Anatomy of the knee joint and the causes of its pathology
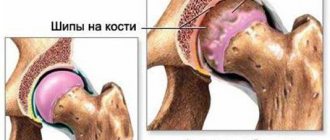
So, according to the anatomical and physiological classification, the knee joint is a biaxial condylar joint. It is formed by the distal end (condyles) of the femur and the lateral edge (condyles) of the tibia, as well as the patella. The condyles are covered with cartilaginous tissue, and between them there are menisci (lateral and medial), also consisting of cartilaginous tissue. Their function is to bring the articular surfaces of the bones closer together and cushion the joint during physical activity (walking, running, etc.). A fibrous capsule is attached to the ends of the femur and tibia, which are the lateral walls of the joint. The elements of the joint are strengthened by ligaments.
All diseases of the knee joint arise as a result of metabolic disorders, traumatic injuries or inflammatory processes. The following signs are the provoking factors for the development of diseases:
- excess weight;
- playing sports;
- accompanying illnesses;
- inactive lifestyle;
- hereditary predisposition;
- old age.
In 1912, at the Congress of Surgeons in Berlin, the Danish doctor Severin Nordentoft gave a report on endoscopy, which, among other things, talked about such a procedure as knee arthroscopy. He spoke about his personal experience in performing manipulation and its significance in the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the knee joint. This was the first mention of a method of diagnosis and treatment that is so popular today.
Currently, with the help of arthroscopy, it is possible to perform surgical treatment for many indications on the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee and ankle joints.
For diagnostic purposes, arthroscopy is prescribed if other research methods have not helped to establish the cause of pathological manifestations in the patient’s joint area.
The essence of the procedure
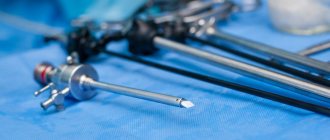
The arthroscopy procedure is performed using an endoscopic device - an arthroscope. Refers to invasive procedures, since this violates the integrity of the skin.
in case of injury, blood is found in the joint capsule, ligament ruptures, damage to the joint capsule; with arthrosis, you can see altered cartilage and articular surfaces of bones; with arthritis, fluid is found in the joint capsule, pus, and signs of inflammation.
Arthroscopy can only be performed in a hospital setting or a clinic treatment room. After completing the manipulations, an aseptic bandage is applied to the knee, and the patient is advised to rest for several days. A specialist will tell you more about the procedure in the video in this article.
We invite you to read: Postoperative rehabilitation treatment of the shoulder joint
What is arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory process in the joint cavity. It can occur for various reasons - infection, consequences of injury, surgical interventions.
With arthritis, the knee becomes swollen and red
Arthritis manifests itself as joint pain and dysfunction. Without appropriate treatment, the disease can lead to disability.
Contraindications for arthroscopy
- High risk of complications after anesthesia. In this case, it is necessary to choose a different type of anesthesia or examination/treatment method.
- Unstable condition of the patient. To solve this problem, preliminary stabilization of the patient's condition is required.
- The presence of acute or exacerbation of chronic diseases. In this case, preliminary drug treatment is required.
- Ankylosis (bone or fibrous) of the joint.
- Purulent processes in the intended area of manipulation.
- Extensive hemorrhage into the joint cavity.
- Violation of the integrity of the joint capsule.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Tuberculosis of bones.
- Period of menstruation.
What will happen at home after discharge?
The rehabilitation period after standard intervention will last at least another three weeks. If the arthroscopic operation was serious and lengthy, accompanied by complications, then the joint may take 1.5–2 months to heal after removal of the destroyed elements and arthroplasty. In this case, complete recovery occurs in 4–6 months. Throughout this period, the patient must not only follow all medical recommendations, but also regularly come for a medical examination to monitor rehabilitation therapy.
To avoid accidental overload on the operated joint, the patient will have to master crutches
What should the patient do to speed up this process as much as possible, but without harming his health:
- from the very first day after discharge, regularly perform the exercises recommended for developing the knee joint;
- do not shorten the exercises on your own: if during training the joints begin to hurt, discomfort occurs, you should contact the instructor, he will adjust the set of exercises and check that they are performed correctly;
- learn to walk correctly. Yes, this process will have to be relearned. When and what kind of loads are allowed to be applied to the leg depends on the type of intervention. After meniscectomy, you are allowed to stand on your leg on the second day after surgery. But during the first week you should use crutches or a cane when walking. After ACL, you will have to use crutches for at least three weeks. In the first days, they walk on crutches without putting any weight on the leg. Then the foot is lowered to the floor. And after a few more days, they gradually begin to transfer body weight to the limb. Any pain or discomfort indicates that the load needs to be reduced and returned to the previous stage;
- after plastic surgery of the cruciate ligament, the joint is fixed with a hinged orthosis for four weeks;
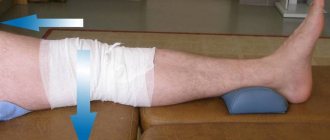
- after arstroscopy of the meniscus, you need to wear an elastic bandage or a special orthopedic knee brace for the same period;
- daily or every other day it is necessary to carry out lymphatic drainage, stimulating massage of the limb.
Gymnastics after arthroscopy in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures will significantly speed up the restoration of joint function.
A course of physical therapy can shorten the recovery period by several weeks.
What not to do:
- Only a doctor can remove bandages, plaster or stitches and staples from wounds yourself.
- Take a hot bath, visit a sauna or steam bath, public swimming pools.
- Freeze.
- Lift weights.
- Run, jump, actively squat and engage in sports related to such movements.
- Wear high heels.
- Give the joint heavy loads, stay in a standing position for a long time.
Anesthesia
During the arthroscopy procedure, the following types of anesthesia are used:
- Local: due to short-term action and unpleasant sensations during manipulation, it is rarely used.
- Conduction: anesthesia of certain nerves, its duration is up to one and a half hours.
- Epidural: with this anesthesia, the patient does not feel his legs and the surgeons’ manipulations. During the operation, the patient does not sleep, so contact with him is not difficult. If necessary, anesthesia can be prolonged after the end of the operation. Anesthesiologist required.
- General anesthesia: the patient spends the entire operation in a sleeping state. Anesthesiologist required.
Features of the operation
This manipulation occurs with minimal pain, and the wound that remains after insertion of the arthroscope heals within two to three days. Restoring joint mobility takes from two weeks to several months. After discharge from the hospital, the patient receives from his attending physician a whole list of recommendations aimed at the fastest and most complete recovery.
The length of hospitalization for this operation depends on the existing pathology of the knee joint. The inpatient stage of treatment usually takes from several hours to several days; if arthroscopic plasty of the cruciate ligaments is performed, it can be extended to three to five days.
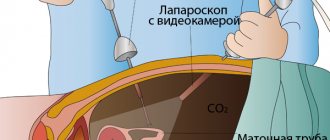
Progress of manipulation
The patient is in the supine position with the shins down and the knees bent at an angle of 90 degrees.
After anesthesia, a tourniquet is applied to the leg to stop blood circulation in the limb. Then the knee and thigh are fixed with special stops in a certain position.
A metal light guide with a camera is inserted through small punctures in the knee joint. It allows surgeons to examine the joint tissue in detail through a small hole and, if necessary, perform manipulations through additional incisions.
The arthroscope is equipped with special instruments for performing endoscopic surgical interventions: stitching, resection, removal, vaporization, taking material for biopsy, etc.
After completing the necessary steps, the wounds (their size is about 5 mm) are covered with a sterile bandage.
General rules for conducting classes
For therapeutic exercises after knee arthroscopy to be effective, the following recommendations must be followed:
- The exercises must be performed daily at least 3 times in sets of 25-30 minutes;
- The load should be increased gradually;
- The occurrence of mild discomfort and mild aching pain after training is normal;
- During classes, you must wear a knee brace, an elastic bandage or a specially selected orthosis by a doctor;
- The set of exercises should be completed by lightly stroking the kneecaps, thighs and shins;
- After exercise therapy, it is recommended to lie on your back for 20-30 minutes, placing a cushion or rolled blanket under your feet.
On a note!
If your general health worsens, your temperature rises, severe swelling develops, and your pain increases sharply, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Complications of arthroscopy
Complications rarely occur when manipulation is performed by specialists (surgeons with experience in endoscopy) using good equipment and in conditions that meet the standards. Still, it’s worth knowing about the possible risks. These include:
- infection (wound suppuration, persecution, empyema, sepsis);
- damage to joint elements during manipulation;
- failure of arthroscope instruments with loss of elements into the joint cavity;
- the occurrence of case syndrome;
- thrombosis, thromboembolism;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- complications associated with anesthesia: sudden cardiac arrest, anaphylactic shock.
In order to avoid complications, it is necessary to identify possible risks for each individual patient. For this purpose, comprehensive diagnostics of the body and drug preparation are practiced. Arthroscopy should only be performed by a professional.
Postoperative period - what will happen in the first 2-3 days
Arthroscopy is an umbrella term that can be used to describe a wide variety of operations. Arthroscopy can be diagnostic, surgical, or sanative. How long the recovery after knee arthroscopy will take depends on what specific measures were performed. For example, if it was necessary to simply examine the joint cavity and take a puncture, the patient will be able to return home within 15 hours after the intervention. But if resection of the meniscus arthroplasty or PCL was performed, you will have to stay in the hospital for 2-3 days.
What will happen during this period of time?
We also recommend reading:
Diagnostic arthroscopy
- Immediately after the operation is completed, the doctor will inject a drug into the joint cavity that relieves swelling, prevents inflammation and protects cartilage tissue. Usually this is Fermatron. To quickly restore joint structures after arthroscopy, it is recommended to administer it four times at intervals of seven days.
- Additionally, painkillers, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial agents can be administered intravenously - this is done to prevent infection of wounds and joint cavity, and to relieve pain.
- To prevent blood clots, anticoagulants are administered. They are recommended to continue to be administered intravenously for another 7 days.
- Then the punctures are sutured and covered with a sterile bandage. If indicated, the joint can be additionally immobilized with a plaster splint.
- Next, the patient is transported to the recovery room, where he will remain for two to three hours until the anesthesia wears off completely.
- It is recommended to place a cushion or pillow under the leg so that it is in an elevated position - this will reduce blood flow and swelling of the limb. In the first 15 hours after surgery, the joint needs complete rest. It is allowed to apply ice to the knee every hour - this also reduces pain and swelling.
- If plastic surgery of the cruciate ligament was performed, the joint is fixed with a special orthosis on hinges in a bent state at an angle of 20 degrees.
- On the second day, physical activity increases. The patient must get up and walk around the room, and begin to do exercises. First, the doctor will examine the leg, remove the plaster splint, and remove the bandage. Punctures are treated with an antiseptic and sealed with a band-aid. Exercise therapy at this stage of recovery consists of tensing and relaxing the muscles of the limb. Loads are still contraindicated.
- The next day, they begin to perform a gentle massage of the limb, and a set of exercises is developed for home physical therapy exercises.
- The wounds usually heal by this time, and the patient can go home. To prevent embolism and thrombosis, the doctor will recommend using an elastic bandage or compression stocking.
On the first day, a heating pad with ice is applied to the operated knee every hour to reduce pain and swelling.
Important! If the rules of preparation for surgery are not followed or the technique of performing it is violated, various complications and side effects may occur. If the patient is discharged from the hospital under his own responsibility before the 3 recommended days have passed, it is important to carefully monitor the condition of the leg and general well-being at home. If even innocent, at first glance, atypical symptoms occur, you should immediately return to the clinic.
Phases of rehabilitation after knee arthroscopy
Early recovery period
This phase lasts from the end of the manipulation until the removal of the drainage. At this stage, it is necessary to use local cryotherapy, applying a heating pad with ice or a special bag to the knee for 30-40 minutes. In order to prevent complications from the vascular bed, it is necessary to perform elastic bandaging of the limb or use compression stockings. In some cases, surgeons recommend wearing a rigid orthosis or splint.
In the first days after surgery, it is necessary to spare the limb and give it an elevated position.
Gymnastics in the starting position lying on your back:
- ideomotor exercises performed mentally;
- tension and contraction of the quadriceps femoris and buttocks;
- straight leg raise;
- performing movements in the ankle joint.
After receiving permission from doctors, i.e. in the absence of contraindications, you can begin to exercise in a standing position.
In case of capsular ligament surgery, joint immobilization is required for 2 weeks. This period is equated to the first stage of rehabilitation.
Early healing stage
At this stage, passive movements in the knee joint with a small amplitude are added to the above exercises (same position) (with the heel not lifting off the surface), then the amplitude is increased. During this period, exercises are added to keep the muscles in a contracted state and they move on to the use of mechanotherapy (an exercise bike) without introducing additional load.
If there are no contraindications, you can go swimming and hiking without getting tired.
If swelling occurs, the doctor will prescribe a drainage massage.
Late healing stage (10-14 days)
Exercises on a stationary bike with a load are added, as well as cycling and resistance exercises.
Recovery stage
Various exercises can be performed, but active sports are still contraindicated.
One month after arthroscopy, in the absence of contraindications, the patient is allowed to walk in an orthosis with full weight bearing on the operated leg. At this stage, it is necessary to strengthen the muscles of the thighs and buttocks.
During the second month, the patient is allowed to perform functional exercises aimed at using several muscle groups to increase strength, endurance and range of motion, as well as adding weights (strength training) and pulley machines.
At the end of the second month, in the absence of contraindications, free movement, balance and coordination exercises are allowed.
Until the joint is completely restored, twisting, sudden and high-amplitude movements are absolutely contraindicated.
Initial stage (3-7 days after arthroscopy)
Consists of the following exercises:
- While in a supine position, bend your knees until they are completely pain-free. As soon as an unpleasant sensation appears, stop the action. The heels are pressed firmly against the plane on which you are lying. In this position, strain the back muscles of your thighs as much as possible for 5 seconds – 10 repetitions.
- Lying on your stomach, place your feet on a small, firm cushion. Straighten the leg with the sore knee so that it presses down on the roller. It is the front muscles of the thigh that should be tensed, not the lower leg. Hold your leg straight for 5 seconds in 10 sets.
- Lying on your back, bend your healthy knee and straighten your affected leg. Tightening the front muscles of your thigh, lift your leg very slowly, not very high, pointing your toes towards you. Hold in this position for 5 seconds – 10 repetitions.
- Stand against a wall so you can use your hands to secure yourself. Standing on your healthy leg, lift the patient in a straight position at 45 degrees and hold it at the top for 5 seconds - 10 approaches. The foot should be straight.
- Repeat the previous exercise, but turning your foot outward from you.
When to go?
The question of when to start walking is decided strictly individually, depending on the underlying disease. Thus, after meniscectomy, measured walking with the support of crutches or a cane is allowed already on the first day.
Deadlines
As a rule, 2 weeks after arthroscopy, patients can walk without relying on crutches. The appearance of pain should not be expected.
All time frames for patients to return to their normal rhythm of life are absolutely individual in each specific case and depend on many factors. Referring to statistics, we can provide the following data:
- Patients whose lifestyle before the manipulation was active, who were involved in heavy physical labor and sports, can return to the workplace after a month. Athletes are allowed to take part in competitions again no earlier than 2 months after arthroscopy.
- Patients whose professional activities do not involve heavy physical labor will be able to lead a normal lifestyle within 2 weeks.
Patient Reminder
So, arthroscopy of the knee joint is over, early recovery after the operation was “excellent”, the attending physician’s feedback on the treatment was positive. If the clinical picture is satisfactory, you will be released from the hospital with outpatient treatment. Upon returning home, in order to avoid complications, you will need to strictly adhere to all instructions and recommendations given by the orthopedic surgeon.
- During the first week, it is necessary, as already noted, for the leg to be positioned as elevated as possible in order to reduce swelling.
- Do not get the surgical suture wet; make sure it remains dry and clean. The question of taking water procedures should be agreed with a specialist.
- The patient needs to see a doctor every two days for 7-12 days for aseptic treatment and dressings. It is possible that if an accumulation of effusion is detected in the joint, during control visits it will be evacuated using a puncture. The stitches are removed no earlier than after a week.
- Vascular, analgesic medications and chondroprotectors should continue to be taken according to the regimen developed by the surgeon. Cold dry compresses are used for approximately 5 days after surgery.
- If a meniscectomy of the knee joint has been performed, in simple terms, resection of the meniscus, rehabilitation already on the second day after arthroscopy includes careful walking with a limited load on the sore leg. You should walk for 5-7 days (in doses!) exclusively with support, using auxiliary orthopedic devices that serve as additional support.
- When recovering from knee arthroscopy, when the meniscus was not removed but sutured, you will need to walk with crutches longer. Crutches are used for about a month, and when moving you cannot transfer your body weight to the problem limb. For ACL reconstruction, assisted walking is prescribed for at least 3 weeks.
- When performing the prescribed exercise therapy after arthroscopy, a moderately stiff knee brace or an elastic bandage is put on the knee joint. The patient may be prescribed to wear an orthopedic device (orthosis), which is fixed at the permitted angle of flexion, for example, if correction of ligamentous structures has been made. During the night's rest, the orthotic device is placed in the extension position.
The basis of the range of rehabilitation measures at each stage is a set of exercise therapy exercises after arthroscopy of the knee joint; the video more clearly displays their methodology. However, video materials should not serve as a reason for not visiting a qualified medical institution.
In the event that torn ligaments or meniscal fragments were compared, the development of the knee will have to be delayed for a certain time until the connected tissues have firmly fused.
Physiotherapy
During the rehabilitation period after arthroscopy, physiotherapy is prescribed according to indications.
As a rule, the patient undergoes treatment methods such as magnetic laser, UHF therapy, lidase electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ultrasound therapy, and massage.
Contraindications for physiotherapy
- feverish conditions;
- general serious condition of the patient;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases or acute pathologies;
- bleeding and tendency to it;
- pregnancy;
- presence of neoplasms.
In conclusion, I would like to say that if all the doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations are strictly followed, both the arthroscopy itself and further rehabilitation will take place without complications for the knee joint. Then the patient will quickly return to his usual work and everyday life.
Rehabilitation after arthroscopic knee surgery - real life example:
Physiotherapy
As for exercise therapy in the initial period, after arthroscopy of the knee joint it solves the problems of stabilization, elimination of inflammation, normalization of blood flow, prevention of contractures, and consistent restoration of motor and support functions. At the same time, axial high-amplitude loads are excluded! The following activities are recommended three times a day:
- static muscle tension in the anatomical plane of the hips and buttocks;
- simultaneous movements of the feet towards/away from oneself, clockwise and backward rotation (do 10 exercises each);
- Exercises for flexion and extension of the knee are gradually introduced in an acceptable range that does not cause pain, and they are mainly done lying down so that the back of the foot is in continuous contact with the surface (number of repetitions - 6-8 times);
- from a lying position, slowly lift the straight limb (45-60 degrees) with the toe facing yourself - hold it suspended for five seconds, then smoothly lower it onto the bed (8-10 sets);
- a similar exercise can be done while standing (when you can start doing it, the rehabilitation specialist decides).
Rehabilitation after arthroscopy of the knee joint, whether resection of the meniscus was performed or restoration of other elements, is always based on exercise therapy and physiotherapy. But remember that only a doctor can prescribe an algorithm for restorative measures taking into account your specific medical problem. You cannot include a single movement without the knowledge and consent of a highly qualified physician. It is also strictly forbidden to independently introduce innovations in rehabilitation after arthroscopy of the knee joints with resection of the meniscus, including after any reconstructive plastic surgery.
Important information! Until the end of the fourth week, rehabilitation after knee arthroscopy at home is not recommended, especially performing exercise therapy via video from the Internet. Lack of close monitoring by professional rehabilitation instructors and an orthopedic doctor, and the slightest errors in exercises are fraught with serious complications, instability and inferior mobility of the bone joint.
Reviews
Patient reviews about the rehabilitation of the knee joint after arthroscopy can be found varied. But as a rule, everyone praises such surgical manipulation and cannot imagine what would happen to them if they were afraid to do it.
Inna, 29 years old: “I had arthroscopy due to the diagnosis of a Baker’s cyst in the left knee joint. In my opinion, the most important thing during the rehabilitation period is the implementation of a special complex of exercise therapy. It is better to do it under the supervision of a specialist, but if there are financial difficulties, then you can do it yourself at home, armed with special benefits. I can also say that regularity is important in this matter. I conscientiously performed all the exercises at home, and also went to physical procedures - electrophoresis with hydrocortisone and a magnet. Now, after quite a long time, I do not regret agreeing to arthroscopy. At the moment, I am able to walk fully on level ground, moderately engage in cycling and, of course, feel much better than before the operation.”
Veronica, 32 years old: “I had a tear of the medial meniscus of the knee joint. Of course, I agreed to knee arthroscopy. For about 1.5 weeks after it, I refrained from walking and observed bed rest. Immediately after the operation, I constantly kept my leg elevated and applied cold for a quarter of an hour at intervals of 2 hours. I was also prescribed Nimesil to relieve pain and an elastic bandage. But the most important thing in the recovery period is exercise therapy. I recommend everyone to be conscientious about rehabilitation, since this is your future.”
Knee arthroscopy rarely leads to serious complications, but how quickly the patient gets back on his feet largely depends on a properly organized rehabilitation period. Complete recovery of the knee joint after surgery may take varying amounts of time. Even if the patient notes that recovery after arthroscopy is slow, you should not stop practicing and your efforts will definitely be rewarded.
Recovery at home
If the patient has undergone arthroscopy of the knee joint, then rehabilitation after the operation should be continued at home. A positive outcome largely depends on whether the patient adheres to the following rules:
Recovery after shoulder arthroscopy
- If the patient keeps his legs elevated for the first 1–3 days, this will help reduce swelling.
- It is important to keep surgical incisions in the knee area dry and clean. The doctor supervises the change of dressings. Water procedures should be performed with extreme caution.
- It is important for the patient to remember to take anti-inflammatory and vascular medications prescribed by the doctor.
- The patient should wear an elastic bandage for the first 5–7 days. If necessary, lymphatic drainage and cryotherapy are prescribed.
- On the 8th day after surgery, a therapeutic massage in the knee area may be prescribed. It is more correct for such manipulations to be performed by an experienced specialist. However, some patients use educational videos, which can be easily found on the Internet, and perform self-massage at home.
The attending physician monitors the characteristics of motor activity during the rehabilitation period:
- After removal of the meniscus, walking with a moderate load is recommended on the day of surgery. During the first week it is good to use a cane or crutches. If a ligature was applied to the meniscus, then the leg is spared for a month and they move only with the help of crutches.
- After plastic surgery of the knee joint ligaments, crutches with an elbow support should be used during the recovery period for up to 21 days. For the first 2–3 days, you should avoid putting stress on the operated limb, but if there is no severe pain, then the axial load is increased.
A follow-up examination by a specialist and a change of dressings occurs in the first 24 hours after surgical procedures, and then every 2–5 days. During the procedure, the patient is replaced with aseptic dressings and, if necessary, accumulated fluid is sucked out. Surgical suture material is removed 7–12 days after the procedure.
The wound is not allowed to get wet until the stitches are removed.