Why is such a test needed?
Red blood cells are red blood cells that perform very important tasks, delivering oxygen and nutrients to all systems and organs. A distinctive feature is the ability to combine into complexes. Because of this, they become much heavier than the other components and, when collected in a test tube, settle after some time. A blood test shows the rate at which this happens and helps make an accurate diagnosis, as well as determine how effective the treatment is.
How much should be normal?
The blood sedimentation rate in men may change with age. For older people, the norm increases.
The ESR level is normal in men by age - table:
| Patient age, years | ESR, mm/hour | |
| Panchenkov method | Westergren method | |
| Up to 20 | 2-10 | 1-10 |
| 20-50 | 2-10 | 2-15 |
| Over 50 | 2-12 | 5-20 |
If in young people the ESR rises to 16, this will mean that an active inflammatory process is underway. And for men aged 65, this figure is considered normal.
Up to 20 years
In young guys 18-20 years old, red blood cells should settle slowly. Therefore, an ESR of 2 mm/hour is the norm for people of this age category. If the resulting indicator is no more than 10, then it fits within the norms of ESR in the blood of men, there is no cause for concern.
If the ESR becomes 12 mm/hour, the doctor may recommend retaking the test. A slight increase in ESR may be due to a recent cold, non-compliance with the recommended diet on the eve of the test, or stress.
Up to 60 years old
In mature men, the ESR in the blood will be higher than in those aged 19-22 years. The increase in level is due to the launch of natural aging mechanisms. People over 30 years old should not have any deviations. But in men after 50 years of age, an ESR of 13-14 mm/hour is not considered elevated; for some, such indicators become the norm at 40-42 years of age.
It is believed that in men over 50 years of age, normal ESR levels may increase. When assessing values, it is necessary to take into account that for some it is normal for ESR to be elevated. In 5-8% of patients this figure may exceed 10-15 even in the absence of health problems.
At 60 years and older
The ESR rate in men over 60 years of age increases. If the test results indicate that the ESR is 14 or 17, this means that there are no problems.
An increased ESR in the blood of men after 60 years of age is considered normal, the main thing is that the level falls within the age-specific reference values. The physiological increase in speed is due to the fact that cells are renewed slowly, their parts, after destruction, are retained in the body, enter the bloodstream and stick together with red blood cells. Because of this, the blood cells become heavier and begin to settle faster.
Determination of ESR according to Westergren
A blood test is carried out by taking biomaterial from a finger and from a vein. In the first case, the method of determining ESR according to Panchenkov is used. An anticoagulant is applied to the glass, after a few seconds blood is added to it, and everything is sent together into a special capillary with 100 divisions. An hour later, the laboratory technician takes measurements of the sediment and writes down the result.
Determining ESR according to Westergren gives more accurate results. And the point is not only that blood is drawn from a vein.
How is the research conducted?
Both capillary and venous blood are suitable for the study, but more often it is taken from a vein at the elbow of the arm, before pulling the vessel above the elbow with a tourniquet.
The blood taken for analysis is diluted in a ratio of 4 to 1 with a 5% solution of sodium citrate, an anticoagulant, and left to settle in a test tube in a vertical position for an hour.
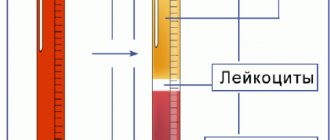
An anticoagulant is necessary to prevent the formation of clots that make measurement difficult. Red blood cells, under the influence of gravity, after some time settle to the bottom, forming a red layer; a transparent layer of plasma remains on top of the test tube. It is measured using a scale applied to the glass of the test tube, thus determining the sedimentation rate in millimeters per hour.
Reviews from doctors about the Westergren method are more positive than about other methods.
Now the measurement process is fully automated, all data is entered into a computer so that, if necessary, the dynamics of changes can be monitored. This also eliminates errors that may occur during the pre-analytical stage of a laboratory test.
Differences, advantages and disadvantages of the method
The Westergren method differs from the Panchenkov method in the use of different equipment and the procedure itself. Blood with an anticoagulant is mixed directly in a test tube, which has not 100, but 200 divisions. This is why a more accurate result is obtained.
Otherwise, the methods for measuring erythrocyte sedimentation rate are similar. In the same way, the result becomes known in an hour.
Note! If the obtained values do not provide the necessary information, a biochemical blood test may be prescribed. And this also has the advantage of taking the ESR test using the Westergren method. There is enough venous blood to conduct additional studies and there is no need for repeated sampling.
This is not to say that the method has disadvantages. It is not without reason that it has been officially recommended for use in medical institutions since the 70s of the 20th century. But, unfortunately, many doctors make mistakes when determining standards and pointing out to the patient the possible causes of deviations. Therefore, it is advisable to get the opinion of several specialists on this matter.
Determination of ESR in blood using the Westergren method
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a very important laboratory parameter in blood tests. Patients are often interested in what it is. It shows how long it takes for blood deprived of the ability to clot to settle under the influence of gravity. Due to certain circumstances, red blood cells stick together, become heavier and therefore settle faster.
Let's look at what Westergren's ESR is, how such an analysis is carried out, and what its results mean.
Why is such a test needed?
Determination of ESR is necessary in the event of symptoms of a disease in which this indicator may increase. The analysis is an auxiliary diagnostic measure, as it helps to make a more accurate diagnosis and determine how the body tolerates the treatment and whether there are any results from it.
In turn, deciphering the analysis using the Westergren method helps to monitor diseases, in particular those of inflammatory origin. Other symptoms in which such a test is required are the appearance of fever or fever. And the higher the ESR, the more active the inflammatory process
Note that today such analysis is recognized in many countries. It has very high sensitivity.
So what does this test show? With its help, the following diseases are diagnosed:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- abscess;
- arthritis of psoriatic origin;
- septic processes;
- vasculitis;
- reactive arthritis;
- polymyalgia;
- polymyositis.
What is the difference between this blood test method?
The analysis according to Panchenkov and according to Westergren has differences, and they are significant. First of all, the ESR analysis according to Panchenkov uses capillary blood.
To determine the indicator, a Panchenkov capillary is used (it has 100 divisions). First, an anticoagulant is applied to the concave glass so that the blood loses its ability to clot. Blood is then applied to the concave glass and placed into the capillary. It is installed in a vertical position.
Usually, after an hour, the specialist measures the height of the transparent sediment, that is, the plasma. The number of divisions is the ESR indicator in millimeters. At this time, this method is the most common in our country.
The Westergren method is more sensitive. For this, firstly, a more accurate scale of 200 divisions is used. Blood is taken from a vein . The blood is mixed with the anticoagulant substance directly in the test tube. The blood plasma column must be measured in the same way.
How is the analysis carried out?
For the patient, blood sampling is not dangerous and does not cause harm:
- The forearm is tightened with a strap or tourniquet. A needle is inserted into a vein at the elbow; the skin at the injection site must be treated with alcohol.
- The patient is asked to clench and unclench his fist several times. When blood is drawn, it goes into a test tube.
- When enough material has been collected, the needle is removed. A cotton swab soaked in alcohol is pressed to the injection site.
The procedure takes very little time and is not painful for the patient. However, in order for the analysis to show accurate results, you need to prepare for it in a certain way.
Preparing for analysis
Blood for analysis is taken on an empty stomach. It is necessary that at least 8 hours pass after eating. It will be better if a day or two before the analysis the patient gives up alcohol and fatty foods. Smoking is prohibited one hour before the procedure.
It is necessary to exclude before analysis:
- physical activity;
- stress;
- taking medications (if this cannot be done, then you must inform your doctor about it);
- X-ray examination;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
What are the ESR norms according to Westergren for different categories of the population?
The ESR rate depends on the patient’s age and gender. In children, this indicator fluctuates within fairly wide limits.
- In newborn patients, the normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 1-2 millimeters. Such low numbers are due to the fact that babies have very little protein in their blood.
- The indicator at the age of one to six months is 12–17 millimeters per hour. The increase in values is associated not with pathological processes, but with growth.
- After six months, normal values decrease and become equal to 1–10 mm per hour.
- Depending on gender, the indicators differ and sometimes very significantly. Thus, the ESR norm for women according to Westergren under 50 years of age is less than 20 millimeters per hour. For older people it may be greater.
- For men under 50 years of age, this figure is less than 15 mm, and then it can increase to 20 millimeters in one hour, and this speed will be considered normal.
What does an increase or decrease in ESR mean?
If Westergren's ESR is elevated, it is necessary first of all to exclude physiological pathological processes in the body. Perhaps the reason for the increase in this indicator is age. There is a certain group of people whose ESR is constantly increased or decreased, but this is not associated with disorders in the body.
When such physiological characteristics of the body are not observed, it is possible that the person has some pathological phenomena in the body.
If Westergren's ESR is elevated, what does this mean? This may be an indicator that certain processes or diseases are developing in the body:
- inflammation of various origins;
- heart attack;
- infections - acute and chronic;
- injuries, especially fractures;
- state of the body after surgery;
- shock;
- malignant tumors.
ESR may also be increased when taking certain medications (glucocorticosteroids). A decrease in the indicator indicates that the water-salt balance in the human body is disturbed (overhydration). A decrease in ESR is also a sign of progressive myodystrophy.
Other causes are not pathological:
- diets associated with low intake of calories;
- vegetarianism;
- taking steroids.
ESR during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the ESR indicator must be measured without fail. After all, certain processes occur in a woman’s body that can affect her condition and the health of the unborn child. In total, during the entire period of bearing a child, the blood for ESR must be checked four times. And the Westergren method will be more informative.
In pregnant women, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate varies from 7 to 45 millimeters per hour. Sometimes it may decrease in the first trimester. At the same time, before childbirth, the rate can increase sharply.
If the Westergren ESR is elevated during pregnancy, this may indicate anemia. With this disease, the delivery of oxygen to the tissues is disrupted, and red blood cells begin to break down faster.
If a pregnant woman eats little meat, then this number also increases.
This indicator may also increase during certain inflammatory processes. If it becomes higher than 50 mm per hour, then do not panic: you may have to undergo additional examinations. Perhaps the metabolism is disturbed or there are other, no less dangerous pathologies.
During pregnancy, ESR may decrease. This happens when taking certain medical projects, with increased blood viscosity and other disorders. In some cases, this can be dangerous to health: there is an increased risk of developing anemia, hypoglobulinemia, and erythremia. In any case, the pregnant woman needs to undergo additional examinations.
How to normalize ESR using folk methods
In many cases, normalization of erythrocyte sedimentation rate is associated with the need to lower it. High values of this parameter in themselves are not a disease. It can be reduced by treating the underlying pathology that caused the high values. Upon recovery, tests return to normal.
Sometimes folk methods of normalizing ESR can also be used. Suitable for this:
- onion garlic;
- citrus;
- bee products;
- beet juice (you can grate the raw vegetable and squeeze);
- tea with linden or raspberry.
To increase the level of this parameter, use a decoction of cyanosis. A glass of decoction (you need to take a teaspoon) should be infused in a thermos overnight and drunk during the day. A mixture based on 1 kg of honey, 20 walnuts, 100 grams of garlic and 50 g of dill seeds also helps. It is used one tablespoon three times a day .
So, the Westergren ESR analysis is an accurate and informative examination. It is prescribed to detect a large number of diseases. Only a doctor can correctly interpret the results obtained and prescribe treatment.
Source: https://prososud.ru/krovosnabzhenie/soe-po-vestergrenu.html
Why do you need the Westergren ESR test?
The Panchenkov study is carried out more often and mainly for prevention. Blood from a finger is donated during a medical examination at work, before entering school and preschool institutions. It is prescribed for seasonal diseases and infections. But if the situation is more serious, if it is not possible to make a diagnosis, or if there is a suspicion that the measures taken are not producing results, a more accurate method of determination is prescribed.
Using the data obtained, it becomes possible to determine or exclude:
- sepsis;
- abscesses of various etiologies;
- autoimmune disorders;
- arthritis;
- myalgia;
- oncology.
Important! No doctor will make a diagnosis based solely on the data received. An additional examination is required and repeat tests are ordered, possibly in another laboratory.
What to do
If, based on the results of the general analysis, it was revealed that the ESR in men by age does not correspond to the norm, it is necessary to repeat the study. If the second analysis shows abnormalities, the doctor must collect anamnesis and assess the patient’s condition to establish a preliminary diagnosis.
At a speed of 32, 35 mm/hour and higher, the examination should not be delayed. This level indicates the active development of the pathological process. If treatment is not started in time, the condition may worsen.
Therapy is selected after the diagnosis is established. There is no specific treatment aimed at reducing ESR levels. The indicator will return to normal if the patient gets rid of the disease or succeeds in achieving stable remission.
How is the analysis carried out?
If a venous blood sample is taken by an experienced nurse, the patient will not even feel anything. In addition, the procedure is completely safe.
The forearm is tightened with a tourniquet, after which you need to clench and unclench your fist several times. As a result, the vein in the elbow begins to bulge. After disinfecting the skin, a needle is inserted into it, the tourniquet is removed, and the required amount of biomaterial is drawn into the syringe.
An anticoagulant is injected into the test tube and blood is added. The contents are shaken and left for an hour. If there is a possibility that further testing may be needed, the remaining blood is poured into a sterile tube and sealed.
An alcohol-soaked cotton wool or napkin is pressed to the injection site. You need to bend your arm at the elbow and sit until the bleeding stops.
There is nothing complicated, and everything goes away in just a couple of minutes. But in order for these Westergren ESR determinations to be as accurate as possible, it is necessary to properly prepare for the test, and here the responsibility lies with the patient.
How to prepare
In order for a general blood test with determination of ESR to give an accurate result, you need to properly prepare for its delivery, observing the following rules and recommendations:
- Eliminate physical activity for the day.
- Go for analysis in a state of emotional and physical peace.
- For a week, stop taking any medications, incl. and vitamins.
- Immediately before donating the biomaterial, you should not smoke or drink coffee.
The test is taken only on an empty stomach in the morning. The less time passes between awakening and the collection of biological material, the more accurate the result will be. If a person must take any medications for medical reasons, and it is not possible to even temporarily stop taking them, the laboratory assistant must be informed about this.
Important information: What do elevated ABS neutrophils in the blood of an adult indicate (causes and treatment)
How the research is carried out
To determine ESR according to Westergren, blood is taken from the cubital vein, or in children - from a finger. A special anticoagulant is poured into the test tube, then the blood taken during the study is added.
The contents are mixed by shaking, after which the test tube is left for 1 hour.
After this time, the laboratory assistant begins to make calculations, determining at what speed the blood cells settle. The results obtained are compared with the norm and entered into a special form.
Preparing for analysis
Before taking the test, you must not eat for at least 8 hours. That is why it is recommended to do it on an empty stomach in the morning.
Physical activity should be avoided. It is necessary to be in a state of maximum peace, including moral peace. Therefore, before entering the office, you need to sit, calm down, and catch your breath.
Smoking is prohibited for at least an hour; tea, coffee and any drinks are prohibited. You can drink some water.
You should also stop taking vitamins and medications. If the appointment is carried out according to a schedule, it is necessary to notify the doctor who sends for tests and the nurse who does the sampling.
If an X-ray or any other examination, including physiotherapy, is prescribed at the same time, they should be carried out after donating blood.
Advice! The results will be more accurate if you give up alcohol, fatty and salty foods at least a day before donating blood.
Decrease in ESR
A decrease in ESR is associated with an increase in blood viscosity. With a low ESR level, it is worth highlighting the physiological and pathological reasons for such a deviation. So, temporary (physiological) reasons for low red blood cell speed are as follows:
- Diet, including vegetarianism.
- Pregnancy (1st, 2nd trimester).
- Taking steroid hormones.
- Stress.
- Smoking.
- Dehydration of the body.
Pathological causes of decreased ESR include:
- Anemia.
- Overhydration (excessive accumulation of fluid occurs in the body).
- Polycythemia (increased red blood cell volume in the blood).
- Spherocytosis (formation of irregularly shaped red blood cells).
- Hepatitis.
- Hyperbilirubinemia (increased bilirubin levels).
- Liver failure.
You can learn more about ESR from the following video:
In the end, it is worth recalling that the analysis of ESR using the Westregren method determines the cause of the deviation, and not the disease. Therefore, after a general blood test, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination to identify possible pathologies.
What are the ESR norms according to Westergren for different categories of the population: table
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate depends on various factors, including the age and even gender of the patient.
Only a qualified doctor can determine whether the indicator is normal, but it is very simple to draw preliminary conclusions using the table.
| Age | Indicator in millimeters |
| For newborns | 1-2 |
| For children up to six months | 10-17 |
| In children 6-12 months | 1-10 |
| In children under 5 years of age | 4-11 |
| In children under 14 years of age | up to 15 for girls and up to 12 for boys |
| In women under 50 years of age | up to 20 |
| For men under 50 years old | up to 15 |
| In the elderly | up to 30 for women and up to 20 for men |
In addition to age and gender, lifestyle, chronic diseases, stress, nutrition and other factors are important and must be taken into account when deciphering.
ESR: assessment methods and clinical significance. Comparative assessment of Panchenkov and Westergren methods
Differential diagnosis of liver diseases with increased liver markers (AlT, AST, bilirubin)
Clinical significance of determining glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
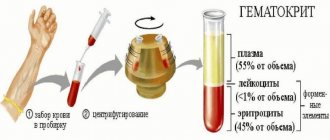
ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is one of the most common laboratory tests. Along with an increase in the number of leukocytes and a shift of the formula to the left, ESR serves as a laboratory sign of the presence of an inflammatory or infectious process.
Characteristics of the study:
ESR is an indicator of the rate of separation of blood in a test tube with an added anticoagulant into 2 layers: upper (transparent plasma) and lower (settled red blood cells). The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is estimated by the height of the formed plasma layer in mm per 1 hour. The specific gravity of erythrocytes is higher than the specific gravity of plasma, therefore, in the presence of an anticoagulant, under the influence of gravity, erythrocytes settle to the bottom. The rate at which erythrocyte sedimentation occurs is mainly determined by the degree of their aggregation, i.e. ability to stick together. The aggregation of erythrocytes mainly depends on their electrical properties and the protein composition of the blood plasma. Normally, red blood cells carry a negative charge (Z-potential of red blood cells), which is caused by charged sialic acid groups on the erythrocyte membrane, which contributes to their mutual repulsion and maintenance of red blood cells in a suspended state. The degree of erythrocyte aggregation (and therefore ESR) increases with increasing concentration of acute phase proteins (fibrinogen, C-reactive protein, haptoglobin, alpha-1 antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin, immunoglobulins, etc.). On the contrary, ESR decreases with increasing albumin concentration. Other factors also influence the Z-potential of erythrocytes: plasma pH (acidosis reduces ESR, alkalosis increases), ionic charge of plasma, lipids, blood viscosity, the presence of anti-erythrocyte antibodies. The number, shape and size of red blood cells also affect ESR. A decrease in the number of red blood cells (anemia) in the blood leads to an acceleration of ESR and, on the contrary, an increase in the number of red blood cells slows down the sedimentation rate.
In acute inflammatory and infectious processes, an increase in ESR is observed 24 hours after an increase in temperature and an increase in the number of leukocytes. The ESR indicator varies depending on many physiological and pathological factors. ESR rates in women are slightly higher than in men. Changes in the protein composition of the blood during pregnancy lead to an increase in ESR during this period. The values may fluctuate during the day; the maximum level is observed during the daytime.
Measuring ESR should be considered a screening test that is not specific for any disease. Typically, an ESR test is prescribed along with a general blood test.
Indications for the purpose of the study:
- inflammatory diseases
- infectious diseases
- tumors
- screening tests during preventive examinations
Research methods:
To determine ESR, the International Committee for Standardization in Hematology (ICSH) recommends the Westergren method. The method is a reference. The study is carried out in special Westergren capillaries with a lumen of 2.5 mm and a graduated scale of 200 mm. The results of the ESR study are expressed in mm per 1 hour (mm/hour).
In our country, the Panchenkov micromethod is more often used; for this method, a Panchenkov apparatus is used, consisting of a tripod and capillary pipettes with a 100 mm scale.
The results obtained when using the Westergren method, in the range of normal values, coincide with the results obtained when determining ESR using the Panchenkov method. However, the Westergren method is more sensitive to an increase in ESR, and the results in the zone of increased values obtained by the Westergren method are higher than the results obtained by the Panchenkov method.
Study of ESR in the laboratories of the CityLab Association:
The determination of ESR in the laboratories of the Association is carried out using the classical Westergren method on automatic StaRRsed analyzers from Radiomet. This analyzer automatically takes a sample, dilutes it with citrate in the required ratio, and the research results are sent to the information system. In addition, the technological features of the device allow automatic corrections to be made to the ambient temperature. When conducting research, the so-called “human factor” is completely excluded.
According to the nomenclature of research in CityLab laboratories, this research is:
01/03/020 - ESR (Westergren)
Taking blood for testing:
The blood is taken into a vacuum tube with EDTA.
Units: mm/hour
Reference values*:
| Age, gender | ESR, mm/hour | |
| Children under 10 years old | 0 — 10 | |
| Up to 50 years | men | 0 — 15 |
| women | 0 — 20 | |
| Over 50 years old | men | 0 — 20 |
| women | 0 — 30 | |
Note: * - Bottiger LE, Svedberg CA. Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and age. Br Med J 1967;2:85-7.
Increase (acceleration) of ESR:
- inflammatory diseases of various etiologies
- acute and chronic infections
- paraproteinemia (multiple myeloma, Waldenström's disease)
- tumor diseases
- autoimmune diseases (collagenosis)
- kidney diseases (chronic nephritis, nephrotic syndrome)
- myocardial infarction
- hypoproteinemia
- anemia
- intoxication
- injuries, bone fractures
- conditions after shock, surgical interventions
- in women during pregnancy, menstruation, and the postpartum period
- in elderly people
- when taking medications (estrogens, glucocorticoids)
To obtain comparable results and monitor the dynamics of the disease, it is recommended that studies be carried out in the same laboratory. However, treating physicians are sometimes approached by patients who have conducted research in different laboratories and the research results are difficult to compare (especially if the research was carried out using different methods, for example, the Westergren and Panchenkov method). As mentioned above, the results obtained using the Westergren method in the region of normal values coincide with the results of the Panchenkov method, but at high ESR values there is no such coincidence.
To facilitate the interpretation of the results of the ESR study, our doctors developed a table of correspondence of the results obtained by the Westergren and Panchenkov methods.
Table 1.
Correspondence of ESR results (obtained by Westergren and Panchenkov methods)
| IN | P | IN | P | IN | P | IN | P |
| 1 | 1 | 31 | 27 | 61 | 48 | 91 | 66 |
| 2 | 2 | 32 | 27 | 62 | 49 | 92 | 67 |
| 3 | 3 | 33 | 28 | 63 | 49 | 93 | 67 |
| 4 | 4 | 34 | 29 | 64 | 50 | 94 | 68 |
| 5 | 5 | 35 | 30 | 65 | 50 | 95 | 68 |
| 6 | 6 | 36 | 30 | 66 | 51 | 96 | 69 |
| 7 | 7 | 37 | 31 | 67 | 52 | 97 | 69 |
| 8 | 8 | 38 | 32 | 68 | 52 | 98 | 70 |
| 9 | 9 | 39 | 33 | 69 | 53 | 99 | 70 |
| 10 | 10 | 40 | 33 | 70 | 54 | 100 | 71 |
| 11 | 11 | 41 | 34 | 71 | 54 | 101 | 71 |
| 12 | 12 | 42 | 35 | 72 | 55 | 102 | 72 |
| 13 | 13 | 43 | 36 | 73 | 55 | 103 | 72 |
| 14 | 14 | 44 | 36 | 74 | 56 | 104 | 73 |
| 15 | 14 | 45 | 37 | 75 | 57 | 105 | 73 |
| 16 | 15 | 46 | 38 | 76 | 57 | 106 | 74 |
| 17 | 16 | 47 | 38 | 77 | 58 | 107 | 74 |
| 18 | 17 | 48 | 39 | 78 | 59 | 108 | 75 |
| 19 | 17 | 49 | 40 | 79 | 59 | 109 | 75 |
| 20 | 18 | 50 | 40 | 80 | 60 | 110 | 76 |
| 21 | 19 | 51 | 41 | 81 | 60 | 111 | 76 |
| 22 | 20 | 52 | 42 | 82 | 61 | 112 | 77 |
| 23 | 21 | 53 | 43 | 83 | 61 | 113 | 77 |
| 24 | 21 | 54 | 43 | 84 | 62 | 114 | 78 |
| 25 | 22 | 55 | 44 | 85 | 63 | 115 | 78 |
| 26 | 23 | 56 | 45 | 86 | 63 | 116 | 79 |
| 27 | 24 | 57 | 45 | 87 | 64 | 117 | 79 |
| 28 | 24 | 58 | 46 | 88 | 64 | 118 | 80 |
| 29 | 25 | 59 | 47 | 89 | 65 | 119 | 80 |
| 30 | 26 | 60 | 47 | 90 | 65 | 120 | 81 |
Note: ESR results are presented in mm/hour; B - Westergren method; P - Panchenkov method.
Literature:
- Lugovskaya S.A., Dolgov V.V. Laboratory Hematology. Tver, Triad, 2006.
- Bottiger LE, Svedberg CA. Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and age. Br Med J 1967;2:85-7.
- Brigden M. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate: still a helpful test when used judiciously. Postgrad Med 1998;103:257-74.
- Saadeh C. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate: old and new clinical applications. South Med J 1998; 3:220-5.
- Sox HC Jr, Liang MH. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate: guidelines for rational use. Ann Intern Med 1986;104:515-23.
- Stuart J, Whicher JT. Tests for detecting and monitoring the acute phase response. Arch Dis Child 1988;63:115-7.
- Wolfe F, Michaud K. The clinical and research significance of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. J Rheumatol 1994;21:1227-37.
ESR during pregnancy
Huge hormonal changes occur in a woman's body during pregnancy. Therefore, this test is performed at least four times during pregnancy. All in order to take timely measures in case of the slightest deviation in the health of the expectant mother and fetus.
In pregnant women, the normal value is 7-45 mm. In the first trimester it can fall very much (maybe 2-7 mm), which is most often associated with anemia. But before childbirth, on the contrary, women’s data can be high.
If the method shows too low data, the woman must be admitted to a hospital and undergo additional examinations. Sometimes the need for hospitalization arises when the analysis shows inflated numbers.
Note! If a pregnant woman eats too little meat, the Westergren ESR indicator in the tests is increased.
Normal and diagnostic values
Normal Westergren ESR values in women range from 2 to 15 millimeters per hour. In men, the normal rate of red blood cell sedimentation is considered to be 1-10 mm per hour.
Young children, including newborns, are characterized by a lower erythrocyte sedimentation rate compared to adults.
For the older age group (60 years or more), some sources indicate a figure of up to 15 mm per hour as the norm. In others, to determine this indicator, a formula is provided, with the help of which it is supposed to calculate the upper limit of the range of normal values. The upper limit of the norm, according to this system, is equal to age divided by 2 for men, and for women, before dividing the age indicator by 2, the number 10 should be added to it. For example, for a 60-year-old woman, this parameter is 35 mm per hour, and for a man of the same age - 30 mm per hour.
The described laboratory test is used to identify inflammatory processes of various etiologies. In addition, the sedimentation reaction of red blood cells helps determine the intensity of the inflammatory reaction. Most often, the Westergren ESR is elevated due to the presence of the following pathologies in the patient’s body:
- Infectious and inflammatory processes of an acute or chronic nature. This, according to statistics, is the most common cause of accelerated sedimentation of red blood cells. About 40% of cases of deviation of this parameter from the norm towards an increase is a consequence of infectious inflammation.
- Hypoxic damage to internal organs, including heart attacks. The acceleration of erythrocyte sedimentation in these cases is provoked by the so-called acute phase proteins, which settle on the surface of the formed elements.
- Diseases based on metabolic disorders, in particular cystic fibrosis, obesity, diabetes mellitus.
- Pathology of the hepatobiliary system.
- Immunopathological diseases.
- The presence of malignant neoplasms in the body.
- Anemia. Erythrocyte sedimentation in this disease, as a rule, is slightly accelerated. The exception is sickle cell anemia, in which this parameter differs significantly from the norm.
- Hypoproteinemia of various origins.
- Septic process. This pathology causes a very sharp increase in the sedimentation rate of red blood cells.
- Autoimmune pathology also leads to a pronounced increase in this parameter.
- Tissue breakdown associated with the presence of an aggressive malignancy.
- Leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma. In particular, myeloma can provoke an increase in ESR to 90-150 mm per hour.
- About 3% of cases of increased red blood cell sedimentation rate indicate diseases of the renal system.
- A slight increase in ESR can be provoked by allergic reactions.
- Some cases of an increase in this parameter may also be caused by dietary features, such as low protein content in food.
Medical statistics have recorded a number of cases where the reasons for the acceleration of blood sedimentation could not be identified even as a result of an in-depth detailed examination of the patient. It is believed that in some cases (rather rare), such an analysis result is a feature of the body that is not pathological in nature.
Both patients and specialists involved in diagnostics must remember that ESR is a nonspecific indicator. This means that, having received a result expressed in millimeters per hour, a specialist will not be able to make a specific diagnosis based on it. To determine the patient’s condition, a more detailed medical examination is required, and identifying ROE is only one of the auxiliary methods that allows us to suggest the direction of further examination.
In some cases, an increase in ESR contributes to the retrospective diagnosis of the disease, since it can remain elevated without returning to normal for up to 4 weeks after the patient has recovered from the disease that could have increased it.
In this regard, it is recommended not to prescribe control tests immediately after completing the course of treatment.
A more objective picture will be demonstrated by the result obtained in a later period, when a residual increase in the ESR indicator will be excluded.
There are reasons not associated with any pathology that can lead to an increase in this indicator:
- decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood during pregnancy;
- taking certain medications (for example, acetylsalicylic acid derivatives);
- period of menstruation.
Decoding the analysis: what diseases the results may indicate
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate varies throughout life. In the female half of humanity it is always slightly higher than in men. You also need to take into account age. The older the person, the higher the data. Although the sharpest jump is observed in the youngest children.
Diagnosis in a child is most difficult. The developing organism undergoes a lot of changes, and when sexual development begins, the data may generally have fundamental differences, even if the analyzes are done with a minimum interval.
That is why all the indicators are only indicative and an independent conclusion about the reasons for the increase or decrease in ESR can only be made approximate.
According to statistics, more than 10% of the total population of the Earth has an overestimated indicator. This is normal and is a physiological feature.
Westergren ESR is elevated, what does this mean?
An increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate occurs when inflammation and other processes begin in the body, causing blood to move faster through the veins and accelerating the production of red cells. It can be:
- any inflammatory processes (including gynecological and related to men's health);
- heart attacks and strokes;
- external and internal bleeding;
- trauma and pain shock;
- postoperative period;
- tumors.
Sometimes ESR is increased in those taking certain medications and especially glucocorticosteroids.
What does a decrease in ESR mean?
When red blood cells lose the ability to unite into complexes, their sedimentation rate decreases. Most often, this means that there is a malfunction in the water-salt balance of the body. This can be caused by:
- diets;
- taking steroids;
- poor nutrition;
- giving up meat (switching to vegetarianism).
Why deviations occur
Deviations can be either upward or downward. In most cases, any discrepancies indicate the presence of pathological processes in the body, but diagnostic errors cannot be ruled out. Therefore, if the results are controversial, when the ESR is not normal, but the patient has no signs of pathology, the blood is tested again.
Increased level
If Westergren's ESR is elevated, this means that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body. Reasons for the increase include:
- Diseases of the ENT system: laryngitis, tonsillitis.
- Diseases of the respiratory system: bronchitis, pneumonia.
- Intoxication of the body with low-quality products, chemicals, drugs.
- Deviations in the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
- Development of diabetes mellitus.
- Injuries: dislocations, fractures.
- Extensive bleeding.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Oncological neoplasms.
Important information: Table of norms for segmented and band neutrophils in children by age
The indicator may be elevated due to the following physiological processes:
- natural aging of the body;
- menopause;
- pregnancy;
- period after childbirth;
- puberty.
The result that turns out to be falsely elevated can be influenced by:
- state of emotional and physical arousal during blood donation;
- intense physical activity;
- weather;
- lack of sleep;
- sudden change in diet.
An increased sedimentation rate of blood cells, which primarily means inflammatory processes, in a pregnant woman may be a sign of other pathologies that pose a threat to normal gestation. This is partial detachment or premature aging of the placenta, the development of fetoplacental insufficiency, circulatory disorders due to blockage of blood vessels with calcifications. The danger of this pathology is that the baby does not receive enough oxygen through the placenta, which leads to hypoxia.
Reduced value
The indicator was lowered for the following reasons:
- anemia;
- weight loss;
- starvation;
- exhaustion;
- impaired blood circulation;
- epilepsy;
- violation of water metabolism.
ESR may decrease due to long-term use of medications that contain mercury, potassium chloride, and salicylates. Low levels are observed in people who are vegetarians and do not eat meat.
In young children, low speed may indicate congenital heart defects or acquired diseases of the heart muscle caused by impaired blood circulation. Another reason is polycythemia, in which there is an increase in the concentration of red blood cells and low protein levels.
How to normalize data
You can increase your ESR quite quickly. Sometimes it’s enough to adjust your diet or take a course of multivitamins. But this is only after consultation with a doctor! But reducing to normal levels is a longer process.
What do doctors recommend?
To restore normal ESR in children, they are most often prescribed iron-containing medications. In men and women, especially after 50, the cause may be rheumatism, arthritis, arthrosis, previous heart attacks and strokes, as well as conditions preceding attacks. In this case, after determining the cause, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and other groups of drugs can be prescribed.
If the situation is more serious and we are talking about tuberculosis, the formation of tumors, the norm in men and women is achieved in parallel with treatment in a hospital.
Important! In parallel with taking prescribed medications and vitamins, you should follow a diet containing large amounts of fresh vegetables and fruits, raisins, prunes, nuts, liver and beef heart.
The norm among children and adults
The ESR rate depends on a number of factors, namely: age; gender; time of analysis; individual characteristics (menstruation, pregnancy). Next, we highlight the normal value of ESR among men, women, pregnant women and children.
Men
ESR among men will be lower than among women. In addition, these indicators depend on age - the older the man, the higher the norm. So the normal value is:
- 10 - 50 years: 0 - 15 mm/h.
- Over 50 years: 0 - 20 mm/h.
Thus, the optimal ESR level is 8 - 13 mm/h.
Important! An ESR level of 15 - 30 mm/h indicates that a hidden pathology is developing. At a level of 30 - 60 mm/h, an inflammatory process occurs in the tissues; more than 60 mm/h, an extremely serious condition of the body is observed.
Women
The average rate of ROE in the weaker sex is 10 - 18 mm/h. The older a woman gets, the more the ESR norm according to Westergren increases:
- 10 - 50 years: 0 - 20 mm/h.
- Over 50 years: from 0 - 30 mm/h.
In addition, in women it is worth highlighting a number of physiological reasons that affect the ESR rate, for example: pregnancy; menstruation; menopause; transitional age. Read more at the link.
Pregnant
An elevated ESR level is normal for pregnant women, as the ratio of proteins in the body changes. Thus, the average ESR rate when carrying a baby varies between 15 and 30 mm/h, namely:
- 1st trimester: 12 - 22 mm/h.
- 2nd trimester: 21 - 25 mm/h.
- 3rd trimester: 25 - 45 mm/h.
Want to learn more about ESR during pregnancy? Then click here.
In addition, the level of ESR is influenced by factors such as:
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Weight – thin women have a lower ESR level than thick women.
- The presence of diseases, for example, anemia, inflammatory processes, disorders of the kidneys.
- Features of pregnancy.
Child
The ESR rate among children increases as they grow older. For example, a newborn has an ESR of no more than 2.5 mm/h. But when the child is 1 month old, the ESR is already 5 mm/h. At older ages, the normal ESR level is:
- Up to 6 months: 1 - 5 mm/h.
- 6 - 12 months: up to 6 mm/h.
- 1 -10 years: up to 12 mm/h.
- 10 - 18 years: up to 15 mm/h.
Would you like to learn more about the ESR norm among children? Then read our material How much is the ESR in a child?
Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate in blood
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a blood test that indicates how quickly red blood cells, or red blood cells, settle in blood that has been deprived of its ability to clot under the influence of gravity.
In this test, a small amount of blood is placed in a vertical tube and a technician measures the rate at which gravity causes the red blood cells to fall to the bottom of the tube over the course of an hour.
When there is inflammation or cellular damage in the body, red blood cells tend to clump together, making them heavier and settling faster. The faster the red blood cells stick together and settle, the higher the ESR. A high ESR indicates that there is active disease in the body.
What is the ESR test (Westergren measurement method) used for?
This test is performed if there are symptoms of a disease that may cause an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (inflammatory processes, tumors, etc.).
This test is also performed if you have already been diagnosed with a disease that causes this indicator to increase. The test allows your doctor to interpret how well you are responding to treatment.
Decoding the ESR allows you to diagnose or monitor diseases that cause pain and swelling due to inflammatory changes in tissues. Other symptoms may include fever and weight loss.
Accordingly, a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate correlates with greater disease activity, and a low erythrocyte sedimentation rate suggests lower inflammatory activity.
Westergen ESR is an internationally recognized method for determining erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which is most sensitive to its fluctuations.
Examples of diseases that are commonly monitored using an erythrocyte sedimentation rate test include:
- rheumatoid arthritis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- abscesses
- psoriatic arthritis
- septic arthritis
- vasculitis
- reactive arthritis
- polymyalgia rheumatica
- polymyositis
ESR is not used as a screening test in individuals without symptoms or a diagnosis of disease, because many conditions, including physiological ones, can lead to an increase in this indicator. An ESR test result that is abnormal does not indicate whether you have any specific disease. It only says that there is an active inflammatory process in the body.
Historical reference
In its modern form, the test for studying ESR has been known since 1921. It was created by the Swedish doctor Westergren based on the developments of the Polish doctor Biernaki and the Swedish doctor Robert Fareus.
Westergren not only improved the test, but also showed the diagnostic and prognostic value of this study in the treatment of patients with tuberculosis. In the USSR, since 1926, a modification of the Westergren method proposed by Panchenkov has been used.
In the USA, since 1935, ESR has been determined using the Wintrobe method, another modification of the Westergren method. Since 1977, the International Committee for Standardization decided to use only the Westergren method to determine ESR everywhere.
In Russia and the post-Soviet countries, the methods of Westergren and Panchenkov are used. The indicators of these studies diverge in the area of increased values, but coincide in the normal zone (from 0 to 20 mm/hour).
This means that you always need to pay attention, especially if the ESR is very elevated, a Westergren or Panchenkov analysis was performed.
What does a blood test for ESR show: norm and deviations
Measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is one of the key tests in the diagnosis of inflammatory processes and infectious diseases.
An ESR test can be prescribed as part of a general blood test for preventive purposes or to monitor the course of the disease.
You can take the necessary tests without queues and get results in just 2 hours in specialized laboratories.
Can't get tested in a laboratory? You can call a specialist to your home - conveniently and quickly.
Discount programs are a good way to save on medical examinations.
Quality control of clinical laboratory tests, carried out according to international standards, guarantees an accurate diagnosis.
The composition of the blood is very sensitive to any changes in the functioning of the body. Therefore, one of the most common diagnostic procedures is a clinical blood test. During its course, the concentration of hemoglobin, red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets and other blood characteristics, such as ESR, are determined. Let's figure out what this indicator means and why it is so important.
Why can ESR differ from the norm?
To determine what exactly caused the increase or decrease in ESR, you need to consult a doctor and undergo additional examinations.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe the patient the necessary treatment, after which everything should return to normal.
A change in the indicator does not always mean exactly a disease or pathology, but it may well indicate it, so you should not self-medicate and try to bring the ESR back to normal, ignoring the cause of the changes.
It must be remembered that this indicator is influenced by many factors: women's ESR is always higher than men's. In infants, the indicator can also be high, but then it decreases.
A decrease in ESR in children is sometimes associated with natural causes; this does not necessarily indicate pathology.
Normal ESR during pregnancy
A healthy non-pregnant woman has an ESR rate of -15 mm/h. An organism subject to various inflammatory processes, bleeding, tumors, anemia, kidney disease will always show a high level of ESR. Also, the ESR level will always be elevated after an illness.
If there is an excess of protein in the blood, the viscosity of the blood increases significantly, and the structure of red blood cells is disrupted. In this case, the ESR indicator will be reduced. The reduction is also facilitated by weight loss diets and an increase in the amount of plant foods consumed.
The same thing happens to a woman during pregnancy. ESR can increase and decrease depending on the processes occurring in the body. It is worth noting that during pregnancy there is a change in the protein composition of the blood, which is why the ESR level increases over the course of nine months. For a woman carrying a fetus, the ESR level can reach 45-60 mm/h and this is considered normal.
In the first six months, most women experience a decrease in ESR. But in some pregnant women the indicator is still too high. On the contrary, the second half of pregnancy gives an increased rate of almost three times the norm for a non-pregnant woman. It is then that it can reach 60 mm/h. This indicator will also be observed immediately after childbirth during the first month, and sometimes three.
A woman's pregnancy is divided into trimesters. The most common ESR indicators during pregnancy for the three trimesters will be: 15-20 mm/h, 25-30 mm/h, 45-60 mm/h. Typically, these standards can be applied for a normal pregnancy, without complications and pathologies, as well as without suffering from various diseases during gestation. But it should be noted that each woman’s body is individual, so indicators may vary and only a doctor can determine the health status of the mother and child.
Incorrect determination of ESR during pregnancy is refuted by repeated analysis in order to destroy assumptions about the woman’s health problems.