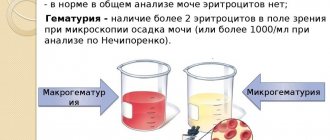
Sometimes tests indicate salts in the child’s urine, the volume of which has become increased. Urine is a liquid that comes in the form of a saline solution, and the salts can begin to crystallize under certain conditions. By the number of these crystals one can judge what the state of the body is and whether there are pathological changes. It should be taken into account that salts can form in a child’s urine due to poor nutrition, so it is imperative to do several screening tests.
To determine whether there are salt crystals, you need to do a general urine test. In addition, in order to establish their type and group, it will be necessary to additionally analyze the function of stone formation. A child may have oxalates, phosphates, urine, residual substances from ammonium uric acid, salts from hippuric acid, and calcium sulfate in the urine.
What salts can be detected
Salt crystals in a child’s urine are specific chemical compounds that have nothing in common with the salt that we are used to seeing in the kitchen.
Such substances are classified according to their composition. They can pile up, “sticking together” with the help of protein. In this way, concretions are formed - more massive formations known as stones. As a rule, three types of salts are found in urine:
- Oxalates
They are most often present in urine. There are many reasons for the appearance of oxalates - kidney inflammation, urolithiasis, poor diet, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, etc. Metabolic processes associated with oxalic acid are of great importance. As for children, the appearance of oxalates in them is mainly associated with excessive consumption of foods rich in oxalic acid - these are various greens, cocoa, chocolate, apples, citrus fruits, radishes, ascorbic acid.
Oxalates are most often present in urine
- Urats
The appearance of urates is associated with an increase in the concentration of uric acid. Its sediment gradually crystallizes, which is why these substances are formed. The reason is a violation of the metabolic process of purines. The pathology has a pronounced symptom - this is the coloring of urine in a reddish-brick hue.
The appearance of urates is associated with an increase in the concentration of uric acid
As with oxalates, diet plays a significant role here too. It is not advisable for a child to overuse meat dishes, mushrooms, fish, and legumes. The same goes for excessively strong tea, chocolate, cocoa and smoked foods. Significant physical activity, frequent diarrhea, dehydration, fever, and urinary diathesis can also provoke the formation of urates.
- Phosphates
These formations appear due to an increase in urine alkalinity. At the same time, the acidity of urine decreases. This situation can also occur in healthy children. Therefore, if a child has crystals in his urine, and these are phosphates, then such a phenomenon may not always indicate any disease.
Typically, the main cause is excessive consumption of foods containing phosphates. These include:
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- fish (especially fatty);
- eggs;
- buckwheat;
- various cereals;
- caviar;
- alkaline mineral waters.
Phosphates appear due to an increase in urine alkalinity.
If phosphates are found in a child’s urine, you should immediately eliminate or reduce the consumption of these foods. However, the reason may lie elsewhere - such a sediment is characteristic of a feverish state, hyperparathyroidism, vomiting, cystitis, and also after gastric lavage.
Treatment
If salts are found in the urine of a breastfed child, this may indicate not only pathologies in the baby, but also problems in the mother’s diet. Therefore, treatment should begin only after a series of tests have been performed, the results of which can only be interpreted by an experienced specialist. If tests indicate the presence of a certain disease, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. If no pathologies are identified, you can limit yourself to only adjusting the daily diet.
Less common types of salts
The salt deposits that occur most often were listed above. But other salts can be found in the urine of children, less common, but no less dangerous.
| Type of salt | What is this |
| Calcium sulfate | Such impurities may appear due to excessive consumption of certain berries and fruits, such as lingonberries, blackberries, apricots or watermelon. A provoking factor can also be the ingestion of salicylic and benzoic acid. Diabetes mellitus significantly increases the risk of calcium sulfate in urine. |
| Ammonium urate | Excessive content of these salts is provoked mainly by urolithiasis. Also, one should not exclude the possibility of a uric acid infarction that develops against the background of birth stress. |
| Hippuric acid | There are a lot of reasons for this. Salts of hippuric acid are often found in urine during long-term use of antipyretic drugs, various liver diseases, and diabetes mellitus. At risk are children who consume plant foods too often and also suffer from kidney stones. |
Symptoms of education
As a rule, large phosphate stones are not discovered by chance - they are always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The formation of tripelphosphate stones is fraught with deformation of the inner surface of the ureters. You can find out about such damage by drops or blood clots that appear in urine from time to time. With infectious diseases of the ureters and kidney pathologies, urination becomes difficult, accompanied by pain, and the urine thickens. One of the signs of struvite formation is a stagnant odor from urine.
Small crystals stick together, forming phosphorus stones against the background of the participation of harmful microorganisms and infectious agents, so the condition is usually accompanied by the following clinical picture:
- hyperthermia, fever, chills, perspiration;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - vomiting, nausea, poor appetite;
- apathy, fatigue, weakness;
- dull, nagging pain.
One of the frequently occurring symptoms accompanying the formation of tripelphosphates is excessive fluid intake. Such obvious thirst often leads the patient to an endocrinologist due to fears of developing diabetes mellitus. However, test results show an increase in the number of phosphates, and the specialist refers the patient to a nephrologist.
Excessive fluid intake is the first symptom of tripelphosphate formation
Problems with urination also become a sign of tripelphosphates - usually urination is difficult and infrequent. If the stones are large, the renal pelvis and calyces expand, and urine output decreases. Due to stagnation of urine, the functions of the kidney parenchyma are lost. Hydronephrosis leads to dangerous conditions, so urgent consultation with a doctor and measures to eliminate the problem are necessary.
What do oxalates mean?
Oxalates are salts that are most often detected in urine:
- when eating dishes and products enriched with vitamin C and oxalic acid (parsley, spinach, sorrel, beets, celery, citrus fruits, radishes, currants, sour apples, ascorbic acid, rose hips, cocoa, chocolate, broths);
- with a congenital failure in the metabolism of oxalic acid, manifested in the form of urolithiasis or inflammatory kidney damage;
- with pyelonephritis;
- for diabetes mellitus;
- with ulcerative colitis;
- with inflammatory bowel disease;
- in case of poisoning with ethylene glycol (for example, antifreeze or brake fluid).
Oxalate crystals often damage the mucous membrane, causing urinary tract irritation and microhematuria. That is why, if they are detected in urine test sediment, it is recommended to include in the child’s diet:
- drink plenty of water (at least a liter of water per day);
- dishes and food products that contain magnesium (squid, herring, millet, seaweed, oats);
- B vitamins (in particular vitamin B6).
Features of salts in the urine of children
Today, salt deposits in the urine are found quite often in children. When a doctor communicates such a diagnosis to parents, they usually have little understanding of what they are talking about. Because of this, unnecessary panic arises or, on the contrary, excessive calm, since such a verdict in itself does not look frightening.
And in fact, salts in the urine of an infant or even older are considered normal from a medical point of view. This diagnosis means that small crystals of various salts were found in the secreted fluid. Their presence can be explained very simply - children's kidneys are still not working at full capacity, and therefore they are not always able to effectively dissolve salts that enter the body with food. Some foods contain more of them than others, so diet is also important.
It is worth noting that using one analysis it is almost impossible to accurately determine whether there are crystals in children’s urine. They may not be present on an ongoing basis, that is, the second analysis will already show that the urine is absolutely clean. But if several tests have shown that salt deposits are constantly being released, it is imperative to take the baby for a detailed examination of the urinary system, as well as the gastrointestinal tract. It is likely that a specific renal pathology will be diagnosed, such as dysmetabolic nephropathy.
Attentive parents will be able to see that something is wrong with their child’s urine even with the naked eye. Naturally, crystals cannot be detected, but their presence is indicated by the lightish turbidity of the urine. This is not yet a reason for panic, but rather the opposite, since such a phenomenon indicates that the kidneys are properly coping with their responsibilities, preventing the gradual formation of concretions, that is, stones.
Problem Definition
Tripelphosphates are stones formed by calcium salts of phosphoric acid, formations that practically do not manifest themselves in terms of symptoms, but are clearly visible on x-rays. Phosphate is a smooth calculus, without sharp edges, so its movement through parts of the urinary system is not accompanied by tissue damage and, therefore, a characteristic symptom - bloody inclusions in the urine.
Crystallized tripelphosphate salts in the urine indicate the need to consult a doctor as soon as possible, as they are very aggressive formations. The only positive point is that the stones have a rather fragile structure, so they are relatively easily destroyed by crushing (lithotripsy).
Causes of salts in the urine of a child
Each type of salt that can be found in children's urine has its own reasons for its occurrence. As mentioned above, oxalates almost always indicate some kind of disease or acid metabolism disorder. In general, the following reasons may affect their appearance in urine:
- renal failure;
- stomach ulcer;
- pyelonephritis, nephritis and other infectious and inflammatory processes of the kidneys;
- inflammation in the intestines;
- acute ingestion of chemicals entering the body orally;
- oversaturation with vitamin C;
- diabetes.
As for urates, they are traditionally diagnosed against the background of severe dehydration of the body. Very often, such salts are present in the urine of those children who are subject to severe sweating (for example, after intense physical activity), vomiting, fever or diarrhea - that is, processes in which a sudden loss of moisture occurs. Also at risk are children who are too fond of a variety of meat products.
But the main provoking factor is foods containing purine compounds. Their excessive consumption leads to disruption of purine metabolism in the child’s body. Every parent should know that it is necessary to strictly control the amount of the following foods in their children's diet:
- smoked meats;
- meat broth, meat;
- legumes;
- sprats;
- mushrooms;
- sardines;
- strong tea.
Phosphates are detected for both completely harmless and pathological reasons. In the first case, we need to talk about excessive consumption of foods that are initially rich in phosphorus. This includes buckwheat, fish, milk, even mineral water. If this is so, and the body is simply oversaturated with this substance, then the presence of phosphates in urine will be one-time.
However, if they are diagnosed on an ongoing basis, then this is already an alarming symptom. Most often, this situation can be provoked by very serious diseases:
- cystitis;
- Fanconi syndrome;
- hyperparateriosis;
- other infectious and inflammatory processes in the urinary system.
Rarely, but there are still cases when the appearance of phosphates in the urine is provoked by fever or vomiting. At risk are children who often undergo gastric lavage - this washes out important microelements involved in alkaline metabolism.
If salts appear in the child’s urine, you should definitely visit a doctor. It is quite possible that the reason lies in the usual overeating of a certain provoking food. But still, in no case can we exclude the possibility that the baby’s body is affected by some kind of infection or inflammatory process.
649
We recommend that you read
Symptoms of diseases Read more » Increased level of urobilinogen in urine: what does this mean? 2,836
Symptoms of diseases Read more » Why urine smells like acetone 1 955
Categories
- Inflammation of the kidneys Nephroptosis
- Pyelonephritis
- Urine and blood tests
Recent Entries
- Is it possible to donate urine during menstruation for tests and how to do it correctly
- Diet for kidney inflammation - what you can and cannot eat
- Diet for renal colic - what you can and cannot eat
- Computed tomography of the kidneys using a contrast agent. Features and nuances
- Diet for urolithiasis in women and men
Uraturia Salts in the urine of a child
Uraturia or uric acid diathesis is increased formation and excretion of uric acid or urate crystals in the urine.
Uraturia is often hereditary and in adults develops into a disease called gout, which is characterized by the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints. In children, a hereditary tendency to increased urate formation is called neuro-arthritic diathesis.
Causes of uraturia
- Hereditary predisposition
- Poor nutrition, excess in the diet of foods rich in purines: meat, offal, broths, chocolate, cocoa,
- Long-term use of certain medications (cytostatics, diuretics).
Diet
Completely excluded from the diet
- offal: liver, kidneys, brains, liver, sausages, broths
- meat of young animals,
- fatty fish,
- soybean,
- strong tea, coffee, chocolate.
Boiled lean fish and meat are allowed only in the morning 2-3 times a week.
Liquid dairy products, vegetables, fruits, melons, cereals, pasta are recommended.
The drinking regime is the same as for oxaluria. Urates are formed in an acidic environment, in concentrated urine, so it is recommended to dilute and alkalize the urine, as with oxaluria and drink alkaline mineral water.
Medications
There are medications that lower the level of uric acid in the blood. These are allopurinol, apurin, ciloprim, ciloric, milurite. They are prescribed in courses of 2-3 weeks, 3-4 times a year.
The drug benzobromarone (normurat, urikovac, hipuric) is prescribed for a course of 5 days, then a 7-day break and again for 5 days, for 1-2 months.
Herbal medicines include oat decoction and flax seed decoction.
Diet for uraturia
If there is a problem such as uraturia, then you need to limit protein in your diet.
For example, you will have to give up meat, fish and cottage cheese dishes. It is also necessary to completely exclude from the diet all foods that are high in uric acid. It is allowed to eat boiled or steamed meat, but no more than 3 times a week. It is recommended to follow a diet based on cabbage and potatoes a couple of days a week. Before eliminating any foods, you should additionally consult with a nutritionist and nephrologist. This is due to the fact that a child’s growing body needs protein, and it cannot be completely eliminated. It is best to limit the consumption of carrots, legumes, onions, tomatoes, and corn. You are allowed to drink strong tea, but in small quantities.
Among berries and fruits, you need to monitor the consumption of gooseberries and strawberries. You will have to limit salt, butter, liver, poultry, beef, and fish. It is forbidden to eat a lot of egg yolks.
Be sure to eat at least a little cabbage, dried apricots, prunes, and fruits every day. You can use seaweed. Wheat bran will be useful. Rye and wheat bread are allowed as bread products, but they must be made with wholemeal flour.
Even if the content of salts of this type is increased, then three times a week you can give your child 100-150 g of meat or fish, but they should not be fatty. Moreover, you can give such products only before lunch. But you need to avoid fatty broths, canned food, pates, smoked meats and offal. Bananas, tangerines, chocolate and honey are prohibited.
What other salts can be in urine
- Calcium sulfate. Calcium sulfate in the urine of children is extremely rare. Why can this happen in the human body? This is mainly due to diabetes. The reason may be that the person has eaten too many foods that are rich in salicylic acid. For example, these are melons, blackberries, apricots and blueberries. If you eat lingonberries, you will have the same effect, since they contain a large amount of benzoic acid.
- Salts of hippuric acid. The salt of hippuric acid in the urinary fluid may appear due to diabetes mellitus, nephrolithiasis, and liver pathologies. If you eat a lot of lingonberries or blueberries, which contain large amounts of benzoic acid, the same effect will be achieved. Salt compounds of hippuric acid will be increased due to fermentation processes and the formation of pus in the intestines. Another reason is an overdose of drugs that have antipyretic properties.
- Ammonium urate salts. Sometimes salt compounds of ammonium urate can also be found in the urinary fluid. In an infant, this is associated with uric acid infarction. The reason may also be the presence of kidney stones.
Treatment of such pathology will be carried out using complex therapy. First you need to do repeated tests to confirm the exact presence of salts. If the patient has salt-type nephropathy, then a number of drugs are prescribed that can be used only if the analysis revealed an excess of the norms of certain groups. For example, for oxalates you need to use pyridoxine. Additionally, vitamins A and E are prescribed. Magnesium oxide will be needed.
If the salt (phosphate) content is increased, then medications are used that can inhibit the production of gastric juice. If urate levels are elevated, medications are prescribed that affect salt metabolic processes. To avoid this problem, you need to monitor your diet. Nutrition should be correct, balanced and complete, which will help enrich the body with useful substances. In addition, children should be active, they should walk in the fresh air more often. The diet is prescribed differently each time, depending on which group of salts will have higher values. If several types of salts have higher parameters, then the doctor selects an individual diet for the baby.
Symptoms
Struvite is not discovered by chance. The formation of these stones is preceded by significant pain symptoms, as the lining of the urinary ducts changes. Symptoms of severe damage are the presence of blood impurities in a portion of excreted urine. Accompanying the formation of phosphate stones are infectious processes and other types of pathological conditions in the kidneys. One of the characteristic signs of the presence of salts of this type is the smell of stagnant urine.
In addition, experts note that in patients with tripel phosphates detected in tests, other types of pathologies are often found:
- Disturbances in the digestive tract - nausea, eruption of gastric contents, refusal to eat.
- Presence of fever, chills, cold sweat, increased body temperature
- Severe fatigue, depression.
- Painful sensations in the abdomen, aching and dull.
It is also noted that with this type of pathology, there is strong thirst. So, in some cases, an increased desire to drink can be attributed to manifestations of diabetes mellitus, and an unplanned trip to the endocrinologist. Doctors have noticed that there is also a disturbance in the process of urination.
Standards for children of different ages
In order for the results of a child’s urine test to be reliable, it is important to thoroughly clean the external genitalia before collecting it. Sometimes the urine that mom collected from the pot may also contain foreign impurities that distort the overall picture
The standard amount of salts can be found in the table below. Some indicators depend on the child's age, as well as what he ate the day before.
| Name of salt | Up to 1 year | From 1 to 4 years | Up to 8 years | Up to 14 years old |
| Uric acid (urate), µmol/l | 0.35-2 | Up to 2.5 | 0.6-3 | 1.2-6 |
| Phosphates, mg per kg per day | Up to 30 | |||
| Oxalates, mg per day | 8-17 |
Often, salts in the analysis are not displayed as numerical values, but rather use symbols in the form of pluses. For example, if the analysis shows traces of oxalates or phosphates, the laboratory technician will write “+”, “++”
It is worth paying attention to this indicator, but it is not critical. According to experts, 2 pluses are a variant of the norm
If there are 3 or 4 pluses, then you should take the test again and undergo additional examination.
Diagnostics
This is done through a general urinalysis. The number of crystals can also be counted in the Goryaev chamber (similar to the standard Nechiporenko test for erythrocytes, leukocytes and casts), but this technique is not widely used. There is also research on salt transport.
General urine analysis
The test is carried out for children of different ages - it can be used to assess how an infant or a patient older than one year feels. It allows you to check indicators such as:
- pH;
- specific gravity;
- protein;
- glucose;
- red blood cells;
- leukocytes;
- cylinders;
- epithelium;
- unorganized sediment in the form of salts.
The urine sample is centrifuged, after which the preparation prepared from it can be examined on a glass slide under a microscope. The laboratory technician sees whether there are crystals or not, and gives a so-called qualitative answer: “detected” or “not detected.” The type of salt must be indicated.
There is also a content rating in pluses:
- “+” – single salts in the field of view.
- “++” – more than average content, there are accumulations.
- “+++” – a lot of crystals.
- “++++” – they cover the drug, sometimes so tightly that they interfere with a full view.
It is important to know! This technique is called semi-quantitative, since the result is approximate and assessed “by eye”. At the same time, it is a fairly good guide for the doctor reading the test data. It is worth knowing that different types of crystals can be found in one sample.
Transport of salts
This test is used in cases where there is a high risk of developing urolithiasis. In patients who have already been diagnosed, the test allows one to assess the quality of therapy and prevent complications.
Biomaterial used:
- deoxygenated blood;
- daily urine.
Salt transport is a test to detect metabolic disorders. This is not only urolithiasis, but also various metabolic nephropathies, or diathesis, often found in childhood. The interpretation is carried out in conjunction with other studies.
Indicators are determined in the blood:
- calcium;
- uric acid;
- phosphorus.
Urine is used to assess the level of acidity, that is, pH, as well as for tests for the content of oxalates, calcium, and phosphorus. Research is carried out using hardware techniques, which makes it possible to determine the exact concentration of the substances being determined.
Preparation rules
Urine is submitted for analysis:
- One time for a general test - in the morning, after a night's sleep.
- Daily - collected within 24 hours, stored in the cold.
- Not consuming coloring foods (carrots, beets) the day before.
- Before diagnostic and therapeutic procedures (X-rays, physiotherapy, punctures).
You need a clean, dry container (preferably a disposable pharmacy one). Before collection, it is necessary to carry out hygiene of the urethral area. In children of a younger age group, the material is obtained by attaching a sterile urine bag to the area of the external genitalia.
Blood from a vein is donated on an empty stomach in the morning (for small children it is worth checking the interval between feedings with the pediatrician in advance). You are allowed to drink water - but only clean water, without gas, dyes, or added sugar.
Types of salts and why they appear
You shouldn't panic right away, but high salt levels may be a sign of increased kidney function, which precedes the appearance of stones. In this case, parents need to make sure that their child undergoes all the necessary medical tests to identify the reason why salts in urine are contained in excessive quantities. Often, sediments of salts such as oxalates, phosphates and urates are detected in urine.
Causes of oxalate formation
The top spot on this list belongs to oxalates. The reasons for their excess may lie in metabolic disorders, in which oxalic acid plays a special role. At the same time, active absorption of this acid occurs in the baby’s intestines, resulting in the appearance of salt in urine, the so-called calcium oxalates.
This condition of a child quite often develops against the background of urolithiasis or other kidney diseases of an inflammatory nature, such as nephritis, pyelonephritis, even renal failure. When urinating, oxalate crystals of salts in a child’s urine can cause a burning sensation, pain or stinging. In addition, hard crystals of these salts can damage the kidneys themselves.
Why are phosphates formed?
The reasons for the presence of phosphate salts in urine may be the excessive consumption of foods that contain significant amounts of phosphorus (milk, fish, caviar, buckwheat, mineral water, etc.).
Constant detection in indicates an alkaline reaction, cystitis or Fanconi syndrome. In addition, the presence of phosphate salts in urine occurs during a fever, vomiting or gastric lavage.
Reasons for the formation of urates
As is known, urates contain uric acid and salt deposits. They are often elevated due to certain pathological conditions. This substance in urine looks like a brick-red sediment.
A high urate content can occur when consuming significant amounts of meat products, as a result of physical stress, excessive sweating, which causes dehydration of the child’s body, vomiting, abnormal bowel movements, or a feverish state.
Surely every parent will be interested in why there may still be an excess content of urates in the child’s urine. This may be due to the consumption of smoked foods, strong tea and mushrooms, hard water, as well as iodine and fluoride deficiency. However, the presence of urates in children's urine may be a sign of pathological conditions such as gout and leukemia.
Urats
Urates are sodium and potassium salts of uric acid that have precipitated. The appearance of these salts, as a rule, signals a violation of purine metabolism, that is, the absence of purine-containing products in the diet.
The presence of urates can be determined visually, as they have a brick-red hue.
Reasons for appearance:
- Consumption of foods containing uric acid in the diet (brewer's yeast, meat, fish broths, pork and sheep spleen, legumes, sprats, smoked sprat, sardines, herring, porcini mushrooms);
- Excessive physical activity;
- Uraturia;
- Fever;
- Leukemia;
- Dehydration (diarrhea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis);
- Nephrolithiasis;
- Uric acid diathesis in infants;
- Gout;
- Iodine and fluoride deficiency;
- Drinking hard water.
Urates in the urine can cause changes in the general condition of the child’s body:
- Loss of appetite;
- Nervousness, fears;
- Stomach ache.
Urates in urine under a microscope
Elimination of salts
If an increased content of salt deposits is detected in a urine test, therapy is required to remove the accumulations from the body. For this, complex therapy is used, including diet correction and drug therapy.
Diet
Dietary changes depend on the type of salts found in children's urine. In accordance with this, the following recommendations are made:
- An increase in oxalate content in urine requires compliance with the drinking regime. It is recommended to increase the amount of fluid consumed. The diet includes various cereals, vegetables, and seafood. Chocolate, concentrated broths, sorrel, celery, and parsley are excluded from the diet. You should not eat foods containing ascorbic acid.
- Urates require drinking enough water. To remove these salts from the child’s body, it is necessary to include fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and eggs in the diet. You should limit your intake of meat, strong tea, coffee, fish, offal, and chocolate.
- Detection of an increased level of phosphates in the urine is an indication for limiting the consumption of high-fat fermented milk products, fish, eggs, cheese, and sour cream.
Drug treatment
Changing your diet is the main treatment for this condition. After its correction, they resort to taking medications. Prescription of medications is based on the number of crystals detected, as well as their types. Depending on this, the following drugs are prescribed:
- With a significant increase in the amount of urate, it is recommended to take herbal preparations that have a diuretic effect. These include Canephron, Urolesan, Fitolysin. The average duration of treatment is 1 month. After which a repeat urine test for the presence of salts is required.
- Phosphates are eliminated from the body with the help of vitamin D. It is a proven fact that sufficient vitamin D content helps to get rid of phosphaturia. In addition, this method is used to combat oxalaturia.
- It is recommended to reduce excessive oxalate levels by taking vitamins A, B6, and E.
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of large amounts of salts appearing in a child’s urine, it is necessary to follow certain rules. These include:
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet. Food should be enriched with vitamins, minerals, micro and macroelements
It is important to maintain a drinking regime. It is necessary to consume enough fluid per day
The diet should be selected taking into account the type of salt crystals. First, it is necessary to diagnose them, after which the doctor will select the necessary diet. Limiting the intake of foods that can increase salt levels in urine.
The appearance of salts in a child’s urine requires a thorough examination and dietary adjustments. Eating a balanced diet will reduce the risk of this condition.
How to prevent pathology in the salt composition of urine?
In a child, the mechanisms of compensation and protection are poorly expressed. Therefore, the loss of water through sweating, vomiting, and diarrhea leads to changes in the concentration of substances dissolved in the urine. Such conditions must be accompanied by an increased drinking regimen.
Parents need to organize the baby’s nutrition in accordance with his age, and older children should not be allowed to drink carbonated water or eat fast food or chips.
If the doctor has prescribed a control urine test, then you should take it and make sure there is no pathology and the results of the treatment. Breastfeeding women need to remember the harm caused to the baby by not eating properly. Adults are responsible for the health of children. The physical development and future of the child depends on the results of a proper diet.
Why does a child have a strong smell of urine?
Newborn babies, feeding only on mother's milk, pee up to 25 times a day, their urine has virtually no odor. When a child begins to receive complementary foods, the urine gradually acquires a characteristic aroma. The older the child gets, the more the bladder secretions smell like an adult's. So, the urine of a baby and someone who is already 2 years old will smell very different.
Urine has characteristic physical properties:
- color;
- transparency;
- smell;
- density.
Normally, urine in children has a specific smell, but not sharp, this smell does not cause unpleasant sensations. Dr. Komarovsky writes that some diseases can change the smell of urine, especially diabetes, in the presence of which the discharge takes on a fruity aroma.
Ammonia smell
The strong smell of urine in a child causes concern among parents, especially if the aroma of ammonia is clearly audible. The first step is to rule out diabetes by taking a blood glucose test. If your baby is constantly thirsty, his skin becomes dry, or he loses weight, be sure to have your child checked by a specialist.
Smell of acetone
Urine smells like acetone if there are a lot of ketone bodies in the blood, which then enter it and are excreted from the body. This phenomenon is called ketonuria. The cause of this disease may be:
- stress;
- significant physical activity;
- long pause in nutrition;
- dehydration.
Children aged 2-3 years especially often suffer from ketonuria; as they grow older, the child is less susceptible to it.
To avoid the appearance of acetone in the urine, protect your child from major emotional shocks, do not allow heavy physical activity, and follow a diet and drinking regime. Komarovsky advises parents to give their child sweet drinks if they see that the child is at risk of ketonuria, or it has already begun.
If you have any suspicions, buy test strips at the pharmacy that will confirm or deny the presence of the disease.
The smell of rotten fish, cabbage, mice, burnt sugar
The urine of people with the genetic disease trimethylaminuria has an unpleasant fishy odor. With this disease, the discharge (sweat, exhaled air, urine) smells like fish. This smell accompanies a sick person throughout his life.
Also, a genetic malfunction (tyrosinemia) causes the cabbage smell of urine. The aroma of mold and mice indicates phenylketonuria. The urine of a patient with leucinosis smells like burnt sugar.
Factors influencing changes in urine odor:
- Violation of the drinking regime. If a child drinks less than usual, or loses fluid through sweat in hot weather, or vomits due to upset bowel movements, the urine becomes concentrated and smells stronger. Provide your baby with enough fluids and everything will work out.
- Food. The smell of urine directly depends on what the child ate. It smells unpleasant to a child who is allowed to eat fast food, too fatty and sweet foods. Seafood, horseradish, garlic, cabbage, and asparagus also change the smell of urine. Irregularities in the diet of a nursing mother also affect the aroma of the infant's urine.
- Taking medications. Some medications can change the smell and color of urine; this is usually indicated in the instructions. Most often, this side effect occurs with antibiotics, because they radically change the microflora of the body.
- Inappropriate diaper. Children's skin is very sensitive, so not every brand of diapers is suitable for a particular child. If in the morning, when changing a diaper, you hear an unpleasant odor, first change the manufacturer.
- Rickets. In children under one year of age, a lack of vitamin D can affect the change in the smell of urine. Other symptoms will also be present: sweaty palms, restless sleep, poor appetite and others.
- Infections of the genitourinary system. Cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis and other diseases sometimes cause parents to notice changes in the smell of their child’s urine.
- Diabetes. In patients with this diagnosis, the urine becomes discolored, the number of urinations increases, and the odor resembles that of ammonia or apple cider vinegar.
- Hepatitis. Parents notice not only the unpleasant smell of children's urine, but also its dark color.
What should parents do if they notice an unusual odor in their child’s urine?
If you heard a strange smell from the discharge in the morning, but in the evening you no longer detect anything, then there is no need to worry. Most likely, the child ate something that affected the smell of urine, or did not drink enough fluids. Keep an eye on the baby
a couple of days to make sure everything is ok.
As you can see, unpleasant urine odor can be either harmless or a sign of serious health problems. Be attentive to such changes!
Crystalluria in pregnancy
Salts in urine appear quite often during pregnancy. This is usually associated with toxicosis, in which nausea and vomiting are observed. This condition can cause a lack of fluid in the body and, as a result, thickening of the urine and excessive formation of salts. Some pregnant women, during toxicosis, change their taste preferences and develop intolerance to certain foods. An unbalanced diet affects the electrolyte composition of urine. In pregnant women, crystalluria is also associated with increased levels of progesterone in the blood; this hormone relaxes the urinary tract, slowing down the flow of fluid.