MRI of the shoulder - features of the procedure
Magnetic resonance imaging is a technique for obtaining images of organs that involves the use of nuclear magnetic resonance phenomena. During the procedure, the patient is placed in a device where the shoulder is exposed to a magnetic field. The body contains hydrogen in varying concentrations, depending on the density of the tissues. In a magnetic field, the protons of an element change their charge and orientation in space, which is detected by highly sensitive sensors.
This diagnostic method visualizes all components of the shoulder joint:
- bones;
- ligaments;
- tendons;
- capsule;
- muscles;
- cartilage.
MRI allows you to detect absolutely any pathology, regardless of its origin - degenerative, inflammatory, infectious, tumor, destructive, traumatic. The image will be formed by the device into a three-dimensional image and transferred to a computer medium, after which it will be examined by a doctor on a monitor or from photographs. Based on the morphological changes found in the shoulder, the specialist will make a conclusion and make a diagnosis, identifying the extent and severity of the damage. The result is given to the patient in the form of pictures, a description of the problems on paper, and in some cases, additionally on a disk or flash drive.
Absolute contraindications and restrictions
Examination with a tomograph is permitted only if there are no contraindications. They are divided into absolute and relative. The procedure is not performed in the first trimester of pregnancy, in case of mental problems and the presence of the following metal objects or devices in the body:
- artificial heart valve;
- pacemaker;
- brain and spinal cord stimulators and most other implanted electrical devices;
- insulin pumps and pumps for other medications;
- certain types of ventriculoperitoneal shunts;
- cochlear implants;
- Foreign metal bodies in soft tissues, such as the eyes, abdomen, or chest.
Relative contraindications:
- presence of claustrophobia,
- prosthesis,
- tattoos with paints containing metal oxides,
- stents in blood vessels,
- contraceptive IUDs.
Anti-anxiety medications usually help with claustrophobia. However, it should be noted that after taking such drugs you should not drive. So that doctors can determine before the study whether magnetic resonance imaging can be performed if there is an implant in the body, it is necessary to provide detailed information about it: where and in what year it was made, from what material, etc. d.
If you have kidney disease, then this is a reason to analyze the safety of using a contrast agent.
Advantages of the examination
MRI of the shoulder is prescribed by doctors quite often, because this procedure provides the most complete information about the patient’s health compared to radiography and ultrasound. The images of soft tissues - cartilage, ligaments, etc. will be especially clear, which makes the method indispensable for many diseases. However, bone structures will also be reflected in the images, although not in as much detail as with a CT scan.
MRI of the shoulder joint has a number of other advantages:
- Non-invasive. Unlike arthroscopy, tomography does not require incisions, punctures, or anesthesia (only in some cases for strict indications).
- Harmlessness. Compared to CT and radiography, this procedure does not result in the appearance of ionizing radiation, which negatively affects the body.
- Data completeness. In one study, you can obtain information about an entire anatomical zone and identify all possible pathologies. When using contrast, it is also possible to assess the condition of the patient's blood vessels.
- High quality. MRI images reflect the condition of the joint much better than the classic method - radiography. That is why the procedure is especially indicated before surgery, when highly accurate data are required, or in the presence of incomplete data obtained from other diagnostic methods.
Contraindications
Despite the complete safety of this procedure, MRI of the brachial plexus has a number of contraindications that make it impossible. These include:
- the presence of non-removable devices, such as pacemakers, implants, heart valves;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- the presence of tattoos made using inks that contain metallic substances.
MRI is the most accurate diagnosis, which allows you to detect a wide range of pathologies and helps you choose the right strategy for further treatment.
Indications for use
MRI of the shoulder is considered a highly informative procedure that has different indications.
Most often, MRI is performed in patients with long-term, progressive symptoms on the side of the shoulder joint:
- impaired mobility - during flexion, extension actions;
- pain when moving, in the morning or at night, at rest, during physical activity;
- edema, swelling in the joint area;
- crunching, clicking when changing body positions;
- any discomfort in the shoulder.
The examination helps not only to find various diseases, but also to establish their cause. Detailed diagnosis is very important, because both arthrosis, arthritis, and tumor processes can provoke similar sensations. Using MRI, a doctor can monitor the condition of the shoulder joint in operated patients who have had an endoprosthesis installed. It is also performed to control the healing of bones and soft tissues.
Tomography of the shoulder is often recommended for complex injuries - it allows you to identify damage to the biceps, labrum, cartilage, other structures, damage to blood vessels and nerve nodes. In childhood, in addition to injuries, examination is done for congenital abnormalities in the structure of the shoulder joint.
Indications
MRI of the shoulder joint is a highly informative procedure. With its help, you can detect even the slightest damage - a violation of the integrity of the rotator cuff, a biceps injury, damage to the labrum, etc. An MRI of the shoulder joint is performed for the following indications:
- degenerative changes in the joint, such as arthrosis or glenohumeral periarthritis;
- violation of the integrity of articular elements;
- rotator cuff pathologies;
- impingement syndrome;
- osteochondropathy;
- congenital abnormalities;
- violation of the integrity of ligaments and tendons;
- infectious lesions of the shoulder (for example, osteomyelitis);
- sports or occupational injuries;
- tumors of soft tissue or humerus;
- internal bleeding;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- damage to the nerve plexus;
- reduction in range of motion;
- pinching of the nerve endings of the cervicobrachial region;
- habitual dislocation;
- pain, the causes of which cannot be determined by other diagnostic methods.
In addition to specific pathologies that prompt doctors to do an MRI of the shoulder, the study is also carried out if necessary to monitor the treatment of patients. For example, they look at the survival rate of prostheses, fracture healing, etc.
REFERENCE. A type of MRI is magnetic resonance arthrography. With this type of diagnosis, a contrast agent is injected into a large vessel or tissue. The anatomy of the shoulder is better visualized; bleeding, pinched vessels, and circulatory deficiency can be seen.
The substance gadolinium is used as a contrast agent. Contrast is especially informative in tumor processes. It helps to establish the presence of metastases, the connection of the tumor with neighboring tissues, and determine the blood supply of the tumor.
Preparation for the procedure
No special preparation is required before an MRI of the shoulder. This procedure does not depend on food intake, because it is not performed on the abdominal organs.
Before the test, the patient will be asked:
- remove any jewelry;
- remove hairpins and headbands from hair;
- remove removable dentures, if any;
- remove glasses, belts with buckles;
- remove keys, cards, and other metal and magnetic products from pockets.
These objects can disrupt the structure of the image that is obtained in a magnetic field, and the picture will be damaged. When performing an MRI of the shoulder joint, it is important to lie still and not move, which can be difficult for patients with claustrophobia. The procedure involves a person being in a confined space, and you need to tune in to it in advance. You can take a sedative at home or in a clinic. In difficult cases, it is necessary to use sedation, which is often required in childhood.
More serious preparation is needed before an MRI of the shoulder with contrast. It is important not to eat 3 hours before the procedure to avoid nausea. It is better to avoid taking heavy, fatty foods during the day, which will reduce the risk of an individual reaction to the contrast. During lactation, MRI with contrast leads to the need to stop breastfeeding for 2 days - during this period you will have to express and freeze milk, or use artificial formula.
Preparation
MRI is a procedure that does not require specialized training. The patient leads a normal lifestyle, which contributes to the person’s comfort and adherence to this technique. Only immediately before the examination, the patient is asked to remove all metal jewelry and objects to prevent deterioration in image quality.
When using a contrast agent, the patient should refrain from eating and drinking liquids 4-5 hours before the examination to prevent complications. Additionally, it is necessary to establish the presence of an allergy to gadolinium. To do this, the patient is given a small dose of the appropriate substance. If reactions such as urticaria or suffocation occur, further diagnosis is prohibited.
How is an MRI performed?
The patient has virtually no abnormal sensations during the examination. Only occasionally does an MRI of the shoulder joint cause a slight feeling of warmth in the shoulder area. Thanks to its non-invasiveness, there is no need to be afraid of pain or discomfort.
Before the procedure, the patient will be asked to remove outer clothing (underwear is allowed) and remove all metal objects. Then the person lies down on a special table, his limb on the side of the sore shoulder is secured with a belt to prevent movements. Often a cushion is placed under the shoulder joint area. The patient must sit comfortably on the table in order to easily undergo the examination.
Afterwards, the table on which the person lies is pushed into the tomograph capsule. He is given a button in his hand that can be pressed if he feels unwell and needs the help of a doctor. Earphones are put on your ears - they will help you not to hear the clicks and hums that the device makes. The magnetic ring of the tomograph will “drive” around, taking a series of layer-by-layer images, which are then interpreted by the doctor. The duration of an MRI procedure on modern installations rarely exceeds 10 minutes. Older magnetic resonance imaging machines can examine the shoulder in 30 to 40 minutes.
The essence of the MTP method of the shoulder joint
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is actively used in modern medicine. MRI is an effective, very informative and safe method of instrumental diagnostics. High intensity magnetic waves affect a specific area of the human body and influence the hydrogen atoms inside cells, causing them to move in a certain order.
Against the background of cell movement, energy is released. A specially designed device scans these processes and creates a tomogram. A picture is displayed on the monitor screen, which the doctor can print on a special film.
To diagnose the shoulder joint, classical research procedures such as radiography or ultrasound are more often used. But MRI of the shoulder joint differs from traditional methods in its high accuracy and information content. This completely eliminates the impact of harmful ionizing radiation on the human body.
In some cases, gadolinium contrast agent is used to clearly determine the structure and size of pathological changes.
MRI with contrast
MRI using a contrast agent is a more serious procedure that has clear indications:
- suspicion of neoplasms, benign and malignant tumors;
- metastatic process in the shoulder area;
- acute or chronic inflammatory process affecting blood vessels and soft tissues;
- various vascular pathologies.
The principle of contrast is that it accumulates in areas well supplied with blood, especially in tumors. Some diseases of the shoulder joint develop due to poor nutritional intake and circulatory problems, so the procedure will be necessary.
MRI with contrast is performed using gadolinium, a rare earth metal, a paramagnetic that is inert to the body and is eliminated from it without residue. A type of examination is MRI arthrography of the shoulder, when contrast is injected into a large vessel in this anatomical area or directly into the tissue, and then a series of images is taken.
results
The diagnostician deciphers the results of the study and gives his conclusion within a few hours after the procedure. Many people are interested in the question: What does MRI show and how does it differ from ultrasound and x-rays? This procedure is better suited for diagnosing pathologies of soft tissues - cartilage, ligaments, tendons and muscles.
What can be discovered by looking at a 3D image of the area under study:
- tendon ruptures and tears;
- damage to the rotator cuff muscles;
- dislocations and subluxations;
- pathology of cartilage tissue;
- bone tumors;
- neoplasms from soft tissues;
- pinching and other damage to the ulnar nerve;
- pathology of large vessels in the joint area.
Using this diagnostic procedure, you can identify many acute and chronic diseases, find out the causes of pain and impaired mobility in the shoulder, and also monitor the effectiveness of the therapy.
What can the examination show?
The procedure is carried out for various injuries - sports, household, in order to detect their consequences in time. It will reflect the presence of complex fractures, in old cases - the presence of scars, adhesions, and other areas that disrupt the normal trophism of tissues.
The examination will help in the search for post-traumatic arthrosis - joint dystrophy, which is quite difficult to cure (it is often accompanied by the presence of hematomas).
The tomogram can also reveal the following pathologies:
- osteoarthritis;
- arthritis – rheumatic, psoriatic, juvenile, infectious;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- gout;
- damage to the rotator cuffs;
- plexitis - inflammation of nerve trunks;
- osteomyelitis;
- bursitis and synovitis;
- periarthritis of the humeroscapula;
- capsulitis;
- tumors;
- neuropathy.
In children, images often reveal hypermobility of the joint and abnormalities in the structure and development of the shoulder, as well as the consequences of birth injuries. There are also cases of systemic diseases - for example, lupus erythematosus, vasculitis. From the images, the doctor will be able to see serious diseases - osteochondropathy (Köhler's disease, Schinz disease and others), causing necrosis of shoulder tissue.
Explanation of the examination
The interpretation of the results is carried out by a radiation diagnostics doctor or radiologist. Usually this process does not take more than 20-120 minutes, depending on the doctor’s workload. In large centers where such procedures are routine, sometimes you have to wait up to 2 days for results. The description must include the following information:
- characteristics of the main articular structures;
- the presence of inflammatory, destructive, tumor foci;
- changes in hyaline cartilage;
- the presence of traumatic injuries, areas of calcification, necrosis, scars, irreversible destruction;
- complete or partial fusion of the joint space;
- accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the shoulder joint.
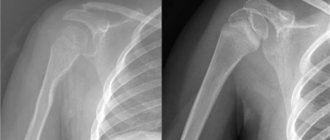
Examination of a shoulder radiograph
X-ray of the shoulder joint
X-ray of the shoulder joint allows you to consider:
- 1 – anatomical neck of the humerus bone;
- 2 – greater tubercle;
- 3 – small tubercle;
- 4 – surgical neck, 5 – diaphysis, 6 – head of the humerus;
- 7 – articular surface of the scapula and 8 – acromion;
- 9 – articular surface of the acromial clavicular end and acromioclavicular joint;
- 10 – scapular coracoid process;
- 11 – clavicular body;
- 12 – angle of the blade from above;
- 13 – medial edge of the scapula;
- 14 – angle of the scapula from below;
- 15 – lateral edge of the scapula;
- 16 – shoulder blade.
The photo shows the x-ray anatomy of the shoulder joint, it is performed using electromagnetic rays of a certain range. They are directed to the area under study and an image is obtained.
Hard tissues are able to absorb radiation, so they acquire a light tone and are clearly visible in the image, while soft tissues are not able to retain X-ray waves, so their structure is dark in the image.
Subacromial bursitis of the shoulder on x-ray
An X-ray of the shoulder joint is not always effective for diagnosing pathological changes, but it clearly shows the elements of bones and joints. Therefore, X-rays of the shoulder joint are performed in combination with MRI and ultrasound, which makes it possible to establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnosed by x-ray for acute pain, chronic algia (pain of various origins), inflammation, fractures and various other injuries, which lead to limitation of movements, swelling, and increased mass of the shoulder joint. X-rays are not performed on children under 15 years of age, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and those with obesity and advanced cancer.
During the procedure, patients wear loose clothing or take it off; there should be no metal elements on it; jewelry and chains should also not be worn. The patient is placed on a horizontal surface and a lead apron is used to protect the pelvic and groin organs from radiation.
If necessary, cover the eye and thyroid area. Infants are fully protected and only the required limb is removed. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes. One or more projections are performed so that the picture of the damage is complete.
To prevent the pictures from being blurry, you cannot move during the procedure. In clinics and commercial offices where images are taken, a radiologist describes the results of the study. Then treatment is prescribed according to this description.
Ultrasound anatomy of the shoulder joint
Ultrasound of the brachial plexus
When examining the shoulder with an ultrasound, you can examine in detail the soft tissues surrounding the joint: ligaments and tendons, muscle fibers and connecting tissue, nerves and blood vessels. If necessary, synovial fluid is taken and examined for the presence or absence of blood, pus, infectious agents and inflammation.
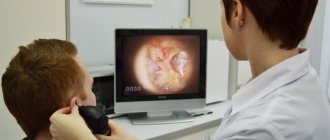
Based on the results of the study, an ultrasound protocol of the shoulder joint is drawn up. Comprehensive diagnostics include arthroscopy and examination of the internal cavity of the joint with an endoscope, therapeutic manipulations are performed, and tissue is taken for biopsy.
Could there be complications?
In the vast majority of cases, MRI of the shoulder joint is a routine examination that does not lead to any negative consequences for the patient. But it can affect the function of devices found in the human body, such as pacemakers. The patient should always notify the specialist in advance about the presence of such devices!
MRI with contrast is a procedure that is potentially dangerous for allergy sufferers. An allergy attack after the administration of a contrast agent can sometimes be severe, leading to angioedema and anaphylactic shock. In order for the doctor to keep powerful antiallergic drugs at the ready, you need to tell him about the tendency to allergies before the study.
How does the procedure work?
For examination, the patient must bring all documents related to his disease: referral, photographs, etc. The duration of MRT of the shoulder joint is from 20 to 30 minutes. This does not include the time it takes to prepare. When examining with a contrast agent, the session lasts 30-60 minutes. After the procedure is completed, the images are printed or downloaded onto a CD and, together with the specialist’s report, are sent to the patient or the attending physician.
Because the device produces strong magnetic fields, all removable metal objects, including piercings, must be removed from the body. If the institution does not provide disposable underwear, then you should remove any clothing that has anything made of metal on it: buttons, zippers, bra clasps, etc. Typically, you are allowed to leave a shirt or T-shirt on.
During the session, the patient is on a flat table (couch) pushed into the magnetic tomograph tube, which covers the head. The legs remain outside. To protect the patient from loud detonation noise, the assistant provides headphones. The subject holds a button in his hand that he can press if any problems arise.
You should lie still. If the patient moves, the images are unclear and blurry. As a result, the procedure has to be repeated.
Applying Contrast Enhancement
Whether a contrast agent is used depends on what structures are planned to be examined on the tomograph. It is not required, for example, for MRI of the brachial plexus or knee joint. Often the agent is administered some time before the study begins. There are 2 ways to administer the substance: into a vein (indirect arthrography) and directly into a mobile joint (direct arthrography). The second is more effective, but the procedure in this case takes longer and is associated with the risk of infection.
Contrasting is used:
- with partial or complete rupture of the rotator cuff tendons or the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle;
- when assessing the periarticular bursa above the rotator cuff due to inflammation (bursitis);
- to examine the labrum around the glenoid fossa and cartilage.
Contrast agents improve image quality. As a rule, they are well tolerated. These substances do not contain iodine and are not similar in chemical composition to those used for X-ray examinations, therefore they are not dangerous if you are allergic to X-ray contrast agents. Within a few hours they are excreted in the urine.
Tomography without contrast is performed if you are allergic to the gadolinium contained in the drugs and the following problems:
- soft tissue tumor
- fracture, fracture
- changing the moving connection,
- p.s. infection,
- inflammation of p.s.
In the last two cases, the introduction of substances is not only useless, but also interferes with the correct assessment of the condition of the synovial membrane.
Contraindications for MRI
The examination is contraindicated for those who have cochlear implants inside the ear, special clips on cerebral vessels, as well as some types of stents and coils in the circulatory system, artificial valves, ferromagnetic and electronic implants.
MRI can give incorrect data if the patient has infusion pumps in the body, as well as metal prostheses and screws. In case of an injury that could cause metal elements to enter the joint, an x-ray is first taken to exclude such a pathology.