Purpose of the survey
Ultrasound is prescribed for a reason. A doctor needs this procedure when a person comes to him with problems with the gastrointestinal tract. An ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone examines such organs as:
- liver;
- gallbladder with ducts;
- pancreas;
- spleen.
The last two organs do not belong to the hepatobiliary zone according to their location, but are included in this system according to the functional criterion.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone is prescribed to a person with the following symptoms:
- prolonged nausea, vomiting bile;
- disruption of food digestion;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- dark urine, light feces;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, feeling of fullness;
- presence of changes in blood biochemistry.
The examination helps to make a diagnosis, taking into account the tests. Ultrasound is used not only for primary diagnosis. Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone is annually prescribed to people who are registered with a gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist with various hepatitis, cirrhosis, and cholecystitis.
Diseases of the hepatobiliary system
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system can reveal the following pathologies:
- the presence of stones or “sand” in the gallbladder or ducts;
- kinks of the bile ducts;
- liver cirrhosis of any stage;
- fatty liver hepatosis of any etiology;
- damage to liver hepatocytes due to hepatitis (infectious and non-infectious);
- acute poisoning with organic and inorganic substances;
- oncological processes, the appearance of atypical hepatocytes.
In general, ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is included in ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which is recommended for everyone to do at least occasionally for health monitoring. A special ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder can provide a more detailed picture. When is it important to conduct such research? So:
- chronic, persistent pain in the right hypochondrium;
- chronic yellowness of the whites of the eyes and skin;
- chronic digestive disorders;
- persistent, chronic changes in the biochemical blood test - for example, alkaline phosphatase is greatly increased (problems with the bladder and ducts), total protein is greatly reduced (problems with the liver), etc.;
- chronic fatigue syndrome, constant ailments, discomfort in the abdominal region, in the right hypochondrium;
- the patient’s condition noticeably worsens after eating excessively fatty foods;
- upon palpation, the liver is determined to be enlarged, with abnormally shifted edges.
It is especially important when several symptoms occur simultaneously. Separately, there are those patients who have already been diagnosed with some kind of pathology that affects the hepatobiliary system: hepatitis, hepatosis, gallstones, etc. In any case, such patients are recommended to be examined at least once a year. Similarly, it is worth monitoring the health of the liver if the patient takes medications for a long time that have a toxic effect on the body (for example, Sulfasalazine).
And of course, such an ultrasound is needed for those who have suffered a mechanical injury (meaning the liver area) or a chemical nature (the entry of toxic substances into the body will inevitably “hit” the liver). With extensive, severe burns, the liver may also be damaged.
How to prepare for an ultrasound
Preparation for ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system reduces the risk of distorted results. Ultrasound does not travel well through air, so it is important that there are no gases in the intestines. Food and feces also negatively affect the result.
The preparatory stage according to the standards takes three days. All this time you will need to follow a diet. Its purpose is to clear the intestines of gas and feces, and prevent flatulence or constipation. Removed from the diet:
- fatty meat, lard;
- peas, beans, beans;
- black bread;
- baked goods;
- mushrooms.
For three days before the ultrasound, you can eat chicken soup, buckwheat porridge, baked vegetables or fruits, and crackers. On the eve of the ultrasound, you can eat and drink, but no later than 12 hours before the procedure. If it is scheduled for 8 am, dinner is no later than 8 pm. A person comes to the ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone on an empty stomach.
If you can’t cope with flatulence or constipation with diet alone, use medications:
- “Espumizan” - carminative;
- Duphalac is a laxative;
- “Mezim” is an enzyme.
Medicines are taken the day before the test; they normalize intestinal motility and cleanse it.
Watch the video on how to prepare for an ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system:
Preparation and performance of ultrasound
Unlike ultrasound of other organs and systems, ultrasound of the GBS organs requires some special preparation from the patient. In order for the study indicators to be reliable, the following points must be completed:
- The study is carried out only on an empty stomach. After the previous meal, at least 6-8 hours should pass. That is, the ideal option would be to conduct the study in the morning, on an empty stomach. If the patient has diabetes, a light breakfast is allowed.
- Before such a diagnosis, you need to follow a certain diet for several days. Beans, milk, black breads, raw vegetables are completely excluded from the diet - that is, all those foods that can cause bloating and increased gas formation.
- It is recommended to take drugs such as activated carbon (or its analogues), enzyme preparations - mezim, festal. This will help further prepare the organs for examination.
For urgent indications, ultrasound examination can be performed without preparation.
The ultrasound takes approximately 30-35 minutes. During this examination, the patient can be in different positions - lying on his back, on his side, standing - depending on what exactly is being examined at the moment.
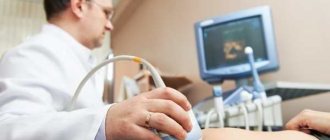
A conductive gel is used that allows ultrasound to better penetrate deep into the body.
The research is carried out in real time, and the results are delivered immediately.
Modern devices used to conduct ultrasound examinations reflect the state of all systems so accurately that it is almost impossible to make a mistake in making a diagnosis in this case. In controversial cases, additional studies may be prescribed, for example, MRI, computed tomography.
Technique
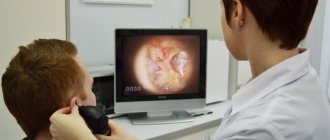
Ultrasound examination compares favorably with other manipulations in its simplicity and painlessness. The person is asked to lie down on the couch and take off his upper part of his clothes. A hypoallergenic gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen, which increases the speed of ultrasound. Using a sensor, the doctor examines the necessary organs of the hepatobiliary system, all parameters are immediately read by a computer and displayed on the screen.
In children, examination of the hepatobiliary system is carried out in the same way. It is recommended to first explain to the child that there is nothing to be afraid of, the manipulation is painless. Very young children are examined in the presence of their mother.
Examination of the gallbladder takes place in two stages. First, a routine examination of the entire system is performed, then the person is given a choleretic breakfast. Usually this is chicken yolk or a glass of sour cream. For an hour, every 15 minutes, the doctor examines the bladder, its peristalsis and fullness.
Watch the video to see how the hepatobiliary system looks on the monitor:
uziprosto.ru
When diagnosing abdominal diseases, especially in pediatric practice, preference is given to painless, informative, safe methods. Ultrasound diagnostics meets all these requirements.
Its widespread use is also due to its low cost and availability. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity allows one to diagnose space-occupying lesions and diffuse changes with high accuracy and specificity, comparable to MRI.
The hepatobiliary system includes several abdominal organs, namely the liver, gallbladder, and intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts. The function of this system is the formation, storage, and transportation of bile. Pathological changes are possible at any stage of the synthesis and movement of bile. The reasons underlying these diseases can be both organic and functional in nature.
Indications for prescribing ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system:
- jaundice
- pain in the right hypochondrium
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, belching, change in stool color)
- dynamic observation of chronic hepatitis
- developmental anomalies
- cholelithiasis
- hepatomegaly
Signs of jaundice
The method has no contraindications, however, the child’s anxiety can significantly complicate the research or make it impossible.
Preparation for ultrasound examination.
Before ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system, careful preparation is important, which should begin no later than 3 days before the study. The main goal is to reduce intestinal pneumatization to increase the imaging window. To do this, follow a low-carb diet. Before the study, the following are excluded or limited as much as possible: raw fruits and vegetables, baked goods, carbonated drinks, alcohol, dairy products, fatty meats.
Enterosorbents are prescribed in age-specific dosages, but only in cases of increased gas formation. In this case, it is possible to perform a cleansing enema on the evening before the study. The last meal should be taken no later than 6 hours before the test. During this period, drinking is also limited. A long food pause not only improves visualization, but also allows you to assess the true size of the gallbladder during an ultrasound.
In older children, the study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach and the preparation is similar to that in adults, however, enterosorbents and cleansing enemas are used very rarely in pediatric practice. Sometimes children are asked not to brush their teeth in the morning before the test, this is due to the fact that children often swallow toothpaste.
Difficulties arise when preparing young children and infants. It is impossible for them to maintain a food break of 6 hours, so the study is carried out before feeding with a minimum interval between feedings of 3 hours. It is recommended to limit drinking an hour before the ultrasound examination. If a child has a bloated abdomen or is bothered by intestinal colic, it is possible to use simethicone preparations in age-specific dosages on the eve of the study.
An important stage in the preparation of young children is psychological preparation and explanation of the essence of the study. The child must be clearly told what will be done to him and that it will not hurt; if necessary, take a toy or book with him to distract the child during the examination.
Carrying out ultrasound examination.
Like the examination of other abdominal organs, the examination of the hepatobiliary system is performed while lying on the back. If necessary, the examination can be performed lying on the left side or standing. Older children may, at the doctor's request, hold their breath, which is sometimes necessary for better visualization of the extrahepatic bile ducts. In infants, the examination can be carried out in the mother's arms and during sleep, which will allow a more detailed examination to be carried out in a calm environment.
Study of gallbladder function.
This method allows you to diagnose disorders of one of the most important organs of the abdominal cavity: the gallbladder, as well as the formation of bile and its movement. This is especially true in pediatric practice, when functional disorders in the form of gallbladder dyskinesia are common.
Ultrasound examination is carried out in two stages. The first stage is similar to a regular study, the second is carried out after a food load. If the initial volume of the gallbladder was less than 8 ml, the choleretic breakfast should be one chicken yolk or 120-150 grams of full-fat yogurt. If the gallbladder volume is more than 8 ml, the volume of breakfast is twice as large. Dynamic monitoring of gallbladder contraction is carried out every 15 minutes for an hour. The maximum contraction (minimum volume of the gallbladder) should normally occur at 30 minutes.
Research results.
Liver pathology.
Pathology in children has its own characteristics. The main detectable changes in the liver are hepatomegaly, as well as cystic formations. Tumor formations are extremely rare. Anomalies of liver development are also rare, the bulk of them are made up of additional lobules located next to the organ in the abdominal cavity, and also having a parenchymal pedicle with it.
Hepatomegaly can be due to acute viral infections (usually rotavirus and enterovirus), as well as hereditary syndromes, including metabolic diseases. Almost always, liver enlargement is accompanied by a change in its echogenicity. The change may be focal or diffuse. Focal changes are observed in disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, diffuse in hepatitis, systemic diseases.
Cystic liver formations are the most common ultrasound finding in pediatric practice. Cysts can be congenital or acquired. Congenital cysts can be single or multiple (polycystic). Single cysts require frequent monitoring, as they are prone to rapid growth and destruction of the liver parenchyma. Multiple cysts often affect several parenchymal organs. Despite the high compensatory capabilities of the liver, liver failure in a child develops quickly. A type of polycystic disease is fibropolycystic disease, which is characterized by a powerful proliferation of connective tissue in the structure of the liver. Children of preschool and primary school age are more susceptible to echinococcal infection. Ultrasound examination visualizes hydatid cysts as an anechoic formation with a clear capsule and internal daughter cysts.
Pathology of the gallbladder, bile ducts.
The bulk of the pathology detected in pediatric practice consists of abnormal forms of the gallbladder (S-shaped, hourglass-shaped, “Phrygian cap”) and constrictions in the cavity of the gallbladder. Overdiagnosis of these anomalies is now common. This is due to the presence of functional kinks and folds, especially with an incomplete gallbladder.
Abnormal forms of the gallbladder
To exclude the functional nature of the changes, a polypositional examination (standing, lying on the left side) is important. When the position changes, the functional kinks and constrictions disappear. True constrictions and abnormal forms of the bladder can be congenital or acquired as a result of inflammatory processes. More rare anomalies are duplication of the gallbladder, its aplasia, and diverticula.
Chocystitis is a rare pathology in pediatrics. Ultrasound signs are thickening of the walls of the gallbladder, their layering, changes in the shape of the gallbladder and the appearance of sediment in its cavity. Risk factors for inflammatory processes in the gallbladder are abnormal shapes, constrictions, and cholelithiasis. Stones, as a rule, are visualized as hyperechoic formations of various shapes of small size with dorsal enhancement, displaced when changing body position.
Cholecystitis on ultrasound
In almost every child, a small amount of loose sediment is detected in the lumen of the gallbladder, which occurs due to the concentration of bile. When a large amount of sediment accumulates and its density increases, dyscholia develops. This condition is initially not a pathology, but with further development it causes blockage of the bile ducts, and as a result leads to obstructive jaundice.
Congenital pathologies of the bile ducts include atresia and cystic anomalies . These anomalies can be either intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts. Diagnosis is often difficult, but a bright clinic helps identify these defects at an early age.
Compaction of the walls of the bile ducts may be due to dyskinesia (impaired outflow of bile) or inflammatory nature. Isolated cholangitis is rare; more often the entire organ complex is involved in the process. Dyskinesia is the most common pathology of the hepatobiliary system in children, which is accompanied by a number of dyspeptic manifestations. The ultrasound picture includes: thickening of the walls of the bile ducts and gallbladder, enlargement of the liver, changes in the structure of the liver.
For further tactics of managing these patients, it is important to determine the type of dyskinesia, which is determined as a result of a functional test. If, 30 minutes after a choleretic breakfast, the gallbladder contracted by more than 65% compared to the original, then we are talking about the hyperkinetic type. And if the gallbladder is reduced by less than 25%, then this is a hypokinetic type of dyskinesia.
Further tactics
The result of the ultrasound examination should be assessed by the doctor who referred for the examination (pediatrician or gastroenterologist). They are the ones who decide whether a repeat study is necessary and after what period of time.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system in combination with determining the function of the gallbladder provides enough information to the attending physician to determine further tactics for patient management. The use of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, as well as MRI and CT, occurs in severe clinical cases when the results of ultrasound, in combination with the clinical picture and test results, do not confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Obtained results
Since ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is usually prescribed in the presence of complaints, the results reveal changes characteristic of diseases. The doctor issues a normal conclusion if a person was examined by this system not for health reasons, but during employment or for military service.
Norm
Normal criteria for the hepatobiliary system include:
- organ sizes corresponding to age;
- acceptable level of tissue density - the liver is the standard for comparison;
- homogeneous structure;
- good contractility of the gallbladder;
- absence of foreign inclusions, cysts, tumors;
- the size of the portal vein is no more than 13 mm.
An indicator of the health of the hepatobiliary zone is compliance with all specified criteria. Mild diffuse changes in the liver are also allowed.
Liver diseases
Ultrasound can detect any disease of the liver system.
- Hepatitis. The inflammatory process is determined by an increase in the size of the liver - hepatomegaly. Diffuse tissue changes of varying severity are visible. Moderate hepatomegaly of the liver in a child under 5 years of age is normal.
- Cirrhosis. Destruction of hepatocytes and the appearance of scars in their place. The liver tissue becomes denser, the size of the organ decreases.
- Cysts. Parasitic or gall. They are represented by a round formation that does not reflect ultrasound.
- Tumor. Benign ones have clear contours and a capsule around them. Malignant ones look vague, there is no capsule.
Sometimes a computed tomography scan is required to clarify the diagnosis using this system.
Gallbladder diseases
Ultrasound evaluates the anatomy and function of the gallbladder.
- Cholecystitis. Non-calculous - simple inflammation of the organ wall, represented by its thickening. Calculous - stones are found that look like very dense round formations.
- Polyp. The growth of the bladder wall looks like a protrusion into the cavity and has an increased density.
- Bubble bend. A change from its normal pear-shaped shape, it becomes like an hourglass.
Bladder tumors are identical to those of the liver.
Pathology video
Watch the video where the pathologies of the hepatobiliary system are clearly shown:
Liver
The anatomy of the hepatobiliary system considers the liver not only as the central organ of bile formation, but also as the most important human organ. It is here that most of the body’s energy is formed, because 20% of the mass of the cells that make up the liver is occupied by mitochondria that synthesize ATP. The liver is the largest gland in the human body, which ensures the constancy of the internal environment of the body. It plays a central role in protein, fat and carbon metabolism, as well as in the metabolism of medicinal substances. The liver is one of the few organs that are constantly exposed to severe stress, but at the same time are able to recover independently in a short time. In the body it performs the following functions:
- bile formation and bile excretion;
- metabolic - in addition to the fact that the synthesis of many substances (proteins, cholesterol, glycogen, urea) necessary for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract occurs here, the liver regulates water metabolism and the metabolism of amino acids and proteins, carbohydrates, fats and biologically active substances;
- storage - the liver is a kind of storeroom where proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, hormones, and minerals accumulate;
- barrier - here foreign and toxic compounds that enter the body with food or formed in the intestines are neutralized;
- excretory - the liver is capable of removing toxic substances that enter it into bile, which, due to its composition, removes them from the body;
- homeostatic - synthesis, accumulation and breakdown of blood plasma components, in particular immunoglobulins and components of the coagulation system, occur in the liver.
Possible contraindications
Ultrasound examination of any body system is safe. It is allowed for newborns, pregnant women, and the elderly. But contraindications still exist - these are conditions that will interfere with the reliability of the procedure. These include:
- damage or inflammation of the skin of the abdomen;
- pronounced flatulence;
- state of alcohol or drug intoxication;
- psychosis.
After eliminating these conditions, a study of the liver system is carried out.
Directions written in the direction of the ultrasound
Many patients, receiving a referral from a doctor for an ultrasound examination, wonder whether they need to follow all the preparation recommendations written on the paper. And it says something like this:
- two days before the procedure, avoid fatty foods and alcohol;
- two days before the procedure, exclude foods that contribute to gas formation - butter (especially flour products with an abundance of yeast), raw vegetables/fruits/berries (after heat treatment it is possible, but dried fruit compote is still undesirable, because it still increases gas production in the intestines), fermented drinks (kvass, kefir), legumes, any soda;
- during meals, take pancreatin drugs Mezim, Festal, Creon, and after meals - drugs against flatulence and gas pollution (Espumizan, Motilium, Smecta);
- in the evening the day before the study, a lean but hearty dinner (such as porridge, but without butter) is recommended; 12 hours before the procedure, abstain from food altogether;
- on the eve of the ultrasound (in the evening or in the morning), you should empty your bowels (if you can’t do it on your own, you can resort to a mild laxative, for example, Duphalac);
- if the ultrasound is in the morning, then you can’t have breakfast, if later, let’s say a light, lean breakfast;
- 2 hours before the ultrasound you should not drink liquid;
- on the day of the study, until it is carried out, you must refrain from smoking.
Cost of the procedure
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is a common technique. It is available to public hospitals and private centers. The cost is determined by the region of residence.
Price table for ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system.
| City | Price |
| Moscow | 480-1000 rubles |
| Saint Petersburg | 350-1100 rubles |
| Ekaterinburg | 500-1500 rubles |
| Novosibirsk | 450-1200 rubles |
| average cost | 445-1225 rubles |
Ultrasound examination of the liver system, gall bladder, ducts of adults and children is aimed at primary diagnosis or control of existing diseases. The procedure is safe, painless, and requires preparation. It is carried out taking into account indications in public hospitals or private centers.
Leave comments on the article and share your opinion. Tell your friends about what you read on social networks. All the best.
Functions of the hepatobiliary system
The hepatobiliary system is represented by 3 organs: the liver, gallbladder and bile duct system. This system performs a huge range of functions in the body, which can be combined into two main ones - digestion and detoxification. Hepatocytes, the main cells of the liver, making up almost 80% of its mass, synthesize bile - a mixture of bile acids (primarily cholic and chenodeoxycholic), high-density lipoproteins (“good” cholesterol), phospholipids, immunoglobulins A and M, bilirubin, mucus and microelements.
It is the synthesis of bile by the liver that realizes its digestive function. Bile is an emulsifier of fats (it transforms them into an emulsion, a finely dispersed state, since lipids are absorbed only in the form of small drops). Bile helps hydrolyze proteins and carbohydrates. Without bile, fat-soluble vitamins cannot be absorbed. Bile largely controls the secretory and motor functions of the intestine, especially the small intestine. Well, there’s nothing to say about detoxification. The metabolism of all chemicals entering the body occurs through the liver.
Interpretation of ultrasound
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system is performed in the same way for children and adults, but the results are different for everyone. Each organ of the GBS is examined by ultrasound for the presence of certain abnormalities. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
- In the liver, they look for possible foci of inflammation, benign formations, and hyperplasia. Diffuse changes can be detected - hepatitis, cirrhosis, etc.
- Stones, abnormal structure of the bile ducts, the bladder itself, and oncological formations are visualized in the gallbladder.
- Inflammation, congenital anomalies, pancreatitis, tumors, and fatty infiltration can be found in the pancreas.
- The spleen is diagnosed for its enlargement during the inflammatory process and the presence of tumors.
- Blood clots may be found in the vessels. The general condition of the blood is also assessed.
The organs of the GBS perform a vital function in the human body. Remember this and be healthy!
GBS organs
The complex system already known to us consists of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts. Its main task is to create and transport bile, which in turn is a product of the liver. The gallbladder, figuratively speaking, is an additional or reserve reservoir. The bile flows through the ducts to it. It is known that its concentration in the gallbladder is 5-10 times higher than in the liver.
After a person has eaten, bile flows into the duodenum through a small lumen. It is worth adding that in addition to the organs mentioned above, the hepatobiliary system also consists of the intrahepatic bile ducts, which are located in the liver itself. They are different along their entire length: they begin as tiny capillaries, and then turn into large bile ducts that extend beyond the boundaries of the liver itself. There are also extrahepatic bile ducts in the human body.