The knee joint is the second largest joint of the musculoskeletal system, ensuring human motor activity. Its injuries and pathologies are a pressing problem in traumatology and orthopedic practices. About 70% of injuries occur to the knee joint, its ligaments and tendons. Difficulties in diagnosing lesions arise due to their diversity and the identity of symptoms. Late-detected or unrecognized injuries are difficult to treat and often lead to patients being unable to work.
MRI is the modern and most informative diagnostic method. It allows you to visualize damage to bones and ligamentous-tendon apparatus. On the obtained MRI images of the knee joint, all violations of the integrity of its constituent elements are clearly visible.
The essence of the method
For diagnostics, a tomograph is used - a device that allows you to perform layer-by-layer non-destructive research. Thanks to MRI, doctors receive detailed information about the condition of the soft tissues, cartilage and bones of the organ. The method is as follows:
- magnetic radiation passes through a closed area in the form of a tunnel;
- reaching the organ, the waves return;
- based on vibrations, the device forms an image;
- After the procedure is completed, the patient is given a photo.
The unit of measurement for magnetic field is 1 T (Tesla). Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see the diseased organ in section and in various projections. To increase the information content, a special substance is injected into the tissue before the procedure, which provides contrast in the photograph.
This identifies pathologies that cannot be tracked by other methods, including visual examination.
Diagnostic capabilities
A patient with sore joints is referred for examination by a rheumatologist, orthopedist, arthrologist or traumatologist. Compared to radiography, CT and ultrasound, tomography provides a more complete picture of the pathology. If the presence of tumors or metastases is suspected, the procedure is prescribed in order to confirm or refute the assumption. The cost of an MRI ranges from 3 thousand to 7 thousand rubles, depending on the region and the pricing policy of a particular institution.
In advanced cases, when degenerative changes have severely affected the joints, an examination is done to determine the cause. This also applies to the initial stages of diseases. In addition, MRI is mandatory for patients diagnosed with the following diseases:
- arthritis;
- osteomyelitis;
- bursitis;
- arthrosis;
- gout.
At the end of the study, doctors have data on all the negative changes that have occurred in and around the joint. Foci of inflammation and their localization are clearly visible.
Elements whose condition can be shown by tomography:
- blood vessels;
- muscle;
- adipose tissue;
- quadriceps;
- collateral ligaments, including internal, external and cruciate ligaments.
The use of a contrast agent allows you to identify different types of damage, including pinching, avulsions, cracks, breaks and other defects. The patient can decide for himself whether a contrast agent should be used because it will make the diagnosis more expensive. But the advantage of this approach is obvious: the doctor receives more detailed, clear and understandable data.
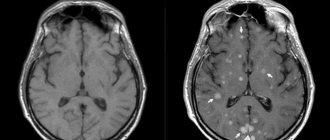
Osteoarthritis of the knee joints on CT
Arthrosis is the name given to dystrophic changes in the joint that begin in the cartilage (chondrosis) and spread to the bone (osteochondrosis). The pathological process develops over years. Articular cartilage gradually loses its elasticity, becomes denser, thinner, becomes rough, lumpy, overgrown with bone formations along the edges, and in some areas is completely destroyed.
In the early stages, degenerative changes are asymptomatic: arthrosis of the knee joint is often detected in advanced stages, when pain, a feeling of stiffness and limited mobility appear.
Computed tomography shows:
- narrowing of the joint space;
- marginal osteophytes;
- increased bone density under the cartilage (subchondral osteosclerosis);
- destruction of cartilage;
- deformation of bones at joints;
- focal cyst-like formations.
Arthrosis of the knee joint, photo of tomography images
Advantages of the technique
When it comes to joint problems, MRI is preferable to other types of diagnostics. The procedure is highly accurate and informative, and does not require surgical intervention. To perform an MRI, there is no need to cut into tissue or puncture vessel walls to take fluid samples. The examination is non-invasive, which means there is no risk of infection. Other benefits of the study:
- short duration;
- minimal number of contraindications;
- no need for complex preparation;
- high detail and clarity of images;
- presence of all data required for an accurate diagnosis;
- the ability to convert data into electronic form;
- safety;
- Possibility of use in childhood.
Indications for use
One of the common indications for magnetic resonance imaging is the suspicion of the presence of synovioma. This neoplasm can be localized in different parts of the synovial membrane of the joint and give metastases. Other indications for MRI:
- swelling, discomfort in the knee of unknown etiology;
- bone fracture if it cannot be examined using radiography;
- kneecap injury;
- pinching of tendons, nerve endings;
- knee pain;
- primary tumor;
- suspicion of metastases affecting soft tissues and bones;
- instability, blocking or limited mobility of the joint;
- pathological processes in bone tissue;
- osteomyelitis;
- osteoarthritis;
- arthrosis;
- ligament rupture;
- upcoming ligament surgery;
- confirmation of the need for arthroscopy or other surgical procedures in the knee area;
- arthritis;
- accumulation of synovial fluid;
- bursitis;
- Baker's cyst;
- osteochondritis;
- accumulation of synovial fluid;
- tendon strain.
Photo tomography of the knee joints
MSCT photos of the knee joint primarily show the bones (femur, tibia, tibia, patella). You can also see in the pictures:
- articular cavity;
- intra-articular cartilages;
- synovial membrane;
- intra- and extra-articular ligaments.
MSCT of the knee joint (coronal projection)
Restrictions and contraindications
The list of situations in which MRI is not recommended or cannot be performed is quite extensive. There are restrictions that can be circumvented, for example, by using special equipment. In other cases, you may need to temporarily change the mode. The patient may not even know that he has a problem for which an MRI is not performed, so initially he must pass all the tests prescribed by the doctor. Common contraindications and restrictions:
- The presence in the patient’s body of vascular clips, metal plates, implants (including cochlear implants), insulin pumps and other devices implanted in various organs. If there is at least one such object, an MRI of the anatomy of the knee joint cannot be performed, because the metal and magnetic waves are mutually attracted, and this can lead to complications.
- Claustrophobia, mental disorders, diseases of the nervous system. Patients with such problems find it difficult to stay in a closed space. A sleeping pill taken before the procedure helps. An alternative option is to conduct an examination using an open tomograph.
- Pregnancy. Medicine does not have data to suggest that radio waves and magnetic radiation have a bad effect on the fetus. There is also no information proving the opposite, but it is better not to expose the body to unnecessary risk.
- Breastfeeding period. The contrast agent injected into the tissue may pass into breast milk in small doses. This poses a danger to the baby, so 1-2 days before diagnosis you should temporarily stop feeding. The doctor will tell you when to resume it.
- Overweight. A standard tomograph is designed for a weight of up to 150 kg. Some clinics have equipment that allows them to diagnose people weighing up to 250 kg.
- Mental illnesses accompanied by medication use. A patient with such a pathology is given a sedative shortly before diagnosis.
Which is better - MRI or ultrasound of the knee?
It is necessary to consider these two most popular examination methods. Ultrasound of the knee joint is performed using ultrasonic waves, and MRI is a computer research method based on magnetic resonance of the compounds of atoms that are part of certain tissues.
Ultrasound is usually recommended for examining internal organs in order to diagnose their disorders. MRI is used to diagnose bone diseases in the human body.
Also, ultrasound is completely safe and has virtually no contraindications, regardless of what area is being examined. But when performing an MRI, a rather large magnetic field is created, which is why this method of examination has certain contraindications and in some cases it cannot be performed.
Do not forget about the availability of such methods. Due to the simplicity of such a study as ultrasound of the knee joint, its cost is very low, and therefore it is available to all segments of the population. But not many people can afford an MRI.
Thus, it is impossible to answer the question of which method of diagnosing the knee joint is better. Therefore, only a specialist can determine the appropriateness of a particular method.
Preparing for the examination
It is advisable to familiarize yourself with how an MRI of the knee joint works and what it shows in advance. When a person understands what he will have to face, he is less likely to become nervous or afraid at the most crucial moment. How to prepare for the procedure:
- during the day, follow a certain diet, eating what the doctor allows;
- in the morning you can eat a light breakfast;
- before entering the office where the equipment is located, you should take off your glasses, jewelry and metal accessories;
- remove clothing that has metal fasteners or fittings;
- If there is an electronic device, it must be left outside the office.
For safety reasons, some clinics provide patients with disposable clothing designed specifically for MRI.
In the office, the doctor asks a series of questions, finding out the following:
- whether sedatives are required;
- what is the patient's weight;
- Does he suffer from claustrophobia?
Children are usually given a sleeping pill because otherwise it will be difficult to diagnose. Due to mental characteristics, it is difficult for even healthy children to remain motionless for half an hour, and for examination the joint must be absolutely motionless.
There is a doctor and an assistant in the office. The patient is explained how everything will happen and how to behave during the diagnosis. Then the laboratory assistant asks if the person understood everything, and once again clarifies whether there are any metal objects on the body or clothing.
CT scan with contrast of the knee joints
Additional tools during CT or multislice tomography (MSCT) of the knee joints are required to improve the quality of visualization of the studied area. Preparations with iodine are used as image clarity enhancers. After injection into a vein, they spread through the vessels and accumulate in places with the most intense blood supply - in areas of inflammation and tumors. Thus, the presence of pathology becomes more obvious to the specialist.
Contrast agents are harmless to health and are completely eliminated from the body within two days. But before using them, it is necessary to take a creatinine test (to rule out kidney problems) and make sure that there is no allergy to the components of the drug.
CT scan of the knee joint with contrast
Procedure
The patient is placed on a flat horizontal platform, after which the doctor fixes the knee. MRI of the right and left joints is done on an open or closed tomograph. A closed one is most often used, but if the patient has claustrophobia or other features, then an open apparatus is used.
While the joint is being scanned, the equipment makes quite loud sounds. This should not be a cause for fear or panic. In some institutions, people are given special headphones that make the person feel calm. How long a knee MRI takes depends on whether a dye is injected. Without it, diagnosing a diseased organ in an adult takes a little time - up to 30 minutes. If the knee is examined with the preliminary administration of a contrast agent, the procedure is extended to 1.5 hours.
Decoding the results
Deciphering MRI of the knee joint provides doctors with important information for diagnosing diseases. Unlike traditional fluoroscopy, MRI allows you to examine not only bone structures, but also the surrounding soft tissue.
The meniscus, the condition of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus, cartilage, and fluid inside the tendon bursae are visualized. MRI images also allow you to see and study the system of blood vessels and nerve filaments, identify vascular abnormalities, atherosclerotic narrowings, determine the location of tumors, their size and nature, and the process of spread to neighboring structures.
Visualization of the joint using an MRI scanner is possible in three-dimensional form with the thinnest sections in various planes. Such visualization of the joint on MRI images allows specialists to examine all structures in detail. The images are given to the patient in paper form, and they can also be recorded on digital media at his request.
In diagnosing knee arthrosis, MRI gives results with an accuracy of 85-90%. Inaccuracies arise mainly due to the fault of specialists interpreting the results. Therefore, a comprehensive examination of the patient is important.
MRI of the meniscus is the most common procedure. MRI images show the meniscus as a dark stripe, and the lesions are highlighted with a white background. No contrast is used for MR imaging of the meniscus. In overweight patients, MRI often shows meniscus damage, since it bears the maximum load when walking in such people.
Unlike meniscal injuries, ligament tears due to injury are more difficult to detect on MRI. A number of tendon structures are small, which makes them difficult to study.
MRI has an advantage over CT scans in that it can visualize blood vessels. Bone tissue receives nutrients only through the small capillaries of the periosteum. If there is insufficient blood flow through large vessels, a lack of capillary blood flow occurs.