Main features of the examination technique
Ultrasound examination is considered one of the most popular methods for diagnosing various pathologies. The examination is not difficult, does not require significant financial costs, is safe for patients, and allows one to obtain accurate information.
Ultrasound of the brain is performed in children, and not in adults, because with age, fontanelles grow between the bones of the skull, ultrasound radiation does not penetrate the brain, and sensors do not pick up signals.
This examination method is called echography because, when passing through soft tissue, signals in the frequency range from 0.5 to 15 MHz are reflected in different ways from substances with a different structure. Based on an analysis of existing reactions after comparison with normal results, doctors make a diagnosis.
The brain is examined in this way only in infants. The maximum age at which an ultrasound of the brain vessels of a child is performed is 1.5 years . The sensor is located between the frontal and parietal bones of the baby, but fontanelles are still present in the area of the temples and the back of the head, and later they heal.
Ultrasound of the hip joints at six months
During this period, there is often a need to do an ultrasound of the hip joints (HJ), because soon the baby will have to stand on his feet, and he will begin to try to do this at 7-8 months. And if there are any pathologies of the hip joints, this can affect a lot.
Ultrasound should be done both for prevention and in special cases:
- When you move your baby's leg away, a click is heard;
- The child has asymmetric folds on the buttocks;
- Hypertonicity in the lower extremities;
- One leg is shorter than the other.
You can visually understand that the hip joint is not developed correctly after a year when the child develops a duck's gait or begins to limp. But in this case, treating the joint is much more difficult. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion, it is better to show the child to an orthopedist and do an ultrasound.
If the hip joint develops incorrectly, a diagnosis of dysplasia is made.
Also at risk are children who:
- Have relatives with a similar diagnosis;
- Born in a breech position;
- They were carried by a woman who had suffered from toxicosis for a long time.
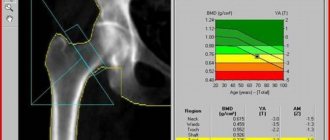
Based on the indicators, which are further classified in the Graph table, a conclusion is drawn about how development occurs.
If there are deviations from the generally accepted norm, a diagnosis of subluxation or dislocation is made.
What is the procedure?
Neurophysiography means performing an ultrasound examination of the brain in newborns and children under 1 year of age. High-frequency vibrations are reflected from the brain and display its outline on a digital display.
The procedure is safe, does not cause pain, and allows you to obtain a lot of information. These circumstances make it possible to carry it out regularly. There is no need to administer anesthesia to the patient ; it is enough to keep the child immobile or wait until he falls asleep. Crying or screaming has no effect on the results.
This method of examination is considered most suitable for infants. It is carried out until the fontanel between the bones of the skull is overgrown.
Ultrasound of the brain in newborns makes it possible to familiarize yourself with all the individual structures of the organ. During a short procedure, doctors will be able to analyze brain processes and the general dynamics of their flow.
How to prepare a baby for a research procedure?
Screening of the hip joints, brain and heart does not require additional preparation. For maximum information content, ultrasound of the digestive organs, kidneys and liver must be preceded by some restrictions.
If the infant is bottle-fed, then short-term restrictions on feeding can be considered preparatory measures. It is important that the baby's gastrointestinal tract is as free from food as possible, given the minimum duration between feedings.
If the newborn is fed by the mother's breast milk, the main preparation for abdominal screening will fall on her shoulders. She should radically reconsider her diet 2-3 days before the expected date of the baby’s examination. The main thing is to exclude allergens and any products that cause flatulence, bloating, or upset:
- fresh vegetables;
- fruits;
- cabbage;
- legumes;
- whole milk;
- black bread.
Other types of ultrasound (for example, pelvic organs, kidneys and bladder) imply maximum fluid filling. Despite the fact that it is quite difficult for newborn babies to control the process of urination, it is possible to fill their bladder only by giving them a drink of water or baby tea 30-40 minutes before the start of the study.
Before ultrasound, the bladder must be filled with fluid. Give your baby enough to drink half an hour before the test.
Indications
For a child in the first year of life, there are many indications for an ultrasound examination. This could be pregnancy and childbirth, suspicions of various diseases, congenital defects, etc. Determining pathology in the primary stages of development gives a better chance of recovery.
The procedure lasts a maximum of 15 minutes. To examine the head, a specialist attaches sensors to the anterior fontanelle and temple area. In rare examples, the occipital areas are examined. An ultrasound is performed to obtain reliable information about the state of the newborn's brain .
The displayed data is compared with the normal state and a diagnosis is made. A total of 12 common diagnostic indicators are used. The neurologist takes into account the examination results when determining the therapeutic technique.
The doctor determines the condition of the wide blood vessels of the brain, identifies deformation of the walls, damage, plexus, neoplasms, and analyzes the structure of the tissues. The main parameters to study are the volume of the ventricles. Excessive indicators indicate violations.
Types of ultrasound diagnostics for infants
In the first month of life, an exploratory ultrasound procedure is performed in certain cases. However, a distinction should be made: during pregnancy, a woman undergoes 2-3 routine ultrasound scans; there is no similar need to examine the baby. Among the diagnostics that make it possible to recognize the most common diseases of infants, the most often prescribed are:
- neurosonography;
- diagnosis of the hip joint;
- examination of the abdominal organs and heart.
Our country has not yet introduced the practice of mandatory ultrasound examination in the first week of a child’s life, but the advisability of carrying out additional procedures, in addition to examination by a doctor, is obvious. Not all pathologies manifest themselves symptomatically. For example, hip dysplasia in a child manifests itself only when the child makes his first attempts to walk. In advanced cases, it is simply impossible to avoid surgical intervention.
Main indications for prescribing neurosonography for a newborn
Indications for ultrasound in newborns determine one or another specific type of procedure. The purpose of the study is within the competence of pediatricians, neonatologists or specialized specialists in the presence of specific symptoms. Thus, indications for neurosonography in infants are:
- premature birth;
- deep prematurity;
- intrauterine oxygen starvation;
- injuries received during childbirth;
- low Apgar score (less than 7 points);
- muscle hypotonicity;
- convulsions.
For both rapid and slow head growth, neurosonography is an indispensable stage of examination. In addition, it is also prescribed in the presence of such anomalies in the development of infants as fused fingers, short neck, etc. The procedure is much easier to carry out, and its maximum information content is explained by the large fontanel that has not yet closed.
Neurosonography in a baby: an unclosed fontanel allows the doctor to see a lot
To detect congenital anomalies that require urgent treatment, disturbances in the blood supply to areas of the brain, and blood circulation, neurosonography is also prescribed. In case of ischemic damage to organ tissue caused by intrauterine hypoxia or stroke, the likelihood of developing severe and often irreversible consequences for the patient is incredibly high. Therefore, in addition to a detailed examination of the cerebral hemispheres, it is worth studying the condition of the large arteries of the base of the skull and neck. This will avoid the development of complications caused by damage during childbirth.
In what cases is an ultrasound of the abdomen prescribed?
An ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in a baby can also be performed as planned, in the first month of life, or carried out unplanned, taking into account complaints from the digestive organs. For such children, screening is often the only gentle and minimally invasive way to identify pathologies and make a diagnosis. Among the indications for the procedure it is worth noting:
- routine examination of congenital anomalies of intrauterine development;
- frequent regurgitation;
- lack or decrease in monthly weight gain;
- progressive congenital jaundice, suspected nuclear form;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- with increased reflux reaction, suspected pyloric stenosis;
- in case of stool disorder caused by a non-infectious functional disorder.
An ultrasound examination will be a mandatory step in examining the baby after an injury to any internal organ, severe pain and screams when touching the abdomen or light pressure.
Other types of newborn screening
In addition to studying the condition of the child’s internal systems and organs, ultrasound diagnostics are no less often prescribed for heart defects confirmed in the prenatal period. Most often, cardiac ultrasound is performed from 1 to 3 months of a baby’s life.
As a rule, infants with suspected pathologies such as dysplasia or hip dislocation are referred for examination of the hip joints. The first disease is one of the most common and can significantly affect the child’s future life.
An examination of the hip joint in a child is usually prescribed by a pediatric orthopedist, who will help draw up a competent treatment regimen to fix the diseased joint.
Ultrasound of the brain in children
Neurosonography indicators are determined by the week in which the baby is born. We list the normal indicators of ultrasound examination:
- The grooves and convolutions in the brain should be located symmetrically, the ventricles and cisterns should be clearly visible.
- The echogenicity index of the subcortical nuclei is normal.
- The anterior horn of the extreme ventricle is approximately 1-2 mm deep. Its size should not exceed 4 mm.
- There is no fluid in the gap between the hemispheres of the brain. The normal width is 2 mm.
- The choroid plexuses in the area of the ventricles are homogeneous.
- The size of the 3rd ventricle is 2-4 mm.
- The stem structures are located in their place.
- The length of the large tank is 3-6 mm.
A neurologist interprets the ultrasound results. He can prescribe the correct therapeutic technique for the baby. Monitor and determine trends in the development of brain tissue, identify possible diseases. The neurologist needs to evaluate the neurophysiography data and compare them with the identified symptoms.
Reviews about the neurosonography procedure
Ultrasound for babies is by far the safest, and at the same time, the most informative. Therefore, all parents who monitor the health of their baby and want him to grow up healthy resort to it.
Reviews about this procedure are extremely positive, because thanks to modern equipment, even the beginnings of deviations can be tracked and stopped, preventing their development and the manifestation of clinical symptoms.
If the child shows any deviations from the norm, then ultrasound helps to monitor them and monitor any changes.
It is important that this procedure is completely painless and does not cause the children the slightest discomfort.
Puncture
(from Latin punctio - injection) - a puncture of tissue with a needle, performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Diagnostic punctures are performed to obtain fluid and cellular elements, to measure pressure, to introduce air or oxygen into cavities, and to introduce contrasting substances into blood vessels. Therapeutic punctures are performed to remove pathologically altered fluid or pus (for example, with a closed method of treating brain abscesses), for bloodletting and blood transfusions, for introducing medicinal substances into cavities and blood vessels.
Cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF) is produced mainly by the choroid plexus and ventricular ependyma of the brain. Absorption of CSF occurs in the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord. A special role in CSF resorption is assigned to the granulations of the arachnoid membrane (Pachionian granulations), protruding into the venous sinuses of the dura mater, as well as the perineural spaces in the area where the spinal cord roots exit the dural sac. CSF has a strictly defined composition, takes part in the metabolism in the tissue of the brain and spinal cord, and also acts as a shock absorber that protects the brain from mechanical damage.
Total volume of liquor-containing spaces
is 120 -150 ml. The ventricular system of the brain contains 30 - 50 ml of CSF. The subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord contains about 80-100 ml of CSF.
Ventricular system of the brain
consists of two (right and left) lateral ventricles, which communicate through the interventricular foramina (foramina of Monro) with the mid-located third ventricle. The lateral ventricles are distinguished by the central part, or body, of the ventricle, the anterior horn, which projects into the frontal lobe, the posterior horn in the occipital lobe, and the inferior horn, located inside the temporal lobe. There is also the so-called ventricular triangle - the junction of the central part of the lateral ventricle with the temporal and occipital horns. From the third ventricle, CSF enters the fourth ventricle through the aqueduct, which communicates with the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord through the lateral apertures of the fourth ventricle (foramen of Luschka) and the median aperture of the fourth ventricle (foramen of Magendie).
If on convexity
On the surface of the brain, the subarachnoid (subarachnoid) space is insignificantly expressed and only in the area of the grooves it looks like cracks filled with CSF; then at the base of the brain, the subarachnoid space forms expansions with accumulations of CSF in them - the so-called basal cisterns. Of these, the following are the most important in practical terms, traceable on pneumocisternograms or scanograms.
Cistern magna of the brain
located in the caudal region of the medulla oblongata, bounded superiorly by the cerebellum and posteriorly by the atlanto-occipital membrane.
This tank communicates with the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord, and through the apertures of the fourth ventricle with the ventricular system. A puncture of the large occipital cistern (suboccipital puncture) is used to remove CSF, as well as to introduce medicinal and radiocontrast substances into this section of the cerebrospinal fluid system. The pontine cistern
consists of a medial and two lateral pontine cisterns localized in the cerebellopontine angle.
Interpeduncular cistern
limited to the cerebral peduncles, the pituitary infundibulum and the medial temporal lobes.
The chiasmal cistern is a cistern in the area of the optic chiasm. In the subarachnoid space
of the spinal cord, anterior and posterior sections are distinguished. The spinal cord usually ends at the level of the upper edge of the II lumbar vertebra (in children, somewhat lower - at the level of the LII vertebral body). Below this level, the membranes of the spinal cord form an extension, the so-called lumbar sac, containing the spinal lumbosacral roots, which make up the “cauda equina.”
The fact that at the level
In the lumbar spine, the dural sac no longer contains the spinal cord, allowing lumbar puncture to be widely used in clinical practice.
Decoding
Often the transcript shows such diseases. Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain occurs if their depth is higher than normal. This is a characteristic sign of hydrocephalus. Externally, in a newborn, this disorder is visible to the naked eye.
The head increases in size, the forehead protrudes forward, moles become larger. Hydrocephalus is diagnosed after bleeding or infectious processes, problems with the development of the child. The child often has migraines, fatigue, undeveloped physical development, and has mental problems.
An increase in the subarachnoid space of more than 3 mm is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a deterioration in appetite. This may indicate meningitis. The disease can develop as a result of hydrocephalus.
A cyst of the plexus of blood vessels is cells of the ventricular mucosa that secrete cerebrospinal fluid. A cyst is formed in the form of a cavity filled with something. They often do not manifest visual symptoms in the child. Such formations do not require treatment, since they resolve over time.
Ischemic disorders in the head. Blood vessels don't do their job well. If these areas are highly dense, brain cells atrophy in fragments, and crust formation is distorted.
If the examination results show the presence of diseases, the neurologist will prescribe prophylaxis or select an appropriate therapeutic technique. Medicines will help accelerate the closure of fontanelles.
If you have high ICP in a newborn, you should not use Aquadetrim. If there are too many abnormalities in brain development, the child will be hospitalized and complex therapy will be prescribed. Children who develop brain diseases should not be vaccinated.
What does the doctor look for during the examination?
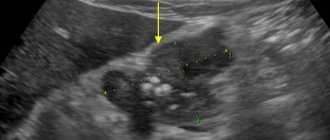
First, the specialist determines the fetometry, or size, of the fetus. He looks at the BPR (biparental size), which should be in the range of 49-55 mm, at the circumference of the head and abdomen, which should be 166-200 and 139-180 mm, respectively, at the fronto-occipital size, the norm of which varies between 60 -72mm, and for hip size – 32-42 mm.
If the child has a delay in development and a lag in size, the doctor will have to find out the reason for this.
During an ultrasound scan at 24 ac. week of pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat in the abdomen is assessed, which should be about 120-160 beats per minute. In addition, it is important to know the state of the blood flow, so the doctor may prescribe Doppler ultrasound, which is an additional study.
However, in this case, the doctor will evaluate the blood flow of the woman’s uterus, umbilical cord and placenta, on which the successful development of the fetus during pregnancy largely depends. If the blood flow is normal at 22-27 obstetric weeks, it means that the baby receives a satisfactory amount of oxygen in the stomach, which eliminates the possibility of hypoxia and, as a consequence, encephalopathy.
And, of course, during this period of pregnancy, the doctor carefully examines the placenta using an ultrasound scan - its structure, location and distance from the internal os of the uterus.
It is important to make sure that there is no premature aging or detachment.
The first factor can negatively affect the development of the fetus at six months, the second can lead to premature birth, which is unacceptable at 24-27 obstetric weeks.
Amniotic fluid at six months also affects the sensations of the baby in the expectant mother’s belly. Ideally, they should be renewed every 4 hours, protecting the fetus from injury due to sudden movements of the expectant mother. Polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios is an equally bad sign at this stage, indicating either fetoplacental insufficiency or the development of an intrauterine infection in a woman. A study of the consistency of the amniotic fluid can confirm the diagnosis at this time.
Very important during the ultrasound process at 22-24 weeks is the examination of the fetus for various defects and congenital diseases.
And although it is the first screening during pregnancy that should diagnose malformations, in practice, tests do not always make it possible to find out this at the initial stage.
Fetal defects can be purely cosmetic, for example, cleft lip, or chromosomal abnormalities such as Lange, Down, or Edwards syndrome.
What does ultrasound reveal?
An ultrasound of a child’s head allows you to examine:
- Ventricles of the brain . In the process of visualizing their volume and contours, the specialist identifies hemorrhages, cysts, dropsy, and processes that contribute to the development of rickets. If diseases are eliminated in time, pathologies of intellectual and physical development will be avoided.
- Condition of wide vessels . Aneurysms are detected in the form of enlargement of arterial walls. As a result, blood flow to the brain becomes difficult.
- Hemorrhages caused by prematurity. This problem needs to be monitored as closely as possible, as the result may be the death of the baby.
- Infections that cause meningitis. If the disease is detected in time, the child can fully recover.
- Oncology is detected in rare cases.
Causes of the disease
Prevalence – 1 case in 2-3 thousand newborns. This figure is small. But the diagnosis of “hydrocephalus” is considered the most common developmental disorder in preschool children.
Girls get sick less often than boys. The disease is detected in the first months of a baby's life. Dropsy in moderate form goes unnoticed. Over time it becomes chronic. The disease manifests itself differently in a child and an adult.
In an adult, the skull is formed and the bones are strong. Excess cerebrospinal fluid leads to increased intracranial pressure. In children under 2 years of age, the bones are soft and flexible. An excess of fluid causes an abnormal expansion of their head circumference.
Interesting: Why does a 6-year-old child have a headache: causes, prevention, emergency care
Water forms in a child's head for many reasons. The disease can be congenital or acquired. Congenital factors include:
- injuries caused by difficult childbirth;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia);
- genetic disorders;
- infections transmitted in the womb.
Method of implementation
Performing an ultrasound of a child's head does not require prior preparation. It is necessary for the baby to be in a calm state, it is better to let him sleep. In such a situation, he will not have any discomfort; you can use a toy to distract his attention.
An ultrasound of a child’s brain involves performing the following steps:
- The baby is placed lying down and held in the correct position. The procedure is performed within 10 minutes. The patient needs to be calmer during this period.
- Newborns are not given anesthesia. You need to hold the head so that it does not move.
- The baby's head is smeared with a gel that differs in composition from the product used for ultrasound in adults. This substance is hypoallergenic and strengthens the sensor signal by eliminating air between the device and the skin.
- A sensor device is applied to the treated area. The specialist moves them around the head, reads data from organs and tissues.
Diagnostics
In children, the diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure is revealed during examination. The specialist will pay attention to the symptoms that are characteristic of the disease. If suspected, the baby is referred for examination to a neurosurgeon. In order not to confuse increased intracranial pressure and increased cerebrospinal fluid volume with other diseases, MRI and radiography are performed. An ultrasound examination is performed. Examine the fundus. Endoscopic methods are used.
Interesting: Symptoms, treatment features and consequences of TBI in a child
Safety of the procedure
When performing an ultrasound of the brain in newborns, the safety of the procedure must be taken into account. A child's fragile body can easily get injured . Similar studies have been carried out frequently for children recently.
Previously, procedures to study the state of the brain were carried out less frequently. Equipment for MRI using anesthetics has performed well in practice. It is easy to understand that this type of diagnosis is complex and can provoke negative consequences.
New methods have made the work of doctors and the lives of patients much easier. The procedure makes it possible to identify various brain diseases in children.
Possible harm from ultrasound of a child's brain
The procedure is harmless and always brings good results. Allows you to identify pathologies at the primary stage of development and improve the baby’s health using conservative methods without traumatic surgical interventions.
When there are indications, ultrasound of the brain in children must be performed . Parents often do not consent to such procedures; as a result, it is not possible to determine in advance the development of dangerous pathologies. Such negligence often leads to negative results.
To make a correct diagnosis and identify the problem in time, a simple external examination of the child is not enough. In some cases, it is necessary to use ultrasound equipment for examination.
Classification of pathology
Dropsy is classified according to numerous criteria. The most commonly used:
- By location. Divided into external and internal hydrocephalus. The internal one is localized in the ventricles, the external one - in the subarachnoid space. There are mixed types.
- According to the form. Open and closed dropsy are determined. When the form is open, nothing prevents the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid; when it is closed, there are adhesions and neoplasms. It is called occlusal. The occlusive form of hydrocephalus affects infants with brain tumors.
- According to the nature of the course, four forms are distinguished. Acute symptoms appear very quickly: within a few days. With this development, surgical intervention is necessary. Symptoms of the chronic form are blurred and visible after 6 months. With compensated dropsy, the cavities remain dilated, but the pressure drops. In this form, dropsy returns after injury to the skull. External dropsy is easily identified. It is large, the fontanel protrudes above the skin. With this form, the baby often throws back his head and arches his back. The internal closed form of leakage is considered dangerous.
Interesting: Fever and headache in a child