Tuberculosis is an incredibly common disease, affecting about a third of the world's population. The number of patients increases every year. In some states with underdeveloped medicine, the number of patients exceeds 80%.
At the same time, the population of even developed countries cannot be confident in reliable protection against tuberculosis due to a number of factors. Among them, the most significant is a decrease in human immune defense. Mycobacterium tuberculosis enters our body, and the immune system is not able to fight them in most cases. Unfortunately, in most cases, modern man's immune system does not function at the proper level.
About the service Our prices
What is tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease. It is caused by certain types of bacteria, most often Koch's bacillus. The disease affects the lungs, and in rare cases it can develop in other human organs.
The most dangerous thing is that in the early stages tuberculosis is asymptomatic. In one case out of ten, the latent disease becomes active.
Symptoms of tuberculosis are:
- prolonged cough, sometimes with blood;
- rapid weight loss;
- general weakness;
- night sweats.
Tuberculosis occurs in two forms, namely:
- open when the Koch bacillus is actively released into the environment;
- closed.
In the open form of tuberculosis, the bacteria that cause the disease are present in all the patient’s secretions: saliva, urine, fistula discharge, even in feces. Mycobacteria also contain the patient's blood. Maximum precautions must be taken to avoid infection.
If tuberculosis occurs in a closed form, a person does not pose a threat to others.
Methods for diagnosing tuberculosis: blood tests and examination
A large number of methods are used to diagnose tuberculosis. The following types of TB tests provide the most effective data:
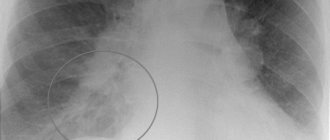
- radiography;
- fluorography;
- tuberculin skin test, otherwise called Mantoux test;
- study of biological material at the microbiological level;
- blood test for tuberculosis.
In turn, blood tests for tuberculosis are of two types:
- enzyme immunoassay, or ELISA;
- PCR diagnostics.
The first method of diagnosing tuberculosis is based on the detection of antibodies to mycobacteria that cause the disease. The advantage of this technique is the ability to conduct a large number of analyzes. However, the use of this type of analysis is most appropriate in regions where the infection rate of the population is not too high.
PCR blood diagnostics is a more effective test. It is used to identify diseases that have different localizations. PCR diagnostics also allows you to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Which blood test is most appropriate in each specific case is determined by the doctor treating tuberculosis. But all doctors urge you to take tests on time: this is the only way to find out the quantitative and qualitative composition of the blood, diagnosis, etc.
To test for the presence of tuberculosis in humans, tuberculin vaccination is most often used. It provides the opportunity for early detection of the disease and timely response. This technique is based on the fact that the body of adults has a certain sensitivity to the tuberculin drug. Its degree depends on whether the person came into contact with mycobacteria. If infection occurs, a tuberculin allergy will be observed (this is a very sensitive delayed-type reaction). This analysis is called the Mantoux test. It is administered subcutaneously, which ensures much greater accuracy of research than with skin examination.
Analysis of tuberculin samples allows:
- identify risk groups;
- carry out timely diagnosis of primary infection;
- carry out a study of clinical forms of tuberculosis using a differential method.
If a person has not previously been in contact with the bacteria that causes tuberculosis, he does not have an allergic reaction to tuberculin. An infected person develops a papule (small swelling). A Mantoux test is considered positive if the size of the papule exceeds 5 mm. Such an analysis is the reason for a detailed examination of a person to identify the disease. At the same time, it also happens that a person’s positive reaction to the Mantoux test does not indicate tuberculosis, but another disease, for example a cold, helminthic infestation, chronic tonsillitis. In order to minimize the possibility of such an error, the TB doctor prescribes additional blood tests. After all, blood testing is extremely important for such a disease.
Tuberculosis is a dangerous disease that is transmitted by airborne droplets. The causative agent of tuberculosis - Mycobacterium tuberculosis (also known as Koch's bacillus) belongs to the Mycobacteriaceae family, stains positively by Gram, does not form spores or capsules. There are 4 types of pathogenic bacteria, of which the most dangerous to humans is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Accurate diagnosis of the disease is carried out only by laboratory methods.
Tuberculosis is widespread: in different regions the number of cases per year ranges from 8-10 to 400-500 per 100 thousand population. Figures from statistical studies indicate that pulmonary tuberculosis most often affects men over 40 years of age. Women become infected mainly at the age of 20-30 years.
The pathogenic properties of the pathogen are associated with the structural features of the cell wall. The high content of lipids, waxes, and fatty acids in the cell membrane provides high resistance of mycobacteria to unfavorable environmental conditions. Koch's bacilli can withstand heat up to 100 0 C, exposure to acids, alkalis and disinfectants.
They persist in soil for up to 6 months, in water for more than a year, in sputum for about 2 months.
Tuberculosis can affect any tissue and organs: lungs, liver, kidneys, joints, bone tissue, genitals. The waste products of mycobacteria cause general intoxication of the body and pathological changes in tissues.
CLINISPOT-TB test
This is the most modern test for tuberculosis. It is also called T-SPOT. The essence of the test:
- if mycobacteria are present in the body, the immune system reacts to them;
- this reaction consists of the release of interferon gamma by some T lymphocytes;
- The essence of the test is to determine the number of such activated lymphocytes.
Spot analysis can detect bacteria even in very small quantities. It is used to identify latent, hidden forms of the disease, as well as to diagnose pathology in people with suppressed immunity (for example, against the background of AIDS). The test is highly specific; false positive results are practically not observed. This means that a positive result almost 100% indicates the presence of tuberculosis.
The sensitivity, that is, the ability to detect infection, of the POTS analysis reaches 96%, even in extrapulmonary forms of the disease. By comparison, the sensitivity of the Mantoux reaction is less than 70%. T-SPOT is produced in the UK.
QuantiFERON-TB Gold in-Tube test is another modern method for detecting tuberculosis in blood. Like T-SPOT, it is used when there is a high risk of infection (for example, living in the family of a patient) in combination with a negative Mantoux test. This test system is produced in Australia.
There are tests for the simultaneous rapid detection of tuberculosis and the resistance of its causative agent to rifampicin and rifampicin + isoniazid. They are used in large anti-tuberculosis centers. These are INNO-LiPA Rif, TB kit and GenoType MTBDRplus. However, they cannot be used to confirm the diagnosis of the disease.
Clinical symptoms of tuberculosis
Most often, the disease is detected during a routine examination of the sick person. With pulmonary tuberculosis, the patient may suffer from low-grade fever, cough, general weakness and weight loss. In the later stages of the disease, chest pain appears, a dry cough is replaced by a wet one, and pulmonary bleeding is possible.
The following groups of people are at risk for tuberculosis:
- patients with immunodeficiencies and chronic systemic diseases;
- people constantly taking medications based on glucocorticosteroids;
- smokers and people who abuse alcohol;
- patients who underwent a course of immunosuppression before organ transplantation;
- people living in unfavorable living conditions.
Also, the likelihood of becoming infected increases with prolonged contact with sick people. Studying the patient's medical history helps to identify the disease in a timely manner.
If tuberculosis is suspected, the doctor, after the initial examination, must prescribe an additional examination to the patient.
Prevention of tuberculosis
To prevent the disease, children are vaccinated with the BCG vaccine in the first days of life. Already 2 weeks after the vaccine is administered, children begin to develop anti-tuberculosis immunity, which lasts for 5-7 years. At the ages of 7 and 13 years, revaccination is carried out. Vaccination significantly reduces the likelihood of disease: among vaccinated people, the incidence of tuberculosis infection and mortality are lower than among unvaccinated people.
To diagnose tuberculosis, children under 15 years of age undergo an annual Mantoux test, which is also called a tuberculin test. Patients are injected subcutaneously with tuberculin, a mycobacterial antigen. The study shows the presence of sensitization of the body to Mycobacterium tuberculosis or the vaccine. The tuberculin test does not provide immunity to the disease. The Mantoux test is mandatory for a child before revaccination with BCG: a positive reaction is an absolute contraindication for vaccination.
The Mantoux test is not highly specific. The result may be positive in people who have recently had tuberculosis or are allergic to tuberculin. Diaskintest is used to detect tuberculosis, differential diagnosis of infectious allergies and hypersensitivity to the BCG vaccine.
The drug contains artificially synthesized antigens of the cell wall of mycobacteria. A reaction to Diaskintest occurs during an active pathological process, except in cases where the patient suffers from concomitant immunopathological disorders. A negative test is also observed in patients in the early stages of infection.
In order to prevent pulmonary tuberculosis and other diseases of the chest organs, adults and adolescents over 15 years of age should undergo fluorography once every 2 years. People working in medical institutions, schools, kindergartens, and the catering industry are examined at least once a year. Using fluorography, indicators such as the presence of compactions and darkening in the lungs, airiness of tissues, clarity of the pattern, and displacement of mediastinal organs are assessed.
When is analysis necessary?
Many people believe that tuberculosis affects the lower strata of the population. But this is not true. Infection is not affected by status or financial well-being. Anyone with a weakened immune system can become infected with Koch's bacillus.
In physiatry, there are many cases when businessmen, medical workers, and police officers treat the disease.
Treatment of tuberculosis is a rather lengthy process, and in its advanced form it leads to pulmonary hemorrhage. Since microorganisms quickly lose sensitivity to antibiotics. Scientists need to constantly improve drugs. For this reason, it is easier to prevent the development of an infectious disease.
Children and adolescents under 18 years of age must undergo a reaction test several times a year. A button that has been familiar to everyone since childhood helps doctors diagnose the disease in a timely manner. After reaching adulthood, people need to undergo fluorography twice a year.
This diagnosis allows us to reduce the risk of developing the disease among the population.
At the first sign of infectious bacteria in the body, you should consult a doctor. He will prescribe a complete and comprehensive examination that will help identify the presence of the disease.
What tests do you need to take to check for tuberculosis?
Laboratory tests for tuberculosis in adults during the initial examination are prescribed as follows:
CBC is not a specific research method, but it can be used to assess the general condition of the body and the response of the immune system to infection. With tuberculosis in the blood of patients there is an increase in ESR, neutrophilia, and slight lymphocytosis.
Sputum examination is carried out for pulmonary tuberculosis. In order for the analysis result to be reliable, the patient should follow the rules for collecting biological material. The study requires the first morning portion of sputum, since mucus accumulated in the respiratory tract during the night is more likely to contain mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sputum is collected on an empty stomach into a sterile container. If sputum discharge is difficult, bronchoscopy is used to collect biomaterial.
The patient's sputum is then examined under a microscope. Koch rods are stained with Ziehl-Neelsen or fluorochrome dyes. To obtain a reliable result, it is recommended to study three portions of sputum. It is impossible to determine the disease from saliva in this way. The test is considered positive if 1 ml of sputum contains at least 10 thousand microorganisms. The result may be affected by the patient's failure to comply with the rules for collecting and storing sputum.
Bacteriological analysis for tuberculosis involves inoculating sputum, cerebrospinal fluid, and punctate from the patient’s lymph nodes onto nutrient media. If the culture result is positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the diagnosis is considered confirmed. But the disadvantage of the method is low sensitivity - a certain concentration of the pathogen in the biomaterial is required for a positive result. The study takes from 4 to 8 weeks. After isolating a culture of mycobacteria, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of this strain to anti-tuberculosis chemotherapeutic drugs.
The essence of the method
Using PCR diagnostics, you can detect fragments of foreign DNA in any liquid environment of the body. The following liquids can be taken for analysis:
- Blood.
- Saliva.
- Sputum.
- Discharge from the genitals.
- Bronchial lavage fluid.
- Gastric juice.
The attending physician himself determines which biological fluid is best to take for analysis for a particular disease.
PCR diagnostics allows not only to detect microfragments of foreign DNA, but also to determine which specific type it belongs to. That is, using PCR, you can not only accurately identify the causative agent of the disease, but also find out what species it belongs to.
The PCR analysis process is very complex. It consists of several stages:
- First you need to detect fragments of malicious DNA in the provided sample.
- Copying a DNA fragment. A small piece of DNA is not enough for analysis, so it is copied. Nucleic acid can be copied in vitro using the enzyme polymerase (outside a living organism). Many clones are formed in a test tube, that is, a chain reaction occurs. The whole process occurs in three stages under the influence of different temperatures.
- When there is enough genetic material for research, then the pathogen is determined by conventional methods.
The PCR method is very accurate and can detect the presence of any pathogen from a small fragment of DNA or RNA.
Is it possible to detect tuberculosis using a blood test?
A blood test for tuberculosis instead of Mantoux using PCR or ELISA is indicated for children, pregnant women and patients with extrapulmonary forms of the disease. The study is absolutely safe for the patient and has no contraindications. The blood test is also supported by the high accuracy of the methods used. When performing real-time PCR, the test result will be ready on the day of blood donation.
The PCR method is based on isolating the genetic material of the pathogen in the patient’s blood. Using the analysis, it is possible to diagnose the disease long before the first clinical symptoms appear.
Testing for tuberculosis using the PCR method is prescribed for patients with HIV and AIDS. In immunodeficiency states, the results of bacteriological culture and tuberculin test are often false negative, which greatly complicates diagnosis.
The disadvantage of this method is its high price. The research requires expensive equipment and materials, which not every laboratory has. Therefore, blood testing using the PCR method is not used for mass screening of the population.
A false-positive test result is possible immediately after a course of anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy, when the pathogen still remains in the body. The method is not effective if a person is infected with mutant strains of mycobacteria. When carrying out PCR, it is extremely important to choose the right biological material: blood testing is most informative in a generalized process and in the early stages of the disease.
Already a month after infection, the patient’s body begins to synthesize specific immunoglobulins of the IgM and IgG classes. Antibodies are detected in the blood using enzyme immunoassay. The test is prescribed if there are vague symptoms of tuberculosis against the background of negative test results by other means.
An analysis for the presence of antibodies to the pathogen in the blood does not allow one to distinguish between latent bacterial carriage and an active pathological process. To confirm the diagnosis, the analysis must be supplemented with other examination methods. When prescribing a test for people suffering from immunodeficiencies, it should be taken into account that their antibody levels may be extremely low.
Blood testing using both PCR and ELISA does not require special preparation. Before donating blood, you should abstain from food for at least 4 hours and from smoking for at least 1 hour. It is recommended to undergo the study in the morning.
A sputum test for tuberculosis can detect infection of the lungs with the tuberculosis bacillus. Thus, there are a number of studies aimed at accurately diagnosing the disease.
An analysis for tuberculosis, like many laboratory tests, is aimed at identifying the presence of an infectious disease in the human body. A pathological disease caused by infection with the tuberculosis bacillus must be diagnosed in a timely manner, both to identify the factors that led to infection, and to successfully ensure a speedy recovery of the person.
It is known that early detection of lung infection in the embryo increases the likelihood of successful treatment by several orders of magnitude. This way the therapy takes place much faster, which reduces the cost. It is worth figuring out what tests need to be taken at the first suspicion in order to identify or exclude tuberculosis in time.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease transmitted by airborne droplets from person to person. The causative agent is Koch's bacillus, which, when it enters the body, is endowed with the property of infecting internal organs. The lungs are the first to become infected.
Symptoms in the first stages of infection are rather weakly expressed in manifestations. A person can be a passive carrier of Koch's bacillus for up to a year until a relapse occurs. In institutions of public organizations (schools, clinics, kindergartens, etc.) there is a procedure for constant monitoring in the form of medical examinations for the presence of infection.
Everyone needs to know the primary symptoms of infection in children and adults:
- a constant indicator of a slight increase in body temperature, especially manifested in the evening;
- increased sweating (especially at night);
- unauthorized loss of appetite (occurs more often in children);
- factor of weight loss for no particular reason;
- increased heart rate;
- general state of weakness;
- pale complexion.
It is worth noting that in children the primary signs of infection are more pronounced. In adults, symptoms can be disguised as diseases of another kind, or explained by sleep patterns, stress and other household characteristics.
The human body is quite secretive, and as noted above, Koch’s bacillus may not manifest itself for a whole year (antibodies mask it). Instead of severe symptoms, both in children and adults, signs of progressive tuberculosis may immediately appear:
- cough (dry or wet) with sputum mixed with blood (and without it);
- wheezing in the chest when listening to the lungs;
- change in breathing when the lack of air is clearly expressed;
- shortness of breath, which is characterized by a reduction in the working capacity of the lungs when affected by Koch's bacillus;
- the temperature rises to 40 degrees, and persists with an aggressive form of tuberculosis development (early stages reveal a temperature of 37 degrees and slightly higher in a constant rate);
- causeless loss of body weight up to almost 10-15% of the total weight in a short period of time;
- presence of chills or fever.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that affects various organs and tissues. The cause of the disease is Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch's bacillus), which often enters the body through the respiratory tract.
In rare cases, a person can become infected through nutrition and contact, and a child can become infected in the prenatal period. Many people are interested in what tests are taken if tuberculosis is suspected? Let's take a closer look.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease in the early stages is complicated by the fact that the first signs have symptoms similar to chronic bronchitis
Importance is attached to timely tests to identify patients with clinical signs of the disease. If a disease is suspected, sputum is collected three times and sent for examination to detect the presence or absence of mycobacteria
Diagnostics also includes other types of examination. The patient undergoes a complete fluoroscopic examination. Fluorography and radiography examine primary changes in the lungs. In addition to sputum collection, Mantoux tests are performed.
What tests do patients undergo? A more complete diagnosis includes the following:
- general blood test for tuberculosis;
- urine analysis to determine protein metabolism disorders;
- enzyme immunoassay for tuberculosis (ELISA);
- polymerase chain reaction analysis;
- microbiological research.
A general blood test will not help accurately determine the disease, but will show the clinical picture of inflammatory processes.
With this infection, a strong excess of ESR and a high content of leukocytes are detected. ESR can be more than 60 units when the norm is 10-15. But this result also happens with cancerous tumors. Blood never shows a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin.
Instead of Mantoux, medical centers use a more progressive and safer method - enzyme immunoassay. Its sensitivity is low and is about 60%. But the use of ELISA can be taken into account in complex studies.
Polymerase chain reaction. Using PCR, the presence of DNA bacteria is determined. To do this, they take biomaterial, for example, blood or sputum, place it in a special reactor and add enzymes. They connect with DNA microbes and synthesize a copy of them. PCR analysis is highly quantitative and is indispensable in accurate diagnosis.
But it is highly informative when analyzing sputum, but when examining blood it often gives incorrect results. If the PCR analysis gives a positive result, this indicates the presence of traces of infection. A negative indicator means the opposite.
For microbiological diagnosis, secretions isolated from the respiratory tract are taken using the cough reflex. A complete examination of sputum is carried out and stained using the Ziehl-Neelsen method with carbol fuchsin. This makes it possible to detect pathogens of pulmonary tuberculosis. To date, this analysis is the most accurate.
For a comprehensive diagnosis of the disease, skin tests are performed. Tuberculin tests can identify people infected with Koch's bacillus.
To determine the presence of tuberculosis bacillus in the body of an adult, donating blood is not enough, since it can only determine the presence of an inflammatory process or a cancerous tumor.
The enzyme immunoassay test and PCR showed that they provide insufficient information about the condition. But a comprehensive examination can show a high degree of information content of these methods. Many countries are actively searching for new diagnostic tests for tuberculosis. America and Europe have already introduced the IGRA test, which is very effective in determining infection. But we don’t use it yet.
Tuberculosis is an insidious and difficult to diagnose disease.
It kills millions of people around the world. Complete cure is only possible with early diagnosis. In advanced forms, treatment takes a long period and sometimes has a fatal outcome.
The task of doctors is to carry out timely preventive measures aimed at reducing the spread of the disease. It is necessary to use new technologies to diagnose and treat patients.
Doctors have discovered a new cause of bad breath: parasite infection.
Blood test
If tuberculosis is suspected, a blood test is prescribed. However, its results cannot indicate this disease with an absolute guarantee. If a person is sick with limited or one of the inactive forms of tuberculosis, a change in the amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells is often detected in his blood. At the same time, the content of red blood elements is within normal limits.
If there are large infiltrates, caseous pneumonia or intestinal lesions, a decrease in the number of red blood cells is observed in the blood.
In addition, many red blood cells are found to be abnormally small. At the same time, they are colored with both acidic and basic dyes. In rare cases, especially in children, macrocytosis is observed - the appearance of giant red blood cells in the peripheral blood. In compensated tuberculosis, the content of erythrocyte precursor cells is 0.1-0.6%, subcompensated - 0.6-1%, decompensated - 1%.
When infected with the tuberculosis bacillus, the number of white blood cells - leukocytes - may increase in the blood of patients. In rare cases, a decrease in their level is observed. This can occur more often with a destructive form of the disease, less often with a limited or mild form of tuberculosis.
In most cases, the leukocyte formula shifts. There is often a shift to the left. Many neutrophils and myelocytes appear in the blood. In uncomplicated pulmonary tuberculosis, immature leukocytes are rare. The appearance of granularity in these cells almost always indicates an advanced disease. In patients with severe forms of the disease, most neutrophils are granular. As soon as the process enters the remission stage, the leukocyte formula is normalized.
The number of eosinophils also depends on the stage of the disease. During exacerbation, they may completely disappear from the blood. As the process subsides, their number can increase sharply. In addition, the content of these cells increases in the initial stages of tuberculosis, immediately after infection.
Many forms of the disease are characterized by a decrease in the number of lymphocytes. Moreover, such a change can be observed for a long time after subsidence. With an exacerbation of the secondary form of tuberculosis, especially in children, the number of lymphocytes remains unchanged or slightly decreases.
Another important indicator that determines this test for tuberculosis is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Accelerated ESR indicates an active inflammatory process in the body, which is observed in active forms of tuberculosis. But even if this indicator is normal, this does not guarantee the absence of Koch’s bacillus in the body. In rare cases, the ESR decreases.
During therapy, blood counts change. The better the drugs for treatment are selected, the faster they normalize. However, we should not forget about the effect of antibiotics on hematopoietic function. When taking them, the eosinophil count sometimes increases. Leukopenia is often observed - a decrease in the number of white blood cells. Sometimes there is even agranulocytosis. Very rarely, an increase in the number of leukocytes is observed.
In addition, tests for tuberculosis include a biochemical blood test. Disturbances in this study are determined by the phase of the process, the presence of complications and other diseases.
During the calm stage, the amount of protein and protein fractions in the serum is often unchanged and within normal limits. In patients with the acute form, in particular in children, a decrease in the albumin-globulin ratio is observed.
To determine the functional state of the liver in tuberculosis, a study is carried out on the amount of certain substances, such as direct and indirect bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase. In patients with severe forms of the disease, their levels are determined every month.
To assess the condition of the kidneys, an indicator such as creatinine is determined in the blood serum. In addition, the glomerular filtration rate is calculated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula. The main purpose of biochemical tests is to control the course of the disease.
Also, to determine tuberculosis, the antibody titer is assessed. This test is called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). It helps detect the disease within a few hours. The disadvantage of the test is its lack of sensitivity. Conducting ELISA is recommended in areas with low levels of tuberculosis infection in the population.
The most effective test is polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is used both to diagnose the disease and to monitor therapy. This analysis allows not only to detect the DNA of Koch's bacillus, but also to count their number.
Testing is prescribed for the child
Mycobacteria increase antibody titers in serum. However, no widely available tests have yet been developed for routine use that have high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing children.
Interferon-gamma plays an important role in regulating protective responses to infection. This led to the development of IGRA tests to assist clinicians in diagnosing latent and active infections.
The test detects bacteria by measuring interferon levels in response to antigens, which are represented by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
www.emedicine.medscape.com
Urine and saliva analysis
To determine the tuberculosis bacillus in children and adults, bacteriological urine culture or PCR testing is performed. However, its absence in urine does not mean that a person is healthy. In subcompensated and decompensated tuberculosis, mycobacteria are often not detected.
Also, if tuberculosis is suspected, a general urine test is required. You can only donate the morning portion. During the night, the bladder fills with urine and the data obtained from its examination will be the most accurate. To take a urine test, you must first perform thorough hygiene of your intimate areas. Urine is collected in a special container, which should be stored in a cool place until submitted to the laboratory. The day before collection, in order to avoid distorting the results, it is not recommended to eat brightly colored foods and spicy foods.
Various changes can be detected in the TAM in pulmonary tuberculosis. One of these disorders is leukocyturia - the presence of a large number of leukocytes in the urine. In addition, erythrocyturia, the release of red blood cells in the urine, and proteinuria, the presence of protein in the urine, may be observed.
The reaction of the material being tested is often acidic. Urinalysis may be normal for inactive TB.
Also, to determine tuberculosis, a saliva test is performed. It is done in children and adults if any pulmonary disease is suspected. Saliva is collected in a special vessel. This can be done at home or at the medical facility where the study will be conducted.
To obtain reliable results, it is not recommended to brush your teeth, eat, use mouthwash, or even drink water 4 hours before collection. 24 hours before taking a saliva test for tuberculosis, you should limit smoking and drinking alcohol. These bad habits can also skew the results.
Saliva analysis involves dripping a special reagent onto a smear, under the influence of which the saliva can change color. If the color has changed, this indicates the presence of mycobacteria in the body; if not, the person is not infected with Koch’s bacillus.
Tuberculosis is a very serious disease that, without timely and proper treatment, can be fatal. Laboratory tests for tuberculosis help determine the presence of mycobacteria in the body. To establish an accurate diagnosis, they are carried out simultaneously with other examination methods.
The child’s body has an immature immune system, and the entry into the body of pathogens of infectious or inflammatory diseases, in particular tuberculosis, causes more serious complications in the child than in adults.
Early diagnosis allows you to quickly assess its condition and prescribe an appropriate course of treatment.
What methods of diagnosing tuberculosis are used in children, can a child have a blood test instead of Mantoux, how else can one check for the presence of the disease without a tuberculin test? Let's find out!
PCR for tuberculosis instead of mantoux
Today, blood tests performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are more effective and accurate. Unlike the mantoux test, PCR analysis can be used to diagnose developing extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Mantoux is often replaced by PCR analysis when speed is required to identify the disease itself and the source that caused it.
The use of the PCR method does an excellent job of identifying a possible relapse of the disease
This is especially important for those who have already had tuberculosis, since a relapse of the disease is possible, approximately, after a year has passed after leaving the rehabilitation period
Replacing mantoux with a blood test to determine tuberculosis is the only solution for patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and patients suffering from serious lung damage.
Carrying out analysis
- A small amount of blood taken from the patient is placed inside a glass flask, which already contains a substance that prevents clotting.
- Cells separated from the plasma are examined under a microscope to determine the presence of a pathogen that can cause disease.
- Finally, the sedimentary material combines with substances that cause a cell reaction, creating the necessary temperature regime. The process ends with the receipt of updated DNA material. The results indicate either the presence of the disease in the body or its absence.
Advantages of diagnostics
The advantages of PCR analysis include:
- The ability of the method to clearly identify the DNA of one specific pathogen, without confusion with any others.
- No age restrictions for analysis.
- The great advantage of PCR is its ability to identify even one bacterium that causes a disease among a variety of others. Difference from other microscopic, bacteriological and enzyme immunoassay diagnostic methods.
- The versatility of this examination method is suitable for application to any of the numerous types of bacteria or viruses. Moreover, the use of PCR is suitable both for detecting the pathogen itself and the specific environment of its localization: in blood, sputum, urine.
The huge advantage of this method over others is the speed of obtaining results: after only 3-4 hours!
Disadvantages of the method
- A significant disadvantage of the PCR method is its phenomenal hypersensitivity, which often leads to false-positive results. This can happen, for example, if there is foreign DNA left on the analysis equipment, even in a tiny amount.
- In most cases, this DNA multiplies, which leads to incorrect research results. This problem is solved by using disposable utensils or materials.
- A significant disadvantage of PCR is the inability of this technique to determine the presence of which pathogen is recorded: living or dead. This may result in the diagnosis of tuberculosis in a recovered patient whose body has not yet been completely cleared of dead tissue of the pathogen.
Preparing for analysis
To obtain reliable results, you must follow the recommendations below:
- Examination by the attending physician to obtain information about contraindications for diagnostics.
- Stop taking antibacterial drugs that lead to distortion of study results.
- Quitting tobacco and alcohol.
The procedure is performed in the morning on an empty stomach or four hours after eating.
Tuberculosis is a serious disease, especially common among children. The difficulty lies in the fact that diagnosing the disease in children, due to different manifestations than in adults, is often untimely. Therefore, the issue of finding methods to detect the presence of tuberculosis in the early stages remains one of the priorities for scientists.
Description of the disease, causes of appearance
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease. The causative agent is Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Koch bacillus). The disease can affect all organs and organ systems.
Koch's wand may remain in a state of standby for some time. This is due to the presence of two types of bacteria: with low activity of metabolic processes and bacteria in which practically no metabolic processes occur.
When favorable conditions appear, the Koch wand begins to show activity.
In a child’s body, mycobacteria begin to secrete toxins, which leads to weakness and loss of body weight.
The main source of infection is a person suffering from tuberculosis or infected cattle. The disease can be transmitted after consuming milk or meat of a sick animal.
Poorly washed hands after touching objects used by an infected person can also cause the disease.
Children, often without washing their hands, can take something edible and eat it. This is how the bacteria enters the body.
Infection can occur if there is a lot of dust in the room. This environment is favorable for bacteria.
Other causes of infection in children:
Requirements for the laboratory
In the room it is necessary to allocate several zones for:
- reception and registration of material;
- DNA studies;
- creating reagents and performing PCR;
- destruction of products formed by increasing the number of copies of a specific DNA sequence by electrophoresis.
The laboratory consists of several zones.
The laboratory will be equipped with additional rooms:
- archive;
- room for medical staff;
- locker room for employees;
- dining room;
- stock;
- toilet;
- autoclave room.
The work rooms are equipped with boxes. In the area for DNA determination, a PCR composition is prepared, and reverse transcription of RNA is performed. The preparation of mixtures is carried out in a box.
Important information: How does eye tuberculosis manifest?
Signs of the disease in children and adolescents
- A chest x-ray will show negative changes occurring in these organs.
- Fluoroscopy determines the amount of fluid in the lungs.
- Computed tomography, MRI. Detects any changes in organs and bones.
The possibility of using these methods is determined by the doctor.
For the quantiferon test, blood is drawn from a vein.
. They carry out chemical transformations and look for gamma interferons in the blood. If they are found, it means there is an infection in the body.
Bronchoscopy is a complex research method, but effective. They prepare in advance and take the necessary tests.
Passes under anesthesia. A bronchoscope is inserted into the child; at the end there is a video camera, which allows, after processing the video recording, to see whether there is fluid in the bronchi and pleura of the lungs.
This method is not the main one; the possibility of use is determined by the doctor. After the procedure, the child will need to take medications to prevent possible negative effects.
The T-cell marker of tuberculosis is based on a whole complex of complex laboratory tests of sputum. The analysis is quite effective; it appeared recently, in 2014.
A septic specialist will tell you about the main methods for diagnosing tuberculosis in children in this video:
Alternative Research
If parents are against their child having the Mantoux test done, a number of alternative studies can be carried out:
- Diaskintest. Similar to the Mantoux reaction, but a different drug is used.
- Quantiferon test. They look for interferons as indicators of the tuberculosis bacillus in the body.
- the child has been coughing for more than 3 weeks in a row;
- Fatigue appears, memory deteriorates;
- the child refuses to eat; as a result - great weight loss;
- the skin becomes pale and dry;
- complains of pain in the chest area;
- sweating increases;
- pain appears in the joints.
in the evening the temperature rises to 37-38 degrees;
These signs are not direct confirmation of the presence of tuberculosis in a child, but if at least some of the symptoms are present, the child should be taken to a pediatrician and undergo the necessary tests.
Learn more about the symptoms and signs, methods of diagnosing tuberculosis, including in children, in this video:
Tuberculosis is curable
. It is necessary to identify the causative agent of infection in the early stages, then the likelihood of recovery is high. The doctor will prescribe a course of necessary medications.
It is important for parents to respond to the child’s complaints in a timely manner, monitor the child’s health and, if suspected, carry out diagnostic measures - from the Mantoux test to bronchoscopy and MRI.