Do blood tests indicate cancer?
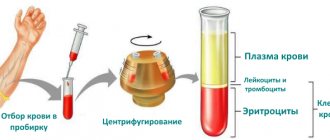
The results of a blood test for oncology allow us to suspect the presence of the disease. However, this analysis does not allow us to determine in which particular system the pathological focus is located. A referral for blood sampling is issued by a physician, and in case of suspicion of a malignant neoplasm, follow-up observation and additional diagnostics are carried out by an oncologist. A general blood test can be performed in a private or public medical laboratory. The execution time does not exceed 1 day.
In most cases, a person affected by cancer experiences an increase in the level of leukocytes, a sharp increase in ESR and a decrease in hemoglobin levels, however, it is unacceptable to make a verdict on the presence of cancer pathology based on one blood test. To make a final diagnosis, additional laboratory methods (analysis for tumor markers) and instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, MRI) are used.
Leukemia results in a decrease in the number of platelets (possibly a decrease in the number of all blood cells) due to bone marrow dysfunction. However, single minor deviations in blood test results are not diagnostically significant. This fact is explained by the fact that all laboratory criteria can vary in a person depending on the time of day and physiological state. These conditions are not life-threatening, much less indicate the presence of a tumor with 100% accuracy.
Read further: What are tumor markers, how much can they be trusted when determining oncology?
Low white blood cells and platelets - causes, symptoms, blood sampling rules
The composition of human blood is not static - it changes, and this depends on many factors.
Everything from the time of day to the individual characteristics of the body, for example: reactions to hot weather, can affect it. To assess how healthy a person is, all indicators must be taken into account. A complete blood test will help assess your health. And if there are low leukocytes, low platelets, you need to consult a hematologist.
Especially if the indicators differ from the norm.
There is no point in delaying a visit - this is the case when a timely visit saves a life.
Leukocytes
Leukocytes are white blood cells that provide protection to the body from pathogenic pathogens. Formed by bone marrow. When an infection or virus enters, the body produces an increased number of white blood cells. They attack the pathogen and dissolve it. And they die themselves. New cells are produced instead of dead ones, and this is how balance is maintained.
Relative norm of leukocytes:
- For adults – 4-9·109/l.
- For newborns from 9 to 30·109/l.
- For children aged 1-3 years 6.0-17.0·109/l.
- For children aged 6-10 years 6.0-11.0·109/l.
- Children over 10 years old are eligible for the adult category.
The number of leukocytes in the blood is not constant. The indicators change, for example: the level increases in the evening or after physical activity, after a heavy meal, a sauna or drinking alcohol.
A decrease in the level of white blood cells is called leukopenia.
Leukopenia
The term "leukopenia" is not an indicator of the disease. It refers to a medical condition in which the white blood cells in the blood are low. This is a serious condition that signals the presence of major problems.
There are 2 causes of leukopenia:
- Destruction of leukocytes. Possible reasons:
- Chronic infection. Due to its constant suppression, the immune system weakens. When a parallel disease develops, there are not enough leukocytes to fight it.
- Severe infection. When there are not enough leukocytes produced to suppress it.
- Worms. Neutrophils accumulate in the habitat of protozoa and do not respond to other pathogens.
- Viral disease.
- Thyrotoxicosis, high levels of thyroid hormone.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Syphilis.
- Damage to the liver or spleen.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Shock.
- Leukocytes are not formed. Causes:
- Congenital disease.
- HIV AIDS.
- Autoimmune disorders in which white blood cells attack the bone marrow.
- Radiation sickness in acute or chronic form.
- Bone marrow cancer or metastases from other organs.
- Vitamin deficiency.
Lack of leukocytes weakens the body's defenses. And any disease, even a simple acute respiratory infection, lasts long and painfully and gives complications. Regular flu leads to pneumonia, and treatment does not guarantee results. Any attempt to “handle” a sore throat is fraught with consequences.
Symptoms of lack of leukocytes
Leukopenia is an acute condition. It is impossible not to notice her. Due to the fact that leukocytes are low, a person constantly experiences a condition similar to a cold. When you are “about to get sick.” But you don’t get sick, but the condition remains.
Typical symptoms include:
- Persistent increase or decrease in body temperature. Daily fluctuations are possible, for example: an increase in the evening due to the fatigue accumulated during the day. Lowering - in the morning, before breakfast.
- Constant weakness, malaise, drowsiness. Symptoms are not related to daily activity.
- Decreased appetite, weight loss. Weight loss may be slight and loss of appetite may not be noticeable. Usually the signs are ominous, and if the weight decreases significantly, you need to see a doctor.
- Headache and heavy sweating. Sweat is not related to ambient temperature. Possible night sweats.
- Cold symptoms that do not go away and are not treated with regular remedies.
- Joint pain. In an adult, those that bear significant loads.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, primarily in the neck. Lymph nodes are mobile, dense and not painful.
- Pustular rashes on the body.
Possibly asymptomatic. But general oppression and depression are present. If some of the listed signs are present, in order to exclude low white blood cells, it is necessary to take a general blood test.
It is important to find out what disease caused the decrease in leukocytes. For some of them, for example: for autoimmune and hereditary ones, there is no treatment. But preventing infections, proper nutrition and following doctor's recommendations prevent the development of diseases.
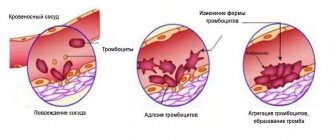
Platelets
Colorless, nuclear-free blood cells. There are two functions: blood clot formation and blood clotting. The role of platelets in tissue regeneration has recently been discovered.
Relative platelet rate:
- For adults – from 180·109
- For women during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy - up to 100 109
- For newborn children – 100-400 109
- For children – from 160·109
To analyze platelet levels, it is necessary to take into account subjective factors and the patient's condition.
If the platelets in the blood are low, the condition is called thrombocytopenia.
Thrombocytopenia
The term is general. Describes a condition and does not indicate a specific disease. A low platelet count is dangerous because it affects the blood's ability to clot. The fewer platelets, the worse the blood clots and the more dangerous any, even minor, bleeding is.
There are 3 causes of thrombocytopenia:
- Destruction of platelets. Possible reasons:
- Wergolf's disease - most platelets are destroyed. The reason is not clear.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Severe poisoning and intoxication.
- As a result of hemodialysis or heart valve replacement.
- Hemolysis after blood transfusion.
- Decompensated renal failure.
- Few platelets are produced. Causes:
- Leukemia is the most common cause.
- Radiation sickness.
- As a result of chemotherapy.
- Lack of vitamin B and folic acid.
- Infections leading to bone marrow damage.
- As a result of side effects of certain medications.
- Incorrect distribution of platelets between the liver, spleen and blood. Possible reasons:
- The spleen is greatly enlarged.
- The liver is greatly enlarged.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Heart failure.
In all cases, blood flow is obstructed. Liver and spleen - due to the increase in size, a large amount of blood accumulates in them. Therefore, enough platelets are produced, but their distribution is uneven.
There is congenital thrombocytopenia, which occurs as a result of mutation of internal organs. Symptoms usually appear from birth. The most well-known disease associated with bleeding disorders is hemophilia.
This is a condition in which you can bleed from minor cuts. And the most famous patient in history who suffered from such a disease is Tsarevich Alexei Nikolaevich Romanov, heir to the Russian throne.
Symptoms of platelet deficiency
Due to the peculiarity of the main function of platelets, the symptoms manifest themselves clearly. And the sick person quickly consults a doctor. Symptoms of the condition include:
- Prolonged bleeding due to minor cuts.
- Formation of large bruises after minor injuries. Such bruises last a long time and disappear.
- With a healthy oral cavity, gums bleed.
- Small subcutaneous hemorrhages, which eventually merge into one large spot.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Frequent hemorrhages in the conjunctiva of the eye without increased blood pressure.
- Long and heavy menstruation in women. Uterine bleeding.
Usually a slight decrease in platelets goes unnoticed. The above symptoms are characteristic of severe thrombocytopenia. To identify and eliminate problems in a timely manner, it is best to take a general blood test once a year.
How and where to get tested
Platelets and white blood cells are only part of the blood test. But a decrease in their level should serve as an alarming signal and a reason to consult a doctor. Especially if there are corresponding symptoms against the background of a decrease.
A general blood test can be taken at a public clinic or a private laboratory. Requirements for passing the analysis:
- It is taken on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Avoid drinking alcohol the day before.
- Do not visit the bathhouse or sauna.
- Women should not get tested during menstruation.
- Warn the laboratory assistant about taking medications.
The test results are ready in a few days. A private laboratory can send them by email. A convenient analysis form allows you to independently assess deviations. If there are reduced indicators, it is better to consult a hematologist. And if necessary, undergo additional research.
Low leukocytes - the body's defenses are reduced, low platelets - the blood loses its ability to clot. Any of the conditions without treatment will lead to serious illness or death. A timely visit to a specialist will help avoid serious consequences.
Loading…
Source: //dlja-pohudenija.ru/serdcze/analiz-krovi/rasprostranennye-prichiny-nizkih-lejkoczitov-i-tromboczitov-simptomy-i-diagnostika
Hemoglobin in oncology
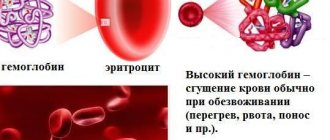
Hemoglobin is a specific protein that is part of red blood cells and transports oxygen from the lungs to all organs and tissues, as well as carbon dioxide on the way back.
Low hemoglobin and oncology may be related to each other, since a decrease in the indicator is recorded in more than 60% of patients. This condition has its own definition - anemia (anemia).
Normal levels of hemoglobin in the blood of a healthy person:
- men – from 130 to 174 g/l;
- women – from 110 to 155 g/l.
Deviations of several units in any direction do not have any effect on the general condition of a person. But in the presence of a malignant tumor, anemia, shock, severe infections, etc. the content of this blood component begins to decrease.
Important: in cancer pathology, the hemoglobin value is ten times less than normal values.
A decrease in hemoglobin levels is indicated by a set of symptoms:
- general malaise;
- attacks of acute pain in the chest;
- rapid onset of shortness of breath even when walking calmly;
- dizziness;
- pale skin;
- brittle nails and hair loss;
- cold sweat;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- reduction of the body's natural defenses (immunity).
If hemoglobin is low, can white blood cells fall?
Content
Low hemoglobin and white blood cells in the blood are quite common in modern society. In both cases, the person’s well-being and physical condition noticeably deteriorate. With a low amount of hemoglobin, anemia is diagnosed in most cases, and low values of blood leukocytes indicate the possible development of leukopenia in the body. In both cases, the development of these pathologies is preceded by certain factors. Let's try to figure out what these factors are and if hemoglobin is low, can leukocytes fall?
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin in the blood in oncology
Hemoglobin levels can change during cancer for a variety of reasons. It is important to establish the reason for the decrease in protein concentration in each specific case in order to know how to increase hemoglobin and prevent complications of the disease in the future.
The cause may be due to internal bleeding. Oncopathology often causes such a complication, especially with the active progression of a malignant tumor or against the background of an adverse reaction from prescribed therapy. Other reasons that may contribute to a decrease in serum hemoglobin levels are also identified:
- gastrointestinal dysfunction resulting from problems with iron absorption;
- spread of metastases to the bone marrow;
- loss of adequate nutrition (with cancer of the stomach, esophagus or intestines), resulting in iron deficiency in the body;
- the use of potent drugs and procedures (chemotherapy or radiation), the adverse reactions of which are a decrease in the ability to form hematopoiesis;
- acute intoxication of the body, due to the constant growth and disintegration of a malignant tumor in the last stages of oncology.
What causes the drop in white blood cell levels?
Leukocyte deficiency can develop not only against a pathological background, but also from taking certain medications. There are also other reasons that contribute to this condition.
Let's consider the main factors that lead to a decrease in the number of blood leukocytes.
Taking certain medications, namely Methotrexate, Aspirin, Adriamycin, Cyclosporine and many others.
Pathological nature associated with damage to the body by certain diseases, this includes:
- pathologies of immunity. With diseases of this category, the body becomes vulnerable to damage by various diseases.
- autoimmune diseases. In this case, a drop in blood leukocyte counts is caused by damage to the body due to multiple sclerosis or transverse myelitis.
- viral infections. Most often, these diseases disrupt the normal functioning of bone marrow cells, for example, meningitis.
- infectious lesions that develop against the background of penetration into the body of fungal, bacterial and viral infections that stimulate the development of inflammation. This category includes the development of malaria or hepatitis in the body.
- systemic diseases affecting the immune system. These diseases lead to the development of various types of inflammation in the body, as a result of which the number of blood leukocytes drops sharply. Diseases in this category can easily include the development of rheumatoid arthritis or damage to individual organs by lupus erythematosus.
- disruption of bone marrow cells. As a result of the manifestation of such failures, the formation of leukocytes greatly slows down or practically stops.
Leukopenia (lack of white blood cells) can also develop against the background of:
- use of special treatment techniques. This technique can be radiation therapy.
- development of acute inflammation. These conditions can be infections that have entered the body through the corresponding wounds.
In some cases, low hemoglobin and white blood cells may be interrelated. Moreover, a decrease in one value can lead to a decrease in another. In most cases, doctors identify such a cause-and-effect relationship in the early stages and prescribe the appropriate type of treatment to the patient.
In any case, to prevent the development of these pathologies, it is recommended to undergo prescribed medical examinations and medical examinations on time. In this way, it is possible to identify any pathological changes in the functioning of organs in the early stages of development.
source
High hemoglobin in cancer
There are cases when a patient with cancer has a high level of hemoglobin, for example, with:
- kidney or liver cancer;
- Vaquez-Osler disease is a pathological condition during which there is excessive production of red blood cells by the bone marrow.
Thus, an increase in hemoglobin in oncology is no less important an indicator than its decrease. Therefore, the diagnosis of cancer cannot be considered complete without a general blood test.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
A high ESR and low hemoglobin in the test results indicate that there is an inflammatory process in the body, and the immune system is currently weakened and cannot cope with the problem on its own. To boost immunity (increase hemoglobin levels), it is recommended to drink pomegranate juice, eat liver, apples and other fruits rich in vitamin C. A visit to the doctor in this situation is mandatory. If hemoglobin levels are critically low, medications containing iron are prescribed and the cause of the elevated ESR level is identified.
This combination is not very good, but it occurs quite often. In this case, doctors recommend visiting an oncologist. But malignant neoplasms are far from the only reason for such analysis results. Other problems may also be suspected:
- an advanced infectious process, especially for those people who take medications for treatment that contribute to the development of anemia;
- toxic effects of poisons, hemolytic agents, heavy metals, and so on;
- various blood diseases;
- injuries;
- disruption of the functioning of certain organs.
How to increase hemoglobin in cancer?
If a blood test shows low hemoglobin due to cancer, it must be increased. For this purpose, special medications are used in combination with diet.
In medical practice, drugs that can increase hemoglobin levels include:
- transfusion of purified red blood cells;
- administration of erythropoietin - a drug to stimulate the functioning of the bone marrow, after which the body experiences increased synthesis of red blood cells and hemoglobin;
- solutions and tablets of iron ion preparations.
A special diet has been developed for cancer patients, which allows you to increase the concentration of hemoglobin and keep it at an optimal level from the very beginning of the disease. It is worth noting that without medicinal preparations of iron ions, this method does not work well, so it must be combined with the above medical procedures.
Products indicated for normalizing hemoglobin levels:
- high in iron (liver, spinach, corn, peas and peanuts);
- oatmeal, wheat, buckwheat and barley porridge;
- fortified food with a high content of vitamins C, B12, folic acid;
- berry infusions, compotes and juices (preferably freshly squeezed). Every day, you should drink 2 liters of liquid;
- sprouted wheat for breakfast.
Read further: What does high hemoglobin signal in women?
Platelets are low, leukocytes are low
Platelets are low and white blood cells are low – what does this mean? The composition of the blood changes periodically and it happens that the test results contain low leukocytes and low platelets. These blood components are undoubtedly important and their changes always lead to different results.
Therefore, it is advisable to understand why they are needed and what consequences their fluctuations lead to. This will help avoid complications and get rid of the problem in a timely manner.
The interpretation of the results for each person will be individual, because the norm has a wide range and depends on many factors.
Norm of leukocytes and platelets
Basically, these indicators for men and women are not too different. But in children, the number of leukocytes and platelets is slightly different. But changes indicate the presence of problems in the body. They can be caused by various factors and affect a person in different ways.
Normally, the indicators look like this:
- leukocytes in adults – from 4.0·109;
- leukocytes in children – from 4.5·109;
- platelets in adults – from 180·109;
- platelets in children – from 160·109.
In newborns, in the first few days the level of leukocytes can be up to 32·109 U/l. Gradually over the years this level decreases and at 6 years is 4.5-5·109. In men, the average is slightly higher than 4.2 109 and gradually decreases with age to 3.9.
In women, the normal level of leukocytes is 3.9. In old age it drops slightly and reaches 3.7.
Normal platelets in adults are not very different, but in women their levels are constantly changing. It is associated with menstruation and pregnancy. At this time, the indicator can reach 100·109. During the newborn period, the normal platelet count in a child ranges from 100 to 400·109. Gradually it changes and at 5-6 years it will have an indicator of 160-180·109.
When receiving the analysis results, the doctor examines the data and necessarily takes into account the possible reasons for changes in indicators.
The diagnosis is not made based on the number of leukocytes and platelets alone. To do this, it is necessary to take into account all indicators and take into account the characteristics of the body.
A clinical blood test will show the number of white blood cells, which are an important part of the immune system. They help in the body's fight against bacteria and viruses that penetrate it. Therefore, changes in the body always affect performance. There are several types of leukocytes, differing in their functional responsibilities.
An increase in white blood cells can occur even in healthy people. But their reduced level will indicate the presence of diseases. This condition is called leukopenia.
There are three reasons for its appearance:
- Problems in the functioning of the bone marrow.
- Death of leukocytes.
- Lack of substances to create them.
The most common reason is the third.
But the reductions in these cases are not so great and the indicators are more likely to approach the minimum norm. Together with them, you can notice a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin.
This is not surprising, because the same substances are used for their synthesis.
With a lack of B vitamins, iron and copper, a gradual decrease in white blood cells occurs. This happens with poor nutrition.
To normalize the situation, it is enough to adjust the diet. If the body is not able to absorb these substances from food, then the doctor prescribes medications.
Another reason is the death of leukocytes. At the same time, they are produced in sufficient quantities, but die. This happens during the redistribution of leukocytes, when a local problem arises in the body. The immune system directs white blood cells to damaged tissue, which reduces their number in the circulating blood.
It also occurs with some infectious diseases. There are different subgroups of leukocytes in the blood, but most of all neutrophils. They have the peculiarity of dying after contact with pathogenic microorganisms.
The doctor must consider the indicators of all subgroups of leukocytes indicated in the study results. When segmented neutrophils decrease, bacterial diseases, influenza viruses or hepatitis are often the causes.
If rods also decrease along with them, then perhaps the cause was poisoning of the body with poisons.
In case of disruption of the bone marrow, a significant decrease in the indicators of leukocytes of all subgroups is noticeable. This happens due to intoxication with poisons, heavy metals and even alcohol. Causes include chemotherapy for cancer, autoimmune diseases and radiation. The appearance of a tumor with metastases to the bone marrow also significantly reduces the level of leukocytes.
In all these cases, the drop will be very pronounced, so do not worry if a slight decrease in white blood cells is detected in the test results.
Causes of decreased platelets
When their level decreases, thrombocytopenia occurs. Adults and children can suffer from this, but the reasons for children are somewhat different. This is especially true for newborn babies.
Their decline occurs for a number of reasons:
- transimmune problems;
- prematurity;
- hemangioma;
- asphyxia;
- insufficient amount of hemoglobin;
- infectious diseases;
- immunodeficiency.
In older children, the cause of a decrease in the number of platelets is allergic reactions, viral infections, lack of folic acid in the body, or intoxication. In women, platelet reduction is caused by menstruation and pregnancy, so such physiological factors do not pose a threat. But some body problems can cause it in adults.
Among them:
- anemia;
- blood cancer;
- bone marrow disease or injury;
- large blood loss;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- autoimmune diseases;
- herpes;
- hemophilia.
Excessive alcohol consumption, some medications and infectious diseases affect the reduction. If a person has undergone hemodialysis, then he will also find a decrease in indicators.
Taking blood thinning medications helps reduce platelets.
Consequences of declining performance
If you do not pay attention to the decrease in white blood cells and platelets, unpleasant consequences are possible. First of all, the severity of these consequences will depend on the magnitude of the reduction. The greater it is, the more difficult it will be for a person. Thus, a decrease in leukocytes leads to a decrease in immunity, and a decrease in platelets leads to bleeding.
Consequences of leukopenia:
- increased frequency of colds;
- frequent occurrence of fungus;
- the body's vulnerability to viruses and bacteria;
- protracted and severe treatment of diseases.
A person becomes susceptible to various kinds of diseases. But even your own microorganisms can worsen the condition. Women may experience frequent relapses of thrush.
If you have chronic diseases, they will only get worse and can spread to other organs.
The consequences of a decrease in platelets are no less terrible. In this case, the occurrence of hematomas is observed even with the slightest pressure, the frequent occurrence of prolonged nosebleeds or with wounds and scratches.
Women experience heavy and long periods. If the platelet count continues to decrease, internal organ bleeding may occur. This in some cases leads to death.
No one is completely immune from a decline in these indicators. Therefore, it is very important to monitor your health and take the necessary tests on time. This makes it possible to take timely measures to eliminate the causes or significantly reduce their impact on the body.
Source: //BolezniKrovi.com/sostav/trombocity/lejkotsity-ponizheny.html
Leukocytes in oncology
In most patients, the number of leukocytes in the blood serum during oncology increases significantly (leukocytosis) to fight mutant cells in the body. The number of white blood cells is under the control of the human immune system. When natural defenses are weakened, malignant cells begin to divide so quickly that white blood cells do not have time to destroy them.
If the normal value of the indicator in people over 16 years of age ranges from 4 to 10 * 109 units, then leukocytes in cancer reach critical values. It should be noted that standard values for the value under consideration in cancer have not been established, since they can vary over a fairly wide amplitude (from slight increases to tenfold).
What do low values of leukocytes in the blood indicate in oncology?
In medicine, this condition is called leukopenia. It is noted that most often this condition develops in patients undergoing chemotherapy. This happens because the human body does not accept the prescribed drug, and there is no positive dynamics in the treatment of cancer pathology. Doctors adjust the course of therapy and transfer the patient to more aggressive treatment methods that negatively affect the cellular composition of the blood.
In addition, malfunctions of the kidneys and liver, which lose their ability to remove toxins from the body, can lead to leukopenia.
A low concentration of white blood cells in diseases, including cancer, can also be detected in bone marrow dysfunction. For example, in patients under the age of 30, leukopenia occurs much less frequently than in older patients. This is explained by the fact that the bone marrow of a young organism has a higher reserve of leukocyte synthesis.
It should be noted that the results of a general blood test also depend on the patient’s diet. In a situation where the body receives few nutrients, it begins to become depleted, which means the negative effects of chemotherapy drugs become more pronounced.
Read further: How to quickly increase white blood cells in the blood after chemotherapy at home?
Functions and norm of leukocytes in the blood
Leukocytes are white blood cells
Leukocytes are the main defenders of the human body, the vanguard of the immune system. They are produced by the bone marrow, and when an infection enters the body or various injuries occur, their production increases sharply. Leukocytes literally, at the cost of their lives, attack the enemy and eliminate it. New cells are immediately produced to replace dead cells, so that the body remains protected.
If there are few white cells in the blood, this indicates significant disturbances in the functioning of the hematopoietic organs or the presence of a number of lesions and diseases.
The following indicators are considered normal:
| Age group | Normal values, /l |
| Newborns | 9–30*109 |
| Children 12 – 36 months | 6–17*109 |
| Children from 6 to 10 years old | 6–11*109 |
| Children over 10 years old and adults | 4–9*109 |
Read: Diagnosis of polycythemia vera: blood tests, bone marrow tests, genetic test
A slight decrease in the level of leukocytes relative to the norm is not a reflection of the disease. It can appear after intense sports activities, physical fatigue, when visiting a bathhouse or sauna, after heavy libations and feasts.
Causes and symptoms of leukopenia
If platelets and leukocytes are low, a more thorough examination of the patient is necessary. Low levels of white cells are called leukopenia and are not a disease in their own right.
Leukopenia can be a sign of a number of serious diseases, and even cancer
She points to the following reasons:
- Destruction of leukocytes in the body. It can be triggered by a severe or chronic infection, viral attack, helminthic infestation, thyrotoxicosis, viral hepatitis, lymphogranulomatosis, liver and spleen dysfunction, syphilis, autoimmune diseases or severe shock.
- The body does not produce white blood cells or produces too few of them. This condition is provoked by radiation exposure, acute lack of vitamins, autoimmune diseases, congenital problems, immunodeficiency and AIDS, malignant bone marrow lesions or the presence of metastases.
If the body does not have enough white cells, this means that it cannot fully fight even a basic infection. A weakened immune system cannot cope with its function, and such a person remains practically defenseless against any disease.
More information about general blood test indicators can be found in the video:
Leukopenia occurs in a patient with symptoms that are very similar to a cold:
- Fluctuations in body temperature, it is either increased or decreased, low-grade fever is often observed, that is, the temperature stays at 37 - 37.5 C, and then begins to “jump” again.
- Weakness, feeling tired, lethargic, not caused by physical activity.
- Headache.
- Increased sweating, and a person is literally drenched in sweat without the slightest physical activity, even at rest. You may experience profuse night sweats.
- Decreased appetite accompanied by weight loss.
- Joint pain.
- Signs of a cold that cannot be treated with conventional methods.
- A pustular rash that can be distributed over different parts of the body.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the neck. To the touch they seem dense, mobile and do not cause discomfort.
A person may not feel pronounced symptoms, but in combination they manifest themselves as severe weakness, fatigue and a general depressed state. If a person suddenly begins to lose weight significantly, so much so that it becomes noticeable in a short period of time, contacting a doctor should be done immediately.
Correction of high white blood cell counts in cancer
The level of leukocytes in oncology increases in many types of leukemia, during which hormonal therapy is prescribed. Taking corticosteroids reduces symptoms and increases bone marrow reserve.
Hormone therapy for severe leukemia can suppress mitotic processes in the lesions, while providing additional resistance to the tumor.
Initially, treatment is carried out in small doses, but if the patient experiences negative dynamics, the administered doses are gradually increased. In severe stages of the disease, as well as in severe hemorrhagic syndrome, treatment is carried out with the maximum permissible doses of steroids.
Unusual increases in analysis results
In some diseases, an uncharacteristic increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is observed. First of all, it is oncology. The tumor dramatically changes the composition of the blood. And:
- sinusitis;
- pneumonia;
- ARVI;
- flu.
It must be borne in mind that any drugs that will subsequently be used to treat a person often cause disturbances in blood composition. The following may also be grounds for a non-standard increase:
- helminthic infestations;
- injuries;
- blood loss (especially internal);
- consumption of B vitamins;
- high cholesterol;
- vaccination, taking hormonal medications;
- poor nutrition, iron deficiency in the blood;
- postpartum hemorrhage, complications.
Any cause must be confirmed in the laboratory. Often, diagnostic results can be erroneous. To exclude this, you must follow all recommendations.
Correction of low leukocyte levels in oncology
Leukocytes in cancer most often decrease while taking chemotherapy drugs. For this reason, the condition of leukopenia requires special attention.
If a week before the expected date of a new course of chemotherapy in a patient, the level of leukocytes does not return to normal, then in addition to therapeutic measures, drugs are prescribed that can cause their additional synthesis. In a situation where blood tests do not return to normal before the start of the main anti-cancer treatment, the drug intake is extended for some time by adding hormones.
Low hemoglobin and white blood cells
Share article on social networks:
Any of the subgroups of leukocytes is produced and matures before entering the blood in the bone marrow structures. Damage to an organ or a change in its functionality under the influence of chronic diseases, including anemia, leads to a change in the percentage of leukocytes in the blood.
Important: anemia is one of the main reasons affecting bone marrow function. However, intoxication, inflammation, infectious invasions, chemotherapy, and taking immunostimulating drugs also lead to changes in the level of leukocytes.