Interpretation of urine analysis for cystitis
Cystitis is a disease of the urinary system, the main substrate of which is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. The disease is widespread, women are more often affected, this is due to the anatomical features of the urinary tract. The results of statistical studies show that in cystitis, inflammation is caused by opportunistic microflora, most often E. coli. The basis for the diagnosis of cystitis is the presence of specific complaints of painful, difficult urination. This is due to the involvement of the urethra (urethra) in the inflammatory process. To confirm the disease and differential diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a urine test. The normal indicators of this analysis allow us to exclude the diagnosis of cystitis. Deciphering a urine test allows you to determine the intensity of inflammation and correctly prescribe treatment.
What is cystitis
Before describing laboratory diagnostic methods, it is necessary to understand what the disease is. Cystitis is an inflammation that affects the walls of the bladder itself and the urinary tract. It can be acute or chronic.
The pathology is often diagnosed in children and women, which can easily be explained by the special structure of the female urogenital tract, and girls and boys are vulnerable due to their fragile immune system. Men suffer from cystitis much less often.
If you suspect inflammation of the bladder, you need to get tested. Making a diagnosis is a matter for a specialist, since cystitis is easily confused with other diseases.
The main causes of inflammation of the main organ of the genitourinary system:
- hypothermia;
- gynecological problems (in women);
- urological diseases, including damage to the bladder.
Indications for diagnostic purposes
Cystitis has severe symptoms, so recognizing it is not difficult. But before making a diagnosis, the doctor must study the test results and only then select a treatment regimen. Manifestations of the disease are as follows:
- pain in the bladder area;
- pain during or after urination;
- feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- constant desire to go to the toilet;
- bleeding when urinating;
- temperature increase.
Bleeding is especially dangerous because it can block the bladder. Congealed blood will accumulate in the urethra, which will cause stagnation of urine and stretching of the bladder. If bacteria enter the bloodstream, infection will begin and the kidneys will be damaged.
What the analysis will show
In some cases, treatment can be prescribed without this study, but in most cases, after receiving the results, therapy is adjusted. Having studied the physical and chemical indicators, the doctor will be able to assess the functionality of the organs of the urinary system and kidneys, and find out what changes have occurred in the body. By doing urine culture, you can identify the causative agent of the disease and determine which drug will help destroy it.
By doing urine culture, you can identify the causative agent of the disease and determine which drug will help destroy it.
The analysis considers the following characteristics:
- Color. Typically, urine is yellow in color, the saturation of which depends on many indicators, including food. Typically, biological fluid is transparent and without any impurities. In a patient with cystitis, the urine becomes cloudy, acquires an unpleasant odor, and flakes may appear.
- Leukocytes. In a healthy person, a small number of leukocytes are present in the urine; during inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system, this figure increases sharply, which is what the analysis reveals.
- Hemoglobin. This blood component indicates the presence of bloody discharge in the test fluid, which may not be visually detectable.
- Red blood cells. There are standards that help determine the presence of inflammation. In a healthy person, about two million red blood cells are excreted in the urine during the day. Deviation from the norm indicates a problem in the body.
- Protein. In a healthy woman, this organic substance is not detected in the urine; if there are any traces, they are very insignificant. When the bladder is inflamed, the protein is easily detected.
- Glucose. A healthy person who does not have diabetes does not have it in their urine. With cystitis, sugar appears, this may also indicate poor kidney function.
- Acidity. In most healthy people, the reaction is slightly acidic, although the indicator is very dependent on external factors (age, food, physical activity). The disease changes this indicator.
- Density and specific gravity. These parameters help determine the kidneys' ability to dilute and concentrate urine. To determine these indicators, an appropriate test is done.
- Ketone bodies. The norm for a healthy person is 20–30 mg of this substance; deviations from the norm are an indicator of inflammation in the body.
- Urobilinogen. During inflammatory processes, the level of this component in the urine increases.
- Bilirubin. Usually this component is absent in the urine of a healthy person, but some inflammatory processes, including cystitis, lead to its appearance in this biological fluid.
Decoding the results
Only an experienced doctor can decipher the received data; you should not do this yourself.
What urine indicators are taken into account, and what signs indicate cystitis?
A patient with cystitis has the following deviations in the results of OAM.
- Leukocytes. When examining the urine of a healthy man, there should be no more than three leukocytes in the field of view, in women and children - a maximum of 7. If more cells are detected, then an exacerbation begins. The higher the value, the more severe the pathology.
- Red blood cells. No more than two units are allowed to be detected in the field of view. Exceeding this value indicates that the vessels of the bladder are affected.
- Epithelial cells. Their normal number is about 20, they appear because the mucosal cells die.
- Protein – up to 0.033 g/l or absent. Everything above indicates kidney dysfunction and intoxication.
- Cylinders. Absent in the urine of a healthy person. The detection of hyaline, granular or waxy casts may be a sign of infection in the kidneys, amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis, diabetic nephropathy and a number of other renal pathologies.
Blood test indicators
You should not decipher the results of a blood test yourself; this should be done by a specialist. Based on the data received, he will draw up a conclusion and prescribe medicine.
With cystitis, a blood test will show an increased number of white blood cells, but the number of red blood cells will remain the same. A decrease in leukocytes is characteristic of hematuria. Severe inflammation is the cause of a significant increase in ESR.
Sometimes cystitis manifests itself clinically, but the test result remains good. As a rule, this is possible with a chronic course of the disease. Advanced inflammation is difficult to treat and will require antibiotics.
What Contributes to Distortion of Results
False data during the decryption process is not uncommon. This happens if the patient did not properly prepare for the study and collected biomaterial without following the doctor’s recommendations.
It is very important to follow simple rules:
- collect material in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- stick to a diet;
- do not overexert yourself;
- do not smoke or drink alcohol;
- notify the doctor about taking medications;
- postpone the procedure if an x-ray was taken the day before.
Urine analysis for cystitis, interpretation of indicators
Urinalysis is one of the most accessible ways to quickly diagnose cystitis. There are a number of criteria by which therapists and urologists make this diagnosis, based only on this method.
A correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment and prescribing the right medications: https://cystis.ru/cistit-lechenie-preparaty.html
This is of particular importance for children and pregnant women.
The urine of a healthy patient ranges from light yellow to straw color. With cystitis, a little blood is released from the injured and loose mucosa. It gives a reddish or reddish hue to urine (depending on the amount).
Urine becomes cloudy due to inflammation. This occurs due to the ingress of a large number of microbes, epithelium and inflammatory cells - leukocytes. Also, urine becomes cloudy if hygienic care is not observed. A healthy person's urine is clear.
Due to inflammation and bacterial metabolic products, the amount of protein and other impurities in the urine increases. They lead to an upward shift in acidity. Simply put, the reaction becomes alkaline.
Normally, the number of cells that can get from the bloodstream into the kidneys, and then into the lumen of the bladder, in women does not exceed 6 cells per field of view, and in men - no more than 3-4. These are protective cells that attack microorganisms, capture them and digest them. Therefore, an increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine indicates an inflammatory process in the urinary tract. In severe cases, there are so many white blood cells that pus can be seen in the urine. This phenomenon is called pyuria. For pus to appear, the bladder must be severely inflamed and the patient’s condition must be severe.
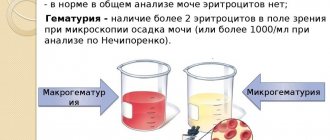
As already mentioned, at the end of urination, drops of blood may enter the urine. Therefore, the presence of red blood cells in the urine indicates damage to the mucous membrane and inflammation. We can talk about microhematuria (the so-called admixture of blood in fresh urine) when the number of red blood cells exceeds 2. Up to two cells in the field of view is normal.
Squamous epithelium lines the path through which urine moves out. During inflammation, some of the cells exfoliate and end up in the urine. The normal number of such cells in the analysis in women should not be more than 5–6 cells, and in men – 3.
Depending on the diagnostic ability of the laboratory and its equipment, the protein standard is set from absent to the presence of traces of protein. With cystitis, the protein level increases, but slightly, to 1 g/l. A higher level of protein will already indicate problems in the kidneys, and not in the bladder.
The presence of microorganisms in the urine clearly indicates cystitis. Normally, urine does not contain bacteria. Bacteriuria can be massive or non-massive depending on their number.
Normally, urine does not contain mucus. It appears when epithelial cells are rejected due to inflammation.
Do not change with cystitis:
- Specific gravity. The changes depend on the ability of the kidneys to concentrate urine.
- The presence of glucose, bilirubin, ketone bodies, urobilinogen in the urine. These substances appear in other diseases.
- Salt. Their appearance indicates metabolic disorders, including the likelihood of kidney stones.
- Cylinders. They enter the analysis when the epithelium located in the renal pelvis and ureters is destroyed. Increases in diseases of these organs.
Urine according to Nechiporenko
This research method involves counting the number of cells in 1 milliliter of water. To conduct the study, an average portion of urine is collected. In a healthy person, the number of leukocytes does not exceed 2000.
With cystitis, an increase in this indicator is observed. In this case, leukocyturia is diagnosed. In 1 milliliter of urine in a healthy person, up to a thousand red blood cells are observed. An increase in their number is diagnosed with cystitis.
Cystitis is a fairly serious inflammatory process that requires timely treatment. To develop the most convenient scheme, it is necessary to take a urine test, as well as conduct additional research methods.
The effect of cystitis on the composition of urine
In order to establish the presence of cystitis itself, it is enough to first conduct a general examination of the patient’s urine. Even a visual inspection of it can show the presence of qualitative changes. For example, urine with this disease acquires the following characteristics:
- turbidity appears;
- the color changes, acquiring reddish shades of varying degrees of intensity depending on the amount of blood in the urine;
- traces of pus are observed (in severe conditions and severely advanced inflammation);
- mucus may appear (due to rejection as a result of inflammation of epithelial cells).
Further, during laboratory research, quantitative and structural changes are detected. The urine of a patient suffering from cystitis has the following characteristics:
- the content of leukocytes increases - a sure sign of the presence of inflammation;
- the number of red blood cells increases (more than two in the field of view);
- the acid-base balance changes;
- there is an increase in protein content (slightly);
- epithelial cells appear as a result of their detachment;
- microorganisms that cause inflammation in the bladder are detected.
Depending on what the urine test shows, the patient is diagnosed in accordance with the classification of the disease and treatment is prescribed.
Much depends on the quantitative expression of each change. For example, protein in the urine with cystitis increases, but not much. A higher content indicates the presence of another disease, for example, pyelonephritis. How I cured CYSTITIS! A true story from Galina Savina. My story Question and answer Video savina.ru
In general, the urine of a healthy person has a certain proportion of the elements it contains. The results of tests for cystitis in women or men should show compliance or violation of this proportion. For example, the Nechiporenko urine analysis mentioned above reveals the ratio of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders. The normal composition is characterized by the following indicators of cells per milliliter (Table 1).
Table 1 - Normal indicators of urine analysis according to Nechiporenko (U/ml)
Deviation from this norm indicates an inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system. Various quantitative indicators can indicate not only cystitis, but also other diseases, for example, prostate adenoma, urolithiasis, etc.
A general blood test for cystitis is carried out to identify other diseases in the body. If the patient does not have any diseases other than cystitis, then the blood test will be almost within normal limits. Minor deviations will indicate the occurrence of inflammation in the body, but nothing more.
Laboratory research
With cystitis, three main ways give a more complete picture:
- general urinalysis (UCA);
- special analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- testing urine for the presence of bacteria.
Before finding out the role of each method in determining the disease, it is curious to know what characteristics are inherent in a healthy person.
Normal indicators
A general examination of urine shows the condition of the mucous membrane of the bladder, whether pathogenic microorganisms are present, the level of red blood cells, white blood cells and protein.
The urine of a person who does not suffer from disease corresponds to the following indicators:
- color - straw or yellow;
- transparency - complete or slightly cloudy;
- density - up to 1.030 g/l;
- acidic environment - up to 7 pH;
- protein - up to 0.033 g/l;
- hemoglobin - not detected;
- leukocytes - 5–6 cells per field of view;
- nitrates - absent;
- ketone bodies - up to 20 mg;
- glucose - not detected;
- bilirubin - absent;
- urobilin - 17 µmol/l;
- red blood cells - in minimal quantities (0–1);
- epithelial cells - up to 6 per field of view;
- cylinders - absent or single inclusions.
When you have cystitis, these indicators look different, since the entry of harmful microbes into the body disrupts the normal functioning of the genitourinary system and causes inflammation.
General analysis of urine for cystitis
Since the disease is caused by inflammatory processes in the walls of the bladder, the presence of bacteria and an increased level of leukocytes and red blood cells are typical. The number of the latter may indicate that the mucous membrane of the canal or bladder is damaged. The content of red blood cells also indicates that there are bleeding wounds.
The number of leukocytes in the urine with cystitis increases 10 times. The growth is due to the fact that the bladder mucosa is trying to turn on local protection in this way.
The presence of a large number of leukocytes makes the urine cloudy and opaque. This is also facilitated by the presence of bacteria and their metabolic products, an admixture of flakes and blood, epithelial cells, mucus and pus.
Due to the proliferation of microbes, the urine reaction changes and becomes acidic, while for a healthy person the norm is a slightly alkaline urine reaction. The activity of pathogenic microorganisms also provokes a slight increase in protein.
Pathology markers
The information contained in the results of a urine test during the development of cystitis is easy to read by specialists, but is not entirely clear to the average person. Although each characteristic is significant and serves as a marker in determining the stage of the disease. Therefore, knowing the decoding, or what each digital value means, will be useful.
So, for a person suffering from cystitis, the following indicators are characteristic:
- Leukocytes. Their number in urine reaches up to 60 in the field of view. If an acute form develops, then this value can be 70-80. Thus, the higher this indicator for cystitis, the more advanced the disease.
- Red blood cells. Their number in the urine of a sick person is up to 20-30 in the field of view. This indicates that the vessels in the bladder are damaged.
- Epithelial cells. They are found in numbers up to 20. This is caused by the death of cells in the mucous membrane of the urinary system.
- Protein. Indicators increase to 3 g/l. In this case, we are talking about a malfunction of the kidneys and the process of intoxication of the body.
- Cylinders. Their content in urine reaches 20 per 1 ml. This may well indicate that the infection has penetrated the kidneys.
Treatment of cystitis, which is caused by the development of pathogenic microflora, is carried out with the help of antibiotics. However, bacterial species respond differently to drugs. To find out which will be effective, you need to donate urine to a culture tank.
Bacteriological research
This method helps to determine the causative agent of the disease, the nature of the pathogenic microbes that provoked cystitis and their number in the body. The main thing is that the analysis reveals the sensitivity of harmful bacteria to medications. To do this, the collected biomaterial is placed in special containers, where a nutrient medium is created for infections, viruses and fungi.
Please note: urine must be examined using the tank culture method no later than 2 hours after collecting the material. The quality of diagnosis depends on the timeliness of the analysis.
By the way, the method is actively used during pregnancy by women, since it allows one to determine the types of bacteria and their reaction to drugs, and most importantly, to preserve the health of the unborn baby.
Pathogenic microbes that can be identified using tank culture include:
- streptococcus;
- enterococcus;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- salmonella;
- E. coli infection;
- Klebsiella microbes;
- gonococci.
In the case of cystitis, most often the results show the presence of E. coli, staphylococcus, Trichomonas, and less often - viral and fungal infections.
After you submit the biomaterial for research and the result is obtained, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial therapy.
Nechiporenko method
If a general analysis of urine shows that there are deviations from the norm, and the doctor needs to clarify the nature of the pathology, another study is prescribed.
Nechiporenko's method, from a diagnostic standpoint, is more accurate and helps to identify not only cystitis, but also other diseases of the urinary system, for example, kidney pathology.
The essence comes down to this: the urine is mixed, part of it is placed in a separate test tube, which is spun using a centrifuge for 3 minutes. The resulting sediment becomes the subject of study. In a special counting chamber, the amount of biological elements in urine is counted under a microscope. The resulting number is multiplied by a coefficient to determine the average volume of substances in one milliliter.
In a healthy person, the normal indicators when examining urine according to Nechiporenko are as follows:
- red blood cells - up to 1000/1 ml.;
- cylinders - up to 20 units/1 ml;
- leukocytes - up to 2000/1 ml.;
- protein - absent;
- bacteria - absent;
- epithelial cells - in the minimum permissible quantity.
Doctors often prescribe such an analysis to women expecting a child. The method allows you to identify individual pathologies that may threaten the normal course of pregnancy.
The Nechiporenko study does not replace a standard urine test, but only serves as a supplement to it.
Bakposev
During the procedure, research material is sown on nutrient media. This allows you to detect the presence of bacteria and fungi in the urine. Microorganisms, entering the nutrient medium, begin to multiply sharply, their number increases to colonies. The laboratory checks the species of pathogens and their sensitivity to antibiotics. It takes at least a week to obtain the results of bacterial culture. Only after this is treatment prescribed. If the disease is caused by pathogens that are resistant to antibacterial drugs, an alternative therapy is selected that overcomes the bacteria’s resistance to drugs. Several antibiotics with different mechanisms of action are prescribed, and antimicrobial solutions are installed into the bladder cavity.
Additional Research
If the bladder disease has become chronic, standard examinations may be ineffective. The problem could have been provoked;
- urinary pathologies – polyps, tumors;
- inflammation of the kidneys, urethra;
- pregnancy;
- diabetes.
The attending physician will propose an examination plan that will help exclude or identify these or other causes of chronic inflammation.
It is important to diagnose the disease as soon as possible, otherwise its advanced form will lead to kidney failure or bladder dysfunction.
General urine analysis
Urine analysis for cystitis is the main study, and therefore collection rules must be followed to avoid false results. With cystitis, certain indicators change in a general urinalysis. Let's sort them out.
Physical properties of urine
The urine reaction changes, it becomes acidic in the case of an acute course of the disease, and in a chronic course it acquires an alkaline reaction and a pungent odor. The presence of an acidic reaction may indicate damage to the bladder by E. coli or Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and an alkaline reaction indicates infection with other bacteria.
Urine loses its transparency and becomes cloudy due to the appearance of exudate in it.
The color may remain unchanged, however, if cystitis is accompanied by bleeding, the color may become darker and more saturated.
Sediment. In acute purulent cystitis it becomes purulent or bloody-purulent. In the case of chronic cystitis, the sediment becomes viscous, mucopurulent.
Other physical indicators, such as the amount of urine and relative density, remain within normal limits.
Chemical properties of urine
Protein in urine. False proteinuria is observed due to discharged exudate. Let us explain the term “false proteinuria”. With false proteinuria, the renal filter functions normally and does not allow protein to pass from the blood. The presence of protein in false proteinuria is always associated with inflammatory diseases, because pus and blood contain protein. The amount of protein in the urine depends on the course of the disease, the type of inflammation and the amount of blood discharged. Purulent inflammation is indicated by a significant increase in protein content, because purulent exudate is more saturated with protein than catarrhal exudate.
Glucose and bile pigments in any cystitis will correspond to the norm (absent), unless, along with cystitis, the patient has diabetes or hepatitis.
Urine microscopy
The degree and nature of pathological changes in the bladder affects the microscopic picture of urine sediment.
Acute cystitis. Leukocytes can be located in a continuous layer over the entire field of view if the inflammation has completely covered the surface of the bladder. It is not possible to examine other formed elements of urinary sediment due to the fact that exfoliated epithelial cells are covered with pus and therefore become indistinguishable. If individual areas of the bladder are inflamed, then the microscopic specimen may contain transitional epithelium in varying quantities. Sometimes the surface epithelium can be seen lying in layers. In this case, the number of white blood cells, as well as red blood cells, may change.
Chronic cystitis. This form of the disease is characterized by a different content of leukocytes, because Due to the pronounced alkaline reaction of urine, swelling and then lysis (destruction) of cells occurs. This feature dictates the need for rapid analysis, because only in this case is it possible to find out the true content of leukocytes and, accordingly, draw a conclusion about the course of the inflammatory process. During microscopic examination, the sediment reveals a lot of mucus, preserved leukocytes, a small number of unchanged red blood cells and epithelial cells, occurring only once in the field of view. Salts of such urine are represented by amorphous phosphate salts, as well as tripelphosphates.
If there is a smell of feces in sour urine, then you can suspect that the culprit of cystitis is E. Coli. To ensure that your suspicions are correct, you need to stain the sediment using a Gram stain. If gram-negative bacteria are detected in the form of rods, a preliminary conclusion can be drawn in favor of this type of pathogen.
If bacterioscopic examination of purulent urine sediment fails to detect bacteria, then one can suspect that the inflammation is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In order for suspicions to be justified, the preparation should be stained according to Ziehl-Neelsen.
Calculous cystitis should be especially noted among the rich variety of cystitis. This condition occurs when sand and stones pass through the ureters into the bladder and form stones in the bladder itself. Irritation and injury to the mucous membrane of the bladder occurs and, as a result, cellular elements characteristic of cystitis (epithelial cells, leukocytes, erythrocytes) appear in the urine.
Rules for preparing for analysis
To get the right result, you must follow a number of recommendations. The rules for collecting urine are as follows:
— for general analysis, average morning urine is required;
- the day before, you should avoid those foods that can stain urine (bright fruits, beets, berries), as well as sour drinks and dishes;
— laxatives and diuretics must be discussed with the attending physician before the analysis;
- It is not advisable to take a test during menstruation;
- Before collecting the material, you need to wash yourself.
It is very important to follow these tips, since in this case the analysis will be truly informative and will allow you to establish the severity of the pathology and choose the right treatment.
We looked at what urine test to take for cystitis.
source
How to prepare for research
For cystitis, a urine test must be taken according to certain rules, otherwise the main indicators will be distorted. The most important thing is that for a correct study you only need fresh morning urine. What not to do before collecting urine for analysis:
- consume foods and drinks that contain pigments and can color the urine;
- eat or drink acidic foods and drinks at night, including kefir and cottage cheese - they can affect the acidity level of urine;
- stop taking laxatives and diuretics 1-2 days before - in this case, the concentration of various elements in the urine may be underestimated and unreliable;
- drinking alcohol.
Collect urine only in a sterile container with a lid. You can purchase a special container at the pharmacy or prepare a jar yourself.
To do this, wash it with soda, then rinse well with hot and cold water, and rinse with boiling water. Before a urine test is collected to diagnose cystitis, the jar is kept tightly closed.
Women should cover the vaginal opening with a cotton swab to prevent bacteria and mucus from the genitals from entering the urine.
Very important: girls and women do not take a urine test during their periods! First you need to wait for the complete completion of menstruation. The first streams of urine go down the toilet, then you need to urinate strictly into a jar - you cannot pour urine into it from another container
For a full study, 50 ml of biological raw materials will be enough
The first streams of urine go down into the toilet, then you need to urinate strictly into a jar - you cannot pour urine into it from another container. For a full-fledged study, 50 ml of biological raw materials will be enough.
The collected urine must be transported to the laboratory no later than two to three hours after collection. If this fails, the procedure is repeated the next day in the morning.
How to properly collect urine
To accurately determine the pathology, the very first morning discharge is needed. Collect them in a dry, sterile container with a volume of 15-20 ml, these are sold in pharmacies and are issued free of charge in some private laboratories. Or you can use your own container, but then it must be glass and you will have to boil it well.
The most suitable urine for examination is urine that does not contain bacteria from the external genitalia. To do this, you need to place a glass to collect liquid not immediately, but a few seconds after the start of urination. And clean it up before it ends, that is, get an average volume of urine. It must be delivered to the laboratory within 1-2 hours after collection.
Tests for bladder inflammation
If a woman has cystitis, the doctor will prescribe tests. Each of them has certain rules for collecting material and preparing for research. What tests are taken for cystitis? Let's look at each in more detail:
General blood analysis. Allows the doctor to determine the presence of an inflammatory process. The main indicators that provide the doctor with information in this case are erythrocyte sedimentation rate and leukocytes. Blood is donated on an empty stomach to prevent the appearance of sediment in the blood. A blood test will give the doctor a general picture of the state of the body, but it is impossible to make a diagnosis using this analysis alone; urine tests will be more informative.
General urine analysis. Shows the presence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Thus, with elevated levels of red blood cells and white blood cells, inflammation of the urinary tract, urinary tract, as well as a disturbance in the functioning of the kidneys can be suspected, which is confirmed by the presence of protein in the urine. There should be no bacteria in the urine; their presence indicates some kind of urinary tract infection. With cystitis, the urine will be cloudy due to the large number of leukocytes, red blood cells, epithelium, and bacteria in it. The urine reaction is alkaline due to the fermentation process in the bladder. For a general urine test, the first morning portion is required.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. Allows you to determine the condition of the kidneys; it is prescribed when a certain pathology is detected in a general urine test. In this study, the average portion of morning urine is collected, that is, the first part is released into the toilet, then the analysis is collected and urination is completed again into the toilet. According to Nechiporenko’s analysis, the cellular component looks like: leukocytes, erythrocytes and cylinders. An increase in any indicator indicates the presence of kidney or urinary tract pathology. If the indicators of this study are normal, then the results of a general urine test should be considered unreliable due to sampling inaccuracies.
Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky. It is a collection of daily urine at certain hours of time. The first portion of urine should be emptied into the toilet. Next, we collect all the urine in a container, after three hours we change the container to another and so on, changing the container every three hours. There should be a total of eight containers of urine. At the same time, throughout the day you should record the amount of liquid consumed, including soups and juicy fruits. In this study, indicators of the volume released, density and specific gravity are looked at. This study allows you to evaluate kidney function.
PCR diagnostics. To detect infectious diseases. The PCR method can be used to examine blood, urine, and smears. The advantages of this study include the speed of the study and the high accuracy of the result. Using this reaction, the causative agent of the disease can be determined.
Bacteriological culture of urine
Detection of opportunistic microflora is a long process, but this study gives accurate results, which is important for selecting treatment. The analysis helps identify microorganisms, the type of bacteria and determine which antibiotic they respond to
In this study, the biomaterial is placed in different environments favorable for the development of microorganisms. If the growth of bacteria in the medium has not begun, then the result is negative; if changes have occurred in any of the media, then the analysis is positive. This study is prescribed in the presence of urinary tract infections.
Analysis of vaginal microflora for dysbacteriosis. Allows you to determine the state of the microflora and determine whether it is possible to introduce this microflora into the bladder. According to the results of this study, it is possible to comprehensively treat cystitis and inflammation of the genital organs, which will avoid relapses later.
Express testing methods for cystitis in women. These methods allow you to quickly diagnose cystitis based on certain indicators. For example, a quick determination of the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and the presence of protein in urine - these indicators are enough for a doctor to determine the presence of urinary tract disease and inflammation of the urinary tract. If there are pathogenic microorganisms in the body, then nitrates detected by the express method will tell about this. These methods allow you to quickly prescribe treatment, but you cannot rely only on these indicators for further treatment, since the condition of the kidneys should be checked.
Tests in adults
The doctor must determine what type of tests to take. Usually the first step is to undergo a general urine test. Even a simple examination of the fluid when performing such a study will help detect the presence of pathology:
- urine becomes cloudy
- it takes on a bloody hue,
- it sometimes contains traces of mucus and pus,
- a strong unpleasant odor also appears.
After a visual examination of urine, studies are carried out to identify quantitative and structural changes in its composition.
Certain proportions of elements contained in urine indicate the state of the body. For example, the normal level of leukocytes in women is 4,000 units/ml, and in men - 2,000 units/ml. The norm of red blood cells in all adults is 1,000 units/ml. The cylinder rate is 20 units/ml.
An elevated level of any indicator indicates inflammation.
Which doctor should I contact for cystitis?
If the first symptoms of cystitis occur, you should seek the advice of a specialist to undergo timely diagnosis and prescribe therapy. A therapist, gynecologist, urologist, or nephrologist can determine the necessary list of tests.
Typically, patients turn to a therapist for help, who prescribes a primary diagnosis and, if necessary, refers patients for consultation to specialized doctors.
The child is examined by a local pediatrician and a pediatric nephrologist. Early seeking medical help prevents the transition of the acute form of cystitis to the chronic course of the disease.
Share this post
▲ error: Who's here?
What tests need to be taken to accurately diagnose cystitis?
Cystitis is an inflammatory disease of the bladder.
The disease is more common in women due to the anatomical features of the urogenital tract and in children due to the imperfection of the immune system. Timely diagnosis of the disease prevents the upward spread of infection, kidney damage and the development of complications. Tests for cystitis are prescribed when the first symptoms of the disease appear and to prevent relapse of the disease. Instrumental examination methods are carried out to confirm the diagnosis.
Additional tests
If you don’t know what urine test to take for cystitis, then no one can tell you better than a specialized specialist. The maximum that a therapist can do is give a referral to a laboratory for a general analysis. All other areas are handled by a nephrologist or urologist.
A general analysis is always repeated upon admission to the department and when contacting a specialist. As for a general blood test, this is not required. But doctors often repeat it to make sure the results are correct and to see if there is an increase in the studied substances in the blood. But there is no guarantee that it will show exactly inflammation in the urinary tract. Such a study will show the general picture and general inflammation, but there is no location of the bacteria.
In addition to taking tests, you must undergo an examination by a gynecologist.
What other tests are taken for cystitis in women? First, an examination by a gynecologist is necessary. To exclude:
- gynecological prerequisites;
- development of inflammation in neighboring organs;
- take a swab to check for fungi.
The latter can reveal the truth about the appearance of sediment in the urine.
To determine red blood cells and white blood cells in urine, a Nichiporenko test is often prescribed. Over the course of one day, all the liquid is collected in several doses. The same time gap is taken into account. Not only urine is examined, but also its sediment. This method is an excellent indicator of complications and the development of the inflammatory process, which in turn can rise from the urethral canal to the kidneys in a matter of days.
What tests should a woman undergo if she has cystitis, if the tests do not show any abnormalities in biochemical parameters, and the symptoms are pronounced? In such cases, a thorough examination is carried out. In addition to a gynecological examination, the woman is sent to undergo cystoscopy. Ultrasound examination is mandatory. In this case, the entire abdominal cavity is examined. The kidneys undergo a more thorough examination. As for urine, the best modern method is called polymerase chain reaction or PCR. With the help of such tests, there is a chance to view the condition of the entire body and diseases that occur in a latent form.
The PRC is based on the search and study of the genetic code of the bacterium or pathogen that causes progression. Blood, serum, urine, and smears are suitable as research material. The only disadvantage of this method is the duration of execution. You will have to wait several days to receive an answer, but the results are 95-97% accurate.
314
We recommend that you read
Urine and blood tests Read more » What do casts in urine mean? 2,790
Urine and blood tests Read more » Oxalate salts in urine: what does it mean? 842 5
Categories
- Inflammation of the kidneys Nephroptosis
- Pyelonephritis
- Urine and blood tests
Recent Entries
- Is it possible to donate urine during menstruation for tests and how to do it correctly
- Diet for kidney inflammation - what you can and cannot eat
- Diet for renal colic - what you can and cannot eat
- Computed tomography of the kidneys using a contrast agent. Features and nuances
- Diet for urolithiasis in women and men
How to properly collect urine?
The result of the study, and, consequently, the prescribed treatment, depends on the correct collection of biological material. When collecting urine, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Urine collection is carried out after washing to prevent dirt from getting into the urine.
- You should wash from front to back.
- It is recommended to collect the morning portion of urine, but the first part must be released, and then what remains is collected in a container.
- If a woman is on her menstrual period, then before collecting tests, a tampon must be inserted into the vagina; this is also necessary if there are gynecological infections.
Smell of urine with cystitis
In addition to other unpleasant symptoms, it is worth paying attention to changes in the smell of urine discharge during cystitis. So what is the characteristic smell of urine in women with cystitis, symptoms and treatment? Due to the proliferation of microorganisms that provoke inflammation, as well as due to the high number of leukocytes, the smell becomes unpleasant and pungent
The patient often discovers such changes herself and consults a doctor. Any pathological signs uncharacteristic of a healthy state should be a reason to contact a specialist. Even if similar symptoms were observed before and effective treatment was prescribed, it is not a fact that if the symptoms recur, the result will be the same. Therapy is selected individually depending on the data obtained from urine analysis.
A change in odor is also observed during treatment - some antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs can affect this parameter. In this case, do not worry - the appearance of an unusual smell indicates that the medications are having their effect.
Tests in children
Cystitis affects not only adults and the elderly, but also children. That is why parents should be attentive to any deviations from the norm. For example, the smell of urine, which is often present with cystitis, should alert you. In this case, you need to go to the clinic and get a urine test as soon as possible. If treatment is not started on time, interstitial (chronic) cystitis will occur.
If the presence of inflammation in the urinary system is suspected, children are prescribed a general urine test. When assessing a sample, doctors pay attention to its color, density, quantity, urine pH reaction, the presence of protein, and acetone in it.
Conducting urine tests for cystitis in a child has its own characteristics. Children have their own standards.
Indicators of urine analysis in children are divided into 2 groups: organic and inorganic sediment.
Red blood cells in a child’s urine are easy to see even without a microscope - the urine will be pink. The presence of red blood cells indicates the development of pyelonephritis. In a healthy state, the number of red blood cells should not be higher than 2 in one field of view of the microscope.
In boys, the number of leukocytes in the normal state is 0.4, and in girls - 0.6 in the field of view.
Collecting urine from children is accompanied by certain difficulties: the inability to predict the time of the child’s next urination, the inability to persuade him to urinate in a certain container.
What research will be needed?
If, based on external symptoms and patient complaints, the doctor suspects cystitis, he will give directions for a general blood test, ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, and may require consultations with other specialists.
But first of all, the results of urine tests for cystitis will be assessed. Here are the ones you will need:
- General clinical. Based on the results of a general urine analysis, it is possible to determine whether the patient has inflammation in the body or not. With cystitis, as a rule, indicators such as leukocytes, red blood cells and proteins are increased, and epithelial cells are detected.
- According to Nechiporenko. If a general urinalysis (UCA) showed a very high content of leukocytes, then you will need to collect all the urine throughout the day in separate portions and examine it, then examine the middle portion.
- Bacteriological or bacterial culture. This urine test is necessary to determine what type of pathogenic microflora caused cystitis. The analysis also shows the sensitivity of bacteria to certain groups of antibacterial drugs, which allows you to correctly draw up a treatment regimen by choosing the right antibiotic.
Rapid strip tests are sometimes used to detect high levels of white blood cells and nitrites, but their use is not necessary if a general analysis has been performed.
What indicators are taken into account?
Urine with cystitis has a number of characteristics indicating a developing pathology. The inflammatory process is caused by opportunistic microflora (Escherichia coli, Candida fungi, etc.). The need for differential diagnosis arises when the patient complains of pain in the lower abdomen, a burning sensation and difficulty urinating. If a urine test with cystitis is normal, then this excludes the diagnosis of cystitis - in this scenario, specialists prescribe additional tests to determine the cause of poor health.
When deciphering the analysis, the following indicators are taken into account:
- color (light or dark);
- transparency (with or without impurities);
- smell (barely perceptible sourish or sharp putrefactive);
- foaminess (formed with an increased level of protein compounds);
- presence of red blood cells;
- leukocyte level;
- presence of protein;
- acidity;
- specific gravity and density;
- the number of ketone bodies;
- presence of bilirubin;
- the presence of foreign microorganisms;
- epithelial cell level;
- presence of urobilinogen.
The presence of bilirubin compounds, urobilinogen, ketone bodies (acetone) indicates inflammatory processes in the body. The presence of glucose may indicate developing diabetes mellitus. Epithelial cells, leukocytes, protein compounds, red blood cells in small quantities are normal, but if their level increases, this indicates the beginning of diseases of the internal organs.
Instrumental research methods
In addition to tests, to determine cystitis, its degree and the correct selection of treatment, there are instrumental examination methods, these include:
Biopsy
A study in which tissue is taken from the wall of the bladder and then examined under a microscope. A biopsy is necessary to identify the tumor.
By examining the material under a microscope, the doctor can also determine the presence of inflammation and its nature. The material is collected using a cystoscope with special forceps; the device is inserted into the bladder through the urethra.
Cystoscopy
This examination is carried out using a special cystoscope device, which is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. When conducting this examination, the doctor has the opportunity to assess the condition of the walls of the bladder and the degree of inflammation. Most often, the procedure is performed with anesthesia due to its pain.
Most often, examination is prescribed for chronic cystitis, blood in urine, urinary retention accompanied by pain, frequent urination and when abnormal cells are detected in a urine test.
Ultrasound examination of the bladder
Using this examination, cystitis can be determined by the following factors:
- asymmetry of the bladder caused by its inflammation;
- the wall of the urea is thickened at the site of inflammation;
- swelling of the urethra.
There are several methods for performing ultrasound:
- Transabdominal . The examination is carried out through the abdominal wall. This method does not cause pain and is performed with a full bladder.
- Transvaginal . The method is used in women. Consists of examining the bladder through the vagina. It is carried out when the bladder is empty.
- Transrectal . Examination of urea through the rectal passage. Prescribed to both women and men. For men, the study allows you to assess the degree of inflammation of the bladder and the condition of the prostate.
Cystitis is a common disease that requires immediate treatment. A doctor should prescribe treatment after conducting the necessary examinations. It is important not to start the inflammatory process, as it can spread to other internal organs. And then the treatment will be more difficult.
What signs indicate cystitis?
If the values of the main indicators diverge from the norm, then, taking into account the diagnostic data of this and other laboratory tests, the doctor concludes that the patient is developing cystitis.
Normally, urine has a yellow or deep yellow color due to the pigments it contains: urochrome A, urochrome B, uroresin, uroethrin, etc. Its shade also depends on the amount of fluid secreted and on its specific gravity. Dark shades indicate a pathological process.
Transparency
A healthy person's urine is clear. If the number of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, pathogenic bacteria, fat formations, leukocytes and blood cells - erythrocytes in it is increased, then this indicates an inflammatory process in the body. When sediment forms in urine, it is important to consider whether it appeared immediately after urination or was noticed a few minutes later.
Specific gravity
This indicator fluctuates in people throughout the day, and this is due to the quantity and quality of fluid taken, as well as the possible development of the disease. Normally, for women, the values should be 1010-1025 g/l. Hypersthenuria (increased specific gravity) is observed in systemic diseases, food poisoning, toxicosis, cystitis, etc.
Acidity (pH)
Normally, urine has a slightly acidic reaction. But this symptom directly depends on what food was previously entered into the body. Meat dishes, which contain a lot of protein, give a pronounced acidic reaction, vegetables – alkaline. For this reason, objective results can only be obtained by providing urine on an empty stomach. The pH norm is -5.3 – 6.5. Cystitis is characterized by a pronounced alkaline reaction.
Chemical analysis of urine
This test includes determining the levels of ketone bodies, glucose and proteins. The normal level of protein compounds is 0.002 g/l. Proteinuria (increased levels of protein compounds) is divided into renal and extrarenal. If a person suffers from kidney disease, then a large amount of protein is due to the fact that the organ does not cope well with its functions. Cystitis is characterized by extrarenal proteinuria, in which protein formed as a result of inflammation of the walls of the bladder (pus and red blood cells contain proteins) enters the urine. The indicator rarely exceeds 1 g/l.
The amount of glucose in the fluid depends on the intake of medications containing glucose, sweet foods and drinks. The appearance of sugar can be caused by emotional shocks and mental stress. The normal content of this substance is 0.-1.6 g/l. With pathological glucosuria (most often caused by diabetes mellitus), this value increases. This sign is absent in the urine of women with cystitis.
Ketone bodies (acetone) are absent in the urine of healthy people. They can appear with excessive consumption of fatty and protein foods. In acute cystitis, these substances appear in the urine, indicating that a severe inflammatory process is underway in the body.
Microscopic examination
This method reveals the presence of organized (epithelial cells, casts, leukocytes, erythrocytes) and unorganized (mucus, uric acid salts) sediment. Normally, the content of erythrocytes in urine is 0-2 in the field of view, leukocytes - 0-5, epithelium - 0-1, there are no cylinders. With cystitis, these indicators are significantly exceeded; pathogenic bacteria can also be found in the urine.