Children under one year of age are under the close attention of doctors. During this period, babies cannot yet point to the sore spot and describe the symptoms of the disease, so problems often arise with carrying out diagnostic measures. Parents should closely monitor the baby’s well-being, and if there are any deviations, immediately seek advice from a doctor. Pediatricians, in turn, are obliged to invite the baby for routine examinations.
…
Why do children's stool contain leukocytes?
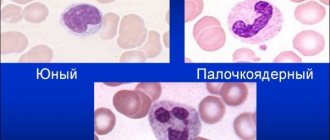
To protect against infections, the body produces white blood cells. Moreover, with increasing age, the norm of indicators decreases. So, in a child aged 14 - 16 years, the normal level of neutrophils is 7.5 * 109 / l, and in an infant - 15 * 109 / l. The newborn’s body more actively fights infectious diseases.
The leukocyte level does not increase without a reason. A newborn's stool is sterile and olive-colored. Then parents notice a change in the color of the stool. There is no cause for concern as the bowel movements will continue to be greenish-brown until the baby is 2 weeks old. During this period, the baby's stool is formed. For children aged 1 year and older, it is formalized.
But if there is a serious excess of leukocytes in the stool, or the appearance of an uncharacteristic smell or color of the stool, you should contact your pediatrician. Perhaps this condition was caused by infectious diseases. To identify and eliminate the causes that provoked this condition, a high-quality diagnosis is required, on the basis of which the doctor will refer you to the right specialist. Most often, a consultation with a pediatric gastroenterologist is needed, who will then determine the appropriate treatment.
Main Treatment Options
At the first stage, it is necessary to establish the cause of negative manifestations. Treatment is prescribed only after they are identified. It is necessary to carefully study the baby’s diet. Perhaps he got his first complementary food too early. If the baby is breastfed, then the mother should take care of her diet. It is not allowed to eat chocolate and citrus fruits during lactation. Too spicy and fried foods can play a negative role. Salt should also be added in moderation.
Types of treatment:
- if the leukocytes are single, there is no need for a medicinal drug. At the same time, the parents do not observe changes in his behavior;
- Probiotics help quickly improve your condition;
- if an infection is detected, it is recommended to undergo a course of antimicrobial therapy;
- To further protect the body, you should regularly take vitamins and other medications.
Important! If treatment is started on time, the level of leukocytes in the stool will quickly return to normal.
Useful video: what does an increase in white blood cells mean in a blood test?
Parents should have their child tested regularly. During the first year of life, feces are sent for examination at least three times. If the doctor makes certain recommendations, then parents must adhere to them exactly.
Diagnosis and signs of elevated white blood cell levels
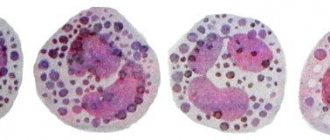
Correct treatment is carried out only after performing a detailed qualitative analysis. Using this diagnostic method, the enzyme state, the number of leukocytes, and the presence of a pathological process in the body are determined. Such research in the laboratory is called scatology, and the feces themselves are called coprograms.
Based on scatological data, a doctor can diagnose a child with:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- ailments of the small and large intestines;
- giardiasis;
- presence of helminths.
Often, a pronounced increase in white blood cell counts is accompanied by diarrhea and other symptoms. During this period, children lose a lot of fluid. For some, mucus and even pinkish discharge are visualized in the coprogram. This condition requires urgent treatment, because mucus in the stool can signal a dangerous disease.
Do you know whether your baby needs an analysis of the number of lymphocytes in the blood? We advise you to familiarize yourself with the material.
conclusions
An analysis of a baby's stool to determine the number of leukocytes is carried out if an inflammatory process in the body is suspected. You can notice the malaise by the baby’s well-being and behavior; an attentive mother will not miss a single symptom that is uncharacteristic of a newborn. A timely visit to a doctor and compliance with all his recommendations will increase the likelihood of accurately determining the cause of the disorder, as well as prescribing effective treatment.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you in detail about dysbiosis and how to fight it.
Diagnosis of leukocytes and mucus in infant stool
If mucus is detected in the stool in children, they are diagnosed with:
- Dysentery. An increased number of neutrophils is often a symptom.
- Spastic colitis. Pronounced symptoms of the disease are poorly digested fiber and an increased number of white blood cells.
- Ulcerative colitis. With it, inflammation spreads only to the large intestine. The newborn develops diarrhea, and in an advanced state, ulcerative colitis leads to intestinal perforation, acute toxic dilatation, sphincter weakness, accompanied by fecal and gas incontinence, and even colon cancer.
- Follicular enteritis. The coprogram contains mucus in the form of lumps.
- Dysbacteriosis. Often accompanied by E. coli or parasites in the newborn’s intestines.
Leukocytes in the stool of an adult - causes
Leukocytes in an adult's stool analysis are a cause for concern. The appearance of nonspecific elements indicates the development of pathological processes in the digestive system:
- acute intestinal infections, in which the mucous membrane always suffers;
- poisoning - to the ingestion of toxic substances, the body reacts with increased synthesis of leukocytes;
- inflammation of any part of the digestive system - an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall and the release of leukocytes into the surrounding tissues are recorded;
- dysbacteriosis - as a result of a disturbance in the composition of the microflora, increased synthesis of leukocytes occurs in response to the appearance of pathogenic agents;
- constipation - unsystematic emptying of the intestines provokes intoxication of the whole body;
- abuse of unhealthy foods that contain dyes, flavors, preservatives, simple carbohydrates, trans fats;
- state of chronic stress, depressive disorders;
- excessive physical activity, heavy sports loads.
Important! Single white blood cells in the stool of adults do not indicate any disease. In women, it is possible to get into feces due to anatomical features - from the vagina or urethra.
The detection of leukocytes in the stool of adults is a reason for a more detailed examination of the patient. Typically, the following diseases are diagnosed:
- colitis, enterocolitis, proctitis;
- anal fissures;
- rectal erosion;
- haemorrhoids;
- bacterial diseases;
- parasitic infections;
- intestinal, hidden gastric bleeding;
- severe allergic reactions;
- disorder of the pancreas;
- dysfunction of the liver, gall bladder;
- hemolytic anemia;
- cholera;
- typhoid fever;
- amoebiasis.
Normal coprogram indicators
Sometimes white blood cells in the stool in children occur after long-term treatment with antibiotics or other medications. In this case, the problem is eliminated after eliminating or replacing the drug. The norm is also exceeded in case of prolonged diarrhea. Moreover, this factor is observed not only in infants, but also in children over 8 years of age. Parents may not worry too much about their children's health if they:
- are not capricious;
- active and cheerful;
- do not experience abdominal cramps or allergic reactions;
- feel good;
- eat with gusto.
But the occurrence of opposite signs is a cause for serious concern.
With constipation in children, there is also an increased content of leukocytes in the coprogram. The same state of the internal nodes of the intestinal veins is signaled by red blood cells in the feces. These blood cells, whose main function is to transport oxygen throughout the body, should not be present in large quantities in the stool. Their abundance in the coprogram indicates bleeding in the intestines or anal fissure. Also, these bodies appear in the coprogram due to improper sampling or placement of the material in a non-sterile container.
The permissible norm for children from 2 to 12 years is from 8 to 109/l; a newborn has more of these bodies in the feces (as well as red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood) than older children. Of course, the norm may be slightly exceeded if the baby has recently been ill, is not eating properly or is nervous. Stress in a child occurs due to teething, fear, tense family situations, difficulties at school, etc. When teething, parents often notice changes in stool, increased irritability of the baby and drooling. But most often, a lot of leukocytes in feces is a signal of disease.
Methods for conducting stool examination at home
If a situation arises that you cannot visit a doctor, but there are suspicions of intestinal problems, then you can use express strips. Before analysis, stool is diluted with saline to form an emulsion. After this, apply a little feces to a certain area on the strip. After a while it will change color and is compared with the scale. In this way, the content of leukocytes in feces is determined if this is urgently needed for a small child. Using a chemical test, you can independently determine not only the presence of immune cells, but also bilirubin, protein, and blood.
Why does the number of leukocytes increase in a baby?
A child’s white blood cell count does not always increase due to infection. Sometimes this happens when:
- Poor weight gain. Leukocytes in the stool of an infant can be observed even with a healthy set, but this does not indicate the presence of pathologies. But when a baby does not gain weight well, experiences colic and often cries during bowel movements, most likely he has problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Impaired digestion. An immature gastrointestinal tract does not produce enough enzymes. Or it functions poorly due to long-term antibiotic therapy. Then mucus may appear in the stool.
- A certain type of nutrition. Pediatricians have noticed that in infants fed artificial formula, immune cells are less often detected than in children fed breast milk.
- The mother's consumption of allergenic foods. This could be chocolate, strawberries, eggs, fried, fatty or smoked foods. These products can cause changes in the baby's stool.
Preparing for a stool test
In order to correctly submit biological material for examination and obtain reliable results, you need to understand how to prepare for its collection. Most newborns are breastfed, so the mother needs to follow a diet for several days before the test.
It is necessary to exclude any foods that promote gas formation and increase flatulence : vegetables and fruits, herbs, meat, fish, fresh milk. To correctly determine leukocytes in the stool of an infant, you must also stop taking any medications for both mother and baby, including rectal suppositories.
The best biological material for research is feces collected in the morning after a child's sleep.
In this case, it is advisable to take it not from a diaper, which partially absorbs feces, but from a diaper. A special disposable container for collecting tests is sold along with a small spoon, with which you need to take a small amount of feces and close it tightly inside the package. It is advisable to immediately take freshly collected material to the laboratory and not store it at home . Then the results of the study will be reliable and will enable the doctor to draw correct conclusions.
Kapshukov V.N., Head of Laboratory Department, Regional Clinical Hospital, Omsk
Preparation for the analysis is an indispensable condition for the reliability of the results obtained.
Often, elevated levels of white blood cells are found in biological material that has not been collected correctly.
Studying coprogram with test strips
If a mother has doubts about the condition of her child’s intestines, she can purchase special tests to study the coprogram. A coprogram is done at any time of the day, and then, using such rapid tests, the presence or absence of leukocytes, the level of bilirubin, protein, the presence of blood and the pH reaction are determined.
Some test strips do not detect the presence of leukocytes in stool, so it is better to purchase multifunctional ones of the OctaFan type. Before analysis, prepare a fecal emulsion by diluting the feces with saline or distilled water to a slightly runny consistency. After thorough mixing, feces is applied to a corner of the reagent field and the reaction of the test is monitored. The final color of the reagent zone is compared with the color indicated on the container scale.
Test strips are used to analyze the child’s coprogram for:
- Alkali. The reaction of the coprogram should be slightly alkaline or neutral. An acidic reaction signals digestive disorders, including colitis or dysbacteriosis. With these ailments, leukocytes are often detected in the stool.
- Protein. Its presence in stool indicates damage to the stomach, duodenum, rectum or colon.
- Hemoglobin. Sometimes these tests visualize “occult blood” that was not recognized by macroscopic analysis.
- Urobilinogen and stercobilin. Often observed with dysbacteriosis and pancreatitis.
- Bilirubin. For children under 3 months of age, its presence is considered normal, since during this period a healthy bacterial flora of the gastrointestinal tract is formed. In older children, its presence signals a severe gastrointestinal pathology: severe dysbiosis or rapid food evacuation through the intestines.
- Leukocytes. Their presence indicates inflammatory processes in the large, small or duodenal intestine. The test can easily determine the intensity of the reaction. If the diagnostic zone has not changed color, the reaction to leukocytes is negative. A low neutrophil count is expressed in a lilac color. But the rich lilac color shows a pronounced reaction to neutrophils. If too many leukocytes are found in the coprogram, a re-examination is required. This is due to a possible psychological disorder of the baby or high physical activity, due to which the test determined the presence of leukocytes in the stool.
What do elevated white blood cells mean in a stool test?
A general stool analysis is otherwise called a coprogram. In this case, significant attention is paid to the number of erythrocytes and leukocytes. Leukocytes in the human body play the role of suppressing infectious diseases. Therefore, if their presence is detected in quantities exceeding normal levels, they may indicate insufficient functioning of the immune system or the development of some kind of inflammatory process.
There are a number of additional symptoms that you need to pay attention to and get tested:
- Increased fatigue and lethargy of the baby.
- Dry lips and mouth.
- Intestinal disorders and dyspeptic symptoms.
- Disorders of urination (dark color, strong odor, very often or, conversely, rarely).
- Temperature increase.
- Anxiety, frequent crying of the child.
- Allergic rashes.
These indicators may indicate reduced immunity and are a reason to take tests, including stool tests.
Diet before taking the test
Regardless of which method the study will be carried out, you should prepare for it by following a diet. Doctors recommend 2 types of diets:
- According to Pevzner. This Soviet doctor developed a number of diets for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and the rehabilitation of those who had cholecystitis and hepatitis. During the diet, the child is fed potatoes, butter, vegetables, vegetable soups, buckwheat and rice porridge, sauerkraut and apples. To improve intestinal motility, crumbs exclude meat, fish and confectionery products from the menu.
- According to Schmidt. The menu includes milk oatmeal, potatoes, eggs, milk and butter. This diet is also prescribed before coprology to check for bleeding. Then the child’s menu should not contain green vegetables, tomatoes, fish and meat.
Parents should also take into account that some medications can distort the results of coprograms. This issue should be discussed with the treating pediatrician or pediatric gastroenterologist before the analysis.
How to prepare for coprogram
In order for the analysis to be truthful and help determine the cause of the disease, the child must be properly prepared for stool donation:
- Before collecting the baby, wash, prepare a sterile container and a disposable diaper for collecting the biomaterial.
- 3 days before the intended procedure, exclude vegetables and fruits from the children's diet, leaving cereals, bread, and dairy products. During lactation, the child’s mother should adhere to such a diet.
- Avoid taking medications.
- You should not give a cleansing enema or give laxatives, or allow urine to get into the analysis.
How to lower the level of leukocytes in a coprogram
Treatment for excess white blood cells involves eliminating the cause and lowering the white blood cell level. The child must be shown to a doctor if the following symptoms occur:
- frequent fatigue and drowsiness;
- general malaise;
- increased body temperature;
- urination less often than usual with an uncharacteristic odor and color;
- quiet crying, with almost no visible tears;
- dry mouth;
- frequent diarrhea with a strong odor;
- vomit.
If a child experiences such signs, immediate consultation with a doctor is required. This is associated with an increased risk of dehydration and even death!
By contacting a doctor in a timely manner, taking tests and immediately starting to treat the child, parents increase the chances of a good prognosis for the disease and rapid recovery of the baby’s body. The doctor prescribes treatment with Lactazar, Acipol, Bifidumbacterin, Linex or other drugs. It is only allowed for children over 3 years of age and adults - infants have hearing problems.
It is also impossible to treat with prescribed medications for too long - dysbacteriosis may occur. But you cannot prescribe or cancel medications on your own - such actions are performed only under the close supervision of a doctor. Incorrect treatment can only make the situation worse.
Study parameters
Stool examination can provide information about diseases of many gastrointestinal organs.
When conducting a coprogram, stool is studied according to several parameters. Firstly, the feces are examined and even the characteristics of the smell are determined. Externally, the following can be determined:
- color;
- consistency;
- smell;
- pathological impurities in the form of blood, mucus, parasites, undigested food.
Secondly, microscopy is determined:
- red blood cells;
- fibers;
- leukocytes;
- crystals.
Thirdly, the chemical composition indicators are determined:
- fats;
- proteins;
- hemoglobin;
- pigments.
The obtained indicators are compared with the norm. If deviations are detected, certain diagnoses related to damage to internal organs are made. You can get information about problems with the stomach or intestines, pancreas or liver.
Norm of indicators
After examining the stool, we can draw a conclusion about the health status of the subject.
Having received a set of indicators after analysis, the specialist compares the result with generally accepted standards.
Based on the set of existing discrepancies, the specialist can draw a conclusion about the health status of the subject. According to external criteria, the norms are as follows:
- consistency is formed (soft/compacted);
- Brown color;
- the smell is mild, specific, usual for feces;
- cylindrical shape.
All unnatural impurities must be absent. Only particles of plant origin are allowed, for example, the skins of fruits and vegetables. They are poorly digested and some are not digested at all.
The general reaction of feces is normally neutral. When studying the material, the presence of hidden blood, protein, bilirubin, and stercobilin is revealed. Only the last component should be in the feces - stercobilin. Thanks to this substance, stool turns brown. There should be no other components. Blood and protein indicate abnormalities.
Microscopic analysis examines how food is digested. If everything is normal, then muscle fibers, connective tissue, neutral fats, red blood cells, fatty acids, and starch will not be found. If a person eats only meat, then there may be individual pieces of muscle fibers.
Single leukocytes, which are said to be “in sight,” are considered normal. Mucus in small quantities and a little bit of epithelium are acceptable. Of course, there should be no parasites in any form, and mushrooms should also be absent.
If even a minimal number of Giardia cysts, amoebas and others are detected, this will be 100% confirmation of parasite infection.