Parasites - what are they?
Parasites are microorganisms that live and feed on other organisms. At the same time, parasites not only live in the body of their host, but also cause harm to him. Conventionally, parasites are divided into plant parasites and zooparasites. Plant parasites include:
- mushrooms;
- bacteria;
- some varieties of plants, etc.
Zooparasites include:
- protozoan microorganisms;
- helminths;
- arachnids;
- insects, etc.
Parasites also include various viruses that live in someone else’s body at his expense.
Having settled in the body, parasites cause its weakening and exhaustion, which sometimes leads to death. Many parasites can act as causative agents of diseases dangerous to human health.
Routes of infection
There are several typical infection mechanisms:
- Helminth eggs are found in the ground, mixed with dust particles. Therefore, unwashed vegetables and fruits pose a danger from the point of view of infection. Helminth eggs are found in the ground, mixed with dust particles. Therefore, unwashed vegetables and fruits pose a danger from the point of view of infection.
- Water. Also, helminth eggs are found in water: not only standing water (ponds), but also running water (rivers), tap water.
- Animals. Pets (cats, dogs, ferrets). These animals can be intermediate hosts of various types of parasites.
- Human. Parasitosis can be transmitted through the fecal-oral route. One of these methods may be inhaling cysts or helminth eggs that “fly” into the air, for example in the spring, when animal excrement is released from under the snow and with warm weather and wind it is easily transported through the air.
Danger of parasites
If the number and size of parasites are small, their presence may go unnoticed for a long time, but the rapid reproduction or growth of parasites and their movement throughout the body during their life cycle often causes the development of serious health problems.
For example, roundworms that accumulate in the intestines can cause constipation and obstruction. Bovine tapeworm grows up to several meters in length and seriously damages the digestive tract, depriving the owner of nutrients and vitamins.
Echinococcus forms cysts in internal organs, including the brain, liver, and lungs. Rupture of such a cyst may occur unexpectedly, after a minor injury or during an examination. The contents of the cyst can cause anaphylactic shock or collapse. Trichinella larvae feed and live in the muscles, gradually destroying them. According to WHO, parasitic diseases account for about 14 million deaths worldwide per year.
Symptoms
In most cases, manifestations of parasite infection are nonspecific. It is difficult to establish the presence of parasites in humans, since infection with helminths can imitate other diseases, for example, attacks of cholecystitis or gastritis.
Parasitosis may be indicated by:
- temperature increase,
- weakness and lethargy,
- decreased performance and mood,
- bad dream,
- irritability,
- stomach ache,
- diarrhea or constipation,
- weight loss,
- nausea and vomiting,
- desire to eat unusual foods or inedible substances,
- the appearance of a yellowish tint to the skin and sclera,
- weight loss,
- tendency to various allergic reactions (most often like urticaria).
The discharge of worms in feces is an important symptom that indicates the cause of the illness. However, this does not always happen, and the presence of parasites in the human body can be suspected only by indirect signs.
Helminthic infestations are often associated with impaired absorption of nutrients and micronutrients. Worms in the human body cause a lack of important vitamins and minerals:
- dry skin,
- hair loss,
- brittle nails,
- reproductive health disorders (impotence, menstrual irregularities, infertility),
- memory loss,
- decreased visual acuity, etc.
Prevalence and causes of helminthiasis
Approximately 50% of people are carriers of various parasites without noticing it. Through direct effects and waste from their life cycle, helminths cause harm to the internal organs of their host. And in especially severe cases they can lead to death.
The carriers of parasites into the body are often:
- Poorly washed foods eaten raw;
- Polluted water;
- Meat and fish with insufficient heat treatment;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- Swimming in open waters;
- Pastel and hygiene items, other reasons.
Children are at increased risk.
Adults cannot completely control all the actions of a child, as a result of which the baby brings parasites into his mouth with dirty hands or becomes infected through close contact with other children and animals. In addition, worms spread in more unexpected ways: for example, through the skin or through the urethra when swimming in a natural body of water. Therefore, you should not urinate while in water, as this type of parasite reacts to the presence of ammonia and thus finds a victim.
Complications of parasitic diseases
Blood test for parasites. When the parasite lives or dies, toxic substances are released into the host's body. They can cause weakness, constant fatigue, dizziness, headache, nausea, and loss of appetite. In addition, these substances provoke sensitization of the body, which causes allergies - rashes, dermatitis, bronchitis.
Many parasites choose to live in the human gastrointestinal tract. When strengthening in the intestines, as well as feeding, parasites damage and destroy mucous membrane cells and blood cells. Extensive damage to the mucous membrane can manifest itself as pain, nausea, disturbances in digestion and absorption of nutrients.
A large number of parasites (for example, roundworms), intertwined into a ball, can cause intestinal blockage and acute intestinal obstruction. The risk of this complication is especially high in young children, because their intestinal lumen is narrower.
The parasite is called so because it does not care much about the interests of the host organism. It takes all the necessary elements from food, depriving the owner of many essential nutrients - minerals and vitamins. Therefore, one of the consequences of parasitic diseases is hypovitaminosis and avitaminosis, which can manifest itself as a decrease in immunity, deterioration of the skin, nails, hair, etc. Significant loss of blood cells (due to the parasite feeding on them) and their insufficient formation (due to hypovitaminosis) leads to anemia.
A parasite such as Trichinella lives in and feeds on muscles, which causes severe muscle pain. Parasites that live or reproduce in the bile ducts (for example, opisthorchid) can cause blockage of the bile ducts, which is manifested by jaundice of the skin and sclera, itching.
Parasites are a source of regular chronic damage to cells, which provokes their malignant changes and the development of cancer.
Another danger of parasites is that an infected person in most cases becomes the cause of infection to other people. As a result, all family members can become ill if one of them has the parasite.
To improve survival, some parasites have a very complex life cycle, during which they change several hosts and exist in each as different life forms. For echinococcus, for example, a person is a dead end in the life cycle and, upon entering his body, the parasite forms cysts and capsules in various organs (brain, liver, lungs). The appearance of cysts in the brain can cause the development of epilepsy and other neurological disorders. In addition, cysts are a source of abscess formation in internal organs.
To protect yourself and your loved ones from parasites, it is necessary to promptly identify and treat parasitic diseases. A comprehensive examination for helminth infections helps with this.
Diagnostic methods
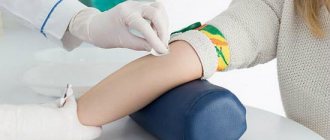
A blood test for parasites is called a parasite enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Using it, you can determine antibodies (immunoglobulin), which are produced as a reaction to an antigen (foreign body). Based on the presence of antibody-antigen complexes, a conclusion is drawn about the presence of certain pathogenic organisms. ELISA will detect parasitic infestations even if the number of parasites is negligible. Blood is drawn in the laboratory from a vein in the elbow. You will have to wait about a week for results.
The polymerase chain reaction shows what kind of infectious agent it is by creating for each its own genetic detector that detects an exact copy of all DNA and reproducing a large number of such samples. Suitable for infections caused by protozoan microorganisms. Material for research - any biological secretion (urine sample, plasma). The serological method of determination is a study of antibody reactions to antigens (immunofluorescence, hemagglutination, latex agglutination). The material for the study is blood serum. The disadvantage of this method is the inability to determine the stage of the disease.
Hemoscans are fairly simple, but very informative methods of examining a drop of blood, which can be used to identify worm larvae. The drop is monitored through a microscope for some time.
These tests make sure there is an infection. They are also used to determine the type of helminths, the presence of viruses, the presence of fungi, and the level of increase in leukocytes and erythrocytes. A complete blood count will also help diagnose harmful organisms if an eosinophil count is 20% above normal.
Types of ELISA
The body responds to the invasion of parasites and their antigens with a protective reaction, producing antibodies (or immunoglobulins) in the blood plasma. ELISA allows you to detect the presence of these specific protein compounds. From the moment of infection with helminths, the amount of immunoglobulins of classes G, M and A accumulates at different times. Their complex is determined during a blood test.
The basis of the methodology for studying these proteins is the immune response and enzymatic reaction. Based on the immune response, the presence of parasites can be determined and their type can be determined.
Based on the immune response, the presence of parasites can be determined and their type can be determined.
The enzymatic reaction allows you to study the types of helminths identified by laboratory assistants with visual measurement of data about them.
Various types of ELISA are practiced in laboratories:
- Straight.
- Indirect.
- Kind of like a sandwich.
- Solid-phase heterogeneous.
These options differ in different technological methods for detecting antigen-antibody complexes. The most commonly used is a heterogeneous enzyme-linked assay (ELISA). It is used to determine the presence of antibodies of the classes IgG, IgA, IgM to antigens of pathogens caused by parasites.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Research
Blood test for parasites. The advantages of testing blood fluid for infectious parasite infections include:
- full automation;
- information content and reliability;
- objectivity;
- comfort;
- early diagnosis of parasites;
- the ability to analyze quality and quantity;
- accuracy.
Minuses:
- high price;
- not available in every laboratory;
- waiting time for results - up to 7 days;
- Not all reagents are always available.
How to take it
An ELISA test for parasites can be carried out with the examination of samples of cerebrospinal or amniotic fluid, mucus from the urethra, and vitreous body. But most often, blood is taken from a vein from a patient in the morning on an empty stomach. In the laboratory, the sample is put through a centrifuge and the separated serum is examined.
3 days before donating blood, you should stop taking all medications except vital ones.
In order for the research results to be as reliable as possible, all laboratory requirements must be strictly followed. Necessary:
- 3 days before donating blood, stop taking all medications except vital ones;
- suspend physiotherapeutic procedures 2 days in advance;
- give up alcohol and coffee 1 day before;
- the day before, do not be exposed to physical activity or emotional stress;
- have dinner no later than 19-20 hours (you can drink some water in the morning).
What tests are needed to detect parasites?
Blood test for parasites. Blood and stool tests can detect the presence of helminths in the body. Parasites living in the intestines reproduce using eggs or entire compartments with large numbers of eggs, which are excreted along with the stool. This is how a sick person becomes a distributor of parasites. A stool analysis is carried out to detect helminth eggs and allows you to determine the presence of a helminth and its type (pinworms, tapeworms, etc.).
Since the active life of the parasite is manifested by the release of toxic substances and sensitization of the body, characteristic changes in the blood formula can be seen in the analysis. A complete blood count helps detect increased eosinophil levels and, less commonly, anemia. This study allows you to suspect or confirm the presence of a parasitic disease without specifying the type of parasite.
Blood test for parasites. Stool analysis is not always informative. The absence of worm eggs in feces gives grounds to exclude only some types of helminthiasis. To detect other parasites, a blood test is performed for antibodies to them (echinococcus, opisthorchid, trichinella, etc.). Determining the type of parasite helps the doctor prescribe the necessary additional examinations or immediately select the correct treatment.
Tests for parasites can and should be taken if there is a suspicion of infection (the appearance of characteristic complaints and health problems), for those who live in areas with an increased risk of infection, employees of child care institutions, the food industry, family members in whom a parasitic disease was discovered, etc. .d.
Timely detection and treatment of parasitoses allows you to avoid threatening complications and health problems.
Which specialist should I contact?
If you suspect the presence of worms, you must immediately go to a doctor who treats worms. Sometimes a visit to a specialist is postponed for a long time, because a person does not know which doctor to go to for worms.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=9G9xF5QMqI0
Various specialists deal with helminthiasis:
- parasitologist;
- helminthologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- gastroenterologist
Initially, you can go to a therapist. He will order tests and advise which doctor deals with treatment for parasites.
Parasitologist
A parasitologist is a specialized doctor for worms. Before making a diagnosis, a specialist will conduct diagnostic procedures and study the symptoms that accompany the disease caused by parasites in both adults and children. A parasitologist prescribes medications to get rid of worms.
The doctor examines all internal organs in which parasites can settle and carries out preventive measures.
Helminthologist
A doctor who deals with parasites may be called a helminthologist. This is a specialist who specializes in all types of parasites, their structure and characteristics. The doctor studies:
- the nature and extent of the impact of helminths on the human body;
- routes of infection;
- susceptibility of helminths to drugs.
A helminthologist knows the clinical manifestations of all types of worms. He prescribes tests for the patient and interprets the data obtained.
Infectious disease specialist
Many types of worms cause intestinal and other infections. These diseases should be dealt with by an infectious disease specialist. Infections under his jurisdiction include:
- intestinal;
- respiratory tract;
- skin;
- blood.
The doctor will identify the symptoms of the disease and prescribe medications that will help cure the disease.
Gastroenterologist
Helminths most often begin to parasitize and multiply in the intestines or stomach, causing a lot of harm to the human digestive system. A gastroenterologist can help you deal with these problems.
What is the name of the doctor who can be consulted and treated if you have parasites? A number of specialists can be named. To finally get rid of the disease, it is advisable to visit all of them.
Tests to identify parasites
The simplest test for the presence of parasites in the body is a stool test. To carry out this analysis, a stool sample is placed in a special sterile container, which must be delivered to the research laboratory within 30 to 45 minutes. During such work, laboratory specialists try to find eggs of worms and others in the provided sample. Such an analysis allows us to determine the existence of:
- roundworms or nematodes;
- flukes or trematodes;
- tapeworms.
Unfortunately, such a study cannot offer high reliability of the result, which is due to some features of helminth reproduction. Even if such an analysis is carried out more than once, its results still cannot be called reliable.
A more modern and effective method is a blood test to check for the existence of parasites. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA) involves detecting antigens and antibodies to parasites in a blood sample. If you take such tests for parasites, you can more likely determine the existence of a wide variety of microorganisms, and at the very early stages of their appearance.
Blood test for parasites. In order to take ELISA tests, it is enough to provide a blood sample taken from a vein. It will take no more than nine days to identify any parasite, and the results obtained will have a reliability of 95%.
Analyzes can be implemented in other ways. So, for this purpose the following can be carried out:
- X-ray and ultrasound examinations of organs;
- endoscopy;
- endobiopsy;
- CT scan.
The doctor usually decides what kind of material needs to be submitted for research and how it will be implemented.
Stool examination
Stool analysis is considered the most accessible, simple and common method for identifying parasites. It is through its implementation that it is possible to confirm or refute the diagnosis of the presence of a helminthic infestation in a child. Also, using stool analysis, it is possible to carry out a differential diagnosis of the disease if infection has occurred with microorganisms that belong to the group of protozoa.
To make the result more accurate, it is recommended to submit feces for this test several times, maintaining a certain time between tests. The fact is that for some time adult helminths may not release eggs.
Taking a stool test requires some preparation.
- You should stop taking the following medications for at least a week:
- antibiotics;
- dewormers
- laxatives;
- drugs that have the ability to eliminate symptoms of diarrhea.
- If necessary, endoscopic examinations of the lower intestines can be performed at least fourteen days before stool donation.
- The material must be taken in small quantities from several areas.
- The sample material should be collected in a dry and clean glass or plastic container with a lid.
- No more than 24 hours should pass from the moment of collection to the delivery of the material to the laboratory. But there are parasites, for the detection of which stool examination should be carried out no later than thirty minutes after collection (for example, with giardiasis).
Blood test for parasites - studies in children
Parasitic infestation is especially common in children. The reason for this is inattentive adherence to personal hygiene rules. It has been statistically proven that every child suffers from helminthiasis at least once in their life. Giardiasis occurs more often in children 1−4 years old. If a child has abnormal bowel movements, attacks of nausea in the morning, decreased or excessively increased appetite, weight loss, pale skin, itching in the anus, grinding of teeth in sleep, moodiness, pain in the navel area, there is a risk that there is a parasitic infection in the body. pathology. This should be an incentive for parents to get tested for parasites.
Blood test for parasites. Standard research methods for suspected parasitic processes in a child’s body are scraping for enterobiasis and stool analysis for worm eggs. Often this is already enough to make a diagnosis. But if there are doubts, and the stool analysis indicators have not given a clear answer, it is better to check again. It is worth doing a detailed blood test for parasites (ELISA or PCR).
Decoding the results
Diagnosis is carried out in specialized medical institutions. They wait about a week for ELISA results, and a couple of hours for PCR results. Hemoscanning is carried out in the presence of the patient. The interpretation of the results is carried out by a specialist in the field of parasitology. The point of diagnosis is to identify antibodies; their three main types are determined: lgG, lgA, lgM. Depending on the positive or negative result, the following conclusions can be drawn for each of them:
- in case of a negative result for the infection under study, all three indicators will have a sign (-): lgG (-), lgA (-), lgM (-);
- if the disease is in the acute stage: lgG (+/-), lgA (+\-), lgM (+);
- there is immunity: lgG (+), lgA (-), lgM (-);
- chronic disease: lgG (+/-), lgA (+/), lgM (-);
- exacerbation of a chronic disease: lgG (+), lgA (+), lgM (+).
IgG antibodies are fixed in the blood fluid no earlier than 2 weeks from the moment of infection, and IgG remain in abundance during the course of the disease and for some time after recovery. “Clean”, completely negative indicators will become only six months after the death of pathogenic organisms. An accurate interpretation can be made by the attending physician or a physician familiar with the work of the laboratory in which the tests were carried out.