If the unexpected happens and the baby has to be born at this time, doctors assure that he has a chance to survive. Immediately after delivery, the baby will be placed in a machine that provides artificial respiration. The fact is that the fetus’s lungs at this stage are not fully formed, and accordingly, he will not be able to breathe on his own. The same can be said about the digestive organs. Even if doctors manage to save the child’s life, he will not avoid major health problems in the future. Therefore, the mother needs to be careful and prevent his premature birth.
Baby movements at 22 weeks
Every day the child becomes more and more active. As mentioned above, with the rapid development of the central nervous system and the improvement of the brain, the fetus can make controlled movements: roll over, somersault, kick, tap on the wall of the placenta. And all this is fully felt by the expectant mother.
The child's movements cause indescribable delight in the mother and father. This also becomes reassuring for them, because fetal movements indicate good health.
Is it necessary to do an ultrasound at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy?
An ultrasound scan at 20 weeks of pregnancy is mandatory for all pregnant women. If the gestation period is normal and there are no complications, this is the second planned ultrasound.
A woman can refuse the examination. However, she must be warned of all the consequences. Ultrasound at 20 weeks of pregnancy is one of the components of the second prenatal screening at 18-21 weeks. This is the most important examination during the entire period of gestation. By this stage of pregnancy, the baby is already fully formed. He has all the organs and systems, and they will only grow further. Therefore, this period is ideal for a detailed examination of all organs in order to identify developmental anomalies.
An ultrasound at 21 weeks of pregnancy is the deadline for screening. If chromosomal pathology and developmental anomalies are detected, if the woman wishes, pregnancy can be terminated up to 22 weeks. If you decide to prolong the pregnancy, an ultrasound scan at 22 weeks or later is acceptable.
Is the defect visible on ultrasound?
You can see the fetal heart at 10-11 weeks of pregnancy, but in order to evaluate its structure, it takes at least 20 weeks. With a qualified examination and modern equipment, heart defects are visible with high reliability, but associated rhythm disturbances, dystrophy or inflammation of the myocardium, and weakness of the heart muscle appear only after birth.
For pregnant women, ultrasound of the fetal heart is mandatory in the list of examinations; some categories may need an extended echocardiography with Dopplerography. In addition to the above risk factors, these include women with the following conditions:
- gestational diabetes mellitus (occurs only during pregnancy);
- atrioventricular block or other types of myocardial conduction disorders;
- taking ACE inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, retinoids, anticonvulsants, antitumor drugs;
- artificial insemination;
- multiple pregnancy;
- the thickness of the fetal collar zone is more than 3 mm on ultrasound in the 3rd month.
Ultrasound of the fetal heart, left ventricle, color mapping
When performing echocardiography, it is possible to identify the following deviations in the development of the heart: septal openings, changes in the location of large vessels, narrowing of the valve opening, vessels, non-closure, fusion or abnormal attachment of valve leaflets, underdevelopment of the ventricle, untimely closure of openings and ducts , as well as their combinations.
What is the purpose of ultrasound examination at 20 weeks?
Performing an ultrasound at 20-21-22 weeks of pregnancy can serve several purposes. Using ultrasound diagnostics, a doctor can determine:
- Malformations of organs and signs of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. This pathology may be detected for the first time, or it confirms changes detected during the first prenatal screening.
- Gender. The reproductive organs are already quite developed, and under favorable conditions, the doctor can easily determine the sex of the baby.
- The length of the cervix is used to diagnose isthmic-cervical insufficiency.
- Complications and features of pregnancy (oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios, single umbilical cord artery, etc.).
- Pathological formations of the uterus and appendages (uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, etc.).
How is an ultrasound examination performed at 20-22 weeks?
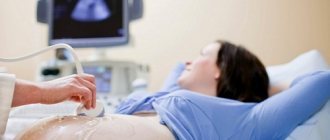
An ultrasound at the 20th week of pregnancy is performed in a transabdominal manner, in which the sensor is moved across the abdomen. To improve the passage of ultrasound through the anterior abdominal wall, a special gel is used. No preparation is required before the ultrasound. The 20th week is characterized by a rather large size of the uterus, pushing the intestinal loops to the side, and there is already a sufficient amount of amniotic fluid to improve the passage of ultrasound waves to the fetus.
If it is necessary to assess the condition of the cervix, the ultrasound procedure is performed transvaginally. The sensor, protected by a condom, is inserted into the vagina. There is no need to be afraid of this method, it is absolutely safe and cannot cause any discomfort in the baby, but this method is still undesirable.
How do they do it?
The procedure itself is simple for a woman and does not pose any danger.
There is no need to prepare specially for it - the amount of amniotic fluid is enough for the ultrasound signals to “reach” the baby.
To conduct the study, the woman must lie down on the couch. The doctor lubricates the patient’s stomach with a special gel and places a sensor on it.
Depending on which area to look at, he moves it. He can tell his mother what exactly he is examining and what condition this organ is in.
How is the development and condition of the fetus assessed at 20 weeks?
To assess the development of the baby, each fetal size obtained at the 20th week of pregnancy is compared with standard values. It is no longer each individual indicator that is assessed, but the values and relationships of all parameters to each other.
At 20 weeks of pregnancy, the fetal size used to determine the gestational age is the biparietal size of the fetal head. This indicator determines the pregnancy period with an accuracy of 5-10 days. The biparietal size of the fetus at 20 weeks is normally 43-53 mm.
Standard values for other fetal parameters are:
- fronto-occipital size of the fetal head – 56-68 mm;
- abdominal circumference – 124-164 mm;
- head circumference – 154-186 mm;
- thigh length –29-37 mm.
The weight of the fetus at week 20 is about 300-360 grams.
To assess the viability of the fetus, its heartbeat is assessed, which normally should be 120-160 beats per minute. In addition, fetal motor activity is recorded.
Fetometric and physiological changes in the baby
By the twenty-second week, the child’s reflex reactions of the nervous system improve. The baby actively responds to external stimulation (fright, touching the stomach, noise). The baby differentiates night and day, is able to express emotions using facial muscles (smile, frown). This can be seen especially well if the study is carried out in 3D format.
Brain cells acquire full value and stable functionality, and therefore the development of brain structures is inhibited. The total volume of the brain increases to one hundred grams. The ventricles of the brain should not be dilated (otherwise, this is a sign of hydrocephalus). The baby moves energetically, making flexion-extension movements not only with the limbs, but also with the body. At twenty-two weeks, the external genitalia are considered fully mature, which makes it possible to determine the sex of the baby.
The process of formation of the skeletal system of the body is entering its final stage. The discs between the vertebrae acquire motor functionality. In the case of spinal curvature, the pathology is clearly visualized on ultrasound. The heart increases in volume, the contraction frequency according to standards should be in the region of 140–160 beats/min. Under the influence of ultrasonic waves, a woman can hear a characteristic rhythmic gurgle - this is how the baby’s heart muscle works. At this stage of pregnancy, a probable congenital heart defect is diagnosed.
According to indications, it is possible to perform intrauterine surgery on the myocardium. With proper intervention, the child is born completely healthy. The child’s digestive organs, immune and excretory systems are fully functioning. If the medical history is unfavorable (the mother has polycystic disease), the doctor pays special attention to examining the kidneys. The baby's liver must be checked; the size of the organ must correspond to the standards indicated in the table:
Sharply increased digital values indicate severe Rh conflict between mother and fetus
Decoding the indicators of the baby’s anatomical development includes measuring the size of the child’s limbs, head and abdomen.
The main fetometric parameters (weight and height) increase to half a kilogram and 26–28 centimeters, respectively. The transverse size (bipariental or BPR) of the head is 5.1–5.4 cm. The longitudinal size (fronto-occipital or LZR) is 6.6–7.1 cm. The circumference of the skull (head) ranges from 16.4 to 20 cm. The size of the bones and the circumference of the child’s abdomen are subject to examination (the norm is presented in the table):
Measurements are taken directly on the monitor screen using a computer program
Carefully evaluates the size of the nasal bones. This indicator is one of the markers for determining downism in a baby. Disproportional development of body parts, combined with abnormal laboratory tests, indicate intrauterine growth retardation.
The correct size of the nose bone in millimeters, and permissible deviations up or down
What indicators help characterize the course of pregnancy?
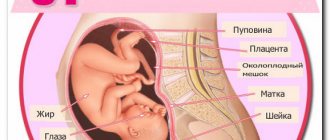
During an ultrasound examination at the 20th week of pregnancy, the condition and location of the placenta is described. The lower edge of the placenta should normally be higher than 6 cm above the edge of the internal os of the cervix. If its position is lower, they speak of low placentation, and if the edge of the placenta ends at the internal os or even overlaps it, this speaks of marginal/central placenta previa.
Placenta previa along with low placentation increases the risk of placental abruption, bleeding, miscarriage and premature birth. Therefore, these conditions require conservation therapy and follow-up.
The thickness of the placenta is measured. Exceeding its normal values may indicate an infection or Rh conflict.
Ultrasound examination describes the amount and transparency of amniotic fluid. Low water may be a sign of infection or placental insufficiency. The location of the umbilical cord and the number of vessels in it are determined (two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein). If necessary, Doppler ultrasound is performed to assess blood flow in these vessels.
The condition of the cervix is assessed. Normally, its length is 30 mm or more, the internal os of the cervical canal is closed. Shortening of the cervix, funnel-shaped dilation of the cervical canal, prolapse of the ovum indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency and the need for maintenance therapy in the hospital. When performing ultrasound diagnostics, the tone of the uterus can be recorded, uterine fibroids and ovarian formations can be detected.
Discharge from the genital tract
The nature of the discharge at this stage of pregnancy is light, moderate, with an unobtrusive sour odor. A change in the color of the discharge towards yellow or green indicates the addition of an infection, which must be treated - an untreated infection from the vagina can rise into the uterine cavity and infect the baby.
There should be no bloody discharge from the genital tract. If even minor spotting is detected, the help of a gynecologist is required.
The mucous membrane may bleed after sexual intercourse, especially if there is erosion. But it is only possible to accurately determine such a source when examining a woman using mirrors. If there are no injuries to the mucous membrane, the probable cause of bleeding may be placental abruption - bright discharge indicates a recent abruption, dark brown discharge indicates an old case.
Significant liquid discharge may indicate leakage of amniotic fluid. For diagnosis, special tests and ultrasound are performed.
What is the second prenatal screening?
The second prenatal screening is carried out at 18-21 weeks. It consists of:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- biochemical research.
Screening at 20-22 weeks includes a detailed examination of the brain, face, spine, heart, lungs, stomach, liver, kidneys, upper and lower extremities of the fetus. The most common malformations of the heart are currently occurring. To register them, a four-chamber section of the heart is used, on which 2 ventricles and 2 atria are visible at once. If there are risk factors, an Echo-CG is performed (a more detailed study of the heart). Tetralogy of Fallot, defects of the interventricular and interatrial septa are sufficiently detected. Other developmental anomalies may include spina bifida (spinal malformation), hydrocephalus, microcephaly, cysts in the lungs, esophageal atresia, hydronephrosis and polycystic kidney disease, among others.
During this period, the genitals are quite developed. This makes it possible to almost accurately determine the sex of the fetus, which is important when inheriting sex-linked diseases.
The thickness of the nuchal translucency as a marker of chromosomal pathology is not informative during the second screening. But the length of the nasal bone does not lose its significance. The thickness of prenasal tissues is of particular importance. An increase in the ratio of its size to the length of the nasal bone by more than 0.8 is a marker of chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus.
When conducting a biochemical study, the levels of alpha-fetoprotein and human chorionic gonadotropin, free estriol are determined. Deviations of their levels from normal values may indicate the existence of a chromosomal pathology. Thus, an increased alpha-fetoprotein value may indicate spina bifida, omphalocele, while a decreased value may indicate Down and Edwards syndrome. Decreased estriol levels and elevated human chorionic gonadotropin levels may also indicate the presence of Down syndrome.
Pregnancy and childbirth with suspected fetal heart disease
If the diagnosis of a congenital anomaly of heart development is confirmed, the pregnant woman requires examination:
- repeated ultrasound of the heart to monitor the dynamics of the defect;
- targeted ultrasound (expert-class device) for examining the brain and internal organs to exclude non-cardiac abnormalities;
- genetic consultation;
- study of amniotic fluid.
If multiple anomalies or defects are detected with an extremely high mortality rate (absence of the left ventricle, subaortic stenosis and myocardial damage), the mother may be offered termination of pregnancy. Childbirth with congenital abnormalities of the heart should be carried out in cardiological centers, where the late pregnant woman is under constant supervision.
After birth, the baby undergoes an ultrasound and is transferred to intensive care or cardiac surgery.
If emergency care is not required, the newborn is admitted to the pathology department or pediatric cardiology department for further examination. This is due to the fact that the symptoms of a congenital defect are not always obvious; they can be masked by diseases of the lungs, brain, and listening data (noises and clicks of valve opening) can also be found in minor anomalies of heart development.
In addition to repeated ultrasound, newborns are prescribed:
- ECG to detect arrhythmia, hypertrophy or overload of the heart;
- X-ray of the chest organs - detect congestion in the lungs, enlargement of the heart, cardiomegaly;
- ventriculography, aortography with contrasting of vessels and parts of the heart;
- sounding to measure pressure, the presence of pathological communications between the parts of the heart.
Who is indicated for a second screening?
If a pregnant woman has encountered factors that increase the risk of malformations and chromosomal abnormalities, she should definitely undergo a second screening. These factors are:
- woman's age over 35 years;
- presence of hereditary diseases in the family;
- congenital malformations and/or chromosomal abnormalities in previous pregnancies;
- the threat of miscarriage in the short term of this pregnancy;
- the presence of harmful environmental or occupational factors;
- bad habits;
- history of spontaneous miscarriages;
- a viral infection suffered in a short period of time;
- taking illegal drugs;
- conception in conditions of consanguineous relationships.
Nutrition
Since weight must be controlled responsibly, it is advisable to adhere to the developed diet, and still choose healthy and natural foods. For the full development of the small organism inside mommy, you will need protein - lean meat and fish, and dairy products are suitable sources. The same dairy and fermented milk products will be a suitable source of calcium. Fresh vegetables and fruits, dried fruits, kefir and yogurt will help improve intestinal motility and avoid problems with bowel movements, as well as the development of hemorrhoids.
It is advisable to limit your consumption of sugar and sweets, products made from white flour: rich in “fast” carbohydrates, they contribute to unwanted weight gain and increase glucose levels in the body, which can lead to the development of pregnancy diabetes. In turn, salt consumption must be significantly limited, since salt retains water in the body and leads to the development of edema.
Often the second trimester of pregnancy is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of iron in a woman’s body and the development of anemia against this background. To prevent iron deficiency anemia, buckwheat porridge, beef liver, dried fruits, and pomegranate are considered useful.
It also doesn’t hurt to agree with your doctor on the advisability, and sometimes even the necessity, of additional vitamin-mineral complexes for pregnant women. Which drug, in what dosage and for how long the expectant mother will need it is up to the doctor to decide after examining the results of regular tests.