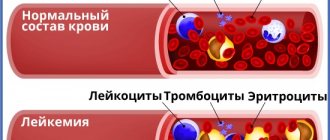
Immature granulocytes are part of the leukocyte formula determined in a blood test.
The analysis results usually show only band (not fully mature) and segmented (mature) granulocytes. These two forms are enough to combat problems that arise in the body. But there are situations when the emerging pathology requires additional forces to fight, which will be young (immature) granulocytes reproduced by the bone marrow.
A change in the level of immature granulocytes relative to the norm usually accompanies the onset of inflammatory processes, or it may be a reaction to some kind of infection entering the body. For this reason, leukocyte formula analysis is used in diagnosis.
Quantitative changes in granulocytes during pregnancy
The number of granulocytes in the bloodstream does not depend on the gender of the patient. However, in women during pregnancy, the percentage of these cells may be increased. An increase in granulocytes is associated with the release of a large amount of estrogens during this period. The peak of these cells in the blood is observed at 30 weeks of pregnancy.
During labor, the number of leukocytes increases, thereby increasing the number of immature granulocytes. Neutrophil levels in pregnant women are about 3%.
Normal indicators
Depending on the ratio of all granulocytes in the blood in the normal state of the body, the following proportions are determined:
- Neutrophils – up to 70%.
- Eosinophils – up to 5%.
- Basophils – up to 1%.
Normal levels of granulocytes in a blood test directly depend on age, so throughout life the ratio of mature/immature granulocytes constantly changes:
- Children under one year of age - immature - no more than 4%, mature - from 15 to 30%.
- Children from one to 6 years old are immature - up to 5%, mature - from 25 to 60%.
- Age from 7 to 12 years – immature – up to 5%, mature – from 35 to 65%.
- Adolescents 13-15 years old – immature – up to 6%, mature – 45-70%.
- Age from 15 years – immature – from 1 to 5%, mature – from 45 to 70%.
There are two main groups of people who are characterized by some changes in the cellular composition of granulocytes. These groups are women during pregnancy and children.
Taking a blood test
They examine blood if there is a suspicion of many infectious diseases and more. Thus, immature granulocytes are detected during a complete blood test. Blood is drawn from a finger. In emergency situations, blood can be taken from a vein.
There are a number of rules that will help make the analysis results “truthful”:
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach.
- A couple of days before the test, it is forbidden to drink alcohol, fatty and salty foods.
- You should also avoid heavy physical activity.
- It is strongly recommended not to take various medications before the study.
The counting of cellular elements occurs automatically, so the results are obtained as accurately and quickly as possible. The final results can be collected the next day.
The following abbreviations are found in the analysis results:
- Abs – means the “absolute” indicator of the number of cells in 1 liter of blood,
- Lic – indicates the presence of large immature cells.
Immature granulocytes are a group of cells that are the first to respond to the appearance of various pathological processes in the human body.
Immature granulocytes are detected in a detailed blood test during bacterial and viral infections and allergic conditions.
Why do neutrophil levels increase in children?
A slight increase in the number of neutrophil granulocytes can occur during severe physical or emotional stress. Eating food can cause elevated neutrophils. In the above conditions, the cell level normalizes over time. Often, neutrophils in a child’s blood are elevated due to diseases of various etiologies.
Common causes of neutrophilia:
- Inflammatory processes: pneumonia, inflammation of the pancreas, appendicitis, dermatitis.
- Viral infectious pathogens.
- Fungal diseases.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Burns of varying degrees and intensity.
- Diabetes.
- Severe blood loss.
- Taking drugs that stimulate leukopoiesis.
- Trophic ulcer.
- Leukemia.
- Anemia (iron deficiency, hemolytic).
Neutrophils are often elevated in a child in the postoperative period. Some pathologies of the skin, digestive tract or kidneys can also cause neutrophilia. It is necessary to constantly undergo examinations to identify pathologies.
Important! If neutrophilia does not go away on its own, this is a reason to contact your doctor to find out the cause of this condition. You should not engage in self-diagnosis or treatment, as this may worsen the child’s condition.
Leukocyte formula
An increase in segmented cells in children may indicate a latent infection. The higher the level, the more intense the pathological processes in the child’s body. An excessively high level of neutrophils may indicate a serious condition called sepsis. The determination of leukocyte shift is of important diagnostic importance. Based on the criterion, 6 main types of neutrophilia are distinguished:
- Hyporegenerative shift to the left. Increase in the total number of band neutrophil granulocytes.
- Hyperregenerative shift to the left. The appearance in the immunogram of “young” leukocytes - myelocytes, myeloblasts, promyelocytes.
- Regenerative shift to the left. The number of band cells and metamyelocytes increases.
- Degenerative shift to the left. Accompanied by an increase in the number of band cells and degenerative changes in the morphology of segmented cells.
- No shift. The number of seminucleate neutrophilic granulocytes increases.
- Degenerative shift to the right. Accompanied by the appearance of excessively segmented neutrophilic granulocytes (more than five segments).
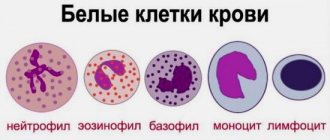
Granulocytes: what kind of cells are they, their types, functions
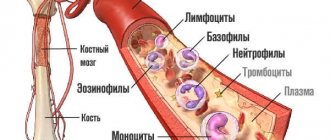
Granulocytes are white blood cells that have granularity. They have a sickle-shaped core. Structurally divided into several segments (up to 5). They make up up to 80% of all leukocytes. These cells arise in the bone marrow and live there. Once in the tissue, granulocytes do not live long - no more than 3 days.
When a foreign agent (bacterial flora or virus) enters the body, granulocytes absorb it and die. If for some reason there are not enough granulocytes to fight infection, their immature forms begin to flow from the bone marrow into the blood. The presence of young forms of cells in the blood indicates serious pathologies: allergies, autoimmune disorders, sepsis.
The following types of granulocytes are distinguished:
| Types of cells | Functions |
| Neutrophils | Responsible for cellular immunity. They perform phagocytosis, like monocytes. Neutrophils surround pathogenic cells, capture them and digest them. Then the cells die on their own, causing the formation of pus. |
| Eosinophils | They are also capable of phagocytosis, but absorb smaller “opponents”. Their main task is to bind mediators of inflammation and allergies (histamine). |
| Basophils | Large cells that contain special granules. When an allergen enters the body, they release these granules to bind it to them. In the process, blood flow and vascular permeability around the site of inflammation increases. Basophils signal monocytes and eosinophils about a pathological threat, calling them to the site of inflammation. |
Neutrophils, in turn, are divided into:
- Mature or segmented.
- Not quite ripe or rod-shaped. They do not live long in this form: very quickly their nucleus is deformed, segments are formed, and the cells become mature.
- Immature granulocytes.
This position of cells in a blood test is as follows: from left to right, first young granulocytes are located, then band and segmented ones.
Human immune system
A sharp shift in the leukocyte formula is determined in myelomonocytic leukemia, as well as in purulent processes. Not only the number of granulocytes changes, but also the “quality” of their cells.
Pathological causes
The appearance of immature granulocytes in the blood indicates, first of all, that there is an inflammatory process in the body.
If immature granulocytes are elevated in a child's blood, parents should not suspect the worst, such as leukemia.
It’s sad that this happens, but most often an increased number of immature leukocyte cells is associated with more harmless pathologies:
- acute infectious diseases,
- burns, cuts with the formation of suppuration,
- acidosis (shift of the acid-base balance towards acidity).
We recommend reading: Ornidazole is an antibiotic or: how it manifests itself, methods of therapy, causes, types of the disease
Types of granulocytes
Granulocytes are of the following types:
- Neutrophils. They belong to one of the most numerous groups, accounting for up to 80% of the total number of leukocytes. The main task of neutrophils is phagocytosis, or the search and destruction of harmful bacteria and viruses.
- Basophils. Small cells with large nuclei and a small amount of cytoplasm. They fight inflammation and participate in anaphylactic processes.
- Eosinophils. Make up less than 5 percent of the number of leukocytes. These cells are responsible for phagocytosis.
Read also on the topic Eosinophil Norm in Children in addition to the current article.
Immature granulocytes are reduced
As already mentioned, the norm is when there are no immature granulocytes in the human blood (with the exception of newborns and pregnant women). How can we talk about their reduced levels in the blood in this case? In this case, we are talking about a decrease in the production of neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils by the bone marrow.
When foreign agents (toxins, pathogenic agents) enter the body, mature leukocytes begin to destroy them, dying themselves. However, the bone marrow cannot supply the required number of new cells, including immature ones, to replace the failed white blood cells.
- Neutrophil deficiency is most often observed with:
- neoplasms in the bone marrow (myelofibrosis, leukemia),
- radiation sickness,
- congenital Kostman syndrome,
- autoimmune pathologies (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and others),
- hypersplenism,
- various types of anemia,
- biological depletion of the body due to chronic alcoholism, cachexia,
- taking a number of medications.
- A deficiency of eosinophils is caused by:
- some acute bacterial infections,
- burns,
- taking a number of hormonal drugs,
- anemia,
- numerous injuries,
- physical overload.
- A lack of basophils leads to:
- adrenal dysfunction,
- hyperthyroidism,
- chemotherapy,
- some hormonal medications.
Granulocytes: concept
All leukocytes are divided into 2 large groups.
The first are agranulocytes, the second are granulocytes. The latter are the ones that are grainy. Agranulocytes, accordingly, lack it. Granulocytes have a nucleus divided into several segments. However, it is of irregular shape. The cells are formed in the bone marrow and make up up to 70% of all leukocytes. The life cycle of granulocytes ranges from 3 to 10 days. After a few days they die. They are replaced by new cells.
Granulocytes is a collective term. These cells include eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils.
Despite the fact that they are united in one group, they are responsible for performing their specific functions. Eosinophils are cells that perform cytotoxic activities. In other words, they help destroy and eliminate parasites from the body. Eosinophils are cells that can also reduce the severity of an allergic reaction. At the same time, they can become a provoking factor in its development.
The main task of basophils is to trigger an immediate allergic reaction. They are also able to attract other granulocytes to the area of the pathological focus. Basophils also increase vascular permeability, improve blood circulation and lymphatic fluid flow, and regulate the coagulation of fluid connective tissue.
Neutrophils are cells that have the ability to move freely throughout the body. They easily leave the blood vessels and move to the pathological area. These cells are also capable of destroying fungi and bacteria. With the development of the inflammatory process, neutrophils absorb pathogenic microorganisms, but at the same time they die, releasing biologically active substances. The latter, in turn, stop the inflammatory process.
The norm and deviations from it
If we talk about the norm, then there should be no immature granulocytes in the blood of an adult healthy person. Their presence in the blood of newborns and pregnant women is considered normal.
In all other cases, deviations from the norm in immature granulocytes indicate certain disturbances in the functioning of the body.
As already mentioned, the norm is when there are no immature granulocytes in the human blood (with the exception of newborns and pregnant women). How can we talk about their reduced levels in the blood in this case? In this case, we are talking about a decrease in the production of neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils by the bone marrow.
Table: neutrophil norms in children of different ages
Child's age
Granulocyte count, %
Immature granulocytes in a blood test - what are they?
Granular leukocytes (granulocytes) are a subgroup of white blood cells that are characterized by the presence of irregularly shaped nuclei and the presence of granules (grains). This is where their name comes from. Cells become visible under a light microscope when stained with a special dye.
Granulocytes are produced in the bone marrow and have a fairly short lifespan. After entering the bloodstream and exiting into the tissues, they live for 2–3 days. This is the most numerous representative of white blood cells - their number is up to 80% of all leukocytes.
Granular cells are divided into:
- neutrophils - the total amount is up to 70%. There are mature (segmented) and immature (young);
- eosinophils - up to 5%;
- basophils - up to 1%.
Each subspecies takes an active part in recognizing and protecting the body from pathogenic microflora.
Normally, granulocytes are absent in a general blood test, with the exception of the presence of immature neutrophils in newborns and pregnant women. If there is an infection in the body, cells capture pathogenic microorganisms and digest them within themselves. After 2-3 days, having completed their task, they die, and a deficiency of granulocytes capable of fighting bacteria is immediately created in the blood. Immature neutrophils come to the aid of the remaining cells, which are detected in the blood when tested.
An increased level of young granulocytes indicates an inflammatory process in the body or the first response of the immune system to an infection. An increase in the indicators of other components indicates various diseases: the number of basophils increases with allergies or poisoning, eosinophils - with autoimmune diseases, viral and bacterial infections.
A clinical blood test is a reliable and informative indicator of a person’s health status. Based on blood components, pathology can be identified in time and measures can be taken to restore normal body function. The first cells that notice abnormalities in the body and encounter infection are granulocytes. What are they and what does the presence of immature granulocytes in a blood test indicate?
Features during pregnancy
Granulocyte indices do not depend on gender. The exception is pregnant women. During pregnancy, significant fluctuations in the level of leukocytes occur under the influence of estrogens (the production of female sex hormones increases during this period). They reach their maximum value at 30 weeks of pregnancy. With the onset of labor, the level of leukocytes increases to 25–30 x10 9 /l (10 to the 9th power).
An increase in the number of leukocytes leads to increased formation of granulocytes. In pregnant women, the rate of immature neutrophils can reach up to 3%.
- second half of pregnancy and childbirth;
- heavy physical activity;
- menstrual cycle;
- stress;
- after meal.
Having seen deviations from normal values in the results of a detailed blood test, many are interested: if immature granulocytes are elevated, then what does this mean?
To find the answer to the question, you need to know the principles of operation of granulocytes, the functions they perform, pathological and physiological conditions, which may be indicated by a high level of such cells in the blood.
Immature granulocytes: normal, what does it mean if they are increased or decreased?
A blood test determines many different factors, including increased or decreased levels of immature granulocytes.
This type of leukocyte appears on tests in most cases only if there is an infection or any pathology in the body, therefore it is an excellent indicator of possible problems.
What it is?
Granulocytes are blood cells, a subtype of leukocytes with a granular structure. Their nucleus has an irregular shape, and the cells themselves seem to be divided into segments.
Click image for a larger view
They come in two types:
- Mature ones are the basis of “white” blood and are fully functional cells.
- Immature - just released from the bone marrow, are produced in small quantities to replace old forms and in large quantities when there is a shortage of mature cells in the blood or the body's need for leukocytes suddenly increases.
According to their composition, these cells are:
- Neutrophils – 70% of the total composition of granulocytes.
- Eosinophils – 5%.
- Basophils – 1%.
Role in the body
Granulocytes are the body’s “line of defense” against pathologies, infections and foreign deposits.
Depending on their type, they perform different functions, united by a common focus - immune:
| View | Functions |
| Neutrophilic | Produce antimicrobial substances. Absorb and destroy bacteria and infections. Cleanse the body of “foreigners”. |
| Basophilic | Their function is to release biologically active substances from mast cells (degranulation), which leads to increased blood flow and improved vascular permeability. Simply put, their task is to mobilize the remaining granulocytes to the site of inflammation. |
| Eosinophilic | Give the immune system targets to attack. They produce substances against parasites. Absorb excess histamine, releasing it back when necessary. |
When a virus or bacteria enters the body, these blood cells absorb the “foreigner,” usually dying along with it.
If the infection is too aggressive, then granulocytes die more intensively and there are fewer of them. If a rapid immune response and the participation of a larger number of cells are required, then their relative deficiency occurs. Then, to replenish reserves from the bone marrow, still immature forms are “called upon” to fill the gaps in immune defense.
When immature granulocytes are visible in the analysis in large quantities, this means that the immune system is under the influence of a pathogenic environment - usually this condition is caused by infectious diseases, allergic reactions, inflammatory processes and autoimmune disorders.
Normal blood levels
In a normal healthy state, the relative number of granulocytes in human blood averages:
- Immature - up to 5% of the total number of leukocytes.
- Ripe - 65%.
When calculating, the level of neutrophils in the blood is taken into account, since they are the most abundant, and a deficiency of this form of granulocytes clearly shows painful processes in the body.
These numbers are not considered absolute amounts - for many people, the fluctuation in the values of these cells in the analysis falls between 45 and 70 percent.
The ratio of mature and immature cells in children is slightly different from adult indicators.
Pregnant women also have a different normal level of granulocytes, due to hormonal changes in the whole body.
In adult men and women
The number of granulocytes in the analysis can be designated by the letter combination GRA or GRAN.
This indicator is written as a percentage relative to the total number of leukocytes.
The standard for adults has the following designation: 1.2 – 6.8*10 (to the 9th power) per 1 liter (of blood). That is, the norm will be 47-72% of mature granulocytes in the composition.
Immature cells also have their own “threshold” of 1-5% - this is a normal volume if a person is healthy.
There is no difference in quantity between men and women - the leukocyte composition of the blood depends very little on the gender of the person. Only during periods of pregnancy can the percentage of immature cells undergo temporary changes that will be considered part of the normal functioning of the body.
In case of disturbances in the body, the leukocyte formula can undergo either a left shift on the scale or a right shift - up or down:
- A value above 5-6% is considered elevated.
- A value below 1-2% is considered reduced.
In children
Childhood is special, even regarding blood composition. The ratio of norms here is different than in adults.
| Table of quantitative norms of granulocytes in children | ||
| Age | Mature cells (%) | Immature cells (%) – no more |
| Infant under 1 year | From 15 to 30 | 4 |
| Child from 1 to 6 years old | From 25 to 60 | 5 |
| Child from 7 to 12 years old | From 35 to 65 | 5 |
| Teenager from 13 to 15 years old | From 40 to 65 | 6 |
| Teenager 15 years and older | From 45 to 75 | Range 1 to 6 |
These quantitative differences from adult indicators are considered the norm at each specific stage of growing up.
Too low or too high values of granulocytes in a child can be considered a sign of pathology only if, with the transition to a new age group, the abnormal level persists and does not fall within the normal range.
In infants, in the first weeks of life, immature granulocytes are elevated, and are almost never at a low level, unless the child is sick. Such an increase in the norm is considered acceptable, since the newborn experiences the stress of separation from the mother and begins to adapt to the new environment. Over time, there is a decrease to normal age levels.
What do pregnant women need to know?
The rate of immature granulocytes in women during pregnancy is usually higher. The production of estrogen affects all body systems and blood composition. Due to such a restructuring, there is a need to increase the number of leukocytes. And along with them, the importance of immature cells also grows.
Typically, this process begins at 30 weeks and is not a sign of pathologies or infections.
Before and during childbirth, the level of granulocytes can also exceed normal values for adults, since the woman’s body is under stress and mobilizes all systems.
How is analysis carried out to determine their level?
The level of granulocytes is detected during clinical collection and testing of blood, which is taken in the standard way - from a finger prick. The procedure must be carried out on an empty stomach and in the morning.
You can take a complete blood count (CBC) in any clinic; the value of granulocytes is prescribed if the doctor asks the laboratory assistant for a “leukocyte formula”.
The procedure is quick and suitable for all age groups - including infants, pregnant women and adolescents. Women, however, are not advised to take the OAC if they are menstruating, as this condition may skew the actual value.
Another group of people whose performance may be distorted are athletes, especially professional ones. Constant loads change the composition of the blood, so the “output” values may be overestimated, although there are no pathologies or infections in the body.
To avoid a “false alarm”, it is necessary to stop training or reduce the intensity of physical activity for 1-2 days before the OAC.
Reasons for increase or decrease
The main reason for the increase in the level of immature granulocytes in the blood is considered to be inflammatory and bacterial processes in the body. The immune system, in order to fight pathogens, requests more neutrophils to eliminate harmful microflora.
The reasons for changes in the number of immature granulocytes in children and adults will be the same.
Factors contributing to increased levels:
- Intoxication of the body (poisoning, insect bites).
- Heavy bleeding.
- Allergy.
- Burn.
- Peritonitis.
- Infections or viruses (flu, scarlet fever, etc.).
- Purulent processes.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Taking certain medications.
- Graft.
- Myeloplastic diseases.
- Otitis.
- Appendicitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Other inflammatory processes.
- Diseases of the blood and hematopoietic system.
Factors contributing to the decrease in level:
- Anemia of various forms and causes.
- Acute leukemia.
- Lead poisoning.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Exposure to radiation.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- The use of chemotherapy drugs in the treatment of cancer.
- Malaria.
- AIDS.
- Hepatitis.
- Alcoholism.
- Diabetes.
- Recent surgeries.
- Polytraumas.
- Aplastic process in the bone marrow.
- Sepsis.
There are also categories of people in whom an increase in the number of immature forms is not considered a sign of pathology:
- Women during menstruation.
- People exposed to stress, including chronic stress.
- Pregnant women in the second half of their term.
- A baby in the first weeks of life.
If the patient does not fall into one of these categories, then an increase or decrease in values should alert doctors.
How to normalize their value?
The first thing to do is to determine what particular pathology or condition of the body led to a change in the values of these immature cells. The diagnosis must be carried out by a doctor.
Further, to normalize the level of granulocytes, the patient undergoes treatment for the pathology that caused the initial change in their number.
After curing or stopping the underlying disease, the composition of leukocytes should normalize on its own - you don’t need to do anything specifically for this.
Dmitrieva Yulia (Sych) – In 2014, she graduated with honors from Saratov State Medical University named after V. I. Razumovsky. Currently working as a cardiologist at the 8th City Clinical Hospital in the 1st clinic.
Source: //infoserdce.com/krov/nezrelie-granulochiti/
Physiological neutrophilia
Having discovered that the number of immature granulocytes in the blood is increased, the specialist makes a note “neutrophilia” in the outpatient card.
Neutrophilia is not an independent disease, but only indicates the presence of some pathology. A specific diagnosis can be made by establishing a complete clinical picture and conducting additional examination.
First of all, it is necessary to divide the causes of neutrophilia into two large groups, since increased granular neutrophils can be found in the blood under the influence of physiological and pathological factors.
Physiological causes in adults include pregnancy, menstruation, stress factors, and increased physical activity.
An increase in immature neutrophils is recorded when blood is taken for analysis immediately after a meal.
A high level of band granulocytes is a normal phenomenon for children in the first days of life (this is explained by the fact that at birth the baby experiences great stress associated with a change in habitat, pain experienced during passage through the birth canal. The child’s body reacts to a stressful situation as times the increase in granulocyte cell production).
The norm in pregnant women is the detection of no more than 3% of immature granulocytes in the blood.
Treatment with androgen-containing drugs, glucocorticosteroids and lithium drugs increases the percentage of band granulocytes.
What to do with neutrophilia?
First, consult a pediatrician for a diagnosis. Therapy depends on the underlying disease. Neutrophilia is a symptom, not an independent disorder. Often a false positive result can occur due to the following reasons:
- Taking tests on a full stomach. Do not feed the child 1.5-2 hours before blood sampling. A small amount of water is allowed.
- Excessive anxiety. Before the procedure, reassure the child, because anxiety affects blood test results.
- Excessive physical activity. Before the blood test, limit your baby's physical activity.
If a child has signs of an infectious disease (low-grade fever, purulent discharge), treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are indicated. In rare cases, resistance is observed and urine culture is performed. In case of viral infections, provide the child with vitamins and microelements in food. Antiviral drugs are ineffective in treating viruses. For fungal infections, antimycotic drugs are prescribed.
Bone marrow diseases are treated with drugs that block the excessive secretion of immature neutrophils.
In case of myocardial, lung, kidney or brain infarction, resuscitation measures are necessary. Neutrophilia in these cases disappears after the patient has fully recovered.
Diagnostic measures
To diagnose the presence of a certain range of diseases, you need to know the range of values of the number of all types of granulocyte particles. These indicators in the blood are independent of the patient’s gender; age matters.
When diagnosing the content of granulocytes in the blood, the specialist prescribes a detailed general examination.
Blood for diagnostic activities is donated in the early hours (with the exception of emergency diagnostics in a hospital setting) and on an empty stomach (eating is allowed no later than 22:00 on the day preceding the day of blood donation).
24 hours before the procedure, stop eating fatty foods and fried foods. Alcoholic libations are not allowed.
Experts strongly recommend that you stop playing sports for the reason that high physical activity can lead to unreliable test results.
It is necessary to stop taking medications and refuse medical procedures. If following the listed recommendations is impossible, then you need to tell your doctor about it.
Blood sampling to study the level of leukocytes is carried out from a finger, but in some cases (emergency operations, comprehensive examination) biomaterial can be taken from a vein.
Laboratories equipped with new technology make it possible to calculate the number of blood elements very quickly, without requiring much participation of laboratory assistants, so the results can be seen the next day; in emergency cases, the examination can be completed in half an hour.
We recommend reading: What is the significance of E. coli: its role in the human body
The results of a detailed blood test record the percentage of all types of leukocyte cells (for this, the so-called leukocyte formula is written).
Granulocyte cells are listed in order of maturity from left to right, with 45 to 65% of mature granulocytes considered normal, and 1 to 5% of the total number of leukocytes considered immature.
The normal level of granulocytes in a child’s blood is determined based on his age. For convenience, the ranges of values are shown in the table:
| Child's age | Norms of granulocyte content | Norms for the content of immature forms of granulocytes |
| First year of life | From 15 to 30% | Up to 4% |
| 1 year – 6 years | From 25 to 60% | Up to 5% |
| 7 – 12 years | From 35 to 64% | Up to 5% |
| 13 – 15 years | From 40 to 70% | Up to 5% |
| 15 and older | About 45 to 70% | From 1 to 5% |
Granular leukocytes are among the first to rush to the rescue if pathogens of pathological processes are detected and act as follows: they capture foreign bodies, absorb and dissolve within themselves.
Normal levels of immature granulocytes in a child and an adult
If you know what it means when immature granulocytes are elevated, it will be much easier to decipher your test results and, if necessary, speed up an appointment with a specialist. Granulocytes are a subgroup of granular leukocytes. It is normal if the blood contains from one to five percent of young neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.
A slight increase in this indicator is considered normal for pregnant women and newborns. Hematocrit is an indicator in a blood test that shows the percentage of formed components.
If it is elevated or decreased, it means that not everything is in order with the body. Read about the signs and treatment methods for iron deficiency anemia in our article.
One thing is for sure: she is enjoying life to the fullest and is actively pursuing her career.
A clinical blood test is a reliable and informative indicator of a person’s health status. The first cells that notice abnormalities in the body and encounter infection are granulocytes.
Granular leukocytes (granulocytes) are a subgroup of white blood cells that are characterized by the presence of irregularly shaped nuclei and the presence of granules (grains).
Granulocytes are produced in the bone marrow and have a fairly short lifespan.
Norm of lymphocytes in the blood
Lymphocytes are blood cells that are produced in the human bone marrow, and in the baby in the womb - in stem cells and the liver. The state of the immune system of the entire body depends on the number of these white cells in the blood. Lymphocytes are a type of leukocyte that perform protective functions.
B lymphocytes - their function is to recognize foreign cells and microbes in the body and produce antibodies.
T lymphocytes must control the immune response. T-hellers are activated to enhance it, while T-suppressors, on the contrary, suppress it. NK lymphocytes (or killer T cells) destroy foreign cells.
When deciphering a blood test in a healthy person, the norm for the number of lymphocytes is 20-35% of all leukocytes. Of these: T lymphocytes - 65-80%, B cells - 8-20%, NK cells - 8-20%
Lymphocyte counts during pregnancy:
- deciphering the general blood test of a pregnant woman can reveal lower levels of lymphocytes;
- The normal level of lymphocytes in a pregnant woman is considered to be from 18 to 44% percent of the total number of leukocytes.
Activation of lymphocytes in the blood of the expectant mother is an unfavorable indicator, often leading to termination of pregnancy or premature birth.
Monitoring the normal number of lymphocytes in the blood of the expectant mother is especially important in the first and second trimester of pregnancy. During this period, the placenta must produce the required amount of suppressants that prevent white blood cells from reaching the fetus, which can lead to miscarriage.
A decrease in the number of lymphocytes in the blood of a pregnant woman is normal.
Norm of granulocytes in children – Dr. Novikov
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell.
Such cells are distinguished by the fact that they have several stages of development: young, fully mature and mature. They often reach full maturity after 3 days, so they spend more time in an immature state. That is why their level in the blood is minimal.
As a result, serious pathologies arise, indicating an increase in the number of these cells. But if granulocytes are low in a child, then this also indicates the development of the disease.
General definition
Granulocytes are granular white blood cells. Their distinguishing feature is the presence of two nuclei that have an irregular shape. Nuclei are subject to the process of division into several lobes.
In addition, certain granules are present in the cytoplasm, which can be viewed under a microscope.
Granulocytes appear in the bone marrow; their acceptable value varies from 50 to 80% of the total number of leukocytes.
Such cells are involved in the process of protecting the body from the penetration of foreign elements. They are able to identify the problem and fix it.
These cells also contribute to the normalization of the immune system, which refers to the effector phase. So, the main function is to restore and strengthen the immune system.
However, there are several types of such cells, so the functions of each type have some differences from others.
When tested, granulocytes are present in the leukocyte formula. But in general analysis, the normal value for everyone has its own limits. Thus, 50–80% will determine that there are 2.5–7 thousand of them per milliliter of blood (eosinophils – 1–5%, basophils – no more than 1%, neutrophils – 40–70%).
When conducting various blood tests, the presence of granulocytes is determined by the GRA% value, which depends on the percentage of the total number of white cells.
Varieties
Granulocytes in the blood are present in 3 types: basophils, neutrophils and eosinophils. Each has certain reasons due to which their content in the body decreases.
Basophils
They are small cells with a large nucleus - two or three segments with cytoplasm. Basophils spread into the blood from the bone marrow. They remain there for some time, after which the cell penetrates the vessel wall and passes to the epicenter of inflammation.
In human blood, they take part in allergic processes through interaction with lymphocytes and other cells characterized by slow development. However, at the epicenter of inflammation, basophils destroy mediators: histamine, heparin. The duration of activity of such cells does not exceed 12 days.
In rare cases, basophils are found in the peripheral blood. If at 200 leukocytes there is one basophil present in the peripheral blood, then this refers to the normal ratio. Basopenia is a decrease in cell number to less than 104 ml. The value of cells can be reduced by:
- Stressful situations.
- Inflammatory process in the lungs.
- Complication after infection enters the body.
- Hyperfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Adverse effects of taking corticosteroids.
- Pregnancy.
A reduced value of basophils is extremely rare, but may indicate a deterioration in the blood supply and their functions. This can also result in serious illness. To determine the cause and eliminate the problem, proper examination and treatment must be carried out.
Neutrophils
These types of cells are present in greater numbers. They are characterized by a high level of their presence in leukocytes (up to 75%). Often their content in peripheral blood does not deviate from the norm.
There is also another name - these are band neutrophils with immature forms. Their presence in the blood of a healthy human body should not be more than 20%.
The main task of neutrophils is phagocytosis - identification and destruction of foreign formations: viruses, tumors, bacteria.
Their granules are special enzymes that get rid of unnecessary proteins. As a result of the confrontation between leukocytes and pathogenic elements, the formation of suppuration in the area of inflammation is observed, which contains the remains of tissue cells and destroyed pathogens.
The growth and development of cells in the blood of children goes through a certain stage, which takes about 12 days. Efficient cells penetrate into the peripheral blood and remain there for at least 10 hours. After this, leukocytes are sent to the walls of blood vessels and find damaged tissue.
The normal value of neutrophils in an adult is 1.7 * 106 ml. Decreased results are the most common. What does it mean? And this is evidence that the body has weak immunity, which causes serious consequences.
Eosinophils
The optimal value of such cells, at which a person is considered healthy, varies from 1 to 5% of the leukocyte content. They provide phagocytosis and also come into contact with other cells and basophils.
In addition, eosinophils take part in the formation of antigen-antibody bonds. If the value of such cells decreases and becomes less than 5*104 ml, then this indicates the development of eosinopenia.
Reasons why cell levels have become lower include:
- Side effects from the use of certain drugs.
- Severe form of bacterial diseases.
- Physical fatigue.
- Stress.
- Recovery period after surgery.
- Burn.
- Sepsis.
- Numerous body injuries.
- Anemia.
- Anemia, which is characterized by a lack of folate.
A low level of eosinophils in the blood necessitates the presence of serious pathologies that interfere with the normal process of hematopoiesis even in childhood.
Reduced value of indicators
With a general blood test, a specialist can detect a low granulocyte count in a child. To begin immediate treatment, it is necessary to determine which species is present in insufficient quantities.
So, if the baby’s readings are low, this is evidence of a serious illness. If the amount is reduced to a critical value, then the likelihood of recovery is extremely low.
The reasons that caused this condition include:
- Cancerous neoplasms.
- Iron deficiency.
- Liver problems.
- Rubella.
- Weak immunity.
- Colds and viral diseases.
- Poisoning.
If the value is low, the cause may be hereditary predisposition to pathology. The presence of such a condition requires monitoring by a specialist, because death may occur. In most cases, the result of such manifestations is skin damage. Inflammatory processes develop in the baby’s body itself.
So, if the level of eosinophils is reduced, this indicates an insufficient development of the circulatory and immune systems. But such changes are considered normal, so you just need to closely monitor the value for a while.
When contacting the causes of infection, the cells may undergo some changes or be completely destroyed, which will lead to a change in value (they become lower). A minor violation affects a person’s well-being, especially children, because they have weak immunity. Due to this condition, some stresses may appear:
- Changes in the structure of blood cells - the body becomes more vulnerable, and bacteria penetrate into it.
- The baby’s well-being suffers - infections spread throughout the body, and reproduction begins.
- Weakened immunity indicates a possible fatal outcome.
A decrease in granulocytes requires an immediate visit to a medical facility for examination, as a result of which appropriate treatment is prescribed. Often, in order to normalize immunity and return the optimal value of granulocytes, you should undergo courses of therapy.
Source: https://doknovikov.ru/norma-granuloczitov-u-detej.html
How much does the study cost, where is it carried out?
A test to determine the level of immature granulocytes in the blood can be carried out in any laboratory specializing in diagnostic procedures.
The average cost of a clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula in commercial medical institutions is about 400 rubles. If blood must be drawn from a vein, you will need to pay an additional 130-250 rubles. Some laboratories provide this service by visiting the patient’s home.
Concept of granulocytes
Having learned the test results, a person wonders what it means. Granulocytes are one of the types of leukocytes (white blood cells) that have an irregularly shaped nucleus - rod-shaped, divided into sectors (from 2 to 5). These cells protect the body from infections and viruses by disinfecting and destroying foreign cells by absorbing them.
They are divided into three types, each of which has its own life cycle:
- immature (young);
- mature, but not completely (rods, in which the nucleus is not yet divided into segments);
- mature (segmented).
The group of granulocytes includes eosinophilic, basophilic and neutrophilic cells, which account for 70% of the total number of leukocytes.
- malignant tumors;
- heart diseases;
- diseases of cartilage tissue;
- disorders of the body's immune function;
- inflammation caused by parasites;
- skin pathologies.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
What are granulocytes
Granulocytes (granular leukocytes) are the largest class leukocytes , accounting for up to 80% of the total volume of white blood cells and which are characterized by the following characteristics:
- Large segmented nucleus.
- The presence in the cytoplasm of granules, which are represented by lysosomes, peroxisomes and modified forms of these elements.
Certain conditions are necessary for the production of granulocytes.
Granulocyte formation
The synthesis of granulocytes occurs in the bone marrow, so these cells are representatives of the myeloid series. The source for their formation is a common cell - a precursor - a pluripotent mother cell. To ensure a complete process of granulopoiesis, substances - inducers are needed:
- Interleukins-1, 3, 5.
- Granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor.
- Granulocyte-stimulating factor.
It takes 13 days for full-fledged cells to mature:
- Three- or five-fold division of progenitor cells – 4 days.
- Morphological ripening – 5 days.
As granulocytes enter the blood, they are immediately divided into two groups:
- Actively circulating cells.
- Marginal cell units are those granulocytes that are temporarily located on the surface of the venules. The marginal location is occupied by cells before they directly enter the tissues from the bloodstream.
For reference. After moving into tissue, the life cycle of granulocytes is about 2 days, and in the blood the average circulation time is up to 7 days.
As granulocytes mature, they undergo several stages of development until they develop into a fully mature form.
Classification
All human granulocytes are divided into three main types:
- Neutrophils.
- Basophils.
- Eosinophils.
As granulocytes grow and mature, these cells are divided into:
- Mature.
- Immature.
The morphological stages of granulocyte development imply their state in several forms:
- Myeloblasts are poorly differentiated cells with an approximate size of 15 microns, the cytoplasm does not contain granules, the nucleus is not located in the center, and also contains from 1 to 3 nucleoli.
- Promyelocytes are large cells up to 24 microns in size. The nucleus is also located eccentrically, and granules already appear in the cytoplasm.
- Myelocytes - the cell size at this stage of development is already reduced to 16 microns, a large concentration of granules is determined. It is during this period that three types of myelocytes are distinguished:
- Neutrophilic.
- Eosinophilic.
- Basophilic.
- Metamyelocytes (young) - after dividing myelocytes into three types, metamyelocytes are also represented by three of the same types. The size of such cells decreases to 14 microns as they differentiate, the number of granules increases, and the ability to mitosis is already lost. At this stage, metamyelocytes undergo differentiation into:
- Band cells are the immediate precursor of the mature form. These cells enter the bloodstream and make up up to 5% of all circulating leukocytes.
- Segmented cells are the final stage of differentiation - the formation of a mature form.
Granules, which are the main feature of granulocytes, appear at the metamyelocyte stage.
Thus, granulocytes, depending on the stage of development, are:
- Mature ones are segmented.
- Almost mature ones are rod-shaped.
- Immature granulocytes - from myeloblasts to metamyelocytes (young).
Each cell has its own specific responsibilities throughout the entire period of its existence.
Functions
Each subtype of granulocytes performs its specific functions in the human body:
- Neutrophil granulocytes – the main component of the nonspecific protective system of the blood, which carries out:
- Phagocytosis (elimination) of foreign inclusions (bacteria, tissue decay products, etc.) and cleansing the body of them.
- Regulation of lumen and permeability of blood vessels during inflammation.
- Production of antimicrobial substances.
- Basophilic granulocytes:
- Release of heparin and activation of lipolysis.
- Binding of antigens, which entails the formation of immune complexes on the basophilic surface.
- Release of triggers of allergic reactions, in particular histamine.
- I take an active part in the development of the allergic response of the whole body.
- Eosinophilic granulocytes:
- They also take part in the formation of the immune response.
- Produce anthelmintic substances.
- Eliminate excess amounts of histamine.
In the normal physiological state of the body, with the exception of some cases, only segmented and band granulocytes are found in the blood. Outside of the disease, a slight presence of immature cells is allowed.
Attention. The release of a large number of immature granulocytes into the blood means the development of some pathological process.