AST (aspartate aminotransferase, AST) is an enzyme involved in the balance of proteins (amino acids). By the level of this enzyme in the body, signs of disease of the liver, heart and other organs can be determined. In addition, it is important to know the test results and the relationship between AST and ALT (alanine transaminase) in order to more accurately establish a diagnosis.
The article is based on the findings of 25 scientific studies
The article quotes the authors of the studies:
- Korea Institute of Science and Technology, South Korea
- Department of Biochemistry, Belgaum Medical College, India
- Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University, USA
- Center for Genomic Medicine, Kyoto University, Japan
- Department of Gastroenterology, Oregon Health Sciences University, USA
- and other authors.
To familiarize yourself with the research, follow the links in the text []
What is AST
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, AST ) - is designed in the body to speed up chemical reactions. This enzyme is found inside the cells that make up the liver and heart, but is also present in red blood cells (erythrocytes), muscle tissue, the pancreas and the kidneys. AST can be found in very small amounts in the blood outside of cells. [, , ]
AST is very similar to ALT (alanine transaminase), because both of these enzymes are contained in the cells of the liver parenchyma. The only difference is that ALT is mainly found in the liver, while AST is also present in the cells of other tissues of the body. Therefore, ALT is thought to be more specific for detecting inflammation in the liver, while AST may indicate disease not only of the liver, but also of heart disease, acute pancreatitis, hemolytic anemia, severe burns, kidney disease, musculoskeletal disease, or trauma ( wounds). [, ]
AST speeds up a chemical reaction in cells that is necessary for metabolism . This chemical reaction occurs primarily in the liver , where one of the end products of this metabolism, glutamate, is redirected to the kidneys to be excreted in the urine. []
LOCATION OF AST AND ALT ENZYME IN THE HEPATOCYTE (CELL) OF THE LIVER
Causes of transaminase fluctuations
If ALT and AST levels are elevated, what does this mean? If these markers exceed the norm in the blood, it means that a negative process is developing in the liver or heart muscle. High levels of ALT and AST indicate the possible development of the following pathologies:
1. Changes in the structure and necrosis of liver tissue, which can be caused by diseases such as:
- Hepatitis of various etiologies (alcoholic, viral, toxic, mechanical).
- Steatosis.
- Fibrosis.
- Cirrhosis.
- Abscess.
- Cholestasis.
- Tumor process.
- Metastases in the liver.
- Wilson's disease.
- Damage to the myocardium (heart muscle).
2 . Parasitic infestations . During their life, parasites release toxic substances that destroy liver tissue.
3 . Mechanical injuries . Bruises or penetrating wounds lead to abscesses and tissue necrosis.
4 . Exposure to drugs . Some drugs, such as NSAIDs and NSAIDs, antibiotics, testosterone, anabolic steroids and barbiturates, destroy the structural cellular integrity and the liver tissue dies.
If aspartate and alanine transamidinase is elevated, the reasons may not be directly related to the liver. Periodic increases in markers are diagnosed in acute pancreatitis, muscular dystrophy, burns, extensive injuries to skeletal muscles, as well as during the breakdown of red blood cells or hemochromatosis.
AST functions
Aspartate aminotransferase is one of the key enzymes that catalyzes the reversible transfer of the α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism.
At the macro level, this transport pathway influences the overall metabolism of amino acids and fats (fatty acids). It also plays a partial role in detoxification (urea cycle) and gluconeogenesis. [, ]
At the micro level, a direct chemical reaction that AST accelerates to convert an amino acid (aspartate) and acid (alpha-ketoglutarate) into another acid (oxaloacetate) and amino acid (glutamate). This conversion is vital for other metabolic processes such as the urea cycle, the glucose cycle and breakdown (glycolysis). [, ]
Normal AST levels
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels are highest in the liver and heart.
A healthy AST blood level ranges from 10 to 35 U/L . The upper limit of AST varies slightly among research laboratories. [, ]
The following AST values are considered reference (average):
- For men 0 – 41 U/l
- For women 0 – 31 U/l
Typically, doctors look at elevated and decreased AST test values, and do not pay attention if the results are within the reference range. But even if the AST test is in the “normal” range, it may indicate some problems in the body. []
Note : Adequate levels of vitamin D help protect the liver from metabolic, inflammatory and fibrotic damage. []
VITAMIN D PROTECTS THE LIVER FROM VARIOUS DAMAGES AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF DISEASES (https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v10/i1/WJH-10-142-g002.htm)
Other diseases in which the content is increased
While aspartate aminotransferase is considered a cardiac marker, alanine aminotransferase has the highest concentration in liver tissue . An increase in these indicators may indicate a number of damages in internal organs.
In various diseases, the ratio of aminotransferases to each other changes. The ratio of cardiac to hepatic marker activity is called the de Ritis ratio . With cardiac pathologies, the value of the coefficient increases, and with changes in the liver, it decreases. However, both values are higher than normal.
Enzymes, in addition to diseases of the cardiovascular system, are elevated in the following pathologies:
- Severe liver diseases - cancer, fatty hepatosis, cirrhosis.
- Mechanical jaundice.
- Hepatitis of various origins. An increase in alanine aminotransferase often occurs even before the onset of symptoms of the disease. Biochemical analysis also determines an increase in bilirubin levels. Aspartate aminotransferase is increased to a lesser extent.
- Cholestasis.
- Acute pancreatitis. The level of alanine aminotransferase increases with the appearance of an inflammatory process in the pancreas. In chronic pancreatitis, a uniform increase in both enzymes is determined.
- Muscle injuries, extensive burns.
The level of transaminases also increases in some pathologies of other internal organs. But in these cases the indicators are not clinically significant.
AST/ALT and ALT/AST ratios, Ritis coefficient
ALT/AST ratio can be used as a marker to detect insulin resistance . A study of 998 normal (BMI < 25) and 344 obese (BMI > 25) Japanese adults found that the ALT/AST ratio was a reliable marker for predicting the development and severity of insulin resistance in people of normal weight. , the ALT/AST ratio was within 0.82, and in overweight (or obese) people this ratio increased to 1.02 or higher.
Another retrospective study examined the AST/ALT as a diagnostic marker in 252 patients with chronic liver disease. Scientists have found this ratio to be a useful and quick way to diagnose liver disease . Progressive liver disease was associated with an increase in this ratio (along with an increase in AST itself). []
Ritis coefficient
The Ritis coefficient is the ratio of AST/ALT (the ratio of the concentration of these enzymes in the blood), which indicates possible heart or liver disease. It is believed that during myocardial infarction, AST increases 8-10 times, and ALT increases 1.5-2 times. With liver hepatitis, ALT increases 8-10 times, and AST increases 2-4 times.
An AST/ALT ratio of about 1.33 is considered normal , with a possible range of 0.91 – 1.75, which is typical for healthy people.
If the Ritis coefficient exceeds the number 2, together with an increase in AST values, then we can talk about possible cardiovascular problems, although a similar increase in AST also occurs with hyperthyroidism, Wilson's disease and liver fibrosis. At the same time, if the Ritis number is more than 2, alcoholic liver disease can also be considered, especially if GGT (gamma-glutamyltransferase) is elevated.
If this Ritis coefficient is less than 1, then this more indicates possible problems in the liver, especially due to viral hepatitis.
Decoding ALT
During the study, Alt is determined along with other transaminases. AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT are closely related to each other; deviations in the parameters of these two indices help to accurately determine which organ has pathology:
- If alt is greater than ast, this means there are abnormalities in the liver.
- If there is an increase in AST, then most often there is a problem in the heart muscle cells.
You can find out the exact indicators by doing a biochemical blood test. ALT decoding implies an indicator of alanine transaminase in the blood. It is determined not by the amount of enzyme released, but by its activity.
In a healthy body, the norm of activity is considered to be 6-37 IU/l (IU/l is an international value that determines the dose of activity of a particular substance).
In a biochemical blood test, ALT is most often tested to determine liver dysfunction. In this case, even in the early stages, it is possible to accurately determine in which area of the liver there are abnormalities. This allows you to accurately determine the diagnosis and predict the further development of the disease. Moreover, an increase in transaminase can occur asymptomatically.
If the study has not been carried out, then the first sign of increased ALT will be the same as with jaundice.
AST and disease analysis
In order for a doctor to prescribe an AST test, there must be some symptoms of liver disease, for example:
- fatigue
- weakness
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- vomit
- abdominal swelling
- yellow skin or eyes
- tight urine
- severe itching of the skin
- abdominal pain
In addition, your doctor may order an AST test for factors that may lead to liver problems, such as:
- infection with hepatitis viruses
- alcohol or drug use
- family history of liver disease
- diabetes
- obesity or overweight
AST levels may become abnormal (increased or decreased) if the following conditions occur:
- renal failure
- inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis
- hemochromatosis
- infections like mononucleosis
- gallbladder diseases
- heatstroke
- blood diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma
- amyloidosis
HEALTHY LIVER (left) AND CIRRHOSIS LIVER (right)
In a clinical study of 56 patients with very high AST levels (3,000 U/L or higher), the medical records of these people were reviewed and additional tests were performed. As a result, 40 patients (out of 56) were diagnosed with various liver diseases. It was concluded that extremely high AST levels are most often associated with liver disease . []
The relationship between risk factors (elevated AST levels) and heart disease was studied in 610 patients with varying degrees of heart disease. Of these, 350 patients with diagnosed heart disease had higher mean AST levels than 260 healthy patients. It was concluded that elevated AST levels could be used as a marker to predict the degree of heart disease . []
The AST content test is also used to diagnose pregnancy complications, in particular to predict premature rupture of the fetal membrane. One study looked at the health of 148 women during the same phase of pregnancy. Of these women, 74 had elevated mean AST levels compared to healthy values. It was concluded that measurement of AST activity in vaginal fluid can be used as a reliable test for diagnosing pregnancy complications . []
Overexposure to the trace element chromium is known to contribute to the development of many diseases such as cancer, ulcers and problems with various organs. A study on chromium-treated rats found increased AST production when exposed to chromium. As a result, it was concluded that toxic effects, including chromium, promote the growth of AST, and the test for this enzyme itself can be used as a marker of toxic damage to the body. []
Preparing for analysis
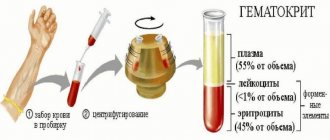
For the study, you need to take blood from a vein; capillary blood is rarely used. Diagnosis occurs strictly on an empty stomach in the morning. In exceptional cases, the doctor may prescribe a test in the afternoon, after a four-hour break from eating. During a routine examination, preliminary preparation is required:
- 3-5 days in advance, you need to stop taking a number of medications that can change the results of your blood test. To do this, the doctor makes adjustments to the therapy or, if cancellation is impossible, the patient provides the laboratory with a list of medications taken the day before;
- per day you need to exclude fatty and spicy foods and alcohol from your diet;
- the last meal in the evening before the test should be light;
- you must abstain from food for at least 8 and no more than 12 hours, during this time only drinking water is allowed;
- Half an hour before the blood test, physical or emotional stress is not recommended, and smoking is prohibited.
Blood test from a vein
How to increase AST
In general, low AST levels in the blood are normal and should not be a cause for concern. Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to low AST levels, so if you notice a decrease in this enzyme, it is worth knowing your vitamin B6 level.
Older people may be particularly susceptible to low AST levels, as they are often at increased risk of malnutrition. Vitamin B6 supplements tend to help increase AST in older patients. []
High AST level
One of the main signs of existing health problems is elevated AST levels ( above 40 U/l ). There are a number of physiological conditions and diseases that can lead to elevated AST levels, including:
- Rhabdomyolysis: This is a process of muscle breakdown in the body that causes large amounts of AST to be produced from the muscles. In addition, this process causes the release of protein (myoglobin), which is difficult for the liver to utilize. This situation leads to the production of increased amounts of AST, which increases the value of AST in the blood. Rhabdomyolysis can occur during strenuous exercise. [, ]
- Viral and alcoholic hepatitis is one of the main reasons for the increase in AST in the body. Inflammation of the liver increases the production of AST, and its significant increase in the blood helps to diagnose hepatitis. Long-term alcohol use (alcoholism) can also increase AST. [, ]
- Fatty liver also leads to increased AST levels, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ( NAFLD ). Excessive alcohol consumption, together with obesity or separately, can lead to the development of liver steatosis (fatty infiltration, also called liver hepatosis). []
- Age (aging). A study of 602 healthy people found an age-related increase in mean ALT (alanine aminotransferase) levels. This increase in ALT with age was also associated with an increase in AST values. It is believed that AST scores may increase with increasing age . []
- Floor. A study of adults in a specific region of China examined the course of metabolic syndrome. Although this was not the main finding of this study, the scientists did notice that AST levels were higher in men than in women. []
- Medicines. Some medications, such as painkillers, chemotherapy drugs, and statins (to lower blood pressure), may increase AST levels. This increase in AST has generally been associated with stress on the liver caused by long-term use or too much medication. [, , ]
- Other diseases that may be accompanied by an increase in AST: myocardial infarction, acute pancreatitis, acute hemolytic anemia, acute kidney disease, dermatomyositis, trauma or wounds.
Restoring normal values
It is important to understand that in order to restore normal transaminase values, the reasons for their increase or decrease must be determined. If the ALT level does not fit into the norm, you need to follow the following advice from doctors:
- Increase your intake of vitamin D, which not only reduces enzyme levels, but also prevents liver damage. Add fruits, vegetables, eggs, fish, cereals, dairy products, mushrooms, etc. to your daily diet.
- Stick to a plant-based diet. Thanks to natural products, liver function is restored, it is cleansed of toxins, new cells are formed, and enzyme levels are reduced. Preference should be given to zucchini, carrots, broccoli, various fresh fruits, nuts, lean meats, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. Such products contain many antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and also have minimal fat content.
- Avoid fatty foods. These foods make it difficult for the liver to process nutrients. If the fat content in it exceeds 10%, this indicates a “fatty” disease, which provokes inflammation of this organ and damages the tissues surrounding it. This is where the ALT enzyme increases. It is necessary to completely avoid coconut oil, butter, deep-fried foods, sausages, carbonated drinks, etc.
- Avoid foods that contain a lot of salt and sodium. We are talking about soy sauce, soda, bacon, pickled foods, and so on. This is due to the fact that excessive levels of these substances in the body retain fluid, provoke swelling, which in turn makes it difficult for the liver to filter waste and increases ALT.
- Stop using tobacco products and alcoholic beverages, which increase the ALT enzyme.
- Exercise daily. This can include fast walking and swimming. Thanks to such a 30-minute load, all toxins are removed from the body with the help of sweat.
Treatment for high or low ALT enzymes also includes taking interferons, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, corticosteroids and herbal supplements. Among the latter, Inositol, milk thistle, and burdock root are most often used.
These recommendations can normalize AST levels:
- Quitting alcohol. Chronic alcoholism increases the enzyme.
- You need to stick to a low-calorie diet, which will prevent heart attack, stroke and reduce the enzyme. Daily caloric intake for women and men is less than 2000 and 2000, respectively.
- Add coffee to your diet. Based on a study by scientists, if you regularly drink a little coffee, your liver will be healthy and liver enzymes will be reduced. This is because caffeine, which contains antioxidants, protects and repairs cells.
- Start taking a dietary supplement containing milk thistle, which has a protective effect on the liver from toxic substances, as well as stimulating the growth of new cells.
- Start taking a dietary supplement containing turmeric powder. This fruit has a strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, which speeds up the healing of various organs, and also reduces AST levels.
- Avoid iron injections, which increase the enzyme.
- Take medications as prescribed by your doctor. Usually these are statins, paracetamol, they lower the enzyme, lower cholesterol levels, and eliminate pain. For hepatitis B, the doctor prescribes Lamivudine, Adefovir Dipivoxil, hepatitis C - Ribavirin, Peginterferon, liver cancer - Oxaliplatin, Capecitabine, Gemcitabine, Nexavar, liver cirrhosis - diuretics that relieve swelling and laxatives that help remove toxic substances from the blood, reduce the load on the liver.
Monitor your health and if you have the slightest suspicion of any liver disease, do not self-medicate, but immediately contact your local clinic. Experienced doctors will order special tests that will help make an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe competent treatment. Timely treatment will help avoid serious consequences.