The essence of the procedure
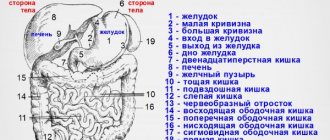
It is one of the most complex and multifaceted studies, because the object of research is an entire system of organs. During the procedure, the doctor will be able to see the following organs:
- Spleen.
- Pancreas.
- Function of the kidneys and bladder. Although the latter is often included in pelvic ultrasound.
- Large masses or loops of intestine.
- Liver. It is considered with all auxiliary structures, these are the gallbladder, ducts and vessels.
- Veins are also visible on ultrasound, namely the splenic, aorta or cava.
Using this type of research, it is possible to detect diseases, abnormalities or disturbances in the functioning of each of the above structures.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uMQpcwznLP4
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is a non-invasive method of research and accurate diagnosis. It involves using ultrasound to create images in real time. This is a kind of echolocator that sends out ultrasonic waves.
Those, in turn, are reflected from the organs and return back. The computer converts this data into a picture and displays it on the screen.
A ship going to sea has a device installed on its bridge that operates on a similar principle. To facilitate work, isolate air access and ensure continuous contact of the sensor with the body, ultrasound gel is used.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity helps to accurately and fully identify pathologies of internal organs: liver, gall bladder and others. This method provides such reliability and information content of the picture that is not available to most other methods.
But the use of ultrasound is not limited to diagnosing possible
. Another of its functions is prevention; the procedure provides such an opportunity.
It is better to know a reliable picture in advance and nip the development of the disease in the bud than to face the fact of the disease when it has already gained strength.
Interpretation of ultrasound results: norm and pathology
The sonologist indicates all the data about the structure of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen observed during pregnancy, revealed by ultrasound.
The specialist indicates the structural features of the internal organs and evaluates their parameters in accordance with the norm. Any deviation becomes the subject of special attention and requires additional research.
Very often, at the same time, the doctor evaluates the functioning of the vascular network, the risk of developing diseases, changes in the volume and contours of organs, the condition of regional lymph nodes, the threat of stone formation, etc.
After the procedure is completed, the patient receives a study protocol with a transcript and a specialist’s conclusion. If any diseases, dysfunctions or worsening of her condition are detected, he refers her to a gastroenterologist, hepatologist, nephrologist, therapist, or surgeon.
Indications for use
An ultrasound of the pelvic organs, or PMT, is done in preparation for pregnancy and several times throughout the entire period of bearing a child. When planning conception, the procedure identifies gynecological diseases that can prevent normal pregnancy. Having discovered pathologies, the doctor prescribes treatment, which increases the chances of a normal pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby.
Pregnancy cannot be established accurately, even if there is no menstruation and the hCG test is positive. Ultrasound is prescribed to confirm intrauterine pregnancy and determine its duration. Subsequently, an ultrasound of the uterus is performed during pregnancy to assess the condition of the fetus. The method reveals developmental anomalies, intrauterine infections, and increased uterine tone. Detection and treatment of these conditions ensures continued pregnancy.
Timing of ultrasound
As stated earlier, screening ultrasound examinations have their own specific deadlines, prescribed in the official protocol.
First ultrasound
The first ultrasound during pregnancy is performed between 10 and 14 weeks, when some organs have already been formed and active maturation of the nervous, genitourinary and cardiovascular systems continues.
Second ultrasound
The second screening is scheduled for a period of 20-24 weeks and is marked by the fact that during its course, future parents find out the gender of their child. With its help, more reliable data on defects, gestational age and fetal position is obtained.
Benefits of Ultrasound
Let us note in more detail the positive aspects of ultrasound; they are especially important if an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed during pregnancy.
- No danger or radiation. Until recently, everyone was wary of ultrasound, fearing radiation or other negative effects on the body. With the passage of time and the development of science, we can say 100% that ultrasound is absolutely safe. Is it possible to do an abdominal ultrasound during pregnancy? The answer is clear: yes. This study is no different from an ultrasound scan of the fetus, so it can be done at any stage of pregnancy.
- There is no painful or unpleasant sensation, the procedure will not cause discomfort to the patient. The doctor simply moves a specialized sensor along the outside of the abdomen, at which time one or another organ or vein is reflected on the screen. You must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations; sometimes you will need to turn on your side, inhale, exhale, or hold your breath for a while.
- Ease of research. To perform an abdominal ultrasound during pregnancy, you do not need to involve several employees, use a large number of devices, or use special tools. But at the same time, the qualifications and knowledge of the doctor are very important so that the results are as accurate and complete as possible, especially if the patient is pregnant.
Advantages and disadvantages of the survey
Ultrasound diagnostics of internal organs has many positive qualities:
- Safety. To perform ultrasound, ultrasound is used, which does not have a negative effect on the functioning of the human body (including the development of the fetus).
- Painless. To perform diagnostics, the doctor moves an ultrasonic sensor over the skin, which does not provoke pain or discomfort.
- Relative simplicity. The procedure does not require bulky equipment or a large number of staff.
- Availability. An ultrasound machine is present in many medical institutions in big cities and small towns.
- Relatively low cost.
The disadvantage of ultrasound diagnostics is the limitation of the method. The result of the procedure depends on the duration of pregnancy and the correct preparation. During ultrasound examinations in different clinics, patients are faced with diagnoses that do not correspond or contradict each other. This is due to the subjective opinion of the doctors performing the procedures. With insufficient qualifications or experience, certain parameters may be recorded or interpreted incorrectly by a specialist.
Another disadvantage of ultrasound is the ability to analyze its results in real time. It is possible to make a correct diagnosis only by observing a dynamic picture on the monitor screen. It is impossible to draw an adequate conclusion from the study using images (as with X-rays or tomography).
At what stages of pregnancy is ultrasound performed?
The ultrasound schedule for a pregnant woman includes three mandatory examinations. If necessary, the doctor prescribes unscheduled procedures. At what time the ultrasound is performed for the first time depends on when the woman came for consultation. According to standards, the first ultrasound is performed at 12-13 weeks. During this period, the vital organs of the embryo are already formed, and their condition can be assessed.
In the very first week, ultrasound will not even be able to determine the fact of pregnancy. The fertilized egg still passes through the fallopian tube. It can be detected in the uterus during the first month, but the embryo is not even visible inside. Its outlines become accessible to ultrasound 30-40 days after conception. Taking this into account, it is determined how many days later an ultrasound can be done if the test shows a positive result.
The optimal period for establishing the fact of intrauterine pregnancy is 5, 6, 7 weeks. A woman can seek consultation 2-3 weeks after a missed period. You can contact us earlier if there is a suspicion of ectopic attachment of the fertilized egg. Symptoms of this include pain in the lower abdomen and spotting brown discharge.
The second planned ultrasound during pregnancy is done at 20-22 weeks. At the 5th month, almost all fetal organs are formed, and the formation of the placenta is completed. The purpose of this procedure is to assess the development of the baby and identify abnormalities of the uterus. At this stage, the gender of the unborn child is clearly visible.
The last third procedure is carried out at 32-34 weeks. The doctor re-evaluates the condition of the fetus, uterus, and determines the position of the child. This is necessary for planning the tactics of childbirth - natural way or cesarean section. If during pregnancy planning a high risk of developing chromosomal abnormalities was determined, or the woman already has children with abnormalities, a genetic ultrasound is performed at 2-3-4-6 months. The procedure is aimed at detecting developmental anomalies.
What is the frequency of ultrasound depending on the stage of pregnancy?
The Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation has introduced three mandatory screenings, during which a mandatory ultrasound examination is also carried out in order to determine the health of the woman and the fetus.
- The first is necessary for a period of 11 to 14 weeks to study the characteristics of the patient’s condition.
- A second ultrasound scan should be performed between 16 and 20 weeks. The most important task is to identify congenital anomalies of fetal development.
- The third , duplex, screening at 30-34 weeks is aimed at checking the position of the embryo and placenta, their size, blood circulation characteristics, the presence of congenital anomalies, etc.
Are there any disadvantages?
Like any other procedure, ultrasound has its drawbacks, but even despite them, the study is performed very often and helps many people. Disadvantages include:
- Dependence of results on the degree of preparation and gestational age. The worse a woman’s preparation is, the fewer organs can be diagnosed and, accordingly, the fewer pathologies can be identified. Also, the longer the pregnancy, the worse the visibility.
- Subjectivity. You can view the abdominal organs without special knowledge, but it is quite difficult to diagnose any diseases or dysfunctions. Research requires a great deal of experience, knowledge and imagination. Therefore, for a qualitative assessment of ultrasound, it is worth listening to the opinions of several doctors.
- The need for dynamics. Each person’s body is individual, this is especially clearly demonstrated when performing an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity during pregnancy. During this period, a woman experiences a number of changes, so it is difficult to see pathologies from one study. It is necessary to do a series of ultrasounds to monitor changes in dynamics.
What ultrasound determines pregnancy?
Sometimes an ultrasound of the pelvic organs helps to understand whether a woman is pregnant.
It is in the small pelvis that the uterus is located, where the chorion is fixed, as well as its appendages. Ultrasound can detect both normal and ectopic pregnancy. This ultrasound is performed after 1-2 weeks of missed period. Pregnancy can be detected not only by the detection of a fertilized egg, but also by an increase in the thickness of the endometrium to 25 mm, as well as a large corpus luteum.
During a normal pregnancy, 3 scheduled ultrasounds are performed: at 10-12, 20-22 and 30-36 weeks. If a violation is suspected or to confirm the diagnosis, additional studies may be prescribed.
The most accurate results in this case are provided by transvaginal ultrasound. During the procedure, a special thin sensor is used, which is inserted into the vagina. A condom is first put on it. The sensor is very thin, pain and discomfort are excluded. It is located at a minimum distance from the uterus. It is completely safe and does not cause any threat of miscarriage or cause any discomfort.
The advantages of ultrasound in diagnosing pregnancy are the most accurate determination of timing. You can set the gestation time to the nearest day. This also allows you to accurately calculate your due date. Studies at 10-12, 20-22, 30-36 weeks do not have such accuracy due to the fact that each child develops individually in the womb.
Types of diagnostics
Pelvic ultrasound is performed in several ways:
- transabdominal method is the most common; examination is done through the anterior abdominal wall;
- transvaginal - examination through the vagina.
Both methods are used at any stage of pregnancy.
As a diagnostic method, ultrasound appeared in the 1970s. Until 2000, there was only one type - two-dimensional research. The internal organs in the picture were depicted flat. Then three-dimensional color examination was invented, which made it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image. Now in gynecology two-dimensional, three-dimensional, four-dimensional ultrasound is used. The latter option allows you to see the movements of the fetus inside the uterus.
Varieties
Ultrasound helps to determine not only what week a woman is at, but also to identify pathological abnormalities in fetal development in the early stages. This type of examination must be planned and any woman must follow the schedule drawn up by her gynecologist.
Ultrasound examination can be of several types:
- Transvaginal or intravaginal. Used in the first weeks of pregnancy and used only as directed. It is considered more informative in terms of diagnosing pregnancy in the early stages. Such an examination can reveal the pathology of the placenta and uterus much faster. Before such an ultrasound, you need to prepare the genitals, carry out hygiene procedures, and it is recommended to have a bowel movement before the procedure.
- Prenatal screening. It is necessary to carry out joint and biochemical screening. This procedure is performed by a sonologist. The ultrasound specialist tries to identify even the most minor abnormalities in the development of the fetus in the early stages. The latest model scanners are used for prenatal screening. It can be carried out both through the vagina and superficially. The first study is carried out in the early stages of pregnancy, and the second - in the 2-3 trimester.
- Doppler. Helps determine where and for what reason the pregnant woman started bleeding. This is carried out using special devices. Often performed as prenatal screening or transvaginal examination. Helps to determine even heart defects in the fetus and oxygen starvation.
- Cardiography helps determine hypoxia in the fetus. The fetal heartbeat can also be recorded.
- Volumetric or color study. Allows you to see the baby as a three-dimensional picture. Thanks to it, you can determine how tightly the fetus is entwined with the umbilical cord and whether there is a malformation of the face or any limb.
Without these types, it is very difficult to determine the presence of any developmental abnormalities in the fetus, and it is also possible to determine the correct gestational age using ultrasound.
Recommendations during pregnancy
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs during pregnancy has a number of specific features. A pregnant woman is not the best patient for ultrasound. As we said earlier, the longer the pregnancy, the less valuable this type of ultrasound is. From the 16th week of pregnancy, the uterus extends beyond the pelvis, which means it begins to displace other organs and fill the entire space. Already at 20 weeks, the fundus of the uterus is approximately at the level of the navel, and at the 37th week at the level of the chest.
Starting from the 36th week, there is no point in doing an ultrasound, although from a medical point of view it can be done. The effectiveness will be minimized, because the uterus will push aside all the abdominal organs. In case of polyhydramnios, large size of the child or in the presence of several fetuses, visibility will become worse and worse.
Therefore, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity during pregnancy should be done before the 16th week, so that visibility is still sufficient and the results are complete.
What are the difficulties of early diagnosis?
Pregnancy periods that are too short at the time of research can lead to physician errors. So, the question often arises: is it possible to confuse a polyp with pregnancy on an ultrasound? This actually happens in medical practice.
This is explained by similar physiological processes in the second phase of the menstrual cycle and the beginning of pregnancy. The cause of such an error may be the incompetence of a specialist. To get reliable information, it is better for a woman to:
- be examined by another doctor using a different machine;
- wait a while to re-evaluate the condition of the internal genital organs.
If both facts, pregnancy and polyp, are confirmed, the woman will have to undergo additional examination and take appropriate measures, since polyps can cause premature termination of pregnancy and miscarriage.
Preparation rules
The preparatory stage depends on what diagnostic method is planned. No special preparation is required for transvaginal examination. It is enough for a woman to carry out normal hygiene measures. You need to take with you a disposable diaper and a condom, which is put on the sensor.
The transabdominal procedure requires more careful preparation. Since the examination is done through the abdominal wall, the quality of the image is affected by the gases contained in the intestines. To avoid their formation, the patient is advised to follow a diet for three days. The diet involves avoiding dairy products, peas, black bread, and fatty foods.
Unscheduled ultrasounds
The need for an unscheduled ultrasound may arise at any time. The reasons may be:
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge mixed with blood;
- multiple pregnancy;
- discrepancy between the size of the fetus and the gestational age;
- abnormal position of the fetus;
- threat of pregnancy failure;
- improper attachment of the placenta;
- fetal hypoxia;
- history of caesarean section and abortion;
- lack of fetal activity, poor hearing of the heartbeat;
- polycystic ovary syndrome in a woman.
If there are medical indications, unscheduled ultrasounds can and should be done in order to maintain your own health and bear a healthy baby. You should not overuse this procedure, however, you should not refuse additional research prescribed by your doctor. In everything you need common sense and moderation.
Video: how many times during pregnancy can you do an ultrasound
Can it be done by pregnant women?
Pregnant women can and should have an ultrasound. Let's start with the fact that using this method, the sex of the unborn child is determined. During a normal pregnancy, abdominal ultrasound is prescribed three times.
In some cases, a larger number of procedures are prescribed, so discussions on whether ultrasound is harmful during pregnancy are meaningless.
Important! If an ultrasound examination of the kidneys is indicated, 60 minutes before the procedure you must drink 0.5 liters of still water and not urinate.
There are some features of using ultrasound during pregnancy, which we will discuss below.
In order for the examination to be as complete and effective as possible, it is necessary to prepare for it. Three days before the ultrasound, it is necessary to exclude foods that cause gas from the diet. These are beans, cabbage, milk, carbonated drinks and flour.
If the examination of the abdominal organs also includes the kidneys, an hour before the procedure you need to drink a liter of water (clean, not tea or coffee!). In this case, you cannot go to the toilet; you need to be examined with a full bladder.
You should not eat 8 hours before the examination, and it is best to do it in the morning and on an empty stomach. These recommendations apply to pregnant women during the first trimester.
If an ultrasound is performed during the second and third trimester, then you should refuse to eat 8 hours before the examination. When preparing for an abdominal ultrasound during pregnancy, there is no need to cleanse the intestines with an enema.
Ultrasound screening
Prenatal screening involves a comprehensive study that includes conventional ultrasound. And at a later date - CTG and a special type of ultrasound diagnostics, which allows you to assess the nature and speed of blood flow in the vessels. As well as a detailed blood test (determination of specific markers) of a pregnant woman, taken from a vein. Not all pregnant women are referred for screening, but most often according to indications.
Although some obstetrician-gynecologists prefer to prescribe it to all pregnant women, even with a good pregnancy. You can do ultrasound screening and even need it for such patients:
- bad heredity;
- a woman in the past had miscarriages, miscarriages, or gave birth to a stillborn baby;
- conception was associated with the use of antibacterial or other embryotoxic drugs;
- first pregnancy after 35 years;
- the woman has an alcohol or drug addiction;
- living in an environmentally unfavorable area or working in a hazardous industry;
- future parents are close relatives;
- the family already has a child with congenital developmental pathologies.
A pregnant woman’s gynecologist will tell her when to go for an ultrasound screening. The timing of regular and screening ultrasounds may differ somewhat. As a rule, all screening procedures are shifted 2-3 weeks earlier than usual studies. This allows, if the picture is questionable or critical, to carry out repeated examinations or, if necessary, to terminate the pregnancy.
The doctor explains when to do this or that diagnosis during pregnancy. But any examination is done voluntarily. How many times and whether an ultrasound examination will be performed at all depends on the decision of the future parents. Every pregnant woman goes for an ultrasound consciously. She must remember that ultrasound examination will contribute to a healthy delivery and well-being of both the baby and the mother herself.
Examination technique
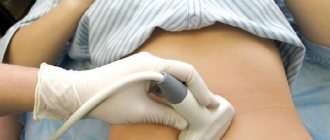
Ultrasound diagnostics during pregnancy is easy to perform. During an abdominal procedure, the patient is asked to lie on a couch with her abdomen exposed. The doctor lubricates the skin with sound-conducting gel, then runs a sensor over it, examining the necessary organs. The inspection takes 7-10 minutes. After this, the woman wipes her stomach with a towel and gets dressed.
A vaginal examination is performed on a couch or gynecological chair. The woman lies on her back, spreads her knees. The doctor uses a special sensor placed in a condom. The sensor is inserted into the vagina up to the cervix. The inspection takes 7-10 minutes.
Conducting research
The technique for performing ultrasound diagnostics of internal organs consists of following the following sequence of actions:
- To conduct the examination, a woman needs to lie on the couch on her back and expose her stomach.
- In the second and third trimester, the doctor gives the woman a cushion to place under the lower back, which will increase the effectiveness of the procedure.
- To improve visualization of internal organs, a special contact gel is applied to the patient’s skin. It is absolutely safe, hypoallergenic, odorless and colorless. The contact gel prevents air from entering the space between the skin and the ultrasound transducer.
- During the examination, the doctor may ask the woman to turn over on her right or left side and hold her breath.
As a result of the procedure, an image of the internal organs and surrounding tissues is displayed on the monitor screen. The doctor records important parameters and then provides the patient with a diagnostic protocol.
Obtained results
An ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman includes examination of the uterus with the fertilized egg inside, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. If necessary, an examination of the kidneys, bladder, and cervix is prescribed. Ultrasound shows pathologies on the part of the fetus and the maternal body.
The fact of pregnancy is confirmed by the detection of a fertilized egg with an embryo inside the uterine cavity. The fertilized egg in the picture is represented by a rounded gray spot with light and dark inclusions. It is located on one of the uterine walls. The image does not show intrauterine pregnancy if the fertilized egg is attached inside the fallopian tube or in the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound results for certain weeks of pregnancy:
- 4 weeks - an embryo is detected inside the fertilized egg;
- Week 10 - major organs are formed, genetic abnormalities can be identified;
- Week 20 - determination of anomalies of internal organs and skeleton;
- 30 week - fetal position, developmental defects.
From the third month, all parts of the embryo’s body are visible inside the fertilized egg. The largest spot is the head. The smaller elongated spots are limbs on which fingers are visible.
| Index | Characteristic |
| Fetus | Quantity, transverse or longitudinal position |
| Presentation | Pelvic or head |
| Fetometry | Size of head, torso, limbs |
| Collar width | Determined at 12 weeks - no more than 3 mm |
| Heart rate | Normal - 110-180 per minute |
Deviations in the development of pregnancy are detected at any stage.
- False pregnancy. A fertilized egg is formed, but there is no embryo inside it. It can be determined from 10-12 weeks. Inside the light gray spot in the picture there is a black space instead of white-gray inclusions.
- Bubble drift. Anomaly in the development of membranes. The picture shows many dark bubbles in the place where the embryo should be.
- Down syndrome. The earliest time for determination is 12 weeks. A sign is a thickening of the collar area of more than 3 mm. At week 20, the syndrome is determined by the length of the nasal bone.
- A marker of IUI (intrauterine infection) is an insufficient amount of amniotic fluid.
- Placenta previa is its location at the uterine os. The photograph shows an oval dark spot in the throat area to which the fetus is attached. Occurs due to multiple scars on the uterus.
- Cervical insufficiency. Determined by its shortening of less than 12 mm.
- Umbilical cord entanglement. The photo shows a dark tourniquet around the child's neck.
- Defects of the heart, limbs, brain.
The specialist conducting the examination provides a description of what he saw. A diagnosis cannot be made based on this conclusion alone. A sonologist can make a mistake for a number of reasons. Visualization of the uterus can be difficult due to the patient’s obesity and excessive gas formation. The child may lie in such a way that his position seems pathological.
After the procedure, you should contact a gynecologist so that he can confirm or rule out the detected pathologies. Often it is necessary to perform ultrasound in dynamics. During pregnancy, the fetus turns several times, and by birth it takes the desired position. If chromosomal abnormalities are suspected, a woman is recommended to consult a geneticist.
Scheduled and additional examinations
Any pregnant woman must undergo three mandatory ultrasound examinations, also called screening examinations. They are held throughout all trimesters and pursue specific goals. If a pathology is detected in both the mother and the fetus, the doctor may prescribe additional functional and laboratory examinations.
Screening ultrasound
The first screening ultrasound during pregnancy corresponds to the end of the first trimester and is very important, since during it the fetus is visualized for the first time. At this stage, organs and systems are already actively being formed.
The main objectives of the procedure are listed below.
- Determination of the number of fruits and their location. The condition of the amniotic membranes is also assessed, and in the case of multiple pregnancies, special attention should be paid to the number of placentas. This will help differentiate monozygotic twins from dizygotic twins.
- Establishment of obstetric gestational age and expected date of delivery.
- Assessing the structure of the umbilical cord and the correct stages of placentation.
- Elimination of signs of chromosomal aberrations. If a child has Down syndrome, thickening of the nuchal translucency, impaired transtricuspid blood flow, and blurred boundaries of the nasal bones can be detected. Such indicators should force the gynecologist to refer the woman to a geneticist.
- Detection of other fetal anomalies from the heart, kidneys, etc. Exclusion of signs of placental abruption or threat of spontaneous miscarriage.
The second ultrasonographic examination of the fetus is performed in the second trimester of pregnancy and also has its own special tasks:
- confirmation of obstetric term;
- determining the type of presentation and position of the unborn child;
- gender determination;
- assessment of the functional state of the placenta, as well as its localization;
- counting the amount of amniotic fluid;
- assessment and measurement of the length and width of the cervical canal during pregnancy (important to exclude isthmic-cervical insufficiency);
During this period, an ultrasound examination of the fetal brain structures is also performed. During the procedure, anomalies in the development of the cerebral hemispheres are excluded, the lateral ventricles, as well as their choroid plexuses, are visualized. The diencephalon and the occipital fossa are examined. The research itself is carried out sequentially, that is, from top to bottom.
The third trimester corresponds to the last planned ultrasound examination. Together with this diagnosis, color Doppler examination and carditocography (CTG) are performed to assess the state of blood flow and cardiac activity of the fetus.
With the help of final ultrasound you can:
- detect anomalies in the structure of organs and systems;
- clarify the nature of the presentation and position of the unborn child and exclude possible entanglement of the umbilical cord;
- calculate the relative weight of the fetus and its body length;
- compare the baby's size and gestational age at the time of matching;
- assess the function, thickness, density, maturity and echostructure of the placental membrane;
- measure the volume of amniotic fluid;
- in women with a history of cesarean section, measure the thickness of the uterine scar.
All data obtained will help you choose the right tactics for the upcoming birth and minimize risks.
Selective techniques
Additional ultrasound examinations are prescribed if a woman has alarming complaints (bloody discharge from the genital tract, intense pain in the lower abdomen), or a chronic underlying disease has worsened or worsened. Also indicated are:
- absence of fetal movement at 20 weeks;
- discrepancy between the gestational age and the size of the uterus;
- premature labor;
- pathological presentation (frontal, facial, leg).
Pregnancy as a result of IVF does not require three procedures.
It is advisable to perform an ultrasound at 5-7 weeks if an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, which in the case of late diagnosis is often complicated by perforation of the fallopian tube, profuse uterine bleeding, even hemorrhagic shock.
Doppler ultrasound technique in the period 20-23 weeks is carried out in the following cases:
- pyelonephritis, diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman;
- development of late gestosis (hypertension, preeclampsia, etc.);
- multiple pregnancy;
- previous pathological pregnancies;
- Rhesus conflict;
Is ultrasound dangerous for the fetus?
Ultrasound diagnostics has been used in medicine for more than 50 years. Experience shows that ultrasound does not cause intrauterine malformations. The high information content of the method also speaks in favor of its use during pregnancy.
However, some medical professionals believe that ultrasound of internal organs should be used only when indicated. They justify their position by the lack of special studies regarding the effect of ultrasonic waves on the fetus.
If an ultrasound is still planned, the woman is advised to prepare for the procedure in advance by eliminating foods that contribute to the production of gases from her diet. This will improve the quality of the study and obtain accurate results. You should also drink a couple of glasses of water before the ultrasound. The fact is that ultrasound waves are better reflected from tissues saturated with liquid.
Ultrasound does not harm the body even in the early stages of development. Some experts do not say clearly how ultrasound affects a child. However, not a single case of the disease was found to be associated with ultrasound, even if it was performed continuously.
The benefits of ultrasound diagnostics have been proven. Frequent ultrasounds during pregnancy do not harm the developing fetus. A timely examination reveals developmental anomalies, which makes it possible to adjust further pregnancy management.
Indications for abdominal ultrasound in pregnant women
In addition to undergoing mandatory screenings, the study may be recommended if the development of various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or other body systems is suspected. During the gestation period, palpation is undesirable, therefore ultrasound, due to its low load on the body, is the preferred diagnostic method.
It is most often carried out if:
- inflammatory processes in the abdominal area;
- hyperthermia;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- infection;
- persistent nausea;
- constant rumbling in the stomach;
- severe general weakness;
- too strong toxicosis;
- abdominal trauma;
- iron deficiency anemia, etc.
What is examined during an ultrasound?
With an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity, it becomes possible to identify various pathologies of the digestive system with a high degree of reliability, evaluate the characteristics of chronic diseases and check a woman’s complaints about the functioning of her body.
Ultrasound helps to study the condition of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas, kidneys and spleen. The sonologist examines their general contours, notes the presence of abnormalities, eliminates the risk of formation of tumors or stones, and monitors the safety of the lumen of the hollow organs.
Ultrasound scanning of a patient over 16 weeks is quite difficult to perform due to the significantly increased size of the fetus and the expansion of the uterine border beyond the pelvic area. Therefore, in the later trimesters the procedure becomes less informative.
Cost of the procedure
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes an ultrasound examination at the antenatal clinic at her place of residence. If she is registered, the examination will be free. The procedure is performed by private medical centers. The cost depends on the type of examination.
| City | Cost, rubles |
| Moscow | 500-3500 |
| Saint Petersburg | 550-4000 |
| Ekaterinburg | 500-3500 |
| Novosibirsk | 550-4500 |
| average price | 525-3875 |
Ultrasound examination is an important procedure during pregnancy. It can be done for the first time in the fifth obstetric week, that is, 35 days after conception. A woman has the right to refuse the study. In this case, she will not know the gender of the unborn child, and there will be no way to timely identify abnormalities in the baby’s development.
Share your experience of undergoing an ultrasound in the comments. Tell your friends about the information you read on social networks; it will be useful not only for expectant mothers, but also for fathers.
Goals and objectives
Ultrasounds are performed during pregnancy on all women, pursuing the following goals and objectives:
- determination and confirmation of pregnancy;
- assessment of compliance with the stages of intrauterine development;
- fetometry;
- examination of the membranes;
- assessment of amniotic fluid volume;
- study of uteroplacental circulation;
- assessment of the condition of the female reproductive organs.
Ultrasound diagnostics of pregnant women is performed in two main ways - through the anterior wall of the abdomen, and also by inserting a sensor into the vagina. In the early stages of pregnancy, the second method is considered more informative.