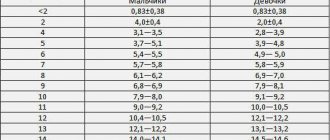
An isoechoic nodule in the thyroid gland is a section of tissue that has a density similar to healthy structures. Due to the surrounding blood vessels that supply it, it is easily visualized using ultrasound.
As a rule, such formations are formed as a result of abnormal synthetic activity. The danger is that neoplasia can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
The initial stages of anomaly formation are usually hidden. Treatment methods depend on the size of the node, its effect on the functioning of the thyroid gland and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Thyroid nodules of varying echogenicity. (a – hyperechoic node, b – isoechoic
What it is
An isoechoic formation means an area that has exactly the same density as the entire surrounding tissue of the organ. This formation can be detected only if there is a shell (see photo) - a capsule, or if there are signs of compression of this segment.
Ultrasound image of an isoechoic formation.
The presence of an isoechoic formation indicates the development of a neoplasm, which may not manifest itself clinically and may not bother the patient. Basically, this pathology can be detected by chance during a routine examination or when diagnosing other problems.
Prevention
Sea kale (kelp) is a natural source of iodine
The appearance of isoechoic nodes can be prevented by leading a healthy lifestyle and avoiding contact with radiation, toxins and harmful substances. The region of residence and place of work must comply with generally accepted environmental standards.
Nutrition plays a special role in prevention. The diet should be balanced; food rich in iodine (seafood, iodized salt, kelp, walnuts and others) and vitamins is recommended.
It is equally important to promptly combat infectious diseases of various etiologies and prevent hypothermia. People who are at risk should regularly visit an endocrinologist.
Isoechogenic formation in the thyroid gland
Isoechogenic formations of the thyroid gland (isoechoic node) are called neoplasms similar in density to the rest of the parenchyma of the organ. On ultrasound, an isoechoic thyroid nodule can be visualized by the presence of boundaries. The borders appear around the node as a rim (see photo above). These formations are discovered completely by accident, since the development of these elements can occur in a hidden form, without manifesting itself at all.
It must be said that the echogenicity of the node can be different - increased, average, decreased and sharply decreased.
Echogenicity of thyroid nodules on ultrasound images.
- If the echogenicity of the neoplasm corresponds to the echogenicity of the unchanged gland tissue, then it is considered isoechoic.
- If the echogenicity is reduced in comparison with the rest of the unchanged gland tissue, then it is considered hypoechoic.
- When echogenicity increases in comparison with the rest of the unchanged parenchyma of the gland, then it is considered a hyperechoic node.
Hypoechoic rim (halo) can occur with both benign and malignant neoplasms. Presumably, the halo is a zone that does not reflect ultrasound waves, at the border between the thyroid parenchyma and the node. Halo bezel is described as - thin, fuzzy, wide, uneven.
Node boundaries—represented in the description as two groups: clear and fuzzy. In addition, the boundaries can be intermittent, microlobular, etc.
The doctor is able to palpate large neoplasms; in this case, the patient is referred for a more detailed examination to an endocrinologist.
Type of nodule in the thyroid gland.
Ultrasound allows you to conduct a more detailed examination of a suspicious element and identify its density, which is usually determined by echogenicity, or, more precisely, by the reaction of the examined tissues to the effects of ultrasound radiation sent by the device. As a rule, the density of the node depends on the stage of the disease. Initially, absolutely all formations in the thyroid gland are exclusively isoechoic. (see How to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland).
This segment has dilated blood vessels along its periphery, which nourish it well and are diagnosed as a capsule on the ultrasound monitor. This pathological segment does not change or affect the functioning of the organ in any way, therefore it is clinically considered harmless until the neoplasm moves to the next stage.
Stages of development of deviation in the thyroid gland
There comes a point when the follicles located inside the affected area begin to die, leaving behind fluid and/or daughter cysts. A cyst forms. On ultrasound, this structure is defined as hypo- or anechoic and can be clinically manifested by choking, voice changes, a feeling of a lump in the throat, or again may occur unnoticed by the patient.
After a long time, the cyst can resolve, overgrown with connective tissue and leaving behind a scar. This is a favorable outcome of the disease that does not require surgical intervention.
Symptoms
It is worth considering the fact that the neoplasm can have a malignant course, therefore, as it grows, symptoms such as compression of the esophagus, trachea, vocal cords, etc. may occur. Accordingly, the larger the node, the brighter the symptoms.
If you have such a pathology, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Any difficulty breathing, symptoms may appear when changing body position.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
- The appearance of irregularities in the neck or a uniform increase in its size.
Any manifestations of the disease depend entirely on the location of the node and its size. If the formation is located on the outside of the organs, then there will be no symptoms of compression of the vessels, trachea and esophagus. Similar formations can be detected by palpation and ultrasound of the throat and larynx.
Palpation (palpation) of the thyroid gland.
Completely different symptoms are observed when the node is located inside the gland. The manifestation of other symptoms is also possible when the organ begins to produce excessive amounts of hormones. As a rule, all signs of the development of thyrotoxicosis are noted:
- tachycardia;
- fast fatiguability;
- excessive sweating;
- significant weight loss;
- sudden change of mood;
- tremor of the upper extremities.
Is it worth treating isoechoic changes in the thyroid gland?
If the formation does not have a negative effect on the patient’s hormonal background and does not cause any negative sensations, then such a node does not need treatment. The patient is advised to monitor the dynamics of the node, this will allow him to keep the condition of the defect under constant control and, if the situation worsens, take all necessary measures to eliminate the negative consequences.
But it should also be noted that if such a node was found in the thyroid gland, this could mean the following:
Carcinoma
Carcinoma on ultrasound can be completely shapeless or, on the contrary, it can have completely clear contours. Such nodes occur in a quarter of all existing cases of cancer. Most often, such nodes have uneven outlines and fully correspond to papillary carcinoma.
Cancer is found in the capsule in almost 50% of cases, having completely normal echogenicity and clear, even boundaries. In this case, the picture on the ultrasound screen is as follows:
- Wrong form of education.
- Clearly preserved contour.
- Fuzzy near the boundaries of the node.
- The presence of any hyperechoic inclusions usually indicates calcification.
- The presence of psammotous bodies inside the node.
- The presence of a convoluted structure in the vessels surrounding this section.
The prognosis is unfavorable.
Benign formation
When monitoring the problematic isoechoic segment, no progression symptoms are detected. Most often, such formations occur in the following pathologies:
- nodular goiter;
- follicular adenoma;
- in nodes of adenomatous type.
The prognosis is unfavorable.
Causes
Isoechogenic nodes are formed for the same reasons as other neoplasms in the thyroid gland.
The main risk factors include the following:
- radiation;
- iodine deficiency;
- the effect of harmful and toxic substances;
- inflammation of an infectious nature (foci can be in any part of the body);
- genetic predisposition;
- negative impact of poor environmental conditions;
- frequent or prolonged stress;
- hypothermia.
The influence of these and a number of other reasons can cause the development of pathologies of the thyroid gland; there is an imbalance in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, which leads to different activity of certain zones or spasm of blood vessels, which subsequently form nodular neoplasia.
Isoechogenic formation in the liver
If isoechoic formations were detected on an ultrasound of the liver (even if the echogenicity of the liver is increased), then this may indicate the following pathologies:
- The presence of an old hematoma that occurred due to trauma to the organ.
- Hemangioma.
- Metastases.
- The presence of a focus of hepatocellular cancer.
- Cystic formations.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need to undergo additional research methods, these may include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), scintigraphy, angiography, and biopsy.
Clinical picture
If the isoechoic node is still small, then it is quite difficult to detect it on your own. As the formation increases in size, the patient begins to feel signs of its presence:
- tightness in the throat,
- difficulty swallowing,
- difficulty breathing,
- pain in the ear and jaw area,
- heart rhythm disturbance,
- excessive sweating,
- fast fatiguability,
- mood swings.
On a note! Isoechogenic nodes in the thyroid gland are usually benign, but they should not be considered safe. Often such formations cause enlarged lymph nodes, suppuration, and inflammatory processes. The nodes worsen the condition and functionality of the organ and the general well-being of the patient.
Isoechogenic changes in the structure of the uterus
The similarity of such formations with the structure of the uterus makes it difficult to detect on an ultrasound examination. They are detected in cases where the inclusion has a capsule, or when there is a feeling of compression of the developing formation. For a long time the process does not manifest itself with external symptoms, the patient is not bothered by anything.
If, after an ultrasound, a focus was discovered in the uterus that had an acoustic density similar to that in the surrounding tissues, then this indicates the development of the following processes:
- Uterine cancer is the presence of an adenomatous node in the mucous membrane of the organ, which appears and takes root on the myometrium.
- Presence of myomatous node.
- Presence of an adenomatous node.
- Rokitansky syndrome.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need to undergo additional research methods. Ultrasound helps to detect the presence of a tumor. Echodensity depends on the stage and degree of development of the pathology. In the initial stage, they are all visualized as isoechoic. As the process progresses (enlarges), malignant neoplasms are characterized by the appearance of hypoechoic, hyperechoic, and anechoic inclusions in the lesion.
Treatment methods
The choice of treatment tactics depends on what pathology is hidden behind the isoechoic changes. If cancer (adenocarcinoma) is present, the patient is sent to a specialized department for radical surgery. If the cause is a toxic effect, then it is necessary to immediately relieve the patient from its effects and leave it under the supervision of a doctor for several months.
If this condition is accompanied by hypothyroidism, then replacement therapy with thyroid hormone analogues is prescribed. For thyrotoxicosis, there are two options: surgery to remove the nodes, or initial therapy with drugs that destroy some of the thyroid cells.
In case of endemic goiter, it is necessary to correct the diet and include foods high in iodine in the diet.
Isoechogenic formation in the mammary gland
The presence of an isoechoic formation in the mammary gland indicates the following:
- Mammary cancer.
- The presence of a normofollicular adenoma of a benign type.
- Fibroadenoma.
For an accurate diagnosis, you need to know on what day of the cycle you need to do an ultrasound of the mammary glands, and you also need to undergo additional studies.
The final diagnosis is established by a mammologist after conducting the necessary examination.
Features of the study
Since the thyroid gland is located on the front surface of the neck, with the help of an ultrasound examination it is possible to examine the organ almost completely, with the exception of those areas that are located behind the trachea and sternum.
During the study, the doctor pays attention to the following parameters and signs:
- Anatomical features of the structure of the organ - normally the gland has two lobes and an isthmus that connects them. If the formation of the gland is disrupted in the prenatal period, the isthmus may be absent and then the organ is not divided into lobes, but is completely shifted into one of them. This situation is characterized as agenesis or aplasia of the gland lobe. In the absence of development of the entire thyroid gland, they speak of aplasia.
- Localization - may be typical (immediately below the larynx), low, aberrant or pathological.
- Contours – normally they should be clear; in case of inflammatory processes of the gland and tumor formations, the contours are unclear.
- Structure – normally the thyroid gland has a homogeneous structure and is granular. Heterogeneous tissue structure occurs during inflammatory processes.
- Size.
- Focal inclusions - their parameters are assessed if the study reveals cysts, calcifications, and nodes.
- Echogenicity is the ultrasonic response of gland tissue on the monitor screen.
- The condition of nearby visible lymph nodes - based on their condition, one can assume the presence of tumor neoplasms at an early stage, the growth of cysts, microscopic calcifications, and an increase in blood supply to the gland.
During the study, the doctor additionally evaluates the condition of the larynx and soft tissues of the neck, located in close proximity to the thyroid gland.
Hypoechogenicity
Reduced reflectivity of ultrasonic waves indicates a pathological process characterized by increased fluid content in the follicles. First of all, this is characteristic of diffuse goiter, a pathology in which all follicles uniformly enlarge due to the accumulation of a large amount of hormone-containing gel in them. Also, when the echogenicity of the thyroid gland is reduced , this makes it possible to detect hollow formations—cysts and fistulas filled with fluid—in the glandular parenchyma. They will stand out on the monitor against the background of uniformly gray healthy tissue in the form of dark formations.
It is possible to accurately determine the size and location of the cyst. This has a valuable diagnostic value during surgical procedures:
- Inserting a punctuation needle during a biopsy – allows you to insert it exactly into the cavity of the cyst;
- For sclerosis, pump out the contents of the node or cyst and inject alcohol;
- For phytosclerosis, insert a light probe.
Main criteria
There are three main types of echostructure of organs.
- Isoechoic. This type is the standard norm. Healthy organs have an isoechoic structure. In the photo they are presented in gray with a distinct graininess.
- Hypoechoic. Such tissues have low density and do not reflect ultrasound well; it almost does not return back to the sensor. A dark gray spot appears on the screen, with almost no grain.
- Hyperechoic. The tissues are very dense, ultrasound is reflected quickly from them. Light, almost white spots are visible on the screen. Their graininess is enhanced.
Anechoic structures also exist. They absorb ultrasound completely. Only a black spot is visible in the photo. Sometimes mixed echogenicity occurs - it is represented by hypoechoic and hyperechoic structures.
The concept of echogenicity
Ultrasound diagnostics is based on the ability of ultrasound to be reflected from internal organs. The sensor picks up the reflected waves and transmits them to the computer. The doctor sees on the screen an image of the internal organs in the form of black, dark gray and white spots.
The procedure is absolutely safe for the human body. Diagnosis is carried out on newborn children and pregnant women without restrictions.
To obtain reliable results, the examination must be carried out correctly. Before an abdominal ultrasound, it is recommended to follow a special diet for three days. For severe constipation or flatulence, laxatives and carminatives are prescribed.
No special training is required to examine other organs. To perform an ultrasound, a sound-conducting gel is applied to the skin. This reduces the likelihood of errors.
To decipher the examination results, there are echographic signs:
- size;
- contours;
- structure;
- pathological inclusions.
Differences between normal and altered organ structure are determined using echogenicity. This concept refers to the degree of reflection of ultrasound from organs of different densities.