If spots are found on the x-ray, do not despair. The presence of darkening or flashing does not always indicate the development of serious diseases. Often the cause of the formation of spots is the poor quality of the fluoroscope. And even the incorrect position of the patient during the procedure also shows spots on the lung image. To find out the exact cause, you need to consult your doctor.
Studying the image
What do the spots mean?
White spotty formations on an x-ray of the lungs may be a consequence of the following diseases:
- Inflammation of the lungs.
- Bronchitis.
- Tuberculosis.
If a patient has had pneumonia or bronchitis in the recent past, and an x-ray shows spots on the lungs, this means that residual effects of the disease are occurring in the body. With proper treatment, the nodules will soon resolve.
Spots on the photo
When diagnosing tuberculosis, light-colored formations will be located in the upper parts of the lungs. With proper treatment, the area of inflammation decreases. During the recovery stage, dark spots in the lungs will appear on x-ray, which indicates tissue scarring.
Dimming
If fluoroscopy shows dark or black spots, this may indicate a chronic form of pneumonia. As a rule, darkening appears in the acute stage. During the healing process, the darkening disappears.
Black spots on an x-ray of the lungs may indicate the development of cancer. However, no conclusions can be drawn based on fluoroscopy alone. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a series of tests and additional examinations. If lung cancer is suspected, a complex analysis of lung tissue is prescribed, which is carried out in a hospital.
Darkening in the photo
Dark formations on an X-ray of the lungs, provided the patient is in relatively normal health, can confirm the fact of many years of smoking. In children, darkened areas on the image indicate the presence of a foreign body in the organ. In this case, surgical intervention is required.
Round shadow syndrome
Doctors talk about round shadow syndrome when an X-ray of the lungs in various projections reveals a round or oval spot. To accurately determine the cause of this phenomenon, the doctor first evaluates the type of darkening:
- A round-shaped spot most often has intrapulmonary formations, for example, tumors, cysts, as well as infiltrates with inflammatory content.
- Oval-shaped spots are formed when round formations are compressed by the pulmonary walls.
- Heterogeneous shadows on the spot are a sign of decay of necrotic tissue (in patients with oncology or tuberculosis infiltrate) or the formation of a cavity.
- Slightly darker areas often indicate incomplete calcification of tuberculoma.
- The presence of a clear and dense edge is a possible sign of an hydatid cyst.
It is worth considering that only spots larger than 1 cm in size are considered round shadows. The remaining darkening is considered focal.
White spots
Unfortunately, a bright spot on an x-ray of the lungs is not always a sign of residual effects of the disease.
Often, white formations in the image indicate the development of such ailments:
- Inflammation.
- Atelectasis.
- Pathological processes in pleurisy.
- The development of diseases associated with human professional activity.
If light spots are detected in the image, the doctor must prescribe a number of additional tests. Since any deviations from the norm must be clarified through a comprehensive examination of the patient. An experienced specialist will never make a diagnosis based on one analysis result. To identify the true cause, a radiologist can determine repeated fluoroscopy in different projections.
White spots
In the initial stage of tuberculosis, white formations also appear in the image. This process indicates primary tissue damage by pathogenic bacteria. An eloquent sign of tuberculosis at the first stage is a characteristic light path from the site of inflammation to the root system.
What causes spots in the lungs?
White (dark) spots appear against the background of pathological processes or are characterized as residual effects after therapy for respiratory diseases.
Compaction syndrome. Low to medium density lesion. Tuberculosis.
Darkening of the lungs causes compaction of the organ tissue during the inflammatory process or the growth of neoplasms, atypical and benign. In addition, darkening and similar phenomena in the image are interpreted as:
- the presence of cystic formations and abscesses;
- collapse of the alveoli with atelectasis;
- tuberculosis damage to lung tissue;
- accumulation of secretions in the pleural cavity;
- neoplasms localized in the ribs and segments of the spine;
- development of tumor processes in the mediastinum;
- enlarged nodes of the lymphatic system;
- pathologies of the upper digestive tract;
- fatty benign tumor in the costal sinuses.
Pneumonia spots
To understand that the image showed the presence of pneumonia, the specialist must know what this pathology looks like. Spotty formations in pneumonia can have different locations and dimensions:
- Small with limited margins up to 3 mm.
- Segmental – located within the boundaries of a segment.
- Subtotal – all fields, with the exception of the upper lobes.
- Total formations covering the entire surface of the lungs.
As inflammation develops, white spots with unclear, blurred contours form in the lungs. In this case, the severity of the severity depends on the degree of development of the disease. The more advanced the disease, the more pronounced the spots in the picture.
Light spots
Summing up
If there are black or white spots on the X-ray image, additional examination is necessary. It is important to understand that if the radiographer’s work is poor, white and dark formations are only a side effect of the functioning of the device. To establish an accurate diagnosis, a specialist will definitely prescribe a series of examinations and tests. Only after receiving all the results, the doctor has the opportunity to assess the picture of the patient’s condition.
A white spot on an X-ray of the lungs with smooth, clear contours of medium intensity - such a conclusion from a radiologist is common. It reflects infiltrative changes in the lung tissue or “plus shadow” syndrome.
What is the seriousness of darkening or brightening?
It is difficult to answer unequivocally only based on an x-ray image whether such enlightenment is dangerous. To assess the situation, you will need to take additional tests and analyzes and consider the patient’s condition.
X-ray is an auxiliary diagnostic method designed to supplement information about the condition of the patient’s tissues and organs. If you look closely, there is no “diagnosis” in the X-ray description report; instead, there is a “conclusion.”
Only a specialized specialist can make a diagnosis based on the diagnostic results, as well as answer the question about the danger of such darkening during fluorography.
What to do if a white spot is detected on the x-ray
When performing a chest x-ray or fluorography in a patient with tuberculosis, a white spot on the x-ray reflects either an inflammatory lesion of the lung tissue or destructive changes in the parenchyma with the formation of abscesses, tubercles, and caverns. Correctly, this symptom should be called darkening, since it reflects the characteristics of the passage of x-rays through objects and their color display on the x-ray.
A white shadow in a photograph is also observed when:
- pneumonia;
- atelectasis;
- exudative pleurisy;
- occupational diseases (silicosis, talcosis, asbestosis).
Radiographs with white spots of various origins: 124.3 – breast piercing, 124.4 – shot in the soft tissues of the chest, 124.5 – professional cementosis, 124.6a – contrast during bronchography, 124.6b – pneumonic focus, 124.7 – interlobar pleurisy (arrows indicate artifact)
This syndrome is a sign of many pathological changes in the lungs, but we will consider the most common options.
If spots are detected, additional research is necessary to determine the cause of the pathology. For these purposes, a radiologist may prescribe an X-ray examination in additional projections or perform layer-by-layer computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
X-ray imaging features
An x-ray is a negative image of the object under study on a special film, obtained using ionizing radiation, which has the ability to penetrate various tissues and biological environments of the human body. A classic fluorography image reflects the reverse correspondence of shadows: light areas indicate the state of organs with the most dense structure, dark areas indicate tissues with a minimum density that easily transmit x-rays.
When studying the result of fluorography, the radiologist relies on strict adherence to the norms - in the image of healthy lungs, the right side looks wide and short, the left - narrow. Both areas must contain a large volume of air, not interfere with the passage of X-rays, and appear transparent on a fluorographic image.
What does a spot look like on an x-ray with pneumonia?
In pneumonia, the spot on the x-ray image has a length depending on the size of the lesion in the pulmonary parenchyma:
- limited – up to 3 cm in diameter;
- segmental – within a segment;
- subtotal – the entire field, with the exception of the tops;
- total.
Pneumonia is an inflammatory disease that affects the alveolar tissue with accumulation of fluid in the acini. Pathogenesis forms a specific x-ray picture of the disease.
X-ray. Focal pneumonia in the lower lobe on the right
The white spot with pneumonia has fuzzy, blurred contours. Its intensity can be low or high, depending on the characteristics of the exudate (inflammatory fluid in the lumen of the alveoli). A path from the root approaches the site of its localization due to lymphangitis.
What does focal change mean?
The focal spot or focal shadow on a fluorogram has a round shape. The area of such a trace is often more than 10 - 12 mm. This darkening is most often recorded during an inflammatory process, possibly resulting from:
- Pneumonia.
- The presence of fluid in the pleural tissue (localized effusion).
- Parasitic diseases (with the formation of eosinophilic infiltrate).
- Development of bronchial asthma.
- Formation of a localized abscess.
However, it is worth noting that the focal spot can also be a sign of tumor formations of various etiologies. Sometimes this phenomenon is observed after rib fractures in the projection of the formation of bone calluses.
Atelectasis of the lung or x-ray semiotics of triangular spots on the image
Lung atelectasis is a disease accompanied by the collapse of a segment, lobe or lung tissue completely against the background of cessation of bronchial ventilation. Radiologically, such changes are called limited darkening, since they do not extend beyond the segment or subsegment and have a triangular shape.
Atelectasis of the middle lobe of the right lung - frontal and lateral radiographs
How to identify atelectasis in an image:
- the size of the spot coincides with the size of the changed segment;
- triangular darkening in the lungs can be seen in frontal and lateral projections;
- during inhalation photographs the size of the spot does not increase;
- the narrow end of the triangular shadow is directed towards the root;
- Holtzknecht-Jacobson symptoms are observed during fluoroscopy (suction of the mediastinum towards the lesion during exhalation).
The morphological substrate of the pathology is the accumulation of infiltrative fluid in the alveoli, infiltration of lung tissue, and tumor growth in the pulmonary parenchyma.
Spontaneous atelectasis occurs in 1-3% of patients due to a defect in surfactant (the substance that forms the framework of the alveoli).
Schematic representation of the topography of segmental atelectasis
Limited darkening during collapse of the lungs requires knowledge of the segmental structure of the lungs, as it reflects atelectasis of a certain segment. By establishing the topography of the shadow, the doctor can guess which bronchus is affected. The substrate of formation (infiltrate, additional tissue, exudate) is almost impossible to determine on the basis of a radiograph.
What does a white spot mean in a picture of tuberculosis?
In tuberculosis, a focal spot on a chest x-ray indicates the infiltrative stage of the disease, when mycobacteria begin to infect the lung tissue. In this case, the x-ray shows a path to the root from the side of the lesion (due to lymphangitis). Such radiological symptoms are called “primary tuberculosis focus”.
Radiographs for various types of tuberculosis
Multiple small disseminated shadows on both sides indicate miliary tuberculosis.
A single large shadow with a cavity inside (clearance) and a fluid level - an abscess formed against the background of destruction of the lung parenchyma - “ring shadow” syndrome.
A spot on an X-ray of the lungs in the projection of the pulmonary fields reflects a pathological process, the causes of which should be established by additional research.
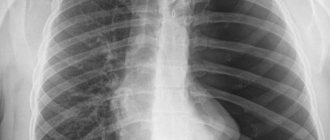
During the annual medical examination, the patient is offered to undergo fluorography to check the condition of the lungs. The procedure involves obtaining an image of a person's internal organs when X-rays pass through the tissues of his body. Thanks to X-rays of the lungs, it is possible to diagnose various diseases in the lungs in the early stages, the symptoms of which have not yet appeared in a person - tuberculosis, lung cancer, atelactase, etc.
What is a shadow on an x-ray, probable causes
A shadow on an x-ray of the lungs most often occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in the lumen of the pulmonary alveoli: transudate (edematous fluid) or exudate (inflammatory). In addition, detection of pathological shadows is possible with obstruction of the bronchus and the development of atelectasis, with compression of the lung, with replacement of the pulmonary parenchyma by other tissues (for example, connective tissue).
Sometimes shading in the projection indicates changes in the surrounding tissues: in the chest, diaphragm, mediastinum, pleura and pleural cavities.
If shadows are detected in the image, it is necessary to treat organic pathologies, and not functional ones (asthma, etc.).
What does a classic x-ray of the lungs look like?
Classic X-ray of the lungs
The human lungs look like this in the picture: the right and left lungs on the sides of the spine, the shadow of the heart, the collarbone, the ribs, the dome of the diaphragm. The images obtained are deciphered by specialists who assess the condition of the patient’s lungs according to the following scheme:
- how the lungs are located in the chest relative to other organs;
- number of pulmonary lobes;
- the shape of the paired organ and its size;
- pulmonary pattern.
The lung tissue of a healthy person has a homogeneous and uniform structure. In some cases, dark or light colored spots appear on x-rays. This may indicate both the presence of serious pathologies and physiological processes in the lungs that are not a deviation from the norm. However, having received such an image, the patient anxiously begins to look for information about the meaning of darkening or light circles in the image. What they mean will be explained below.
Reasons for the appearance of spots in the photo
Reasons for the appearance of spots in the photo
There are many reasons for the appearance of dark spots on the lungs. When a pathological process affects an organ, its structure changes noticeably - areas with compactions appear, which, when exposed to X-rays, absorb rays in greater quantities than healthy tissue. This is why dark areas are visible in the pictures. These areas can vary in shape and size:
- Focal darkening. Usually detected during inflammation and cancer processes in organ tissues. They look like small spots, up to 10 mm in diameter. Based on their presence, it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis. Additional studies are needed - CT scan, blood, urine and sputum tests.
- Round shading. They are visualized as single round shadows. Usually they are an indicator of the inflammatory process in the lung tissue. This picture is indicative of pneumonia, abscesses, benign formations in this organ, bronchial asthma, and even rib fractures. Less commonly, round single dark spots indicate oncological processes in the lungs.
- Segmental darkening. Localized in the shape of a triangle (triangles) on one or both lobes. They can be either single or multiple. Single segmental opacities may indicate a foreign object in the organ or tumors within the bronchi, which can be either benign or malignant. Multiple segments in the images indicate the presence of pneumonia, central lung cancer, narrowing of the central bronchus, pleurisy, and oncology of neighboring organs.
- Darkening of fuzzy shape. These dark areas do not have definite contours and cannot be compared with geometric shapes. Most often, the presence of such dark areas of uncertain shape indicates infectious lesions of the lung - staphylococcal pneumonia, exudative pleurisy.
- Partial darkening. These are clearly defined and clearly visible shadow boundaries in photographs, having curved, convex and other shapes. This type of darkening indicates chronic diseases in the bronchi.
Dark spots in the lungs on x-ray
The anatomical structure of the lungs, their ability to be filled with air that freely transmits x-ray radiation, makes it possible to obtain, during fluoroscopy, an image that reflects in detail all the structural elements of the lungs.
However, darkening in the lungs on an X-ray does not always reflect changes in the tissues of the lung itself, since other organs of the chest are located at the level of the lungs and, therefore, the radiation beam, passing through the body, projects on the film a superimposed image of all organs and tissues , falling within its range.
In this regard, if any darkened formation is detected in the image, before answering the question of what it could be, it is necessary to clearly differentiate the localization of the pathological focus (in the tissues of the chest, diaphragm, pleural cavity or, directly, in the lungs).
Main syndromes on radiographs
On an x-ray taken in an anterior projection, the contours of the lungs form pulmonary fields over the entire area, intersected by symmetrical shadows of the ribs.
A large shadow between the pulmonary fields is formed by the combined overlap of the projection of the heart and great arteries.
Within the contour of the lung fields, one can see the roots of the lungs located at the same level with the anterior ends of the 2nd and 4th ribs and a slight darkening of the area caused by the rich vascular network located in the lung tissue.
All pathological changes reflected on x-rays can be divided into three groups.
Dimming
Appear on the image in cases where the healthy part of the lung is replaced by a pathological formation or substance, causing the displacement of the air part by denser masses. As a rule, it is observed in the following diseases:
- bronchial obstruction (atelectasis);
- accumulation of inflammatory fluid (pneumonia);
- benign or malignant tissue degeneration (tumor process).
Change in pulmonary pattern
This group of changes can be considered the most common. Despite the huge list of lung pathologies, all possible changes in the X-ray picture can be attributed to one of 5 syndromes:
- total (complete) or subtotal (almost complete) blackout;
- limited dimming;
- round (spherical) shadow;
- ring shadow;
- focal darkening.
Enlightenment
The clearing in the image reflects a decrease in the density and volume of soft tissues. As a rule, a similar phenomenon occurs when an air cavity forms in the lung (pneumothorax).
Due to the specific reflection of x-ray results on photographic paper, areas that easily transmit radiation are reflected in a darker color due to the more intense effect of x-rays on the silver ions contained in photographic paper; areas of a denser structure have a light color. The wording “darkening” in the image is actually reflected in the form of a light area or focus.
X-ray showing a pulmonary pattern of healthy lungs
Total blackout syndrome
Total darkening of the lung on an x-ray is a complete or partial darkening (at least 2/3 of the lung field). In this case, gaps are possible in the upper or lower part of the lung.
The main physiological reasons for the manifestation of this syndrome are the lack of air in the lung cavity, an increase in the density of the tissue of the entire surface of the lung, the content of fluid or any pathological content in the pleural cavity.
Diseases that can cause such a syndrome include:
What is bronchoscopy?
- atelectasis;
- cirrhosis;
- exudative pleurisy;
- pneumonia.
To carry out differential diagnosis of diseases, it is necessary to rely on two main signs. The first sign is to assess the location of the mediastinal organs.
It can be regular or offset, usually in the direction opposite to the darkening focus.
The main landmark in identifying the displacement axis is the shadow of the heart, located mostly to the left of the midline of the chest, and less to the right, and the stomach, the most informative part of which is the air bubble, always clearly visible on the images.
The second sign that makes it possible to identify a pathological condition is an assessment of the uniformity of darkening. Thus, with uniform darkening, atelectasis can be diagnosed with a high degree of probability, and with heterogeneous darkening, cirrhosis can be diagnosed.
Interpretation of the results obtained using the radiographic method consists of a comprehensive assessment of all visually detected pathological elements in comparison with the anatomical features of each individual patient.
Limited dimming syndrome
To identify the causes of limited darkening of the pulmonary field, it is necessary to take an image in two directions - in direct projection and lateral.
Based on the results of the obtained images, it is important to assess the localization of the darkening focus.
If the shadow in all photographs is located inside the pulmonary field and is similar in size to its contours or has a smaller volume, it is logical to assume a lung lesion.
If there is darkening adjacent to the diaphragm or mediastinal organs with a wide base, extrapulmonary pathologies (fluid inclusions in the pleural cavity) can be diagnosed. Another criterion for evaluating limited shades is size. In this case, two possible options should be considered:
- The size of the darkening clearly follows the contours of the affected part of the lung, which may indicate an inflammatory process;
- The size of the darkening is smaller than the normal size of the affected segment of the lung, which indicates cirrhosis of the lung tissue or blockage of the bronchus.
Particular attention should be paid to cases in which there is a darkening of normal dimensions, in the structure of which light foci (cavities) can be traced. First of all, in this case, it is necessary to clarify whether the cavity contains liquid.
To do this, a series of photographs are taken in different positions of the patient (standing, lying down or bending over) and changes in the level of the estimated upper limit of the liquid contents are assessed.
If fluid is present, a lung abscess is diagnosed, and if it is not present, then the likely diagnosis is tuberculosis.
Important! The detection of several cavities with limited darkening of the lung is characteristic of pneumonia caused by staphylococcus. Such a lesion has an unfavorable prognosis, and often treatment is only possible through surgery. X-ray shows limited darkening of the lungs in two projections
I identify round shadow syndrome when the spot on the lungs has a round or oval shape on two photographs taken perpendicular to each other, that is, from the front and the side. To decipher the results of radiography when a round shadow is detected, they rely on 4 signs:
- form of shading;
- localization of darkening relative to nearby organs;
- clarity and thickness of its contours;
- structure of the internal shadow field.
Since the shadow reflected on the image within the lung field may actually be located outside it, assessing the shape of the darkening can greatly facilitate diagnosis.
Thus, a round shape is characteristic of intrapulmonary formations (tumor, cyst, infiltrate filled with inflammatory contents).
An oval shadow in most cases is the result of compression of a round formation by the walls of the lung.
The structure of the internal shadow field is also highly informative.
If, when analyzing the results, the heterogeneity of the shadow is obvious, for example, lighter foci, then with a high degree of probability, it is possible to diagnose the disintegration of necrotic tissue (with disintegrating cancer or disintegration of tuberculous infiltrate) or the formation of a cavity. Darker areas may indicate partial calcification of tuberculoma.
A clear and dense contour indicates the presence of a fibrous capsule, characteristic of an echinococcal cyst. Round shadow syndrome includes only those shadows that are more than 1 cm in diameter; shadows with a smaller diameter are considered lesions.
Ring shadow syndrome
A ring-shaped spot on the lung on an x-ray is the easiest syndrome to analyze. As a rule, a ring-shaped shadow appears on an x-ray as a result of the formation of a cavity filled with air.
A mandatory condition under which the detected darkening is classified as ring-shaped shadow syndrome is the preservation of a closed ring when taking pictures in all projections and in various positions of the patient’s body.
If in at least one of the series of photographs the ring does not have a closed structure, the shadow can be considered an optical illusion.
If a cavity is detected in the lung, the uniformity and thickness of its walls should be assessed. Thus, with a large and uniform thickness of the contour, one can assume the inflammatory origin of the cavity, for example, a tuberculous cavity.
A similar picture is observed with an abscess, when purulent melting of tissue occurs and the contents are removed through the bronchi.
However, with an abscess, the remains of pus most often remain in the cavity and their complete removal is quite rare, so usually such a cavity is a tuberculous cavity.
The unevenly wide walls of the ring indicate the process of decay of lung cancer. Necrotic processes in tumor tissue can cause the formation of a cavity, but since necrosis develops unevenly, tumor masses remain on the inner walls of the cavity, creating the effect of an “uneven” ring.
Important! The main difficulty in assessing the ring-shaped shadow is determining the localization of the formation, since in most cases a similar syndrome is observed in extrapulmonary processes (deformation of the ribs, gases in the intestines, gases in the pleural cavity). The image shows a ring-shaped shadow in the lower lobe of the right lung
Spots on the lungs larger than 1 mm and smaller than 1 cm are considered lesions.
On an x-ray, you can see from 1 to several lesions located at a considerable distance from each other or in a group.
If the area of distribution of foci does not exceed 2 intercostal spaces, the lesion (dissemination) is considered limited, and if the foci are distributed over a larger area, it is considered diffuse.
The main criteria for assessing focal darkening are:
- area of distribution and location of foci;
- shadow contours;
- darkening intensity.
When one or more dark spots are located in the upper parts of the lung, this is a clear sign of tuberculosis.
Many foci with limited spread are a sign of focal pneumonia or the result of the disintegration of a tuberculous cavity, located, as a rule, slightly above the detected foci.
In the latter case, a round or ring-shaped shadow may also be observed in the picture.
The reason for the appearance of a single darkening in any part of the lung is, first of all, considered the likelihood of developing cancer or tumor metastasis. This is also evidenced by the clear contours of the shadow. Fuzzy contours indicate the inflammatory origin of the darkening.
To assess the intensity of darkening, they are compared with the image of the vessels visualized in the image.
If the severity of the lesion is inferior to the shadow of the vessel, this is a low-intensity darkening characteristic of focal pneumonia or infiltrated tuberculosis.
With medium and strong darkening of the focus, when the severity is equal to or darker than the vascular pattern, one can judge the attenuation of the tuberculosis process.
Since extensive dissemination of lesions can indicate more than 100 diseases, to distinguish between causes, the size of the shadows should be assessed. Thus, tiny foci covering the entire area of the lung may indicate pneumoconiosis, miliary tuberculosis or focal pneumonia.
The image shows small focal shadows
Important! Regardless of what changes are observed on an x-ray of the lungs, when analyzing the results, one should take into account the presence of a normal pulmonary pattern, which is characterized by the presence of shadows of the vascular system.
In the vast majority of cases, a final diagnosis cannot be made on the basis of lung x-rays, since analysis of the resulting image allows us to identify only a syndrome characteristic of a particular disease.
If the x-ray showed darkening of any area, then to clarify the diagnosis and assess the dynamics of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a set of laboratory tests and additional diagnostics using MSCT, bronchography, biopsy, etc.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/rentgen/zatemneniya-legkih-rentgene
What dark spots look like on an x-ray in various diseases
Spots in the lungs on x-rays may appear due to the following diseases:
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
With this disease, the upper parts of the organ are seriously affected. In the image, this is manifested by the presence of multiple darkened lesions of small size - up to 2 mm in diameter. In this case, foci can merge, forming larger locations.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
In pneumonia, the presence of dark areas is noted in the lower parts of the lung tissue. The symptoms of the disease will be most clearly visible in the photographs at the time of the development of the disease. Visually, this will be manifested by an increase in the root of the lung due to the infiltration process, a change in the pulmonary pattern, shadows with an indistinct, blurry contour and numerous spots of different diameters.
With pneumonia, on an X-ray of the lungs, these spots have unclear contours and a heterogeneous structure.
In addition to pneumonia, the presence of multiple lesions in the lower parts of the pulmonary lobes indicates the consequences of pneumonia or bronchitis. With complete recovery, these marks will disappear.
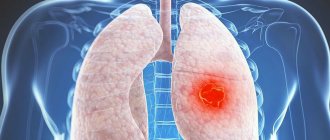
Lungs' cancer
Lungs' cancer
Lung cancer is a life-threatening condition. Its manifestations can also be noticeable during fluorography or x-rays. It is worth noting that in the presence of formations up to 2 mm in diameter, x-rays will not be able to detect the tumor. It is visualized on photographs when it reaches a diameter of more than 3 mm. For accurate diagnosis, x-rays are performed in two projections at once - lateral and direct.
In the image, if cancer is suspected, the following signs can be detected: a shadow on the periphery of the lung with a vague and bumpy outline, a thin outline of rays around the cancer focus, a large white spot stands out against the background of a strong shadow - this is how the picture of tumor disintegration appears.
However, when diagnosing oncology, you should not rely only on the image. The patient is referred to specialists who take a tissue biopsy and conduct additional studies - MRI, CT of the organ - to make the correct diagnosis.
Pleurisy
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is inflammation of the pulmonary lining. In this case, the darkening is not explained by obstruction of air in those zones. In this case, fluid accumulates in the cavities from the folds of the pleura.
In the presence of dry pleurisy, the dome of the diaphragm is raised upward and the lung tissue is opaque. With effusion pleurisy, the angle of the diaphragm is smoothed out due to the accumulation of fluid, the lower part of the lung is darkened by an oblique border.
Nicotine addiction
Smoker's lungs
Heavy smokers also show dark spots on fluorograms or x-rays. They are explained by the thickening of the pulmonary pattern and the formation of cavities in the bronchi. The roots of the lungs in smokers are blurred - it is difficult to determine their structural boundaries. The blurring of the contours of the roots is explained by an increase in the pulmonary vessels due to respiratory failure. In addition, the image of a heavy smoker can reveal bronchitis, tuberculosis, and lung tumors.
Presence of a foreign body in the lungs
Dark spots in the lungs can be caused by the presence of a foreign object in the lung tissue. This can most often be found in children who are careless with small objects. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to detect an object in the bronchi or lungs on an x-ray due to swelling of the organ, so endoscopy is preferable to x-rays.
Listed above are the main reasons for the appearance of dark spots on the lungs on X-rays. It is very important to know that the shadows in the image itself look like the lightest areas, because... these are negatives. And vice versa - enlightenments in this paired organ will be reflected in the negatives as the darkest fragments. It is impossible to understand the symptoms of the disease and make a correct diagnosis based only on photographs. This should be done by a qualified radiologist.
Quite often, to provide the most informative and accurate state of the respiratory organs, doctors prescribe such a common study as an x-ray. This procedure is often indicated in order to clarify the result of previously performed fluorography or based on the general clinical picture of the patient’s condition. For example, with certain lung diseases, the density of some lung tissues becomes increased. In the resulting images, each of which shows the condition of the lungs, similar phenomena are noted in the form of spots and darkening in the lungs on the X-ray.
If the patient is informed about the discovery of spots, the first reaction of most is fear, many think that this is a malignant formation. Cancer gives some darkening, but is far from the only reason for the appearance of spots. In order to avoid wasting unnecessary nerves, and also to begin to act as quickly as possible when blackouts are detected, it is worth studying their types, as well as becoming familiar with the main reasons for their occurrence.
Spots on the lungs on X-ray: types and causes – About Lungs
Lung X-ray or fluorography is an affordable and simple way of primary diagnosis of many quite serious diseases. Sometimes even the patient himself, picking up an x-ray, can detect noticeable spots on it. What can they form from?
Dark spot on x-ray
In fact, the presence of dark spots in the lungs, visually visible on x-rays, does not in 100% of cases indicate the development of various ailments. Other organs are also localized at the level of the lungs, so that the radiation beam, while passing through the body, will project on film an image of all organs, as well as tissues that fall within its range.
Only a doctor can determine exactly what a spot on the lung found on an x-ray is. Sometimes additional tests are required to make a valid diagnosis.
If, during a routine annual fluorography, doctors discover a spot on a patient’s X-ray, this does not become a reason for immediate hospitalization in a tuberculosis clinic or for compulsory treatment. A patient with such a disorder is shown a detailed X-ray examination, when photographs of the chest are taken in various projections. This allows you to determine an accurate diagnosis.
Sometimes spots in the image are explained by natural causes - an error in the X-ray machine or poor-quality film. Also among the relatively safe causes of such darkening are scar changes after surgical interventions, abscesses and diseases.
What could a black focal spot mean?
They speak of focal spots when small nodules are detected on an x-ray of the lungs - about 1 cm, no more. Such traces can be explained by:
- Vascular disorders.
- Primary stage of cancer. Such lesions usually have clear contours.
- Many diseases of the respiratory organs. In particular, during inflammatory processes, the contours of the lesions are unclear.
- Post-myocardial infarction.
On an x-ray, only 1 lesion may be visible, but sometimes several of them are recorded, even at a significant distance from each other. So, if dark spots of this kind are localized in the upper parts of the lung, most likely they indicate tuberculosis. And multiple foci in a limited space may indicate focal pneumonia.
What does focal change mean?
The focal spot or focal shadow on a fluorogram has a round shape. The area of such a trace is often more than 10 - 12 mm. This darkening is most often recorded during an inflammatory process, possibly resulting from:
- Pneumonia.
- The presence of fluid in the pleural tissue (localized effusion).
- Parasitic diseases (with the formation of eosinophilic infiltrate).
- Development of bronchial asthma.
- Formation of a localized abscess.
However, it is worth noting that the focal spot can also be a sign of tumor formations of various etiologies. Sometimes this phenomenon is observed after rib fractures in the projection of the formation of bone calluses.
What disease causes lobar spots?
Lobar darkening usually has clear contours, which are clearly visible on the fluorogram. Such spots are distinguished by a certain convexity or concavity and most often indicate the presence of various chronic pulmonary ailments.
Among the most common causes of lobar shadows are:
- Cirrhosis.
- Bronchiectasis.
- Formation of a purulent cavity.
Lobar opacities can be seen very well and diagnosed with detailed CT scans.
Segmental opacities
Such spots on the lungs visually appear on x-rays as segmented areas with fairly clear contours and usually have a triangular shape. The appearance of isolated darkenings of this kind can be provoked by:
- Previous injuries to lung tissue.
- Formation of endobronchial tumor.
- Entry of foreign bodies.
However, the presence of several segmental changes is considered a rather alarming symptom and can be observed with:
- Inflammations of varying severity, which have an acute or chronic form.
- Cancer diseases.
- Tuberculosis.
- Stenosis of the bronchial branch.
- Metastasis.
Round shadow syndrome
Doctors talk about round shadow syndrome when an X-ray of the lungs in various projections reveals a round or oval spot. To accurately determine the cause of this phenomenon, the doctor first evaluates the type of darkening:
- A round-shaped spot most often has intrapulmonary formations, for example, tumors, cysts, as well as infiltrates with inflammatory content.
- Oval-shaped spots are formed when round formations are compressed by the pulmonary walls.
- Heterogeneous shadows on the spot are a sign of decay of necrotic tissue (in patients with oncology or tuberculosis infiltrate) or the formation of a cavity.
- Slightly darker areas often indicate incomplete calcification of tuberculoma.
- The presence of a clear and dense edge is a possible sign of an hydatid cyst.
It is worth considering that only spots larger than 1 cm in size are considered round shadows. The remaining darkening is considered focal.
Ring shadow syndrome
A ring-shaped spot found on an X-ray of the lung is considered by doctors to be one of the simplest diagnostic cases.
Most often, such darkening is a consequence of the formation of a cavity filled with air.
At the same time, taking pictures in different projections confirms the closure of the ring in all positions of the patient’s body. Features of ring-shaped spots contribute to the correct diagnosis:
- A large and uniformly thick contour indicates an inflammatory process, for example, with a tuberculous cavity (less often with an abscess).
- Unevenly wide boundaries of the ring-shaped shadow are a symptom of the disintegration of a cancerous tumor.
A visually noticeable ring in the image is also recorded in case of extrapulmonary phenomena, for example, deformation of the lungs, accumulation of gases in the intestines or pleural cavity.
Undefined changes
Spots on the lungs, which have an indefinite shape, can indicate various ailments:
- Inflammatory lesions caused by staphylococci.
- Pleural effusion.
- Heart attack.
- Exudative pleurisy.
Sometimes shapeless spots are a consequence of hematogenous infection of the lungs from existing purulent foci (for example, when a patient develops osteomyelitis, andexitis, etc.). In this situation we are talking about quite dangerous secondary staphylococcal pneumonia.
Total blackout - what is it?
When a spot on an X-ray image extends to 2/3 of the lung field or more - sometimes even to the entire organ, doctors record a total darkening. There may be gaps in the upper or lower region of the lung.
A similar picture can be observed if there is no air in the pulmonary cavity or the tissue over its entire surface has become denser.
Also, total darkening occurs in the presence of fluid or other pathological contents inside the pleural cavity.
Total blackout is possible with:
- Cirrhosis.
- Atelectasis.
- Exudative pleurisy.
- Pneumonia.
To fully interpret the X-ray results, the doctor not only evaluates all visually noticeable pathological elements, but also takes into account the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient.
How does cancer appear on an image?
Lung cancer is not always visible on X-rays. In particular, if the size of the tumor does not exceed 2 mm, the tumor will simply be invisible. For early diagnosis to be truly successful, doctors recommend taking x-rays in several projections at once. Cancer in the image can be suspected by:
- Shadows on the edges of the lung, which is distinguished by blurry and tuberous borders.
- The presence of a thin border of rays near the focus.
- A visible white spot against the background of the shadow.
Of course, cancer can also manifest itself with other signs, which only a competent specialist can detect in an image. At the slightest suspicion of oncology, the patient is advised to conduct additional studies.
White spot on fluorography
Sometimes spots on X-ray photographs of the lungs do not appear as darkening, but, on the contrary, as light areas. In this case, they most likely indicate a decrease in the level of density, as well as the volume of soft tissue. This situation can be explained by pneumothorax - the formation of an air cavity in the lung itself.
It is worth considering that when independently analyzing an X-ray image, the patient may simply misinterpret it and see darkening as light spots.
What to do if you find it?
Most often, chest radiography cannot be a sufficient basis for a final diagnosis. Detection of dark spots on an x-ray is a reason to conduct a whole range of different studies:
- MRI and CT.
- Bronchography.
- Biopsies, etc.
The image is interpreted by a radiologist. He can make a preliminary diagnosis, which is later confirmed or refuted by the attending physician. It is simply impractical to draw conclusions about existing stains on your own.
Treatment
Of course, not a single doctor in the world treats spots on the lungs. Therapy depends on the detected disease and the individual characteristics of the patient:
- Tuberculosis is a reason to undergo long-term anti-tuberculosis treatment using several strong antibiotics. The closed form of the disease can be successfully treated at home, while the open form is treated only in a tuberculosis clinic.
- Pneumonia is most often also treated with antibiotics, but in addition, the patient is shown targeted therapy designed to support the body, relieve intoxication and facilitate recovery.
- A detected effusion in the pleural cavity (fluid accumulation) may not be treated in any way if it is asymptomatic. Most often, it resolves on its own with successful treatment of the underlying disease. However, sometimes the fluid needs to be removed by drainage.
- Cancer diseases require complex treatment aimed at suppressing the activity of pathogenic cells and reducing tumor size. Sometimes doctors decide to remove a lobe of the lung to save the patient’s life.
There are quite a few bronchopulmonary diseases, the development of which may cause spots to appear on the images. Treatment methods for such ailments most often differ and are selected individually by the attending physician.
Source:
Round and focal shadow syndrome on radiography | Second opinion
In radiology, the spot is called a shadow. A spot-like shadow less than 1 centimeter in diameter is a focal shadow. A focal shadow is a lesion whose size ranges from 0.1 cm to 1.0 cm. These pathological lesions are characteristic of various nosological forms.
By origin, these lesions can be of inflammatory and tumor origin, and are also caused by hemorrhage, edema, and atelectasis. X-ray experience proves that lesions in the lungs occur in inflammatory diseases that pathologically change the structure of the pulmonary parenchyma.
In our country, foci are also characteristic of tuberculosis (focal tuberculosis). In practice, it often occurs when there are 2-3 lesions in one lung, then radiologists talk about a group of lesions in the lung.
Inexperienced and young specialists mistake the cross-section of a vessel, the shadow of the nipples of the mammary gland, as well as calcium deposits in the cartilage of the ribs as focal shadows.
A focal shadow has the following characteristics:
1) Localization of focal shadow. 2) Prevalence of focal shadow. 3) Contours of focal shadow.
4) Intensity of focal shadow.
This patient has a lesion in the middle lobe of the right lung with a decay cavity in the center (indicated by an arrow). According to the clinic, the patient was diagnosed with tuberculosis.
White spot on x-ray of lungs/white spot on x-ray of lungs/white spots on lungs/two spots on lungs/lung disease spot on lung
For each disease there is a characteristic localization of the outbreak. Tuberculosis (focal tuberculosis and tuberculoma) is characterized by localization in the apices of the lungs and under the collarbone.
Source: https://gorclinbol.ru/kashel/pyatna-na-legkih-pri-rentgene-vidy-i-prichiny.html
Causes of spots on the received images
The main reasons for the appearance of spots or darkening in an x-ray photo can be the following causes of darkening in the lungs:
- Erroneous operation of modern X-ray medical equipment, use of very low quality film, violation of certain standards for its development.
- Presence of foreign objects in the lungs.
- Previously performed surgical interventions. Dense and rough scar tissue often forms at the site of the operation. Due to its higher density, in the photo such places may appear as light or dark spots.
- Various inflammatory processes that occur in the respiratory organs and lungs, they also appear in the form of white dense darkening.
- The cause of the appearance of the spot can be the accumulation of various harmful parasites, which are very often localized in tissues. The most common is alveococcus or primordium.
- Previously received various rib injuries, complex and milder fractures also very often take the form of spots.
- Accumulation of large amounts of fluid in the respiratory organs.
- Various types of tumors and metastases also tend to cast shadows, which stand out as white spots in the image.
If such darkening is detected, doctors usually prescribe additional forms of examination. This is based precisely on a large number of reasons that can lead to their formation. Competent treatment is prescribed only after the nature of the formations and the causes of darkening in the lungs have been fully established. Normal symptoms and health status are taken into account.
When diagnosed with pneumonia, an x-ray is the only option to identify a serious illness.
What spots might there be in the picture?
In the process of conducting an additional medical examination and carefully studying the resulting images, the specialist evaluates the darkening according to the following parameters:
- The location of the spot is the upper, lower or middle part of the lung. It can also be the outer, inner and middle lobe of this organ. This way you can get a clear picture of the disease;
- The size makes it possible to determine the total area of pathology;
- Level of expression. Based on this feature, the degree of density of the lesion present can be determined. The severity can be moderate, weak and intense;
- General outline. Pay attention to whether the stain has smooth or uneven edges. Often on this basis it is possible to determine the nature of education.
In addition to the differences listed above, spots in the image can be classified according to other criteria. Doctors must take them into account in order to establish a more accurate diagnosis.
Spots and dark spots that occur in the lungs and trachea can be characterized by their location, but also by appearance and general shape. The distribution is as follows:
- Share. The spot has a clear outline and can be particularly concave or significantly convex. Darkening can develop against the background of inflammation, cirrhosis or destruction. If a spot of this type is located in the middle or lower part of the lung, the doctor may suspect a malignant formation.
- Focal. These are relatively small centimeter-sized formations that can prove the presence of inflammation, the development of pathology of veins and blood vessels, as well as the development of peripheral cancer, dangerous tuberculosis and sudden pulmonary infarction. If such lesions were found against the background of headache, cough and pain, bronchial pneumonia can be judged.
- Indefinite in form. These are special spots that do not have a bright expression or outline. To give the patient the most accurate diagnosis, more modern types of examination, such as CT or MRI, are prescribed. Such white spots often indicate pathologies such as pleurisy, pneumonia, hemorrhage, as well as various types of tumors. The diagnosis is clarified not only with the help of CT, but also by laboratory tests.
- Liquid. This is direct evidence of pulmonary edema. The fluid collected in the lungs may be due to increased pressure in numerous vessels and the degree of permeability of their alveolar wall. In this case, the liquid immediately enters the lung tissue, disrupting their functionality.
- Segmental. We are talking about darkening in the form of a triangle. This is evidence of pathologies such as a cancerous tumor, various benign formations, pneumonia, the presence of metastases coming from other organs, tuberculosis and fluid accumulation. The doctor’s competence is very important here, since the earlier measures are taken, the greater the chance the patient will have if a fatal pathology is detected.
- Focus. As a rule, these are single spots, the size of which is on average 1 cm. Such lesions occur against the background of pneumonia, with increased fluid content in the organs, breathing, tuberculosis, and they can also be cysts and purulent abscesses.
Making an accurate diagnosis based on the type and location of spots alone is impossible. It is for this reason that additional high-quality examination is required.
If darkening is visible in the image, you should immediately consult a doctor who can identify or exclude the presence of a dangerous disease.
Why might darkening appear on the lungs?
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to undergo fluorography at least once a year. If darkening is visible in the image, you should immediately consult a doctor who can identify or exclude the presence of a dangerous disease. In this case, vigilance on the part of the patient is important, since the course of treatment of the pathology and rehabilitation depend on it.
A spot on an x-ray may appear:
- after the inflammatory process;
- due to bronchitis;
- for tuberculosis;
- if there are malignant formations;
- as a result of injury;
- when a foreign body enters;
- with fluid accumulation;
- due to prolonged smoking;
- for abscesses.
Among these causes of darkening of the lungs, there are those that are dangerous not only for the life of the sick person, but also for the society around him. In any case, if you find a darkening on fluorography, you need to undergo a more detailed examination to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Sometimes the following can act as a stain:
- enlarged lymph node;
- formation on the rib;
- dilatation of the esophagus;
- formation on the spine.
Decoding of received images
A few minutes after the fluorography office, a person receives a picture and its detailed transcript. Comments on the image may contain the following information in the form of medical terms, each of which characterizes certain health problems:
- Enlargement of the roots of the right or left lung, which may indicate bronchitis or pneumonia; Heavy roots are special pathological changes that occur due to smoking or acute bronchitis;
- The presence of an in-depth pattern of the vessels of the right or left lung indicates a violation of blood circulation in the respiratory organs, various problems with blood vessels and the heart, bronchitis, as well as inflammation in the lungs, which may be the initial stage of the oncological process;
- Fibrosis and fibrous tissue are a consequence of previous surgical interventions and injuries;
- Focal shadows, which are specific shadows. If such shadows are accompanied by an increase in the general vascular pattern, the doctor can judge pneumonia;
- Calcifications of the right or left lung - means that the person had contact with a patient with tuberculosis. At the same time, the healthy body of an uninfected person encloses the rod in a calcium shell. It is the power of immunity that prevents the spread of infection;
- Changes in the diaphragm - all this can be the consequences of problems such as obesity, pleurisy, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Spots and dark spots found in the image can be evidence of several dozen different diseases; it is for this reason that after the x-ray it is necessary to continue a high-quality medical examination of the right or left lung.
Methods for deciphering a fluorogram
After completing the diagnostic procedure, the patient is given a photograph and its description. Often, darkening in the lungs on fluorography is accompanied by some features. Let's pay attention to the most frequent comments and their meaning.
- If the roots enlarge, suspicions arise about the presence of bronchitis or inflammation;
- If a person smokes regularly or has bronchitis, stringy roots will be visible in the picture;
- Deep drawing of blood vessels indicates poor blood circulation in the lungs, the presence of heart pathologies and problems with the cardiovascular system. Also, such a picture may mean that the patient has bronchitis, pneumonia or the initial stage of cancer;
- Fibrous tissue may be the result of previous operations, illnesses or injuries;
- If a clear vascular pattern is visible in the darkened area, then it should be assumed that the patient has pneumonia;
- The presence of calcifications indicates that the patient had previously been in contact with a person sick with tuberculosis, but his body did not allow the infection to spread by forming calcium inclusions;
- Changes in the diaphragm can be diagnosed due to obesity or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- A sinus is detected if the pleural folds form fluid cavities of an adhesive nature.
A spot on a fluorography image may indicate the presence of various diseases and pathologies, so to make an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to undergo additional examination. For this, a pulmonologist (or oncologist) prescribes special procedures.
Follow-up examination
To conduct further examination, the doctor may send the patient to a pulmonologist or oncologist, where he will be shown to undergo certain specific procedures. Here are the most common ones:
- This may be a diaskintest, which can determine the presence of tuberculosis. If we compare this procedure with Mantoux, which quite often gives a false and inaccurate result, such an examination does not respond to BCG, which often shows a complete absence of a problem in the child. This is an ideal opportunity to diagnose tuberculosis as accurately as possible.
- The study of sputum of children and adults is another mandatory analysis that is carried out in the laboratory. Based on the results obtained, it is possible to detect tuberculosis bacilli, the presence of malignant cells, as well as various impurities that may be characteristic of certain pathological conditions.
- Quite often, doctors prescribe a more modern examination method - computed tomography of the lungs. This is an additional, informative method for diagnosing diseases of the lung tissue, pleura and mediastinum. It turned out that this is the most reliable method.
- Lung bronchoscopy or tracheobronchoscopy may also be used. This procedure is performed using medical endoscopes that are quite flexible in design and are inserted through the nose. Through this form of examination, you can see the lungs and also take material, completely painlessly. The collected material, as a rule, is subjected to subsequent diagnostics - bacterial, histological and cytological.
If a doctor suspects lung cancer based on an x-ray, a tumor marker test may be prescribed. The analysis makes it possible to detect specific proteins that are usually produced by emerging malignant tumors.
Is additional examination necessary if spots are detected?
Any darkening on fluorography requires additional information. If radiologists find a spot, the attending physician sends the patient for further examination, which includes the following measures:
- X-ray in two projections or computed tomography;
- general clinical, biochemical tests;
- Diaskintest (tuberculin test);
- culture of sputum.
If the presence of spots on fluorography indicates diseases of the mediastinum, heart or vascular anomalies, an ECG, echocardiography, MRI with contrast, a blood test for cholesterol and glucose, as well as consultation with a cardiologist will be required. If cancer is suspected, the patient will have to donate blood for tumor markers. These studies are often enough to make an accurate diagnosis and select treatment.