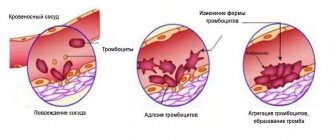
Biochemical processes in the body occur constantly. Without this there can be no normal life. The count goes into tens of thousands, hundreds and millions of conditional “operations”.
Each one works to perform a specific function of the body. If we talk about special cases, we can highlight reactions involving the so-called ferritin.
What it is? We are talking about a special complex of protein and substance, iron.
The compound performs several important tasks in the body.
In more detail:
- Depositing an element of the same name. Easier - storage in tissues. Under normal conditions, up to 30% Fe is concentrated. However, less than a percent is spent. This is normal, since the rest is deposited in cellular structures.
As soon as the need for iron arises, it is released from this protein complex. Then hemoglobin drops. These are parallel processes, which is quite normal.
- Transport of iron from the mother's body to the fetus. Simply put, the transfer of a substance to an unborn child. This is one of the main tasks of ferritin.
- Binding of toxic forms of iron. Normally, free Fe ions are highly toxic. They are able to react with cell membranes and oxidize them. Thus, cytological structures are also destroyed.
Recovery after this is impossible. The protein binds iron elements and inactivates them. Stocks up.
- Indication of inflammatory processes. The function is indirect, however, very important. A lack of ferritin, as well as its increase, accompanies inflammatory and infectious phenomena.
Ferritin can be reduced as a result of metabolic disorders, inflammation, bleeding, genetic mutations, other diseases and natural causes.
This is not a normal condition, but it is common. What should you know about the disorder?
What is ferritin and what is its function?
Ferritin is a water-soluble protein whose main function is the intracellular deposition (storage) of iron. In other words, it is an indicator of iron reserves in the human body. This protein can be found in all organs and fluids, mainly in bone marrow, liver, intestinal mucosa and plasma, but most of it is found in the middle of red blood cells and is part of hemoglobin.
Ferritin is able to easily mobilize iron from the depot, which is necessary for effective erythropoiesis (the formation of red blood cells - erythrocytes). At the same time, the deposition of iron protects the body from its toxic abilities, while the microelement is in a soluble (non-toxic) and physiologically accessible form.
More about ferritin:
Table: normal indicators
| Age | Ferritin content, µg/l |
| Children | |
| Up to 28 days after birth | 25–200 |
| 1 month | 200–600 |
| Up to 1 year | 25–85 |
| Up to 10 years | 25–55 |
| From 10 to 15 years | 30–140 |
| Adults | |
| Women under 20 years old | 10–40 |
| Women from 20 to 50 years old | 15–100 |
| Men under 20 years old | 20–100 |
| Men from 20 to 50 years old | 20–300 |
| Men and women after 50 years | 20–300 |
| Pregnant | |
| 1st trimester | 56–90 |
| 2nd trimester | 25–74 |
| 3rd trimester | 10–15 |
Ferritin levels during pregnancy
While carrying a child, the value of this indicator in a woman is significantly reduced. This fact is explained by the fact that iron begins to be actively transported to the developing baby. Lack of sufficient protein can cause miscarriage, delay of normal intrauterine growth, fetal hypoxia, disturbance of placental blood flow, placental abruption, etc.
The above has determined the high importance of ferritin analysis for pregnant women. Normal values for each trimester are presented in the table.
| Pregnant women, average normal value | |
| Up to 8 weeks | More than 70 µg/l |
| 8 – 12 weeks | More than 61 µg/l |
| 12 – 30 weeks | More than 32 µg/l |
| 38 weeks | Not less than 12 µg/l |
According to information from the Obstetric Hematology Center, ferritin levels during pregnancy are:
- in the 1st trimester - about 50% of the norm for a non-pregnant woman;
- in the 2nd trimester – about 30%;
- and in the 3rd trimester - at least 12%.
After the birth of the baby, the amount of protein is gradually restored in the woman’s body. Therefore, you should not be afraid if a low value of the indicator in question is detected in the tests of a pregnant patient. It is strictly contraindicated to try to decipher the research results on your own. Such attempts can negatively affect the health of the expectant mother and baby.
Deficiency symptoms
Symptoms of low iron levels in the blood are very diverse and at the same time nonspecific; they can be confused with the clinical picture of other diseases. The main signs of iron deficiency include:
- dizziness;
- fatigue;
- headache;
- weakness and discomfort in the legs;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the heart area;
- pale skin;
- dry skin;
- bluish tint to the whites of the eyes;
- cardiopalmus;
- decreased muscle strength;
- sensitivity to cold;
- irritability;
- sleep disorders;
- inappropriate behavior;
- depression;
- enlarged spleen;
- ulcers on the tongue, palate, in the corners of the lips;
- concave, thin, brittle nails;
- taste disturbance;
- constipation;
- frequent colds;
- pustular skin lesion.
When to take a blood test for serum iron:
Can hair fall out?
A lot of women and men suffer from hair loss, no matter what shampoos or masks they use - all to no avail. And the reason for this may be low ferritin levels. Due to deficiency, hair follicles become weaker and the result will be hair loss. The pathogenesis of this phenomenon is explained by the fact that the body tries to compensate for iron deficiency for vital functions by taking the microelement from the hair.
Hair loss as a symptom of decreased ferritin
Why do my legs hurt?
Insufficient iron in the body negatively affects the transfer of oxygen to needy cells. The muscles of the legs are no exception, therefore, if there is insufficiency of a microelement, pain occurs in the lower extremities.
Doctor's Note: If your legs hurt, it could be restless legs syndrome. It is often treated with iron supplements.
Pain in the legs may be a consequence of a lack of iron in the body
Help of medications
When ferritin levels are low, the oral method of delivering the microelement is quite effective. This means introducing an important element into the body through the mouth, which allows you to increase the indicator. However, therapy with tablets or capsules, syrups, and chewable lozenges results in the development of side effects due to the active substance entering the stomach. Oral products differ in the type of trace element present in them:
- divalent form (Fe+2) - aqueous solution of iron;
- trivalent form (Fe+3) - salts insoluble in water.
The most effective medications are those enriched with the divalent type Fe+2; this form of the substance is easier for the body to absorb. Salts of the trivalent analogue have less bioavailability due to the action of gastric juice. Preparations containing the divalent element include Totema, Sorbifer, Ferroplex. In the line of medicines enriched with trivalent Fe+3, the most popular are Ferlatum, Maltofer, Fenyuls.
Review of iron-based preparations
If there is a deficiency of ferritin in the blood, this is a condition where we are talking about an insufficient amount of Fe+ in the blood, which is dangerous for a woman’s health. The problem is detected by testing blood from a vein. To increase the level of a specific protein, the doctor prescribes iron-based medications.
| Medicine | Brief information |
| Preparations based on divalent Fe+2 | |
| Totema | Available in the form of a solution, taken for at least six months, 2-4 times a day, 100 ml. |
| Sorbifer | Tablets containing 100 mg of iron are prescribed twice a day (control by analysis). |
| Ferroplex | The drug in the form of pills is taken 3 times a day, two pieces. The course is individual. |
| Products based on trivalent Fe+3 | |
| Ferlatum | Taking the solution in disposable bottles is indicated 2 times a day, 1-2 pieces for six months. |
| Maltofer | The course of treatment with syrup or chewable tablets (3 pieces each) lasts 4-5 months. |
| Fenyuls | The drug in capsules is taken 2 times a day, one capsule for three months. |
Women are not recommended to take the test during menstruation due to a decrease in hemoglobin levels. A false decrease in ferritin is often observed during therapy with medications containing corticosteroids. During treatment with medications, it is important to follow the instructions for the drug.
How to increase ferritin with home methods?
Doctors say that almost everyone is at risk of falling protein enzymes, so they advise monitoring its levels. Opponents of drug therapy can be offered help from folk remedies that have been tested by many women. The most effective include infusions of nettle leaves or rose hips.
In the first recipe, 1 tablespoon is poured into a glass of boiling water; a rosehip decoction is prepared from 1 teaspoon of berries, poured in 150 ml of boiling water.
Doctors warn about the dangers of self-medication of low ferritin not only with medications, but also with traditional recipes without first undergoing tests and doctor’s prescriptions.
The most popular remedy among women is a mixture of dried fruits and nuts. A set of dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots, prunes) and nuts (usually walnuts) are ground using a meat grinder. Add honey (50 mg) to the mixture, mix well and store in the refrigerator. A tasty medicine that stimulates the growth of immune defense, take a tablespoon three times a day for at least two weeks.
Diagnostic methods
To suspect low ferritin levels, you need to pay attention to a person’s appearance, well-being, lifestyle, ask about surgical interventions, and the presence of chronic diseases. The next step is a blood test.
In medical institutions, the following methods are used to determine the amount of ferritin: radioimmune, immunoenzyme, fluorescent. The material for the test is venous blood (taken 8 hours after eating). The day before, physical work, drinking alcohol, and a lot of fatty and protein foods are prohibited.
Pathological reasons for the decline
The reasons why ferritin is low are varied. They are often associated with diseases in which iron absorption is impaired.
Causes of low ferritin:
- Endometriosis.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Oncological diseases.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Stomach operations.
- Chronic enteritis.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Celiac disease.
Ferritin levels can also be reduced after surgery, with long-term use of calcium supplements, or as a result of post-traumatic bleeding.
Why is the level falling?
Common causes of low ferritin include:
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- celiac disease;
- insufficient amount of iron in the diet;
- diarrhea;
- hypochlorhydria;
- gastric bypass;
- bleeding;
- menstruation;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- stomach and/or duodenal ulcer;
- pregnancy;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
Ferritin and pregnancy
During pregnancy, the amount of ferritin can drop significantly. So, for example, by the 20th week its level drops by 50%, in the second trimester by 70%, and in the third by 80%. The causes and risk factors for decreased ferritin are:
- malnutrition;
- hyperpolymenorrhea;
- the interval between pregnancy and the last birth is less than two years;
- multiple births;
- more than four births during life;
- bleeding during pregnancy;
- impaired iron absorption (gastrectomy or gastrectomy, maladsorption, chronic enteritis, intestinal amyloidosis);
- chronic diseases;
- oncological diseases;
- parasites and worms.
Preeclampsia, abortion, polyhydramnios, increased blood loss, septic complications after childbirth, hypogalactia are the consequences of iron deficiency in pregnant women. Low iron levels can also affect the baby in the womb. If there is not enough ferritin in the antenatal period, then the newborn baby may have a number of problems, including: iron deficiency anemia, impaired hemoglobin formation, delayed mental and motor development, chronic hypoxia, imbalance of the immune system.
Why do levels decrease in women?
Every month, a woman loses iron with the onset of her period, so each of them is at great risk of low ferritin. Moreover, the list of contributing factors complicates the situation. These reasons include:
- heavy and prolonged menstruation;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- surgical operations, including gynecological;
- excessive consumption of foods that contain a lot of calcium (milk, cheese), tea, coffee.
What are the dangers of iron deficiency anemia:
Causes in children
Children and adolescents tend to decrease ferritin levels during periods of rapid growth and puberty (hormonal changes). Just think about these numbers: 20% of all infants are iron deficient, in children under 4 years old - 40%, and in children 5-12 years old - 37%.
If there is a lack of ferritin, children will have iron deficiency anemia, the consequence of which is slower physical and mental development, decreased immunity (frequent acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, adenoiditis).
Nutritional deficiencies are put in first place among the causes of deficiency in children. Other factors include increased demand, malabsorption, chronic diseases and helminthic infestation. Excessive physical activity in children can also reduce iron levels in the body.
Celiac disease is another cause of iron deficiency. Nonspecific damage to the small intestinal mucosa by gluten disrupts the absorption (process of assimilation) of iron. This disease develops in 1% of children and manifests itself mainly at 2–3 years of age.
Low ferritin levels in men
Loss of blood negatively affects the amount of ferritin, moreover, it is a popular source of this problem. This reason is mainly associated with the digestive system (gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, hypoacid condition), nasal, post-traumatic, pulmonary bleeding. Donation, intravascular hemolysis, and vitamin C deficiency are also considered risks of ferritin deficiency.
Mechanism of development of the disorder
The pathological process (relatively speaking) is based on a number of disorders. They can be grouped into several large categories.
Inflammatory processes
Mostly of an infectious nature, but not only. The bottom line is that the disorder develops in response to the body's need for iron. As soon as deposition stops, reserves begin to be used up and ferritin concentrations understandably drop.
Recovery is carried out in parallel or after the acute condition has passed. The question remains at the discretion of the treating specialist.
Previous surgical interventions
This is an iatrogenic mechanism of the pathological process. That is, one that is determined by the actions of a specialist.
The phenomenon is quite logical, since surgical treatment involves trauma to the body. The blood flows away, and accordingly, there is less hemoglobin, as well as iron. It is necessary to cover this shortcoming.
The goal is achieved by releasing ferrocontaining components from tissues. But in some cases, auxiliary correction of the pathological process is required.
Endocrine system dysfunction
First of all, disorders of the thyroid gland. When hormones become too little or too much. The result is approximately the same.
The fine biochemical regulation of iron deposition processes changes. Accordingly, ferritin begins to be consumed, albeit in vain. Because the substance does not go to useful work. This is a waste of resource.
It is necessary to quickly restore the patient's health.
Women's diseases
Numerous in nature. From inflammatory processes to proliferative disorders. For example, endometriosis.
There are dozens of options. The bottom line is that almost all female diseases are accompanied by intense bleeding. Or not so strong, but regular.
Accordingly, the normal functioning of the body is disrupted. Iron is released mechanically. Hence the need to make up for this deficiency in one way or another.
The only way out is to release the substance from its natural storage: a protein complex known as ferritin.
Genetic factors
They are quite rare. But in some cases, the body, for natural reasons, cannot store iron normally in tissues and cells.
This pathological phenomenon is accompanied by reduced resistance of the body to abnormal external factors.
Attention:
Low ferritin with normal hemoglobin practically does not occur; it is a rare phenomenon and indicates a predominantly genetic nature of the deviation.
In some cases, we can talk about natural factors in the development of low protein concentrations.
Hyperferritinemia
Ferritin levels may be higher than normal. This is an unfavorable sign and may indicate various pathologies.
Possible reasons:
- hemochromatosis;
- liver pathology (hepatitis);
- hemolytic anemia;
- acute lymphoblastic and myeloblastic leukemia;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- starvation;
- mammary cancer;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- acute pathological conditions (burns);
- chronic diseases of connective tissue (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, osteomyelitis), kidneys;
- blood transfusion (several times);
- pulmonary infections (Legionnaires' disease).
Treatment
First of all, you need to seek advice from a varch. Based on the cause of the deficiency and laboratory parameters, he will draw up the necessary list of measures and medications to solve the problem.
A special diet will help raise your iron levels. Her diet should include the following foods: apples, pomegranate, grapes, black currants, rice, meat (especially veal), liver (pork and beef), eggs.
Gallery: High Iron Foods
Grapes Veal Blackcurrant Rice Pomegranate Eggs Apples Liver
Ferrotherapy, agreed with the doctor, includes iron supplements that are used according to the regimen. The dosage form depends on the presence of impaired absorption of the digestive system. In this case, it is necessary to abandon oral medications and switch to parenteral administration.
The most popular drugs are: Sorbifer Durules, Feramide, Ferro-gradumet, Ferroplex, Ferroceron, Ferrum lek, Totema. They should be taken one hour before meals or 2 hours after meals.
Gallery: medications
Totema Ferroplex Ferrum Lek in ampoules Ferrum Lek Sorbuffer Durules