When an adult falls ill, it is enough for him to consult a doctor so that a correct diagnosis can be made through test results and some diagnostic procedures, but with children, and especially with newborns, everything is much more difficult. The point is not even that their small body is much more vulnerable to most ailments, the problem lies in the impossibility of using many diagnostic and treatment methods, for example, a small amount of medicine can be given to an infant, because many drugs can only improve his condition.
Many parents are also interested in whether it is possible to do a regular x-ray on a newborn, because the child may develop RDS. The abbreviation RDS is an ailment called respiratory distress syndrome; it is characterized by serious respiratory failure, and RDS occurs immediately after childbirth or a short period of time after it. But you should not assume that RDS is the only reason why it may be necessary to take an x-ray of the child’s body.
Description of the procedure
Let's first understand the principle of radiography. This method is based on the use of ionizing radiation, which is sometimes also called X-rays, or more precisely, on its basic physical properties. The fact is that such rays can easily penetrate the human body, but to some extent they linger there, on the basis of which photographs are taken. As you might guess, dense bones are much lighter in the image because they absorb X-rays quite well. For this reason, it will not be difficult for specialists to distinguish the location of the tubular bones from others. As for soft tissues, it is almost impossible to study them using X-rays, especially if it is performed without contrast (the use of a contrast agent cannot even be considered if we are talking about a newborn child).
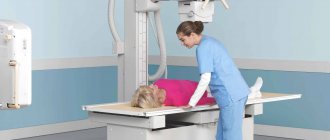
X-ray of the abdominal and chest area of a newborn.
As for the advantages of radiology, among them experts always highlight the speed, low cost of the procedure, as well as sufficient effectiveness in many situations. Of course, there are more modern and safer diagnostic methods, for example, magnetic resonance imaging, but in many situations the overpayment is pointless, and if we are talking about the need for an X-ray for a newborn child, then this is almost impossible, because a person must be in the MRI machine for a long time (it can be difficult to explain this even to children, and a newborn baby will definitely not lie motionless). Using MRI, it is also impossible to study the condition of the long bones or, for example, the skull of a child’s head, because bone tissue is very poorly visualized.
Experts note that X-rays are practically not prescribed immediately after birth, because ionizing radiation can cause great harm, and the consequences can be extremely serious, because radiation will cause various pathological processes in a small body. For this reason, radiography of tubular bones or anything else in children under the age of 14 can only be performed if indicated. It is worth noting that only digital equipment should be used, because film devices have a much higher radiation dose.
Advantages of x-ray of tubular bones over other methods
X-ray has been one of the main areas of imaging diagnostics for many years. Almost every patient undergoes this procedure. Radiography has rich traditions, which to this day have not exhausted their capabilities under the dominance of modern diagnostic methods.
- accessibility to every patient;
- research is carried out as quickly and painlessly as possible;
- the patient does not have to undergo any special preparation procedure for radiography;
- the price of x-rays is low (compared to other modern diagnostic methods);
- The images obtained as a result of an X-ray examination can be taken with you and shown to other doctors or even in other medical institutions.
- injuries: various dislocations, cracks in bones, their fractures (and you can also monitor the process of fusion of tubular bones);
- infections: arthritis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis (the focus of infection can be seen in the image; but additional research is also required at the same time);
- oncology: the image shows metastases and the initial stages of tumors in bone tissue;
- metabolic diseases: osteoporosis, rickets, osteitis;
- the presence of a foreign body in the bone itself, as well as in the periosteal tissues.
Indications for use
If dental x-rays are almost never taken at this age (dental x-rays are not necessary immediately after birth, and if there are dental problems related to dentistry in infants, then most often they can be solved in another way), then the same x-ray lungs for RDS or any other illness dangerous to the child may well be necessary. X-rays of the skull or, for example, tubular bones may also be required.
To the question of why the baby was x-rayed or why doctors recommend doing it, only one answer can be given - the need to make a competent diagnosis as soon as possible. It is worth understanding that under no circumstances should a newborn child be given a preventive x-ray, because such training is unjustified. And if a diagnosis can be made using safer diagnostic methods, then they are always preferred (we are talking primarily about ultrasound).
X-ray of the abdominal area.
Experts note that X-rays of a newborn child are often performed for the reason that there are signs of injury during childbirth, for example, a fracture of any tubular bones. Sometimes the situation can be so serious that it is impossible to do without an x-ray. Here are the main situations in which radiography is indicated, that is, the harm from it is neglected in order to avoid the occurrence of terrible consequences:
- the need for diagnostics after the occurrence of injury during childbirth;
- the need for diagnostics in the event that a newborn child receives some kind of grass, for example, falls from a changing table (such situations are very dangerous, because the child cannot even complain about anything, and bones at this age are incredibly fragile);
- if you suspect the development of any pathological processes associated with the musculoskeletal system (this includes rickets or, for example, osteoporosis);
- for any reason, foreign objects entering the gastrointestinal tract or even the respiratory tract (radiography will help identify the location of this foreign object);
- the need for diagnosis if the development of intrauterine pneumonia is suspected due to infection entering the mother’s lungs when the fetus was just developing;
- the need to identify intestinal obstruction;
- upcoming surgeries for which doctors may need information that can only be obtained using x-rays.
Note! This list is provided for informational purposes only; experienced specialists always study the problem in more detail, that is, they focus on many other factors. For this reason, you should definitely not insist on an x-ray or refuse the procedure; listen to the opinion of an experienced doctor!
X-ray of a newborn: should I be afraid and how to do it correctly?
What to do if the doctor insists on x-raying the baby? Fear of harm from radiation should not be a reason for refusal, because often the child’s very life depends on timely diagnosis. What is radiography and how harmful is it for a newborn?
Fun fact: the first X-ray photograph in the Russian Empire was taken 122 years ago, at the end of the 19th century. In those ancient times, the equipment was very imperfect, and the doses of radiation were truly horse-like.
Today, the doses are hundreds of times less than the myths and misconceptions that the radiography method has acquired over the century. X-ray for a newborn helps to prevent trouble in time and diagnose diseases and pathologies. X-ray examinations have become much safer in the digital age.
Fun fact: the first X-ray photograph in the Russian Empire was taken 122 years ago, at the end of the 19th century. In those ancient times, the equipment was very imperfect, and the doses of radiation were truly horse-like.
Absolute contraindications
As mentioned earlier, the harm from radiography at a young age is incredibly great, and it is prescribed only in situations where there is a very serious reason for it. It is worth understanding that girls should never have the area where their reproductive organs are irradiated; boys, accordingly, should not have their testicles irradiated. Here are the absolute contraindications, in the presence of which it is strictly prohibited to conduct research:
- extremely close location of organs;
- the presence of any disturbances in the development of paired organs (for example, unevenness of this process);
- violation of an individual character;
- Training in the thyroid gland area is also prohibited.
An infant can be x-rayed from the first day of life, but there is some danger.
What it is?
Study of the internal structure of objects that, thanks to X-rays, are projected onto paper or film. Bone radiography is used to take pictures of bones. It helps determine the condition:
- brushes;
- wrists;
- forearms;
- elbow joint;
- shoulder;
- feet;
- ankle joint;
- shin bones;
- knee joint;
- hips;
- hip joint;
- pelvic bones;
- spine.
Many people are already familiar with the procedure, since indications for bone x-rays cover a wide range of diseases, not including injuries and fractures.
What could be the consequences?
We will not consider how X-rays are done for babies, as well as what stages the study consists of, we will only consider the harm of the procedure and possible consequences. It is worth noting that the penetrating power of X-rays is extremely high, and when passing through the body, especially if we are talking about a child, radiation can change the structure of atoms or molecules. For this reason, somatic diseases of various types arise, and various genetic abnormalities that affect future offspring are not uncommon.
Fortunately, the risk of dangerous consequences can be reduced if the procedure is performed using modern digital equipment (in this case, the training will be short-term, and the radiation exposure will be significantly reduced). As you might guess, a serious danger arises when exposure to radiation is prolonged.
Preparation for radiography of long bones
Mostly, x-rays of tubular bones do not require any special preparatory procedures. During the examination, you need to completely expose the part of the body that will be irradiated. A special shirt must be put on first and given to each patient in the office. It is also necessary to remove jewelry, dentures, and metal items. They negatively affect the image quality of the photo.
A woman must provide the radiologist with information about a possible pregnancy. This is necessary in order to take all measures to protect the fetus.
What can be a substitute for x-rays?
According to experts, if it is possible to avoid x-rays for a newborn, then it is best to use it. Nowadays, medicine, fortunately, is developed enough to have some choice among diagnostic procedures. Doctors recommend performing an ultrasound examination, that is, ultrasound. Thus, it becomes possible to identify many dangerous ailments without harmful ionizing radiation. This method helps to easily determine the presence or absence of dysplasia when it comes to the hip joint, and it can be used to identify dislocation or even subluxation of the hip without any problems. It is worth mentioning that ultrasound cannot always replace radiography, just as X-rays in some cases are less informative compared to ultrasound. For this reason, the diagnostic option should be selected only by a highly qualified specialist.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to carry out safer research methods on infants (we are talking about procedures such as magnetic resonance or computed tomography), because they require a person to remain in a stationary position for a long time (it is impossible to explain this to a baby).
Procedure: how to properly prepare and carry out?
X-rays of a newborn are performed in the presence of one of the parents or guardians. The main problem is to achieve immobility of the baby or its limbs, if only they are examined. Most offices have bandages or special devices that allow you to fix the baby motionless. Everything that is possible is covered with protective aprons and protected by screens so that harmful radiation does not affect other parts of the child’s body and organs.
Important: usually the X-ray rooms are quite warm, but it still doesn’t hurt to make sure that the baby is comfortable, then he won’t become capricious.
The procedure takes little time: you yourself have probably undergone it several times and know well that radiography does not take long.
After the picture is taken, it is deciphered by a doctor and a diagnosis is made; the results are given to the parents or the attending physician.
Ultrasound or X-ray examination?
Most often, ultrasound is prescribed when the pediatrician suspects a violation of the structure of the hip joints, dysplasia, etc. The bones of the newborn are not yet sufficiently strong and formed, so they can be perfectly scanned using ultrasound.
Another advantage of ultrasound is its relatively low cost. Not all parents can afford X-rays and computed tomography. Therefore, they opt for simpler and more accessible diagnostics.
X-ray radiation can be harmful, but its medical benefits are obvious. This method of examination is used in cases where it can bring much more benefit than harm. A child’s body is more sensitive than an adult’s, so some parents refuse to have their child x-rayed. But there are situations when you can’t do without it.
Radiation is dangerous if its exposure exceeds a certain threshold. If this is not observed, then there is no need to talk about the dangers of ionizing radiation.
Everyone who has undergone an X-ray examination has a special radiation passport, which records all doses of radiation received. But the patient or his parents must monitor the excess of the permissible norm themselves, since each of the doctors purposefully solves his own problems. A surgeon, for example, may need a photo of a broken arm, a traumatologist - a photo of the back to identify curvatures, and a pediatrician will refer you for a lung examination. Another danger is having X-rays done for children for a fee, without a doctor’s prescription, since you can exceed the permissible level of radiation.
Currently, X-rays are done for children using classical and digital methods. Digital technologies have a significant advantage, however, this diagnosis is currently only carried out in paid clinics; public medical institutions have limited funds to purchase expensive equipment. Modern technologies have made it possible to significantly reduce the dose load and improve image quality.
Parents are often interested in the age at which children can have x-rays. It is used exclusively in the presence of special indications from infancy. It should only be taken into account that the benefit from it must exceed the risk.
Why is it worth getting x-rays done at the SM-Doctor clinic?
- Our center uses special children's equipment that fully meets the strictest safety standards. Only children's x-rays provide minimal radiation exposure and allow you to limit the area of its exposure as much as possible.
- Experienced staff work with children who will do everything so that you do not have to undergo the examination again due to the child’s incorrect position or an unclear picture.
- Before the procedure, the child is examined by a doctor (even if the examination was prescribed by a doctor, but from another clinic) to make sure that it is really necessary.
- The conclusion is written by experienced pediatric radiologists, to whom you can ask any questions that concern you.
- The doctor’s conclusion, as well as the images themselves, are given to you directly on the day of the examination.
When a doctor tells the parents of an infant that he needs to have an x-ray, they immediately have worries and doubts: isn’t x-ray radiation dangerous for the baby, since he is still so small and weak?
Perhaps the diagnosis is not so serious, but an X-ray for a baby is difficult to predict the consequences... Thinking about this, it is worth remembering that there are very few absolutely safe methods of examination and treatment; they can literally be counted on one hand. The number of all kinds of injuries and diseases, unfortunately, is enormous, and the more complex they are, the more likely it is that relatively harmless means will have to be used to identify and correct them.
Chest X-ray for a child - facts about pediatric X-ray diagnostics
During the procedure, the small child is fixed to avoid poor-quality x-rays when the baby moves. The duration of the study is about 10 minutes. The duration of the examination depends on the type of radiography and the purpose of the examination.
Chest X-rays of small children and infants are performed in a lying position. You can explain to an older child that the procedure is similar to taking photographs and does not cause pain.
First, parents should familiarize themselves with the features of the examination and ask the doctor about the radiation dose that the baby will receive.
Modern digital radiography can reduce the patient's radiation exposure. Before the study, the child’s parents should find out what equipment the procedure will be used on and whether there are permitting documents.
To reduce radiation exposure to the patient, areas that are not being examined are covered with a lead apron.
If the baby cannot lie quietly on the examination table on his own, the parents provide assistance to the child. Shielding devices are used to protect adults from radiation.
It is very important that the child does not move during the exposure. Any movement disrupts the quality of the image and leads to diagnostic errors when reading images.
Attention! If the child is taking medications or has mental or neurological illnesses, the radiologist should be familiar with them before performing x-rays.
The main methods of radiographic examination that are prescribed to children:
1. Fluoroscopy is a method of obtaining an image on a fluorescent screen and then transmitting the image to a monitor. A distinctive feature of the procedure is the ability to study internal organs while they are working under an X-ray TV screen; 2. Linear tomography – layer-by-layer study of internal structures, carried out at a certain depth. The image is obtained by moving the film and the X-ray tube in the opposite direction. Such images are taken to study tuberculosis lesions of the lungs; 3. X-ray computed tomography - a modern scan that allows you to make sections of an organ at a certain depth in order to determine tissue density; 4. Electroradiography and fluorography are not used in pediatric practice, as they are characterized by a high radiation dose.
Dangerous? How to watch
It is not so easy to give a small child an X-ray examination. You have to use special devices, although no child will appreciate such manipulations
What can you say to mothers who are afraid to x-ray their young children? In fact, in life we often encounter situations when we need to choose the lesser of two evils. For example, everyone knows about the risk of dysbacteriosis while taking antibiotics, but this does not stop us when a doctor diagnoses an infant whose temperature is off the charts and has difficulty breathing with acute bronchitis and prescribes those same medications. What if there is a suspicion of pneumonia? X-ray is today the only way to obtain reliable information and not miss a dangerous disease.
Modern X-ray machines are aimed at low-dose radiation. In ordinary life, we also encounter radiation in similar doses every day: while flying on an airplane, watching TV, or spending a long time in the sun. So they cannot cause any radiation sickness. By the way, with the tomographic examination that is popular today, X-ray radiation is higher.
In addition, targeted irradiation is common, when non-examined organs are covered with special protective capes in the form of aprons containing lead. The reproductive organs and thyroid gland are not exposed to X-ray irradiation. The radiation dose after the procedure is recorded in the child’s card so that the total amount can be monitored throughout life.
Types of X-ray examinations
Radiation diagnostics of bones occurs using various units and research methods. It all depends on some factors:
- patient's age;
- clinical situation;
- underlying pathology;
- associated factors.
This method is indispensable in recognizing the causes of pathology and plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis and treatment of the patient.
In medical practice, there are the following types of bone x-rays:
- Film radiography.
- Digital.
- CT scan.
- X-ray densitometry.
- X-ray of bones using contrast agents and other methods.
All these devices serve as an excellent aid to doctors in providing the necessary assistance for:
- bone fractures and dislocations;
- clarification or detection of the location of bone fragments during fractures;
- identifying foreign bodies in soft tissues or in the bones themselves;
- control of orthopedic surgical interventions (joint replacement, spinal stabilization, etc.);
- specification of certain diagnoses (arthritis, pathological proliferation of bone tissue, arthrosis and others);
- suspected bone cancer.
Having received the results of these studies, the specialist already has a more objective picture and draws appropriate conclusions.
The effect of X-rays on the child’s body
In children, internal organs are located close to each other. Often, when X-rays are performed, healthy parts of the body are also affected, which means that the amount of radiation received also increases.
During one x-ray session, a child will receive from 0.01 mSv to 0.6 mSv. This is considered minor exposure and does not adversely affect the child's body.
In a small child, the red bone marrow occupies a larger area than in an adult. It reacts to x-rays more than other organs. X-rays ionize blood cells. Some doctors believe that this leads to the formation of malignant tumors. Other groups of doctors see no harm in taking x-rays and no connection with the development of cancer cells. But research on this topic is still underway, and no group of doctors has an exact conclusion.
Indications for which it is better not to refuse x-rays
X-rays for newborns are used only in exceptional cases; doctors resort to X-ray examinations of children under 3 months with great reluctance. However, there are no age restrictions: in practice, X-rays are taken on newborns from the first day of life, but only for indications that pose a significant threat to the life of the newborn. If there are any, you can be sure: doctors will do an X-ray as many times as they deem necessary, at least ten times, at least twenty.
Modern X-ray machines generate tiny doses: for example, in order to “get” to the safe total annual radiation threshold, you need to try very hard: this is approximately 2000 (two thousand) images per year for an adult, for a newborn - let there be 200 or 100 images, but still this is a big number.
What are the indications for x-rays in babies under one year of age?
- Birth and household injuries, damage after an accident. Head injuries are especially common, the diagnosis of which in infants is very difficult.
- X-ray of the hip joint in an infant to diagnose a possible dislocation.
- Ingestion or inhalation of foreign bodies, which is not that uncommon.
- Suspicions of cancer.
- To identify pathologies of the structure and development of the musculoskeletal system (asymmetry of the skull bones, problems with bone mineralization, rickets).
- Suspicion of pneumonia or acute bronchitis: an x-ray of a baby is the only way to urgently diagnose.
- Before surgery, especially intracavitary operations.
From this list it is clear that in most cases children undergo x-rays for reasons the consequences of which can be simply catastrophic for their health. In such cases, is it worth talking intelligently about the harm from radiation and how much it affected the future health of the newborn? The child needs to be saved here and now!
As Dr. Komarovsky says, “the diagnostic advantages of radiography always outweigh the possible disadvantages in the future.”
Features of radiography for young children
Since the radiation exposure to the child should be minimal, the main task that has to be solved when radiography of young children is obtaining the most informative image on the first try.
And this is not easy. An adult can be placed or placed in the desired position and asked to hold their breath. You cannot explain to a newborn what is required of him. Therefore, when radiography of children, special devices are used to help hold the child in the desired position. This is provided for by the methodological recommendations of Rospotrebnadzor (approved on April 27, 2017). X-ray diagnostic rooms of modern clinics are equipped with mobile X-ray stands with cradles. The cradle moves in three planes and allows you to securely fix the child in the position necessary to take an image in any projection. Such cradles are used to perform X-ray examinations on children from birth to two years of age.