Characteristics of the method
The blood clotting process is achieved due to the content of a special protein called fibrinogen. When the blood clotting mechanism starts, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin threads, which tightly clog the damaged vessel. The function of this protein is to form blood clots and increase blood viscosity. This physiological process is very important for the human body, since if it is disrupted, a person is at risk of bleeding. In case of serious deviations from the norm, a person risks encountering complications such as profuse bleeding or thrombosis of large vessels.
In order to determine the blood clotting time according to Sukharev, capillary blood samples are taken from a finger. During the analysis, laboratory staff determine the concentration level of enzymes that regulate the coagulation process. Assessing the rate of blood clotting according to Sukharev makes it possible to identify the body’s potential for self-defense in the event of traumatic injuries, and to identify the degree of risk of internal bleeding.
The speed and quality of coagulation directly depends on the health of the human nervous and endocrine systems, as well as on the functioning of the liver. When receiving disappointing test results, medical specialists have reason to suspect abnormalities in the functioning of certain organs and systems.
Medical diagnostic practice uses the two most effective methods for determining the characteristics of the blood coagulation system. These methods include:
Lee White method. To carry out the analysis, blood must be taken from a vein;
Sukharev's method. In order to measure blood clotting time, capillary blood is taken from a finger.
How to properly prepare the body for the Sukharev test
It is recommended to donate blood from a finger in the morning, completely on an empty stomach. If, due to certain circumstances, the test is taken at a different time of the day, then you should not eat at least three hours before. You are allowed to drink only water, but drinking juice, tea and coffee, especially with sugar, is strictly prohibited - otherwise the result will be erroneous.
Indications
This diagnostic technique is prescribed to people in the following situations:
Before carrying out planned surgical interventions, to prevent massive bleeding;
For acute and chronic liver diseases;
If bleeding of various kinds occurs that does not stop for a long time;
Before a caesarean section;
If symptoms occur that indicate a decrease in blood clotting ability;
If excessive blood viscosity is suspected.
This laboratory study is of particular relevance for pregnant women who need constant monitoring of blood clotting rate. This diagnostic event is one of the components of a successful delivery.
Preliminary preparation
To obtain a reliable result of a laboratory test, each patient is recommended to adhere to medical recommendations regarding preparation for the analysis. The list of preparatory recommendations contains the following items:
12 hours before collecting biological material, you must not eat;
Important! 10 minutes before the laboratory test, the patient is allowed to drink a glass of clean water. After this, the person needs to take a sitting position to normalize heart rate and blood pressure. If blood is taken from children, then parents need to make every effort to calm the baby.
Bleeding time
There are many methods for studying the duration of bleeding, differing in the method of blood sampling and the method of implementation.
Currently, three methods are especially widely used:
- Ivy:
- Duke;
- Sukhareva.
The duration of bleeding according to Ivey is determined as follows: a tonometer is fixed on the patient’s shoulder, with its help a pressure of 40 mm Hg is injected. st, then a small incision is made with a blade on the inside of the forearm. After this, the time is recorded on a stopwatch, and a special filter is applied to the incision every half a minute to absorb blood. When there are no traces of blood left on the filter, the bleeding is considered to have stopped.
This method can only be used with older children and adolescents - it is considered quite aggressive.
The Duke method is more popular and is considered more gentle. To test using this method, you do not need to use a tonometer or make an incision - a small puncture of your finger or earlobe with a special Frank needle is enough. A paper filter is also applied to the puncture site, but not every half a minute, but every 15 seconds. The blood clotting rate in the Duke study does not exceed 4 minutes.
This method is used more widely and is more often used in children.
Sukharev's method is as follows: a blood sample is taken from a finger, then placed in a test tube; The tube is tilted from side to side until the blood sample begins to thicken. The norm from start to finish of coagulation is no more than 5 minutes.
Normal blood clotting time
If we talk about the average statistical indicators that correspond to the physiological variant, both in women and men, then the norm of blood clotting according to Sukharev is in the range between 2 and 5 minutes. The initial period of physiological blood clotting lasts from 30 seconds to 2 minutes. For final blood clotting, the standard time is 2 to 3 minutes. These results indicate the normal functioning of the human body in general, and the coagulation system in particular. Changes in indicators indicate various diseases that are indications for taking anticoagulants such as Warfarin.
Normal physiological clotting times for blood samples may differ in children of different ages. During the first year of life, the baby's liver does not have sufficient capacity to produce vitamin K, which in turn stimulates blood clotting. In the period from 2 to 10 years, the child’s body experiences increased production of biological substances that ensure blood clotting.
Coagulation indicators and their norm in children
Blood is not a homogeneous liquid, but a suspension of many cells in a water-protein solution - plasma.
There are many types of blood cells, which (to simplify somewhat) can be divided into three groups.
- The first is erythrocytes, also known as red blood cells, which transport oxygen to tissues.
- The second is leukocytes, white blood cells that absorb and neutralize foreign objects (viruses, bacteria, etc.).
- The third is platelets, the cells responsible for the ability of blood to clot.
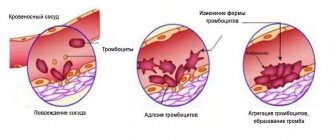
When the integrity of the vessel wall is damaged, special substances are released from the damaged tissues, the so-called coagulation factors (mainly proteins).
They activate platelets and cause them to stick to the edges of the wound and connect with each other, forming a dense clot that covers the damaged area.
In turn, platelets also secrete a special substance that activates the fibrinogen protein dissolved in the plasma.
It begins to transform into the protein fibrin, which is capable of forming long elastic cords in which red and white blood cells “get stuck.” Thanks to this, the clot covering the wound becomes denser, and its edges begin to tighten.
The blood clotting process is characterized by many indicators.
- Platelet level is the number of cells responsible for the blood clotting process.
- The duration of bleeding is the time that passes from the moment the integrity of the vessel is damaged until a blood clot forms.
- Clotting time is the duration of formation of a blood clot.
- Prothrombin time is the rate of activation of a certain factor (namely factor VII, proconvertin) involved in the “launch” of the coagulation process in the early stages. This factor activates the formation of thrombin, a substance that promotes the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin. In other words, this is the rate of formation of a blood clot after exposure to substances from the tissues of a damaged vessel.
- Thrombin time is the rate at which fibrinogen is converted into fibrin.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is the duration of the formation of a blood clot without the participation of external factors, i.e., without damage to the vascular walls and the release of corresponding substances, solely due to factors initially present in the blood in an inactive state.
- Fibrinogen level is the amount of fibrinogen protein that can be converted into fibrin.
- Antithrombin III level is the level of antithrombin III protein in the blood, which prevents blood clotting. This protein is needed in the blood so that coagulation processes, relatively speaking, do not start without a serious reason. Increased blood clotting is no less dangerous than decreased blood clotting - it often causes the formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
The values of these indicators for children aged 3 to 14 years are almost the same:
- number of platelets in thousands per 1 cubic milliliter of blood – 180-320; in girls in adolescence, at the onset of menstrual bleeding, the platelet count may decrease to 75-220;
- duration of bleeding - can be determined in accordance with different methods: according to Duke, the norm is 2-4 minutes, according to Ivey and Lee-White - less than 8 minutes, according to Sukharev less than 5 minutes;
- clotting time – from 2 to 5 minutes;
- prothrombin time – 11-15 s;
- thrombin time – 15-18 s;
- APTT – within 24-35 s; specific indicators may vary significantly depending on the determination method and the reagents used;
- fibrinogen level – 2-4 g/l;
- antithrombin level - 101-131% - in children from one to 6 years old, 95-134% - in children from 6 to 11 years old, 96-126% - in adolescents under 16 years old.
The importance of these indicators and their role in the blood clotting process should be considered separately.
Progress of the procedure
To carry out this type of laboratory test, a small amount of capillary blood is taken from the patient's ring finger. After introducing a scarifier (puncture), the first drop of blood is removed, as it may contain elements of tissue fluid and pathogenic microorganisms. The next drop is the material for research, which is placed in the so-called Panchenkov apparatus.
During the test, a sample of capillary blood is placed in a glass capillary, which is subsequently tilted left and right. In parallel with this action, the laboratory doctor records the time that will be spent on the formation of a blood clot. The onset of this process is not difficult to determine, since the blood in the glass capillary begins to coagulate and stops moving.
In simple terms, we can say that Sukharev’s technique is aimed at assessing the interval between taking a blood sample and the beginning of the formation of a fibrin clot.
When VSC is higher than normal
This diagnosis is made when the process of blood clot formation is too rapid. This blood condition can cause blood clots to form, which is dangerous to the child’s health. This condition is observed with certain disorders:
- autosomal diseases;
- DIC syndrome at the initial stage;
- disruption of the cardiovascular system;
- problem in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- infectious disease;
- intoxication.
Individual reasons for non-compliance with the norm
A change in the normal time of physiological blood clotting according to Sukharev does not always indicate the development of a particular pathological condition. We are talking about people for whom an increase or decrease in these numbers is a physiological norm that does not cause discomfort. This category includes the following people:
People who constantly experience traumatic injuries to soft tissues (extreme recreationists and athletes);
Women during pregnancy or during menstruation;
People who are deficient in vitamin K in the body;
Elderly people whose bodies experience age-related changes in the coagulating ability of the blood.
Before performing the analysis, the medical specialist questions the patient for the presence of these factors.
What factors influence the result?
In women, results may be slightly abnormal due to menstrual bleeding, use of oral contraceptives, or pregnancy. In such a situation, the doctor may consider the test reading to be normal.
Age also affects VSK. In children, due to the lack of certain substances in the body and the functioning of internal organs, the VSC is low, and this is normal. In older people, blood clots faster because it contains a lot of fibrinogen.
VSC also depends on diet and lifestyle. Fasting and deficiency of nutrients reduce coagulation, increase the likelihood of extensive bleeding and damage to the vascular walls.
Hobbies for extreme sports and physical injuries also have a bad effect on VSC.
Pathological changes in the norm
A decrease or increase in blood clotting rates is dangerous for a person at any age. A reduced clotting time according to Sukharev is accompanied by prolonged formation of a blood clot and an increase in the duration of bleeding. The following factors can provoke this condition:
Insufficient liver function caused by acute or chronic diseases;
Hereditary pathologies (hemophilia);
Plasma deficiency in the body;
Leukemia;
Decreased hemoglobin levels;
Development of DIC syndrome (disseminated intravascular coagulation)
Deficiency of vitamin K and calcium in the body.
Important! The danger of low blood coagulating ability is that even minor damage to soft tissue or parenchyma of internal organs can lead to the formation of prolonged and massive bleeding.
The opposite condition is hypercoagulability, which is characterized by accelerated blood clotting and blood clot formation. In the absence of timely treatment, this condition threatens to develop into thrombosis of arteries and veins. The following factors can provoke hypercoagulation:
Various food intoxications and intestinal infections;
Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
Increased platelet production;
Prolonged and massive bleeding in the postpartum and postoperative period;
Initial stage of DIC syndrome;
Acute and chronic diseases of internal organs.
Tests such as blood clotting according to Sukharev and coagulogram are carried out exclusively in medical diagnostic institutions and laboratories. The deciphering of the finished VSK results is carried out by the attending physician, whose competence includes prescribing appropriate therapy based on the results of normal or pathological conditions. In order to decipher normal or pathological clotting time, a special table is used.
conclusions
A blood coagulation test is a necessary condition for the timely detection of blood coagulation pathology (hemostasis disorders). This is especially true during preventive examinations, as well as during preparation for planned surgical interventions. Before you begin to determine your results, the following factors must be taken into account:
A decrease in the duration of blood clotting is a common consequence of massive bleeding;
Normal coagulation, as a rule, directly depends on the age of the patient. Older people tend to take longer to clot;
Coagulation indicators in the female body are prone to constant changes, which is due to the influence of the menstrual cycle on the functional state of the body.
You may also find articles on this topic useful:
The beginning of blood clotting in a healthy person is from 30 s to 2 minutes, the end is from 3 to 5 minutes. Blood is taken from a finger into a clean and dry capillary from the Panchenkov apparatus. The first drop of blood is removed with a swab, then a column of blood 25-30 mm high is drawn into the capillary and transferred to the middle of the capillary tube. Turn on the stopwatch and tilt the capillary at an angle of 30-45° every 30 s. Blood moves freely inside the capillary. As coagulation begins, its movement slows down. At the moment of complete coagulation, the blood stops moving.
Blood clotting time is an approximate indicator of a multi-step enzymatic process, as a result of which soluble fibrinogen is converted into insoluble fibrin. This indicator characterizes the coagulation process as a whole and does not make it possible to identify the mechanisms leading to its disruption. At the same time, blood clotting time can be shortened only as a result of accelerating the formation of blood prothrombinase (phase I of coagulation - increased contact activation, decreased level of anticoagulants). Therefore, a shortening of blood clotting time always indicates an increased formation of prothrombinase in the patient’s body. Due to the fact that blood prothrombinase, to enhance coagulation processes, is easily replaced by tissue prothrombinase, the formation of which is completed 2-4 times faster (in 1-2 minutes), a shortening of blood clotting time is often due to the appearance of tissue thromboplastin in the bloodstream due to mechanical damage tissues, burns, extensive operations, transfusion of incompatible blood, sepsis, vasculitis, etc. A shortening of clotting time indicates the need to prevent hypercoagulation, which often threatens thrombosis and thromboembolism.
Blood coagulation slows down significantly due to congenital or acquired deficiency of prothrombin-forming factors (primarily VIII, IX and XI), with an increase in the blood concentration of anticoagulants, as well as fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products (FDP). Pathological changes in blood clotting time according to Sukharev are reflected in the table.
Table Diseases and conditions accompanied by changes in blood clotting time
A blood test for coagulation rate according to Sukharev is performed to assess the plasma hemostasis factor.
The ability of blood to clot is an important protective function. Hemostasis includes the ability of blood to remain in a liquid state and the response to vascular damage in the form of stopping bleeding due to two parallel mechanisms: thrombus formation and blood clotting.
Blood collection process in laboratory
Sukharev's coagulation time is a determination of the period of time during which plasma fibrinogen, under the action of enzymes, polymerizes and precipitates in the form of an insoluble fibrin polymer. This test allows you to evaluate the dynamics of coagulation, but does not differentiate its mechanisms.
Time tests
Clotting time is included in the parameters of hemostasis. There are circumstances when it is necessary to know about this indicator, for example, during a certain period of life or during a person’s illness. Most often, studies are carried out by taking part of the blood.
The clotting period is divided into two stages:
- Primary hemostasis . At this time, to stop blood loss, vasoconstriction occurs and a blood clot is mechanically formed to prevent bleeding from the site of platelet damage.
- Secondary hemostasis is coagulation.
General recommendations for all analyzes include:
- Almost all tests are taken in the first half of the day, since over the next hours the indicators may change depending on nutrition, physical activity, etc.
- During the day before the test, food should be light, and 12 hours before going to the laboratory, eating is completely prohibited.
- You should not drink sugary drinks at this time. It is better to drink regular boiled water.
- You should definitely notify your doctor about taking medications.
It is very important to know over what period these two stages should normally occur. For this purpose, special analyzes are carried out.
The video explains how to determine blood clotting using a general analysis and at home:
According to Sukharev
For this test you do not need to donate blood from a vein. The sample is taken from a finger, since capillary biological fluid is sufficient. This test examines the amount of enzymes.
Attention! Thanks to blood testing according to Sukharev, doctors can learn about the body’s ability to withstand severe blood loss or other hemostasis disorders.
At the same time, the analysis gives a general picture of the state of the nervous and endocrine systems.
How the analysis is carried out:
- In the morning before the test, you cannot eat anything; the test itself involves taking blood in the morning.
- It is acceptable to drink ordinary water, but without gas.
- First, a puncture is made in the finger using a scarifier needle, and the required amount of plasma is squeezed out of it.
- To check the thickness of the blood, the laboratory technician begins to rock the test tube so that the liquid flows down the walls; depending on the time of flow, the result is recorded. That is, the time is recorded from the beginning of blood flow to the formation of a clot.
What results does Sukharev’s method give:
- If the clotting time is normal, then this indicates the absence of diseases associated with hemostasis.
- If clotting occurs in a short period of time, there is a risk of blood clots. An exception may be pregnancy, when rapid blood clotting is due to the protective functions of the body. A similar phenomenon can occur after taking contraceptive medications. This is also observed after childbirth, operations, heavy blood loss, extensive burns, and certain illnesses.
- If clotting does not occur for a long time, then the person loses a lot of blood, which affects his well-being and can be life-threatening. This happens due to various pathologies or while taking certain medications.
A normal analysis indicator is considered to be a clotting time in a healthy person of 3 to 5 minutes.
In childhood, this figure is slightly reduced and is 2-5 minutes.
In older people, for health reasons and some physiological changes in the body, the clotting time is reduced to 1.5-2 minutes , as the liquid becomes thicker.
The same indicators during pregnancy ( 1.5-2 minutes ). This is due to the fact that the body develops protective mechanisms to protect the growing fetus.
What is the essence of Sukharev’s method
This study is an important part of a complex of coagulogram tests, along with an analysis of fibrinogen, platelets, and prothrombin index.
Determination of blood clotting time (BCT) is a mandatory test before operations to prevent critical patient conditions associated with bleeding and thrombosis.
Coagulation tests are carried out for the following diseases:
- Pathologies of internal organs;
- Suspicion of hereditary hemostatic pathologies;
- Pregnancy;
- Thrombosis, varicose veins;
- Heart failure;
- Diabetes;
This analysis is also performed regularly during coagulant therapy.
Important! Pregnant women should undergo monthly monitoring coagulation tests.
Blood sampling for the Sukharev clotting test is performed from a finger. The device with which the test is carried out is a capillary from the Panchenkov apparatus kit.
After the puncture, the first drop of blood is removed with a cotton swab. Then a small amount of blood is drawn into the capillary (up to the 30 mm mark). Every half a minute it is tilted in different directions, moving the column of blood. Simultaneously, from the moment the blood is placed in the capillary for the blood clotting test according to Sukharev, a stopwatch starts. It is used to record the time when the blood has completely clotted.
Initially, the blood mass, which is in a liquid state, moves freely. With the beginning of the process of clot formation, its movement slows down, and by the time of complete coagulation the blood mass stops moving. The stopwatch data at this moment is the coagulation time according to Sukharev.
When does it become necessary to get tested?
In some situations, your doctor may strongly recommend a blood clotting test.
These may be the following reasons:
- If a young couple plans to get married and subsequently conceive a child. In this case, it is especially important to test for hemosyndrome or MCV.
- When the patient has autoimmune systemic diseases.
- In case of liver failure.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
- Before surgery, during a routine examination, a plasma coagulation test is taken. The analysis will also be needed after the operation.
- If a diagnosis of thrombophilia is made. This is a tendency to quickly form blood clots.
- Varicose veins.
- If a person often finds bruises on his body.
- If a person experiences prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction, surgery, or other injuries.
- For prolonged nasal, uterine or hemorrhoidal bleeding.
- If the causes of decreased immunity in a person have not been determined.
- If there is acute inflammation in the body.
Attention! Also, a coagulogram is indicated for newborn babies (to exclude congenital pathologies of hemostasis), women entering menopause, pregnant women, and all people over 40 years of age.
Preparation for Sukharev's test
If the blood sampling technology is broken, an inaccurate result may be obtained when determining coagulation. But such factors are a priori excluded.
Hemostasis subtly responds to the current state of the patient’s body. The dynamics of clotting changes depending on food intake, medications, and emotional state. It is these factors that can situationally change the results. Therefore, the patient should follow simple rules for preparing for the analysis:
- Within two days, switch to a liver-friendly diet (exclude fatty, fried, spicy foods, alcohol);
- Do not eat anything for 8 hours before the test;
- Refrain from smoking;
- Avoid stress and injury;
- Tell your doctor about all medications you are taking or have recently stopped taking.
Half an hour before testing clotting, you can drink a glass of plain water. During the collection of material, the patient must be calm. Excitement and rapid heartbeat (danger factor) trigger the production of prothrombinase.
Important! Difficulties often arise when preparing a child, since children in the laboratory experience severe emotional stress.
Clotting rate
Normally, the first clots become noticeable within 30 seconds from the start of manipulations with the capillary tube. Complete thickening occurs in 3-5 minutes.
Table of normal results of the coagulation test according to Sukharev
According to Sukharev, the norm for blood clotting in infants is lower (longer) than for adults. In children under one year of age, the liver function to produce fibrinogen is undeveloped, therefore the rate of blood clotting according to Sukharev is reduced. By the age of one year, coagulation indicators in tests are already close to the norm for an adult, but reaches full compliance only by the period of puberty.
Norm by age (table)
Today there are about 30 types of laboratory blood clotting tests. The material is taken from a vein or finger - depending on the study being performed, it allows you to determine the hemostasis of individual plasma units.
There is a different norm for adults and children. Each test uses its own calculation scheme.
Note! Platelets are the main components of blood, their quantity affects hemostasis. For adults, 150-400 g/l is considered normal, for children – 150-350 g/l.
Standards according to test type
To analyze coagulation by age, the Quick test is used.
Age standards according to Kwik's test
Reasons for deviations
A deviation in a blood test for coagulation in any direction from the norm indicates a violation of hemostasis and is a reason for an extended examination.
Accelerated blood clotting
The blood clotting time according to Sukharev is reduced as a result of the accelerated formation of coagulation factors (blood prothrombinase) in the patient’s body.
In the body, blood prothrombinase can be replaced by prothrombinase produced when tissue is damaged. Therefore, the acceleration of coagulation can be explained by existing tissue damage (after surgery, burns, vasculitis, tuberculosis) or be a normal condition with regular injuries (in athletes).
Important! High coagulability can be determined in people leading an active lifestyle associated with regular injury (extreme sports, heavy physical labor).
Fibrin strands clog the injury site
Shortening the clotting time requires prevention, as it threatens the appearance of blood clots, the development of thrombosis and thromboembolism.
Hypercoagulation is determined in the following diseases and conditions of the body:
- Liver pathologies;
- Poisoning;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Thrombophilia.
In women, clotting may be increased during long-term use of oral contraceptives.
Factors contributing to increased clotting may include:
- Radiation, cancer;
- Hyperfunction of the spleen;
- Dehydration of the body, decreased pH;
- Excessive consumption of sugar, carbohydrates;
- Excess weight, prolonged bed rest, sedentary work;
- Hormone replacement therapy.
Delayed blood clotting
This condition is characterized by prolonged bleeding and occurs as a result of:
- Congenital (hemophilia, von Willebrand disease) or acquired deficiency of factors involved in prothrombin formation (VIII, IX, XI);
- High concentrations of antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants (heparin, acetylsalicylic acid) in the blood;
- Leukemia;
- Thrombocytopenia;
- Impaired production of fibrinogen by the liver in cirrhosis, hepatitis;
- Lack of plasma as a result of acute blood loss with rapid replenishment of blood volume by infusion;
- Low hemoglobin, anemia;
- Lack of calcium, vitamin K.
Important! Slow coagulation in women during pregnancy is dangerous due to severe bleeding during childbirth.
To reduce the duration of coagulation, the patient is prescribed inhibitors of fibrinolysis and clot dissolution (aminocaproic acid, contrical), direct (fibrinogen, thrombin) and indirect (vitamin K, Vicasol) coagulants.
Often such patients are given a transfusion of plasma, which contains a complex of coagulation factors.
What is it and what does it affect?
Knowing the viscosity of a person's blood is important. With the help of clotting, the body protects itself, maintains the required blood volume, and prevents its loss.
Coagulability depends on the physicochemical actions of plasma at the molecular level:
- the main role is played by the protein fibrinogen;
- exposure to certain reactions turns into insoluble fibrin, which falls out in the form of very thin lines;
- a dense network of small cells is formed from the threads, in which the formed elements are retained;
- these changes form a blood clot. Gradually it thickens, the wound heals, heals;
- As the clot tightens, a yellowish liquid called serum is formed.
Platelets are a component of plasma that ensures the compaction of a blood clot.
To better understand the coagulation process, it can be compared to the conversion of milk into curd: the process of curdling of casein (milk protein) leads to the release of whey. Gradually the wound heals, the fibrin clot dissolves.
Interesting fact! The test is carried out before an upcoming surgical intervention, pregnancy, or the likelihood of large blood loss.
A blood clotting test is prescribed if the following is suspected:
- pathological liver damage;
- malfunction of the immune system;
- phlebeurysm.