- home
- MRI
- MRI of the head and neck
18.08.2017
When there is a lack of oxygen and nutrition, nerve cells are the first to die, so most brain damage is associated with poor circulation. When diagnosing brain diseases, vascular angiography plays a decisive role. Along with MRI of nerve tissue, MRI angiography of the brain is performed to establish the cause of the pathology, prescribe treatment and predict the course of the disease.
The essence of the method
Angiography is a diagnostic method that helps identify diseases of the veins and arteries in tissues and internal organs. Previously, it could be used as part of radiography or computed tomography. But both methods involve irradiation with X-ray frequency waves. With the discovery of magnetic resonance imaging, it became possible to obtain images of the vascular network of the human body without harm to the patient. Let's find out how it works.
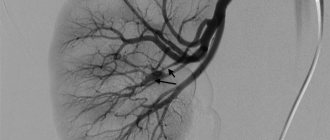
The essence of MRI in angiography mode is nuclear magnetic resonance. The fact is that the nuclei of hydrogen atoms vibrate at a certain frequency, creating a magnetic field around themselves. If they are placed in another magnetic field created by a tomograph, then these fields will overlap each other and intensify. If you ensure that the magnetic field inside the tomograph oscillates at the same frequency as the nuclei of hydrogen atoms, a phenomenon called resonance occurs. At this time, the strength of the magnetic field increases sharply, which is recorded by the device’s sensors. Collecting signals, the computer analyzes them, converting them into a graphical form of information. The result is a picture that accurately depicts the structure of veins and arteries, as well as their location.
Diagnosis using MRI is safe for the patient because it uses only a magnetic field and radio waves. Unlike X-rays, they do not irradiate the body.
Features of MRI angiography of vascular structures of the brain
Carrying out magnetic resonance imaging to study blood vessels involves placing the patient in a closed tomograph in a horizontal position. The procedure can last up to 30 minutes. In some cases, when the patient suffers from claustrophobia or cannot remain motionless for a long time, he is put into a state of sleep under anesthesia.
The main difference between MRI angiography and conventional tomography is the use of certain software to visualize and construct a three-dimensional image of the vascular network.
You need to understand that assessing the condition of the neck vessels is no less important than determining the condition of the brain vessels, since disturbances in their functioning can lead to serious pathologies of the brain. Thrombosis of neck vessels or aneurysms in this area pose a great danger.
An MRI is necessary to determine the location of the main focus of vascular pathology. The dynamic nature of the study significantly increases its information content. Based on the results of angiography, a specialist can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe the optimal therapeutic course.
Preparing for the study
MRI angiography does not require special preparation from the patient. There are no restrictions on nutrition, exercise, or taking any medications. If the study is carried out with contrast, a special drug is administered intravenously before its implementation.
What organs are examined and in what cases are they used?
Magnetic resonance angiography can provide images of blood vessels in any organ. But most often there is a need:
- In the study of cerebral vessels;
- In the study of veins and arteries of the head and neck;
- In the diagnosis of cardiac vessels.
Indications for angiography using MRI are:
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Vasculitis (inflammation of the vascular walls);
- Vascular atherosclerosis;
- Phlebeurysm;
- Aortic dissection;
- Congenital heart defect;
- Visual and hearing impairments;
- External vascular compression syndrome;
- Frequent headaches;
- Narrowing of arteries in diameter;
- Suspicion of cancer.
Most brain pathologies have a cause-and-effect relationship with the condition of the vessels of the neck and the brain itself. Therefore, the possibilities of angiography are extensive: it can reveal not only the disease, but also the causes that caused it.
Indications for the study
MRI angiography is prescribed to confirm the suspected diagnosis or its initial formulation. A number of patient symptoms and complaints determine the appointment of an angiographic procedure. Among the main indications are:
- Frequent attacks of headaches.
- Recurrent dizziness.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the visual and auditory analyzers.
- Traumatization.
- Suspicion of acute circulatory disorders.
- Progression of diabetes.
- Suspicions of oncological pathologies.
Classification depending on pulse sequences
To diagnose veins and blood vessels, MRI in angio mode is used. This procedure can be performed in three ways:
- Phase-contrast angiography (used to study the venous vessels of the brain);
- Time-of-flight angiography (only this option is performed to study the condition of the cervical and cerebral arteries);
- Angiography-4D (can be used to study any blood vessels).
The phase-contrast MRI angiography method is necessary for visual assessment of blood flow velocity. The signal transmitted by the tomograph contains phase and amplitude components. This is the longest procedure and can last from 20 to 60 minutes.
Time-of-flight angiography uses a pulse sequence with a short spin relaxation time (“gradient echo”). This allows you to scan vessels in a plane perpendicular to the direction of blood flow. If a high signal comes from the blood, this indicates that it is flowing into the slice of vectors that are not suppressed by excitations of radio frequency waves. Suppressed stationary vectors undergo partial relaxation between these excitations. In this case the signal will be low. The examination time is only 10-15 minutes.
In some cases, 4D angiography is performed. This is the shortest time-consuming procedure that can reveal various disturbances in blood flow (dynamic study of blood vessels).
Possible difficulties
The occurrence of side effects is rare. Sometimes the following occurs:
- Spreading of the drug. It is observed when drugs with iodine get into the tissue layers located near the punctured vessel. Occurs near the walls of the veins from a puncture or additional pressure from the infusion of medication. Using 10 ml does not lead to such consequences. The spreading of a large volume of liquid leads to inflammation of the skin, and possible death of the integument.
- Iodine intolerance is a serious manifestation. Modern contrast agents have a reduced risk of allergies. It may appear unexpectedly. Characteristic symptoms of swelling at the puncture site, redness, sweating, decreased blood pressure. Rooms for angiography of cerebral vessels are equipped with medications to provide emergency medical care.
- Acute renal failure. Impaired renal function leads to renal ischemia of the cortex, exacerbating existing diseases. A check of the urinary system before the examination is mandatory.
After the study, a person may experience the following changes in health:
- nausea, vomiting;
- redness of the skin, difficulty breathing, itching;
- decreased blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- anaphylactic shock;
- convulsions;
- detection of vascular spasms (can lead to stroke);
- inflammation due to contact of medications with the skin.
Timely diagnosis of the brain allows you to avoid serious diseases and serious consequences.
Preparing for the examination
Usually, before tomography in angiography mode, a radiologist recommends coming for an examination after abstaining from food for 4-6 hours. Then the data obtained as a result of the study will be reliable.
It is better to come to the diagnostic room in loose clothing without metal fittings, because the procedure requires the absence of metal. Otherwise, you will have to change into hospital clothes: a shirt or gown. You also need to remove all jewelry in advance: piercings, earrings, rings, chains and watches.
If there is metal in the part of the body that will be examined, inquire in advance about its composition. All metal implants and prostheses must be free of ferromagnetic materials. Otherwise, the results of the procedure will be uninformative.
If the MRI requires the administration of a contrast agent, then you should warn the doctor in advance about diseases such as renal failure and bronchial asthma, as well as about pregnancy, if it is present or only suspected.
Benefits and Risks
Comparing MRI angiography with other methods (radiography, computed tomography), we can highlight a number of its advantages:
- high accuracy and information content;
- non-invasive process;
- absence of radionuclide exposure;
- high speed of the procedure and absence of a recovery period.
But some limitations should be taken into account:
- the presence of metal implants in the body of the subject;
- severe forms of claustrophobia when performing procedures using closed-type tomographs.
Methodology of the procedure
MRI with angioprogram is performed as follows:
- The patient prepares for the procedure and informs the doctor about possible contraindications to it.
- If an MRI with contrast is indicated, a contrast agent is administered, and if the patient is nervous, a sedative is also administered.
- The patient lies down on the table and his head is fixed so that it is completely motionless during the angiography.
- The table slides into the tomograph tunnel, and the device begins to scan the blood vessels.
- After the tomograph has finished working, the table slides out and the patient can leave the diagnostic room, changing into his own clothes.
The examination time can vary from 5 to 60 minutes. It all depends on factors such as the type of angiography performed, the need for contrast and/or sedation, and the amount of work performed by the tomograph.
Sometimes, after undergoing angiography, the patient remains in the clinic for several hours. This happens if the procedure was performed under anesthesia. If the anesthesiologist does not detect any abnormalities during this time, the patient can go home.
Typically, MR angiography is performed in closed tomographs. But if the patient suffers from claustrophobia, the study can be carried out in an open-type apparatus, because in most cases, a high-field operating mode is not required to diagnose vascular diseases.
How to prepare for MR angiography
There is no special preparation for this examination.
Before lying on the tomograph table, the patient must get rid of electronic gadgets and remove all metal objects and jewelry.
You can take earplugs with you for comfort - the equipment creates quite intense noise during operation.
The procedure may take 30-60 minutes, so you need to be patient.
There is no need to be afraid - if the patient experiences any unpleasant sensations, the procedure can be interrupted at any time (although this is usually not required; the examination can be tolerated without problems even by children).
Once the diagnosis is complete, the patient is released and the MRI physician begins to interpret the results.
Contraindications and restrictions
MRI with vascular angiography is not always possible. The procedure has the following contraindications:
- The presence of implants in the middle ear (if they are made of metal from the ferromagnetic group);
- Installed pacemaker (the magnetic field will simulate the heart rhythm);
- Foreign metal bodies in the examined area of the body;
- Clips installed in the brain to stop bleeding in order to exclude subarachnoid or intracerebral bleeding;
- Body weight is greater than the maximum permissible load for which the tomograph is designed (usually the limit for MRI is 120-140 kg);
- Individual intolerance to gadolinium (when performing a procedure with contrast).
The above are absolute contraindications, but there are also relative ones:
- Claustrophobia;
- Pregnancy in the first trimester;
- The presence of dental implants, which can distort the real picture;
- Colds and runny nose, as well as other inflammatory diseases with very pronounced symptoms (diagnosis loses some information content);
- Kidney failure and bronchial asthma (if a substance is administered to obtain clearer images).
Tomography is safe for women during pregnancy at any stage (and for the fetus too). However, in the first trimester, when all the organs are developing, it is better to play it safe. Especially if we are talking about a study with the introduction of a contrast agent.
MR angiography allows you to look inside the vessels, but unlike other diagnostic methods that involve x-rays, it does not visualize calcium deposits inside them. Therefore, the results of CT and MRI may differ from each other. In addition, the image of small vessels and capillaries will be blurry and not clear enough.
MRI or CT angiography, which is better?
MRI and CT of vessels are the two main non-invasive methods for diagnosing angiopathologies at an expert level. The information content of magnetic resonance and computed tomography is very high, but each of them has its own disadvantages. The main disadvantage of vascular CT is the presence of radiation exposure to the body. This diagnostic method cannot be considered completely safe. The average radiation dose per scan can reach 5-7 mSv.
It is difficult to examine the vessels of the lower extremities using MRA. For this area, ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities or CT is better suited. Due to the low sensitivity of the MRI machine to weak blood flow, doctors may falsely diagnose pseudostenosis or occlusion during MR angiography. CT angiography of the vessels of the head will show an aneurysm better than MRI of the vessels of the brain.
With computed tomography, doctors have the opportunity to scan the vessels of almost the entire body at one time, which is impossible during MRA, where the examination is limited to certain areas of the body.
MR angiography, compared to computed tomography, has a longer duration of examination, which does not always allow examining patients in serious condition or young children who will require general anesthesia to remain immobile.
The advantage of MRI using the angiography protocol compared to CT is the absence of harmful effects on the body due to the absence of ionizing radiation and toxic contrast agent containing iodine.
The final decision about whether MRI or CT angiography is better should be made by the attending physician. His knowledge of the medical history, patient's health status and diagnostic goals will allow him to make the right choice between magnetic resonance or computed tomography angiography of blood vessels. If the patient himself decides that he needs to undergo vascular diagnostics for preventive purposes, then it is better to start his diagnostic path with a safe MRI of the vessels of the brain and neck or ultrasound of the vessels of other parts of the body.
Previous Next
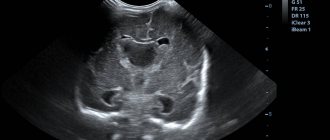
Decoding images
Examination of blood vessels reveals the following pathologies:
- Aneurysms (pathological expansion of the walls of blood vessels) and their dissection;
- Congenital heart defects;
- Arterial atherosclerosis;
- Inflammation of the vascular walls (vasculitis);
- Stenosis (pathological narrowing) of blood vessels.
Unlike conventional tomography of the brain, angiography diagnostics can detect hemorrhagic types of strokes. This method, combined with contrast, is also good for detecting tumors. Inside them there is always a densely woven vascular network. When a contrast agent passes through it, the neoplasm stands out in the image as a bright spot with clearly defined edges.
MRI vascular angiography is completely safe for the body, but this type of diagnosis is very informative. It detects the presence of tumors and visualizes pathological structures. All this is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment for vascular diseases.
What is magnetic resonance imaging?
This is the study of organs and systems using electromagnetic influence on hydrogen atoms in the human body, in a special electromagnetic field. Hydrogen atoms react to this constant magnetic field with the help of protons that are part of the nucleus of the atom and intensively change to the radiation of the magnetic field, this is analyzed and collected by a tomograph.
Angiography of the brain does not harm a person and does not cause any side effects, so its frequent use is permitted. It is possible to use magnetic resonance contrasts that contain the chemical element gadolinium or various iron oxides. They add clarity to the images and increase the accuracy of the study; they pass through the entire circulatory system, showing duct abnormalities.
The pictures look like sections of the human body at various distances (depending on the settings).
It is possible to isolate a specific area of the brain matter (or any other) and display it in a three-dimensional image for better study. The results are stored electronically on information media or printed.
Useful to know: Micropolarization of the brain as a modern method of treating many diseases
to contents ^