A smear on the vaginal flora is today one of the most common tests, which is carried out directly in the gynecological office. Any woman expecting a child has encountered this study before pregnancy. In the new situation, a smear on the flora during pregnancy becomes more important. At this time, you should pay more attention to this analysis and understand what its results mean.
Flora smear in women
Leukocytes are white blood cells whose main function is to protect the body from pathogenic agents (internal and external).
When an infection penetrates, leukocytes begin to actively multiply, absorbing foreign cells and blocking the spread of infection. Based on the number of leukocytes in a gynecological flora smear, a specialist assesses the condition of a woman’s genitourinary system.
Indications for testing
A flora smear is a standard test performed by a gynecologist when examining a woman’s genital organs. The procedure involves taking a small amount of biomaterial from the vagina, urethra and cervix. Analysis is prescribed in the following situations:
- presence of complaints of discomfort in the perineal area, atypical vaginal discharge, unpleasant odor of discharge;
- preventive examination;
- after a course of treatment for genitourinary infections;
- to monitor the effectiveness of current therapy;
- before performing procedures or surgery in the genital area;
- planning conception and pregnancy;
- change of sexual partner or detection of a urogenital infection.
During pregnancy, a smear for flora is taken in accordance with the medical examination plan for the pregnant woman. However, an extraordinary test must be taken if:
- discomfort and itching in the groin area;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain when urinating;
- uncharacteristic appearance, smell and consistency of discharge;
- discomfort during sex.
Preparation for analysis, frequency of delivery
Before pregnancy, a smear for flora should be taken in the middle of the menstrual cycle (approximately between the 10th and 20th day). After conception, the test is taken on any day of the month. When preparing for the study, the following requirements must be met:
- 48 hours before taking biomaterial, refuse sexual intercourse and do not douche;
- within 24 hours before the study, do not use vaginal suppositories, tablets, creams and lubricants;
- refrain from urinating 2-3 hours before collecting biomaterial;
- on the day of taking a smear, carry out hygiene procedures without using soap and other hygiene products.
The frequency of testing before pregnancy depends directly on the woman’s health status. If nothing bothers her, it is recommended to do a smear once every 6 months. During the period of bearing a baby, the frequency of delivery also depends on the medical indicators of the pregnant woman. For a healthy woman, the test is prescribed three times: upon registration, at 30 weeks and after 36 weeks (as decided by the doctor).
Decoding and indicators of the norm
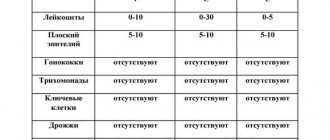
The smear is assessed according to the following indicators: the number of leukocytes, epithelial cells, mucus, the presence of key cells, yeast fungi, gonococci, trichomonas, etc. The specialist makes a decoding based on medical standards for the content of each element in the material. Depending on the established quantitative indicators, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
A lot of leukocytes indicates the presence of an inflammatory process or infection in the genital tract. A low level of leukocytes is observed when the hormonal system is disrupted and in women who have not had sexual intercourse for a long time.
Increased mucus content also indicates inflammation or infection. Yeast and other pathogenic microflora appear in genitourinary diseases. A small number of gram-positive rods, Doderlein rods and lactobacilli are observed when the internal flora in the vagina is disrupted. The table shows the norms of leukocytes and other smear indicators for flora.
When should you check your microflora?
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is important for a woman to monitor her body's signals. You should seek medical advice if:
- Itching appeared in the genital area.
- Vaginal discharge has become profuse and has a cheesy consistency.
- After urination, a burning sensation appears.
- The discharge has a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Periodically there are nagging pains in the lower abdomen.
The listed symptoms indicate the development of an inflammatory process and the need for urgent treatment. A smear on the flora helps determine the type of pathogen, but in some cases the infection may be hidden. In this case, it is necessary to undergo additional tests.
How to reduce leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy: treatment
Normalizing the level of leukocytes is directly related to eliminating the problem that caused this condition. Based on the results of an assessment of symptoms, as well as the data obtained from additional examinations, the doctor determines the cause of the increased number of leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy and the necessary treatment regimen
It is important to remember that self-prescription of drugs is strictly unacceptable.
Drug treatment of leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy
If a disease is detected, then herbal treatment alone will not be enough. An integrated approach to eliminating the disease includes both local and general therapy.
- Antibacterial therapy is prescribed, but only if there are absolute indications. For example, when gonorrhea, ureaplasma or syphilis are detected, Ceftriaxone, Azithromycin, and Erythromycin often become the drugs of choice.
- Treatment for genital herpes is not always prescribed. But in cases where the doctor sees the feasibility of therapy, Zovirax ointment can be used.
- In cases of candidiasis, treatment with drugs such as Pimafucin, Polygynax, Livarol, Clotrimazole, Terzhinan is possible (the last 3 drugs are prohibited for use in the first trimester of expecting a baby)
- Solutions of potassium permanganate, miramistin, chlorhexidine, and chlorophyllipt can also be used to treat the genitals.
Methods of traditional therapy for leukocytes during pregnancy
If no serious abnormalities are found, the woman can turn to traditional medicine. But even in this case, a preliminary consultation with a doctor is necessary.
- Herbal decoctions will help normalize vaginal microflora. St. John's wort leaves, chamomile, aloe, oak bark or red root are suitable for these purposes. To carry out the procedure, you must prepare a warm sitz bath with a healing decoction. Sage, coltsfoot, and calendula also have a good effect.
- Candles with sea buckthorn oil. Mix 10 g of oil with beeswax. Melt the resulting composition in a water bath, while simultaneously mixing in 3 g of pine resin. Pour the resulting mass into molds (for future suppositories) and cool. Insert 1 suppository vaginally before bedtime.
- It is necessary to improve nutrition by saturating the diet with fermented milk and protein products.
- Until complete healing, abstinence from intimate relationships is recommended.
Do not worry too much if, after the analysis, a large number of leukocytes are found in a smear during pregnancy. Additional tests and examinations will help determine the exact cause of the violations and effectively deal with them.
Swabs for tank culture and PCR
During pregnancy, tank cultures can be taken from the cervical canal or directly from the cervix. The essence of the procedure is tank smear culture, which allows you to identify a quantitative indicator of bacteria that are present in the woman’s reproductive system and determine the conditionally pathogenic flora - types of pathogens. The culture result indicates the presence of:
- Escherichia coli and enterococci;
- yeast fungi;
- staphylococcus;
- Proteus;
- gonococcus;
- Trichomonas;
- gardnells;
- leptrix;
- citrobacter.
The results of this type of smear also determine the nature of further treatment, because a laboratory worker can immediately conduct a test to determine the sensitivity of a particular organism to a group of drugs. This method of research is carried out, as a rule, in the process of preparing for pregnancy, and not for diagnosing it. There are no obvious markers in the microflora that can be released during fertilization of the egg.
The number of leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy
Leukocytes - white blood cells - are responsible for protecting the body from various infections (viruses, bacteria, pathogenic microorganisms). Ideally, any offending bacteria is immediately destroyed by defender cells. If there are too many infectious agents, there is a need to increase the number of leukocytes at the site of the lesion. When they are eliminated, blood cells are destroyed. An inflammatory reaction occurs, which is manifested by swelling, redness, and fever.
When registering, a woman undergoes a full diagnostic examination of the body and visits the necessary specialists. Since the new condition affects all organs, changes hormonal levels and reduces immunity, exacerbation of chronic or development of hidden pathological processes is possible. This will be indicated by the level of leukocytes in the smear and in other tests. The degrees of purity of a vaginal smear for flora are distributed as follows:
Grade 1 contains 0-5 leukocytes, which indicates the absence of any infectious agent.
Grade 2 allows 5-10 leukocytes. This amount indicates the minimal presence of pathogenic microorganisms that do not affect the functions of tissues and organs. All other indicators (lactobacteria, epithelium, mucus level) do not exceed the indicators. Therefore, this degree is considered a variant of the norm.
Grade 3 has more than 10 leukocytes (up to 50). The smear reveals a lot of epithelium and mucus.
4th degree - the number of leukocytes cannot be counted and the term “complete” is indicated. Pathogenic microflora (Trichomonas, gonococci) is clearly detected, lactobacilli are not detected.
In grades 3 and 4, the cause of the infection is determined and, if necessary, treatment is carried out. If the inflammatory process is not eliminated, bacteria may enter the uterine cavity and infect the amniotic fluid and fetus, which will inevitably lead to miscarriage or premature birth.
During pregnancy, the body activates defense mechanisms, so a slight increase in the number of leukocytes in a smear is acceptable (10-15 units per field of view). But this does not mean that any infection has occurred. Under the influence of estrogens, the acidity of the vagina increases, which blocks the development of pathogenic flora, attracting a small number of leukocytes.
Infectious screening during pregnancy - indications for implementation
Normally, during pregnancy the following is indicated:
- double tank culture from the cervical canal;
- triple smear during pregnancy;
- a three-time test for syphilis (at registration, at the thirtieth week and before birth - two to three weeks);
- double HIV testing (at registration and at the thirtieth week);
- analysis for TORCH upon registration, as well as tests for hepatitis B and C (twice: upon registration and in the third trimester).
According to indications, in case of previous miscarriage, the following is indicated:
- bacteriological, bacterioscopic smears every 2-3 weeks;
- virological examination of smears every 2-3 weeks;
- PCR for mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma in the presence of symptoms of the inflammatory process.
The norm of white cells in a smear in pregnant women
The number of leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy can vary from 0 to 30 units (under a microscope in the field of view).
At the same time, the permissible norm of white cells in a smear taken from the vaginal passage, urethra and cervix differs from each other.
Thus, in the analysis of material taken from the vagina, the number of leukocytes should not exceed 15 units, in a smear from the urethra - 5 units. In an analysis taken from the cervical canal, the leukocyte level can reach 30 units.
During pregnancy, a woman should take the first test for leukocytes in a smear at 12 weeks; a repeat smear is prescribed at approximately 30 weeks.
If a pregnant patient has complaints of discomfort in the vagina, a smear is taken when visiting a doctor. A routine final leukocyte smear is prescribed before delivery after 36 weeks.
Table of leukocyte norms by week of pregnancy:
Based on the above indicators, one can judge the state of health of a pregnant woman only superficially - a doctor can only determine the exact reasons for the increase in leukocytes in a smear based on the results of additional studies.
As mentioned above, in women carrying a child, the vaginal flora changes and the immune system is weakened, which makes it easier for infections to enter the body. For this reason, pregnant women should take more careful care of their intimate areas.
The result of a smear analysis of the vaginal flora is very important during the period of bearing a child, since it is vaginal infections that provoke premature birth and can cause planned termination of pregnancy at a later stage.
Therefore, if a pregnant woman is constantly worried about vague pain in the lower abdomen, itching in the vaginal passage, discomfort when urinating and unusual discharge, then in order to save the child she needs to undergo a series of examinations, after which the direction of treatment will be chosen.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the risk of vaginal infection increases, which equates to the threat of miscarriage.
For this reason, it is advisable for a pregnant woman to take a smear on the flora twice before giving birth (at 30 and 36 weeks).
If during the examination a significant increase in leukocytes in the smear is detected, then the woman is prescribed additional tests, because leukocyturia can be a sign of inflammation of the genitourinary system, which at an early stage is often asymptomatic.
Types of strokes
When registering with the antenatal clinic, expectant mothers are interested in what smears are taken during pregnancy and whether this is really necessary. It should immediately be noted that examining a woman’s health status in early pregnancy is of particular importance for the doctor. Only diagnostics will show the true picture and eliminate the threat of miscarriage.
In gynecological practice, there are several types of smears showing the state of women's health. They are classified as follows:
- Flora smear - allows you to identify an imbalance of good and bad vaginal microflora. The analysis shows the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and dead epithelial cells. Based on the results, the degree of purity of the smear is assessed;
- Cytology smear – necessary to diagnose changes in cervical cells;
- Sterility smear - prescribed to determine the composition of the vaginal microflora, helps to see deviations in hormonal levels;
- A smear for hidden infections - PCR diagnostics is extremely important during pregnancy. The method allows you to detect infections that a microflora smear cannot detect.
Urogenital infections pose a serious threat to the life and normal development of the fetus. Therefore, having received a referral from the attending physician for the diagnosis of hidden infections, the expectant mother should not delay the examination.
Leukocytes in a smear - the norm in women, table
Depending on how many white blood cells are found in your smear, your doctor will prescribe treatment. The table shows data on what amount is normal for women. If deviations are present, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations in order to stabilize the state of the microflora.
| Place of crop collection | Norm | Ideal indicator |
| Vagina | 0-10 | 10 |
| Urethra | 0-5 | 5 |
| Cervix | 0-30 | 15 |
class="table-bordered">
However, this table does not indicate the norm of leukocytes in a smear in women by age, and it may differ. For example, after 40-50 years, the ideal level of these cells in the vagina and urethra may change by two units, and in the cervix by one. Such deviations are possible due to the fact that menopause is approaching, and with age, women become more likely to have diseases of the genital organs in remission.
This table shows the norm of leukocytes in a smear in women after 40 years of age:
| Place of crop collection | Norm |
| Vagina | up to 12 units |
| Urethra | up to 7 units |
| Cervix | up to 16 units |
class="table-bordered">
Norm of leukocytes during pregnancy
The formation of an embryo in the body stimulates the launch of a number of processes that must proceed smoothly
To achieve this, it is important that all endocrine organs that produce hormones work in a balanced manner.
Changes in the hormonal balance provoke changes in the functioning of the organs and systems of the female body, the load on the kidneys increases, the vaginal microflora changes and, accordingly, the number of leukocytes. Thus, in the number of leukocytes in a smear in women, deviations from the norm are possible not only by age, but also during pregnancy (by 1-3 units).
The norm of leukocytes in a smear before menstruation
Often, a significant change in the number of white blood cells before menstruation (in 40% of cases) is associated with the presence of hidden STIs in the body. However, in 1% of subjects, such changes may be natural and not indicate problems with the genitals. The following table shows the norm of leukocytes in a smear in women before menstruation.
| Place of crop collection | Norm |
| Vagina | 35-40 |
| Urethra | to 10 |
| Cervix | up to 30 |
class="table-bordered">
The norm of leukocytes in a smear after menstruation
If you take a smear for flora immediately after menstruation, you can notice a significant deviation in the number of white blood cells from the standard by 1-3 units, since in the first 48-72 hours after menstruation the uterus may not yet be completely cleansed.
If you do not adhere to the rules of hygiene or use tampons incorrectly during monthly bleeding, the number of white blood cells can increase significantly, but these indicators, as a rule, normalize after a few days if hygiene is improved.
Important! Frequent use of tampons and neglect of the rules of washing during menstruation can cause the development of serious inflammation in the female reproductive system
The norm of leukocytes in a smear in virgins
The permissible number of leukocytes in girls who have not previously had sexual relations corresponds to the norm for women who are sexually active. Causes of leukocytosis in virgins:
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- masturbation;
- petting;
- hypothermia;
- using someone else's underwear;
- wearing only purchased underwear without washing;
- going to a public pool/sauna.
Causes and manifestations
If a woman has a “bad” smear during pregnancy, she must first figure out what is causing it. To do this, you need to take into account all the analysis indicators. When only leukocytes increase, and all other cells are within normal limits, then most likely there is no need to worry. It is known that during pregnancy the immune reactions of the female body change, which can affect the composition of the vaginal environment. And when pronounced violations are visible, the alarm should be sounded. They may indicate the following diseases:
- Vaginal dysbiosis (bacterial vaginosis or gardnerellosis).
- Candidiasis (thrush).
- Nonspecific colpitis.
- Inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis).
- Gonorrhea.
- Trichomoniasis.
In turn, these diseases are characterized by certain symptoms. Most often they are local in nature, that is, they reflect the development of microbes on the vaginal mucosa. These symptoms include:
- Pathological discharge: thin or thick, white, yellow-green, brownish, abundant or scanty, with an unpleasant odor.
- Feeling of burning and itching in the intimate area.
- Discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
The mucous membrane of the vagina or cervix (with cervicitis) is hyperemic, swollen, and covered with plaque. It is easily vulnerable and is characterized by contact bleeding. With bacterial vaginosis, there are no signs of inflammation, so nothing but discharge bothers the woman.
If an infection develops in the vagina, there is a high risk for the course of pregnancy and the health of the unborn child. It is known that inflammatory pathology of the lower genital tract increases the likelihood of the following conditions:
- Spontaneous abortions.
- Premature birth.
- Intrauterine infection.
- Weakness of labor.
- Postpartum hemorrhage.
Therefore, it is in the interests of a woman to take smears for flora on time in order to prevent dangerous phenomena during pregnancy. And if changes are detected in the analysis, then it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
The causes of a “bad” smear are associated with dysbiosis or an infectious-inflammatory process in the vagina. This gives corresponding symptoms and complications.
What is microflora?
Vaginal microflora is a collection of microscopic data from the organisms that inhabit it. It is characterized by strict individuality, for which reason the use of other people's hygiene products is strictly prohibited.
In the normal state, the vaginal microflora consists of lactobacilli, the purpose of which is to produce lactic acid. In turn, it is due to the acidic environment that negative conditions are created for the life activity and subsequent spread of pathogens, which acts as a protective barrier against pathological factors. Another name for lactobacilli is Dederlein bacilli or lactomorphotypes.
However, the vagina is also inhabited by a pathological environment consisting of microorganisms that pose a potential danger. Their activation is facilitated by a number of specific factors:
- stressful conditions;
- decreased immunity;
- use of powerful drugs;
- changes in hormonal levels.
The pathogenic environment is inhabited by:
- various coccal infections;
- gardnerella, which provokes a bacterial form of vaginosis;
- candida fungi, which cause the development of thrush.
However, during pregnancy, pathogens that enter the vagina from the external environment pose a particular danger, which most often occurs due to infection during unprotected intimacy. Such bacteria are characterized by rapid reproduction, which becomes the cause of severe gynecological diseases of a venereal nature.
When a smear is taken for flora during pregnancy, the pathogens present are identified at the very beginning. This analysis makes it possible to identify the species and quantitative characteristics of pathogens, which acts as a determining factor in therapy. It must be said that it does not detect gynecological diseases, being exclusively a preparatory research method, after which, if pathogenic microflora is detected, a culture becomes necessary.
What changes occur in the vaginal microflora during pregnancy?
To understand why this analysis plays such a role, let’s consider what happens in the body of a pregnant woman and what a smear on flora is during pregnancy. Hormonal changes cause the number of epithelial cells in the vagina of the expectant mother to increase. In addition, these cells begin to store glycogen.
The secretions serve as a substrate for lactobacilli, which produce lactic acid. Thanks to this process, an acidic environment of pH 3.8 - 4.5 is maintained in the vagina, which is optimal for healthy microflora and destructive for harmful microorganisms.
Gradually, during pregnancy, the number of lactobacilli increases, it increases tenfold. Compared to non-pregnant women, expectant mothers have a reduced number of bacteria in the cervical canal. This is an important condition for protecting the fetus from infection by pathogens as it moves through the mother’s birth canal during childbirth.
A healthy body constantly contains a large number of different microorganisms, including bacteria and bacterial bodies. About 95-98% of the microflora are Dederlein's bacilli. These are bacterial structures consisting of several types of lactobacilli - Lactobacillus Casei, L. acidophilus, L. Cellobiosus, L. Fermentum. They look like stationary curved or straight lines or sticks. These rods produce lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide, maintaining the acidic environment of the vagina, preventing other microbes from attaching to its walls, and also activating the immune system of the expectant mother.
In addition to Dederlein's rods, bifidobacteria are present in the vagina. Often, even in the absence of symptoms of inflammation, small amounts of Candida fungi are detected in the smear.
Under stress or due to taking antibiotics, a woman's immune defense may weaken. Then the number of lactobacilli will decrease, and the colonization of mucous membranes by fungi will increase. This condition is called vaginal candidiasis and is accompanied by itching, burning, and the appearance of cheesy discharge from the vagina.
Flora smear procedure
A smear is the most painless and fastest way to take biomaterial for research. While the woman lies in the gynecological chair, the doctor runs a sterile disposable spatula along the urethra, vaginal wall and cervical canal. A total of three samples are obtained, which are applied to a glass slide and sent to the laboratory. Here the biomaterial is stained using the Gram method and examined under a microscope. In addition to the microbial composition of the samples, the content of blood cells (leukocytes and erythrocytes), key cells (epithelial fragments covered with bacteria), the laboratory technician evaluates the color, smell and amount of discharge.
Sometimes women ask the question “Does a smear indicate pregnancy?” No, it only gives information about its progress. Based on this analysis, the degree of vaginal cleanliness is assessed, reflecting its condition. There are four degrees in total:
- The first degree characterizes the healthy microflora of the vagina. Opportunistic pathogens and leukocytes are either not present at all or an insignificant amount is detected. An acidic vaginal environment and a lot of lactobacilli were revealed.
- The second degree of purity is assigned if the flora indicators are slightly increased, but remain within normal limits. For example, the number of leukocytes in the vagina has increased to 20. This is acceptable during pregnancy, in the absence of other signs of the inflammatory process.
- The third degree or dysbiosis is the predominance of pathogenic microflora over the natural one. Few lactobacilli are detected, the vaginal environment becomes alkaline, and symptoms of inflammation are observed. These indicators signal the development of bacterial vaginosis.
- The fourth degree or vaginitis is a condition when the smear on the flora exceeds the norm of leukocytes, a large number of pathogenic microorganisms and a lot of red blood cells are detected. The vaginal environment is alkaline. All this speaks of acute inflammation occurring in the woman’s body.
It is clear that ideally, the smear test certificate of the expectant mother should indicate the first or second degree of cleanliness of the genitals. However, if another condition is established, then this is a reason to clarify the disease and begin treatment.
"Degree of purity"
When conducting research in the laboratory, indicators such as the smell and viscosity of the diagnosed material are assessed. Depending on the indicators of pathogenic microflora that smears may contain during pregnancy, the specialist assesses the degree of purity. There are four such degrees in total:
- The first degree indicates an ideal smear for microflora. The number of lactobacilli reaches 95%, which indicates the correct acid-base balance and good protection against the development of pathology.
- The second degree is given if a small amount of opportunistic microflora was found in the smear, but these values are within normal limits. The number of lactobacilli, as in the first degree, should prevail over the others and be at the level of 90%.
- The third degree indicates the development of dysbiosis (bacterial vaginosis). There are fewer Doderlein rods in such a smear than are necessary for the normal state of the flora. The number of gram-negative bacteria increases.
- The fourth degree is characteristic of vaginitis. In such a smear, an alkaline environment predominates, an increased number of leukocytes and epithelium is observed. Bad smears during pregnancy are a reason to undergo a repeat test.
Taking a smear: norm and deviations
If, based on the results of a flora analysis, a lot of leukocytes are found in a smear in pregnant women, this means that an inflammatory reaction is developing. Bacterioscopic smear analysis makes it possible to examine pathogenic microflora, detect accumulations of pathogenic organisms and find the causes of hormonal imbalance.
Preparing for analysis
In order for the research results to be as authentic as possible and reflect the actual picture, you need to properly prepare for your visit to the clinic. General recommendations of gynecologists are the following simple rules:
- A day or two days before the test, stop douching and refrain from sexual relations.
- On the eve of your visit to the clinic, do not use any intimate products, including personal hygiene soap.
- For several hours before the test, try to refrain from urinating.
Normal indicators and interpretation of the analysis
The number of leukocytes in a smear is one of the basic parameters of flora analysis during pregnancy. Indicators of the normal concentration of white blood cells in a smear range from 0 to 30 units. If the number of units exceeds the number “30”, this should motivate a woman in this position and her loved ones to take action as soon as possible.
Scrapings are carried out sequentially. In each subgroup, the norms vary slightly. Below is a breakdown of the analysis:
- U-uretra (when scraping a smear at the entrance to the urethra). The number of leukocytes is from 0 to 5 units per field of view.
- V-vagina (when scraping a smear from the vaginal walls). The number of leukocytes is from 0 to 15 units.
- C-cervix (by scraping a smear from the cervical canal of the cervix). The number of leukocytes is from 0 to 30 units.
How often should a pregnant woman have a smear test?
A pregnant woman should take a smear test under the following circumstances: when she first registers, in the seventh month of pregnancy, and also immediately before giving birth. An unscheduled examination may be required if the patient complains of feeling unwell, in case of polyhydramnios, if there is a threat of miscarriage, or if the fetus is infected.
If during pregnancy in the 2nd trimester a lot of leukocytes are found in the smear, this means that the inflammatory reaction is progressing in the body. However, the threat of developing infectious diseases in the 2nd trimester is minimal, so at this time a pregnant woman is rarely sent for examinations. If the concentration of blood cells during this period is slightly higher than normal, this is not yet a reason to panic. A slight deviation from standard indicators can occur with a general increase in the production of blood cells, which provide additional protection to the body of the mother and child from viruses.
Flora analysis in the 3rd trimester is prescribed twice: at a period of 7.5 and 9 months. During pregnancy in the 3rd trimester, the expectant mother has a high risk of developing vaginal infections, therefore it is necessary to ensure that the leukocyte counts in the smear are normal. At this stage of gestation, the risk of miscarriage increases if the fetus becomes infected. Therefore, a pregnant patient needs to closely monitor her well-being and not reject the doctor’s recommendations.
Correction
Detection of pathological symptoms of the vagina during pregnancy – both laboratory and clinical – is an indication for therapeutic correction. In this case, the type of therapeutic measures is determined by the nature of the disorders and their cause. In most cases, medications are used. However, their use is limited due to the possible negative effect of some drugs on the fetus. To prevent this, the doctor prescribes local remedies: ointments, creams, vaginal suppositories and tablets, douching. And if there is a need for systemic therapy, then it is carried out in the second trimester of pregnancy. The following medications are used:
- Antiseptics (Hexicon, Miramistin, Betadine).
- Antifungal (Pimafucin, Diflucan).
- Antiprotozoal (Trichopol).
- Probiotics (Linex, Hilak Forte, Bifiform).
The use of antibiotics is limited, but if necessary, the safest drugs are used (from the group of penicillins, cephalosporins). During treatment, a woman must follow all the doctor’s recommendations, and after treatment, she must take a control smear from the vagina to determine the effectiveness.
A vaginal smear is indicated for every pregnant woman. It is done repeatedly during the entire period of bearing a child, but this is necessary for early detection of changes in the composition of the vaginal environment. If the smear turns out to be “bad,” then most likely you will have to undergo a course of therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation and infection and restoring the vaginal microflora. Timely correction of pathology will help avoid adverse consequences, especially those that are dangerous to the fetus.
Timing for taking a smear during pregnancy
In a normal pregnancy, a smear for bacteriological examination is taken when the woman is registered, at 30 weeks and before birth. However, if there is a history of spontaneous miscarriages, threatened miscarriage, polyhydramnios, intrauterine infection of the fetus, or chorioamnionitis, then studies are carried out over time at the discretion of the doctor and additional diagnostic methods are used to verify the causative agent.
A smear is taken during a routine gynecological examination on a chair, the material is collected with a sterile or disposable instrument from the urethra (urethra), the side wall of the vagina and the cervix, and then smeared onto a labeled glass slide and sent to the laboratory. The quantity, color and smell of mucous discharge, and the condition of the walls of the vagina and cervix are assessed. In the laboratory, the smear is Gram stained and its microbial composition, the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells and key cells (epithelial cells covered with bacteria) are studied. There are the following degrees of vaginal cleanliness:
- The first degree of frequency (normocenosis)
is characterized by an acidic reaction of the environment, a large number of Dederlein bacilli, and a small content of facultative flora. Red blood cells and white blood cells are rare in the field of view. - Second degree (intermediate type of smear)
. The reaction of the environment is acidic, the number of lactobacilli predominates over other microbial cells, the number of leukocytes increases to 15 in the field of view (during pregnancy, up to 20 are allowed in the absence of signs of inflammation). - The third degree (dysbiosis)
is observed with bacterial vaginosis. Lactobacilli are almost absent; the smear contains a large number of gram-positive cocci, gram-negative rods, and obligate anaerobic bacteria. - Fourth degree (vaginitis)
. There are no lactobacilli, an alkaline reaction of the environment, a large number of erythrocytes and leukocytes, key cells and pathogenic microorganisms are present.
Additionally Normally there should be the first or second type of smear.
1–2 days before taking a smear, sexual contact is not recommended; douching, the use of vaginal suppositories and tablets, as well as local disinfectants should be avoided. On the day of going to the doctor, genital hygiene is carried out without using soap.
results
After taking vaginal smears, you will have to wait no more than a day for the results. The doctor will then tell the patient what changes have been identified. As stated earlier, the material is taken from three different places and is therefore analyzed separately. For the vagina, cervical canal and urethra, the following basic indicators are determined:
- Leukocytes.
- Flat epithelium.
- Microflora.
- Gonococci.
- Trichomonas.
- Key cells.
- Fungi.
- Slime.
Each of these components is important for the doctor. But first you need to figure out what is normal for a pregnant woman, because serious changes occur in her body that can affect the readings of a vaginal smear. Oddly enough, all her indicators should coincide with those for non-pregnant women. Namely: no more than 10 units of leukocytes (30 and 5 units, respectively, for the cervix and urethra), from 5 to 10 epithelial cells, a predominant number of lactobacilli, a moderate amount of mucus. All other cells should not be present in the smear.
Based on the content of its main components in the microflora - lactobacilli or, as they are also called, Doderlein bacilli, the doctor makes a conclusion about the degree of cleanliness of the vagina. This is an extremely important concept that allows us to establish the severity of disturbances in the natural biocenosis and the risk of inflammatory processes. According to the existing classification, the vagina has the following degrees of cleanliness:
- I – there are many lactobacilli, the environment is acidic, there are few leukocytes and epithelium.
- II – the number of lactobacilli decreases, coccal flora develops, the environment is slightly acidic, leukocytes increase.
- III – single Doderlein rods, many cocci, up to 40 leukocytes in the field of view, neutral or slightly alkaline medium.
- IV – there are no lactobacilli at all, pathogenic microbes are detected, there are many leukocytes, the environment is alkaline.
The first degree is considered the absolute norm, i.e. the vagina is “clean”. The second is quite acceptable for pregnancy and should not cause much concern. The third degree indicates severe dysbiosis, and the fourth indicates vaginitis - an inflammatory process in the vagina. Therefore, the latter are precisely the “bad” smear that everyone is wary of during pregnancy.
The results of the smear describe the cellular composition of the vagina and the degree of its cleanliness during pregnancy.
How to properly prepare for the analysis?
Leukocyte smears are usually performed two to three times during pregnancy.
It allows you to identify violations of the vaginal microflora in a woman during pregnancy, so it is important to take it after basic hygiene procedures to reduce the likelihood of contamination of the smear
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Only a clean smear will accurately identify possible pathologies in the body of the expectant mother. In addition, before taking a smear, a woman needs to abstain from sex 2 days before the test.
Also, a few days before going to the doctor, you should not use various alkaline products for intimate hygiene, as well as use suppositories, tablets, ointments, and creams for the vaginal area. It is also better not to visit the restroom for two hours immediately before the procedure. But even with a full bladder, you shouldn’t go for testing.
If a significant number of leukocytes are detected in a vaginal smear, urgent treatment is necessary. The use of some antibiotics is allowed. Before prescribing treatment, the doctor prescribes additional tests and a culture tank. Tests are also carried out to determine individual sensitivity to various drugs.
Of course, aggressive treatment is not always prescribed. It depends on the type of infectious disease, as well as the stage of its development. In any case, it is necessary to undergo a vaginal smear test to avoid health problems for the child and the woman herself.
Author of the article
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Rating: No rating
Leukocytes are responsible for the state of immunity, and during pregnancy it is very important to monitor their number. What are they? What is the normal leukocyte count? What are the causes of possible deviations, and how to treat them?
“Good flora” - what does it mean?
Microflora is a collection of various bacteria that constantly inhabit the vagina. In an ideal state of health, lactobacilli are predominantly found there - Doderlein bacilli, which produce beneficial lactic acid. If there are enough of them, pathogens have no chance to survive in the acidic environment of the vagina.
During pregnancy, test results change slightly. The number of vaginal epithelial cells increases significantly, which contributes to the accumulation of glycogen necessary for the production of lactic acid by Doderlein bacilli. Maintaining the required acid-base balance (pH 3.3-4.5) throughout pregnancy, thanks to good microflora, helps block the development of pathogenic bacteria and prevent infection of the embryo (or fetus).
When do leukocytes appear in a smear in women?
In the normal state of the female body (without developing pregnancy), leukocytes in the smear may appear and reach a high concentration in the following cases:
- inflammation of the cervical canal – cervicitis;
- inflammation of the vaginal mucosa – colpitis;
- inflammation of the uterine mucosa – endometritis;
- inflammation of the urethra (urination channel) - urethritis;
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes, appendages and ovaries - adnexitis;
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- diseases caused by sexually transmitted infections;
- oncological diseases of the reproductive system;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
Many people believe that inflammatory processes of the genitourinary and reproductive systems can appear in women who are sexually active. This is wrong. Diseases of an infectious nature, like many other ailments, can also be detected in young girls - virgins.
This is explained by the fact that many types of infectious pathogens can be transmitted through ordinary contact and household methods, for example, when using common things or failure to comply with the rules of personal intimate hygiene.
A smear is taken from virgins in the usual way, but instead of a speculum, the doctor uses a special thin probe inserted into the opening of the hymen.
If a high number of leukocytes is detected in a smear, additional examinations and special tests must be carried out, since in most cases it is impossible to determine the disease based on the results of a smear, since the analysis has limited diagnostic value.
Assessment of a pregnant woman’s condition based on various criteria
New sensations after sexual intercourse, delay, pharmacy test, two strips, what to do?
Nothing unusual. The normal situation in the life of a woman who has become sexually active begins with questions on forums like “can a smear determine pregnancy or not?” No matter how much you put it off, the time has come to get ready to see your “favorite doctor,” climb into the hated chair and undergo a full gynecological examination. Many women do not like the very fact of visiting an antenatal clinic. You need to submit material for laboratory tests - a vaginal smear, blood, urine, and also get in line for an ultrasound. Doctors' offices and laboratories take up a lot of time and do not bring the most positive emotions, even if the future baby is so desirable. But does a smear detect pregnancy, like streaky tests? He has a different goal, and analysis alone is not enough.
An experienced gynecologist can use subtle signs to determine not only the “interesting position”, but also the duration of pregnancy in most women. They have their own methods, even if the patient came without a proven test strip and an exact indication of the day of delay.
The doctor has suggested methods for detecting early pregnancy. You shouldn’t ask him, “Is it possible to determine pregnancy by smears?” You will have to take all the tests, even if they monitor the microflora of the vagina, and not the fact of fertilization of the egg.
Each specialist has a whole set of probable and accurate signs of conception in his arsenal, for example:
- without a smear, he will be able to judge conception by palpating the uterus;
- the presence of sexually transmitted diseases will be determined by the soreness of a smear from the urethra;
- The shape of the cervix will tell you whether there has been childbirth or this is your first pregnancy.
It is difficult to determine pregnancy from smears alone, but when a sample is taken, there is access to visual signs of conception. Pregnancy is also a diagnosis, and before an ultrasound and a blood test for hCG, it is made in advance.
Attention: Further the fetus will develop, by its heartbeat doctors have the opportunity to monitor that the fetus does not freeze, tests will show the level of hemoglobin in the blood of the pregnant woman in order to eat properly. A smear will help determine whether the microflora is normal.
Therefore, it is not so important for the doctor whether the pregnant woman has decided to get rid of the embryo or will patiently follow all the instructions to maintain the pregnancy. The specialist must fulfill his medical duties by prescribing tests to monitor changes in the female body. There is no way to do without this.
Leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy
It is not for nothing that blood is called the most valuable liquid, which, along with all other components, ensures the normal functioning of the human body. And blood also consists of many elements, each of which performs its own function that is vital for life and health. One of these elements is leukocytes, or white blood cells, one of the outposts of the human immune system. It is leukocytes that are responsible for the body’s ability and activity to resist pathogens and help a person cope with all the challenges that hostile viruses and infections pose to him.
Thus, leukocytes produce special enzymes that destroy microorganisms that are foreign and dangerous to the body. And some of the forms of leukocytes even produce special antibodies - they attack all foreign forms of life that enter the mucous membranes, organs and tissues of a person. Thus, leukocytes perform a very important function: they are an indicator in the event of an inflammatory process in the body, signal about a disease and make it possible to begin adequate treatment in a timely manner - after identifying the cause that caused the increase in leukocytes in the blood.
By taking appropriate tests to determine the level of leukocytes, a person has the opportunity to determine the presence of the disease already at its initial stage. And this becomes especially important for a woman during pregnancy: tests for leukocyte levels are taken repeatedly during this period. One of these tests is the collection of a vaginal smear, in which the number of white blood cells is then calculated. The first such analysis is recommended to be carried out immediately when the pregnant woman is registered.
In a vaginal smear, a certain number of leukocytes are already present initially. Their presence is determined using a microscope at high magnification. Normally, leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy should be present in an amount of 10-20 units. If, according to the study of the smear, the level of leukocytes is observed to be elevated, this clearly indicates the occurrence of some inflammatory or infectious process in the body. And the higher the level of leukocytes, the more pronounced this process is and the more acute it is. Determining the number of leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy is only the first stage: it only allows one to identify the presence of a disease process in the body. But what exactly caused it will have to be determined through additional tests, which may include bacteriological culture, immunological studies, or PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
PCR smear for latent infections during pregnancy
- This analysis allows you to identify bacteria that microflora testing cannot detect. This technique allows you to accurately identify bacteria or viruses even in small quantities.
- PCR diagnostics are highly accurate. It allows you to establish both the species and genus of bacteria. Thanks to the results obtained, the most effective treatment can be prescribed.
- Very often, PCR analysis is used to detect sexually transmitted infections. For example, most sexually transmitted pathologies (chlamydia, gardnerellosis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis) do not manifest themselves in any way in the early stages of development.
- The first symptoms appear only with serious progression of the pathological condition. But smear readings, thanks to PCR analysis, show their presence even at the earliest stages and, accordingly, eliminate them in time.
- The analysis can also detect viral infections such as papilloma and hepatitis. At the same time, other diagnostic methods do not detect the viruses themselves, but only their metabolic products or antibodies to them.
PCR testing can detect infection in any environment:
- saliva;
- urine;
- blood;
- on mucous membranes.
It is also used to isolate viruses in water and soil.
Advantages of PCR analysis:
- High accuracy of infection detection;
- The research requires a minimum of material;
- The ability to isolate the virus, rather than antibodies to it or its decay products;
- Speed of research;
- Infection can be detected in any environment;
- The only effective method for isolating a number of infections.
Table of norms by week of pregnancy
Based on the table below, you can roughly estimate the probability of the disease based on the smear results.
| Weeks of pregnancy | White blood cell count in the vagina | White blood cell count in the cervix | The number of leukocytes in the urethra |
| 1–13 | up to 10 in view | up to 25 in field of view | up to 3 in view |
| 14–26 | up to 10 in view | up to 25 in field of view | up to 3 in view |
| 27–39 | up to 15 in view | up to 30 in view | up to 5 in view |
Test results can be obtained within three days; some laboratories offer results on the day of the smear test.
In a healthy woman, the concentration of blood cells in the smear is low. Ideally, they should not exist at all, but this is rarely observed. Most often, up to 5–10 leukocytes can be detected in a smear; if the number is above 15, this is a cause for serious concern.
Analysis transcript
The results of an analysis of vaginal microflora can reveal the following indicators:
- Leukocytes - an increase in the norm indicates the development of inflammation. In the vagina there should be 10-15 of them in the field of view, in the urethra - no more than 5, and in the cervical canal - up to 5.
- Epithelium – normally this value should not be more than 10 in the field of view.
- Gram-positive bacteria - the main part (approximately 90%) consists of lactobacilli.
- Gram-negative bacteria - pathogenic microflora is normally completely absent.
- Mucus - smears during pregnancy reveal the absence or moderate amount of mucus in the vagina and cervix.
- Fungi of the genus Candida are acceptable in a small amount in the vagina, but they are normally completely absent in the urethra and cervical canal.
- Cocci – normally streptococci, staphylococci and enterococci may be present in small quantities. The presence of gonococci indicates the development of gonorrhea.
- Trichomonas - they are absent in a good smear.
Normal, why indicators may be increased
An increase in white blood cells in a smear in women is a sign of an inflammatory process in the body.
You can find out their level by taking tests:
- flora smear;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine.
Women are most often prescribed a smear test for flora.
This study allows you to identify diseases of the urinary canal, kidneys or bladder; recognize the inflammatory process in the urogenital area.
Material for research is taken:
- from the vaginal wall;
- from the mucous surface of the cervix;
- from the mucous membrane of the urethra.
Normal levels of immune cells in a smear:
- from the vagina - no more than 10;
- from the urethra - no more than 5;
- from the uterine cervix - no more than 15.
Table of the norm of leukocytes in a smear in women and other analysis indicators:
During the study, it is necessary to take into account the following features:
- The number of white blood cells (leukocytes) increases after sexual intercourse; elevated levels last for 24 hours after the act.
- Increased levels are observed during the installation of an intrauterine contraceptive device.
- Microtraumas of the vaginal walls also increase the indicators.
The main reasons for an increase in the number of leukocytes in a smear in women are:
- Sexual infections transmitted directly during sexual intercourse (STIs):
- Gonorrhea.
- Chlamydia.
- Ureaplasma.
- Syphilis.
- Trichomoniasis.
- Mycoplasma.
- Papillomaviruses.
- HIV.
- Candidiasis.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Actinomycetes.
- Genital herpes.
- Bacterial vaginosis. This disease is better known as vaginal dysbiosis. Occurs when the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the vaginal flora increases. Prerequisites for the development of the disease are hormonal disorders, decreased local immunity, or the use of vaginal suppositories.
- Allergic reaction to gels and lubricants for intimate hygiene or douching products.
- Oncological diseases of the reproductive system.
An increased content of white immune cells in a smear indicates the presence of the following diseases:
- Colpitis is an inflammatory process of the vaginal mucous tissues.
- Cervicitis is an inflammatory process of the cervical canal.
- Endometritis is an inflammatory process of the mucous surface of the uterus.
- Adnexitis is an inflammatory process of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Urethritis is an inflammatory process of the urethra.
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestines or vagina.
- Oncology of the reproductive system.
Deviations from the norm
Absence of squamous epithelium
indicates a decrease in estrogen saturation of the body, and an increase in its content is observed with severe inflammation.
Information Increase in white blood cell
always indicates an inflammatory process.
Gonococci, Trichomonas, yeast-like fungi
(at a concentration of more than 104 CFU/ml) and
key cells
are observed in the corresponding disease.
Copious mucus
also indicates inflammation.
For any deviations from normal values, additional studies are carried out. A bacteriological examination of vaginal discharge is carried out to clarify the pathogen and determine resistance to antibiotics. It is necessary to test for STIs (sexually transmitted infections). And based on the test results, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
During pregnancy, preference is given to local remedies (suppositories, creams) that do not contain antibiotics, but if systemic therapy is necessary, antibacterial drugs can be taken starting from the second trimester of pregnancy. Some infections can occur hidden, but they pose a danger to the normal development of the fetus, therefore, when planning pregnancy, all women are recommended to be tested for sexually transmitted infections.
Sexual infections
During pregnancy, smears for infections - sexually transmitted diseases - should be taken without fail. Diseases such as ureplasmosis, herpes, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus do not always make themselves felt, but this does not mean that they do not pose a danger.
Hidden infections can be detected using PCR diagnostics, culture and the Gram smear staining method. Another popular method is the enzyme immunoassay of blood serum.
How does the procedure work?
Going to the gynecologist is not the most pleasant procedure. The doctor uses a sterile disposable instrument to make a smear from the back wall of the vagina, cervix and urethra, apply it to a glass and send it to the laboratory. A stronger discharge may appear within a few days after the test is taken. This is due to the fact that the walls of the vagina become more vulnerable during pregnancy. But after 1-2 days everything will return to normal.
Not all gynecologists decipher the details of laboratory tests for us. And I really want to figure out for myself what these incomprehensible terms mean. We tell you how to read test reports.
This is what the analysis of a healthy woman looks like:
The most important indicators that allow us to judge the health of a pregnant woman are red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. Normally, the analysis should show the presence of lactobacilli and a certain number of leukocytes.
Red blood cells appear in the smear if an inflammatory process occurs in the vagina or there is injury to the mucous membrane. Normally there can be several of them (up to five).
Leukocytes are always present in the smear and protect the body from pathogenic bacteria. The more leukocytes, the more developed the inflammatory process. The following numbers indicate the norm: up to 20 in the cervix, up to 10 in the vagina and up to 5 in the urethra.
Beneficial microorganisms
Under the influence of hormones in pregnant women, the number of lactobacilli (Dederlein bacilli) increases tenfold, which creates an acidic environment in the vagina and protects the child from pathogenic microorganisms. Healthy flora is 95% represented by lactobacilli.
Opportunistic
Cocci (staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci), enterobacteria, gardnerella (cause vaginosis), candida fungi (candidiasis, or thrush).
What is dangerous about microflora disturbance?
Quite often, women are faced with a situation where, having taken smears during pregnancy, they find out that they have a violation of the vaginal microflora. A decrease in the number of lactobacilli is extremely undesirable during this crucial period and therefore it is necessary to establish the cause of the pathogenic condition. Opportunistic microorganisms, of course, are present in the vagina of every healthy woman, but their number should be small. If the number of bad bacteria increases, it means that dysbiosis begins to develop, most often causing vaginal candidiasis (thrush).
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to take smears. During pregnancy, in the early stages, such a disorder can develop against the background of reduced immunity. Any deviation from normal indicators is dangerous, first of all, for the baby and the further development of pregnancy.
Nutrition in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
During this period, the child is actively gaining weight, so the mother must control her weight gain and follow the rules of balanced nutrition:
- All unhealthy foods should be excluded, and everything that children are not allowed to eat (convenience foods, soda, fatty and fried foods, fast food, sausages, smoked foods, too salty and spicy foods, mushrooms, chocolate, citrus fruits, baked goods made from premium flour, sweets) ;
- exclude products that have not undergone heat treatment: raw eggs and those cooked with liquid yolk, soft cheeses, blue cheeses;
- It is better to replace sweets with fruits or nuts with a little honey; you can make homemade cottage cheese casseroles;
- exclude coffee - caffeine constricts blood vessels and impairs blood circulation in the placenta;
- eat small portions 5-6 times a day;
- eat a varied diet;
- consume dairy products so that about half of the protein from food comes from them;
- give preference to steamed and baked dishes.