indicated norms must be divided into days.
Recipe 4: grind a cup of walnuts and a glass of raw, thoroughly washed buckwheat in a blender, add 1 glass of natural honey to the mixture, mix everything. Give your baby 1 tablespoon of the mixture every day. It can also be consumed by a nursing mother - it perfectly supports the heart and stimulates lactation. It is enough for children to consume 1 tablespoon daily.
As we see, if the situation is not critical, then it is quite possible to increase hemoglobin in children with simple healthy and natural products, which, moreover, will also be sources of energy and vitamins for the growing organism.
Means for increasing hemoglobin in a child’s blood are extremely varied - you just need to choose the one that suits your baby.
14 Ways Cats Show You Their Love There is no doubt that cats love us as much as we love them. If you do not belong to the category of people who are favorable to this.
Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few have thought about why it might be needed. Interestingly, it was originally a place for storage.
10 interesting facts about intimacy that you probably didn't know Check out the most interesting and impressive facts about sexual activity that will surprise you.
13 signs that you have the best husband Husbands are truly great people. What a pity that good spouses don't grow on trees. If your significant other does these 13 things, then you can s.
Why you can’t look a cat in the eyes for a long time There have long been many superstitions associated with cats. One of the most common is that you can’t look them in the eye. Below we will tell you where yes came from.
How to look younger: the best haircuts for those over 30, 40, 50, 60 Girls in their 20s don’t worry about the shape and length of their hair. It seems that youth is created for experiments with appearance and daring curls. However, already last.
Other Important Recommendations
Almost all metabolic processes in the body are accelerated when the level of vitamin D in the blood increases (as it helps accelerate the absorption of calcium and its concentration gradually decreases).
Therefore, doctors recommend walking outdoors as often and as much as possible , as well as sunbathing (with caution for children under 3 years old, since their skin is practically not protected from ultraviolet radiation and it is extremely easy to get burned).
You can also increase hemoglobin through active games and physical activity - all this also speeds up the absorption of proteins and amino acids, which precisely enter into a biochemical reaction with iron molecules.
It is also important to adhere to activity and rest regimes - blood is mainly produced at night during sleep. Therefore, the child needs to follow a routine and go to bed at the same time every day.
You can also increase hemoglobin using hematogen - this is a kind of dessert obtained from the formed elements of the blood of cattle. Sold in the form of candies or chocolates in pharmacies, it can be given to children aged 2 years and older (this information should be specified in the instructions).
There are also special variations of hematogen with a high content of iron and B vitamins - this can be used in the active treatment of anemia.
A little theory about low hemoglobin in children
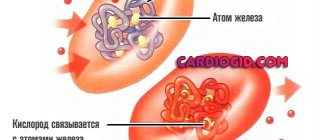
Hemoglobin is a complex chemical compound consisting of two parts: an iron atom and a special protein. It is found in red blood cells and gives the blood its red color.
The function of hemoglobin is to capture an oxygen atom in the lungs and carry it through the arteries to every cell of the body. The cells exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide, which is transported through the veins back to the lungs. Where hemoglobin is ready to pick up a new portion of oxygen again. This endless process allows all tissues and organs of the human body to fully develop.
A decrease in the number of hemoglobin in the blood leads to the fact that the body, and primarily the child’s nervous system, does not receive enough important oxygen. This reduces the performance of organs and resistance to diseases. With a constant lack of oxygen, increased fatigue and lethargy appear, and appetite decreases. Children are developmentally delayed and have difficulty learning new material.
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin in children
In order to know how to avoid anemia, you need to understand the causes of low hemoglobin.
- The origins of this problem may lie at the very beginning of the formation of the child’s body, that is, at the stage of pregnancy. If a woman carrying a child is poorly nourished and has low hemoglobin, then the baby is born with anemia.
- After birth, the second reason for a decrease in hemoglobin in a baby arises - inadequate nutrition of the nursing mother. Nature created it so that breast milk contains everything that is necessary for the development of a child. But this is violated if a woman purposefully excludes meat and cereals from her diet. And two people suffer, because both mother and baby lack iron.
- In the case of artificial feeding, the baby’s body cannot absorb a sufficient amount of iron from formulas. And cow's milk binds iron and removes it from the body.
- Another cause of anemia may be an insufficient amount of vitamin B12, which mediates the transfer of iron into the blood.
- Among other things, anemia can be caused by: allergies, worms, diseases, bleeding, constipation and diarrhea.
How to increase hemoglobin in a child
How to increase a child's hemoglobin without resorting to medications? This is possible if the decrease is insignificant. If there is an acute lack of iron, then you cannot do without medications prescribed by a doctor. But even in this case, experts recommend adjusting the nutrition of mother and child so that it regularly contains foods rich in iron and vitamins B12.
It is worth noting that it is very difficult to increase hemoglobin in a child under one year old only by adjusting the mother’s diet and introducing healthy foods into the baby’s diet. Therefore, here the doctor will definitely prescribe iron-containing drugs.
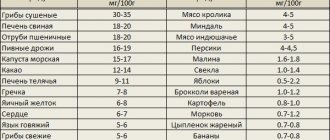
Foods containing sufficient amounts of iron and vitamins include:
- buckwheat, beans, peas, lentils;
- meat and fish;
- beets, potatoes, pumpkin, spinach, parsley, carrots;
- pomegranate, apples, persimmons, apricots;
- cranberries, currants, blueberries, strawberries;
- egg, nuts, dried apricots, hematogen.
Among other things, you need to take a walk every day and play outdoor games. After all, if there is enough hemoglobin and little oxygen, then the body will continue to suffer and not develop fully.
Prevention of anemia
To prevent a decrease in hemoglobin in children, the following is necessary:
- timely treatment of anemia in pregnant women;
- breastfeeding, since iron is best absorbed from mother's milk;
- complementary feeding of infants from 6 months, not forgetting that early feeding with cow's and goat's milk increases the risk of rickets and iron deficiency;
- in older children, a sufficient amount of foods high in iron in the diet;
- walks in the fresh air to stimulate the synthesis of red blood cells;
- if there is a risk of iron deficiency, take oral medications at half the dose;
- annual blood test.
Normal hemoglobin level in children
You will need to do a general blood test. Try to periodically monitor your results and check monthly.
Take into account generally accepted standards for hemoglobin levels in the blood:
- Up to 2 weeks – 135-200 g/l.
- From 2 weeks to 1 month – 115-180.
- 1-2 months – 90-130.
- 2-6 months – 95-140.
- 6-12 months – 105-140.
- From 1 to 5 – 110-140.
- From 5 to 10 – 115-145.
- From 10 to 12 – 120-150.
After 12 years, the norm is different for girls and boys. So, for the former it is in the range of 112-152 up to 15 years and 115-153 up to 18 years. The guys have 120-160 and 117-160, respectively.
In infants under 6 months of age, a decrease in hemoglobin is often observed. This is explained by the fact that the iron received during intrauterine development has been used up, and a new portion can only be supplied with breast milk or formula. Therefore, mother should eat more foods containing iron. The mixtures, of course, must also be balanced.
Drug therapy
Sometimes proper nutrition does not help normalize the level of hemoglobin in the blood, then the doctor prescribes medications. The choice of medications depends on the patient's age and severity of the disease. Usually the therapeutic course lasts from 3 months to six months.
Medicines for the prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemia:
- Sorbifer Durules is an antianemic drug prescribed to children over 12 years of age;
- Ferrum Lek is a medicine that replenishes iron deficiency in the blood; the dosage depends on the child’s weight;
- Totema is an effective anti-anemic remedy that strengthens the immune system, suitable for children from 3 months.
Ferretab, Iron Gluconate, Ferronal, Maltofer, etc. are also used for the prevention and treatment of anemia.
Thus, to prevent anemia, carefully monitor your child’s condition and consult a doctor when the first symptoms appear. After a blood test, the doctor will clarify the diagnosis and determine a treatment regimen.
Now you know how to increase hemoglobin in a child at different ages. From an early age, teach your child a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. Eat healthy foods while pregnant and breastfeeding. And remember, self-medication is dangerous to your health!
Treatment
Identified anemia requires urgent action. The pediatrician is obliged to determine its cause and prescribe the correct treatment. Often you can get by with diet correction, but in difficult cases this will not be enough.
Drug treatment consists of taking long-acting or short-acting iron-containing drugs.
Children are prescribed oral medications - their effect occurs several days later than after injections, but has virtually no side effects.
Injections are permissible only in exceptional cases, in case of serious intestinal diseases.
The course of taking the drugs lasts 3 months. It should not be interrupted even after iron deficiency has been eliminated. In this way, microelement reserves are replenished, which prevents the re-development of anemia.
Medicines for children are safe, well tolerated, come in a convenient form for all ages and have a pleasant taste. These can be drops, syrup, chewable tablets. A noticeable result from the treatment occurs within a month.
If no effect is observed, the dose may have been chosen incorrectly or the diagnosis may have been misdiagnosed.
Do not self-medicate under any circumstances! Exceeding the dosage may lead to complications including vomiting, dermatitis and allergies. Many parents try to cure anemia with hematogen alone, forgetting that this is just a nutritional supplement and not a medicine.
How to increase hemoglobin in a child: treatment
It is necessary to influence the cause of the decrease in hemoglobin [1].
When intrauterine iron deficiency is diagnosed, the expectant mother is treated. In her diet from 4.5 months of pregnancy, the daily amount of iron should be at least 40 mg.
Principles of therapy for iron deficiency and low hemoglobin in children:
- Iron supplements are required; without this, effective treatment is impossible.
- Treatment is carried out mainly with oral medications.
- Therapy after bringing the Hb concentration to normal is not canceled immediately. Dr. E. Komarovsky notes that taking iron-containing medications should be carried out for at least 3 months.
- Blood transfusions (hemotransfusions) are carried out only under strict indications (with hemoglobin less than 70 g/l and hematocrit less than 0.3), in life-threatening conditions, hemolytic anemia.
For early anemia of prematurity (after 8 days of life), recombinant human erythropoietin is administered in combination with iron-containing agents (5-6 mg/kg/day). Introducing it earlier may worsen retinopathy of prematurity, causing future vision problems.
Intravenous administration of iron (III) hydroxide-sucrose complex is possible up to the 15th day of life, 2 mg/kg/day or 6 mg/kg/week.
When treating anemia, the child is provided with proteins and folic acid, since their deficiency affects the synthesis of red blood cells that carry hemoglobin.
Therapy for iron deficiency anemia in infants and older children is prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account the whole complex of factors of its development and the child’s condition. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Hemolytic anemia requires hospital treatment because its complications are life-threatening.
Medicines prescribed by a doctor
The drugs are produced in the form of drops, syrup, dragees, chewable tablets with a certain iron content, which the doctor takes into account when prescribing to children of different ages.
Treatment of anemia with folk remedies
The first and most important thing to improve low hemoglobin is to improve the nutritional value of the foods you eat. But what to do if this is not enough, and it is not possible to take iron-containing medications? In addition to nutrition, you can use proven folk remedies.
- Equal amounts of beet, carrot and radish juice are mixed in a glass or ceramic container. Cover it with dough and put it in the oven for 3 hours at a temperature of 60 degrees. This remedy must be stored in the refrigerator. It should be taken one tablespoon before meals. The result will be visible after the first week of treatment.
- Carrots are good for increasing hemoglobin. It must be grated and mixed with sour cream. This dish is best consumed on an empty stomach. If the hemoglobin level is at a critically low level, then it is recommended to take this remedy in the evening for three months.
- Various herbal preparations are also used to treat anemia. Grind St. John's wort (3 tbsp), dead nettle (2 tbsp), blackberry leaves (2 tbsp), jasmine flowers (2 tbsp), pour in 3 cups of boiling water, wrap in a towel or blanket and leave for three hours. You can crush it after straining it hot, 1 glass 3 times a day. The minimum treatment period is one month.
- A good helper in increasing low hemoglobin is rose hips. In addition to the fact that it contains a large amount of iron, it is also rich in vitamin C, which is so necessary. The rose hips should be chopped. Pour five tablespoons of the resulting powder into a liter of boiling water and wrap in a blanket or towel for at least 12 hours. This infusion must be consumed in full within one day.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia is a long and labor-intensive process. It is necessary to increase hemoglobin levels only under the supervision of specialists. Moreover, the results depend not so much on the correct use of medications, but on a set of interrelated measures. This includes proper nutrition, elimination of possible hidden and obvious bleeding, increased intake of vitamin C, and general strengthening of the body.
Blood is the most important biological fluid for humans. It transports and distributes nutrients and oxygen to all internal organs
For the body to function fully, it is necessary to maintain normal all its quality indicators.