Radiography is one of the very first methods for diagnosing pathological changes occurring in different structures of the human body. It is based on the use of X-rays, which project the structure of internal organs onto film.
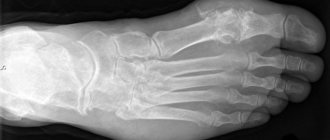
The study allows us to identify diseases of infectious and non-infectious nature occurring in the genitourinary, digestive, cardiovascular, respiratory and musculoskeletal systems. In particular, an image of the knee joint is important for the timely detection of a number of pathologies that have serious consequences.
Features of X-ray examination
A special feature of X-rays is their ability to penetrate human tissues and organs, leaving an imprint on the film. In medicine, radiography as an examination method has been used for more than a century. In the picture, a specialist can examine in detail the structure of the tissues and see the changes that have occurred in them.
The density of the fabric is indicated by the color of the print in the photo; The denser it is, the lighter the image of this area will be, since it is more difficult for rays to penetrate through such a structure. Muscles and tendons are less distinguishable than bones. The cartilage is not visible in the image; the thickness of the cartilage layer can be judged by the size of the joint space.
There is an opinion that radiography is harmful to the human body, but modern devices pose a minimum of danger in this sense. The radiation dose during the procedure is minimal. A person receives approximately the same amount from natural radiation exposure in 2-3 days. Nevertheless, it is often still undesirable to carry out such a procedure.
An X-ray of the knee joint is taken with the patient in a supine or standing position; the knee must be freed from clothing. The procedure is short-term and does not cause discomfort. Contraindications to x-rays include pregnancy, schizophrenia and the presence of metal pins in the knee. In all these cases, it is more advisable to replace the use of x-rays with ultrasound.
Features of the examination:
- The patient's pelvic organs must be covered with a special cape with lead plates;
- if you are overweight, it is impossible to achieve high clarity of the image;
- the device must be at a certain distance from the object, this gives a clearer image with clarification of the smallest details;
- During the examination, the child must be held or fixed with special devices so that he remains motionless, otherwise the image will be blurred.
Sometimes the doctor is forced to order x-rays of the knee frequently in order to monitor and, if necessary, adjust the progress of treatment. In this case, the patient is advised to increase fluid intake to reduce the risk of negative consequences. This could be drinking water, green tea, fruit and vegetable juices, milk.
Indications for use
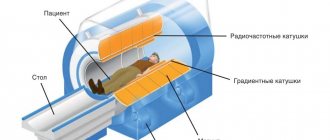
An X-ray of the knee joint shows the structure of the bones and the presence of deformities in them. This is the most common diagnostic method that the doctor uses first. If you need to additionally look at the condition of the soft tissues, it is better to perform an MRI - an expensive, but more informative procedure.
The doctor gives a referral for an x-ray if there are clear clinical indications, when the patient has suffered a knee injury, is experiencing pain, swelling and redness in the joint area is visible, the joint has lost its mobility or is deformed. Direct indications for radiography are:
- bone fractures in the knee joint;
- damage to the patella or meniscus;
- dislocation or subluxation;
- sprain;
- cracks in bone tissue;
- presence of osteophytes;
- arthritis or arthrosis;
Congenital joint abnormalities and detected osteoporosis also require examination. After an accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Advantages
The advantages of x-rays are undeniable. This technique helps to quickly determine the presence of damage or disease. X-ray diagnostics help doctors differentiate the diagnosis if there were similar signs.
Doctors have the opportunity to control the stages of treatment, for example, the installation of special structures, healing of fractures, and the correct position of the joint after a dislocation. X-ray diagnostics makes it possible to determine damage to the meniscus, which can be difficult to determine by other means.
If an X-ray is taken some time after the injury, the diagnosis will help establish the long-term consequences of the injury. For example, some patients develop Rauber's disease, where spines form in the joint.
What allows you to see
To ensure that the data is not distorted, the procedure must be carried out in compliance with the rules. It is necessary to accurately perform the X-ray technique and place the limb in the correct position. But even if all the requirements are met, only a specialist can correctly decrypt the image.
The method allows the doctor to assess the condition of the joint, muscles, and ligaments. Using an x-ray, you can determine the presence of inflammation in the joint and the accumulation of fluid in the joint capsule. Also in the image you can notice deformation, proliferation of bone tissue or its destruction. The doctor will immediately see deviations, because he knows what a healthy joint should look like.
Using the procedure, you can see the following in the image:
- cracks in the bone, on film they look like dark stripes;
- various depressions and outgrowths (osteophytes) are also easily distinguishable;
- if tendons and ligaments are damaged, the injury will manifest itself as an increase in the size of the intra-articular gap;
- the gap in the joint increases and with arthritis, at the same time the thinning of the bone plates is noticeable;
- arthrosis is characterized by deformation and proliferation of bone edges, a decrease in the cartilage layer;
- various tumors, cysts and other formations during a comprehensive examination;
- congenital anomalies of joint development, the presence of foreign bodies.
The procedure is also informative when determining bone structure. For example, with osteoporosis, bone tissue becomes thinner and looks lighter, with clearly defined boundaries.
Diagnostics
To find out the cause of the problem, doctors may order imaging tests and laboratory analysis of joint fluids, as well as an evaluation of your medical history and symptoms.
Knee fluid is removed by joint aspiration, in which a long, thin needle is inserted into the affected area. This fluid may be tested for bacteria, blood cells that indicate infection or inflammation, or the presence of specific proteins that may indicate diseases such as gout. During this examination, some of the fluid may also be drained to relieve pain at the site.
Some of the imaging tests that may be ordered include X-rays, MRIs, ultrasounds, and CT scans, which help the doctor see the condition of the joints.
Stages of implementation
The procedure does not require special preparation or a long time to perform. The knee should first be freed from clothing so that the examination result is more accurate. If the joint is in a cast or has a bandage on it, they are not removed. The patient's position depends on the pathology; most often, x-rays are taken while lying down. Sometimes the doctor asks you to bend your leg at the knee. Some cases require comparison of the diseased joint with the healthy one, so pictures of both legs are taken.
The pelvis is covered with a special apron with lead inserts to protect the reproductive organs from exposure to X-rays. While the device is operating, the patient must hold his breath and remain motionless. Children who have to be held or fixed in a stationary position require a special approach. The doctor asks adult patients with pain to take a painkiller in advance if they need to bend their knee.
An X-ray of the knee joint in two projections - frontal and lateral - gives a more complete and objective picture. In this case, the doctor can assess the condition of the articular joint from all sides. First, the image falls into the hands of a radiologist, who deciphers it and gives a written report on the examination results. After this, the attending physician makes a diagnosis.
Contraindications for radiography and radiation exposure
Like any other type of examination, radiography has its contraindications.
Although the radiation exposure during the image is minimal, the procedure is contraindicated in certain conditions or diseases:
- pregnancy;
- metal prostheses and bolts in the knee;
- severe obesity distorts the image;
- schizophrenia;
- serious condition of the patient.
Women are advised to refrain from conceiving for 1 month after the X-ray examination. Men should use protection for 3 months. If, according to indications, you often have to take x-rays, you can minimize radiation exposure by drinking green tea, natural juices with pulp and milk.
Radiation exposure when photographing the knee joint is 0.001 millisievert (mSv). This dose corresponds to the daily dose of radiation received by a person in normal life when using a mobile phone and other technologies.
But X-rays have cumulative properties, so the danger is posed by the total annual radiation exposure, which should not exceed 5 mSv.
Each written doctor’s report contains a note about the radiation exposure received, which depends on the device. The more technologically advanced the device, the less radiation exposure.
Various techniques
The projection in which the picture should be taken depends on the disease. The doctor gives directions for an X-ray of the side of the knee where there are visible changes. If there is a suspicion of a knee fracture, a direct x-ray is taken in a horizontal position. To assess the size of the joint space, the patient is examined while standing.
In a standing position, a condyle imprint is obtained if torn ligaments, gonarthrosis and bone destruction are suspected. Direct projection allows you to assess the condition of the surface of the joint and patella. A side view shows the presence of fluid in the cavity of the joint capsule and its general condition. When diagnosing a ligament rupture, the patient must shift his body weight to the affected leg during the x-ray.
To determine how the patella relates to the tibia, the leg should be bent at the knee. To get the most complete picture of the condition of the tissues of the joint and its vicinity, an X-ray of the knee joint is taken in 2 projections - front and side. In some cases, the leg must first be bent and then extended when the image is taken. The doctor may ask you to flex the joint at different angles to more accurately assess the pathology.
Digital radiography
Today, digital equipment is replacing old-type X-ray machines. With its help, you can get a clearer picture, but the radiation dose will be lower. The image from the device is immediately transferred to the computer, and the doctor examines the characteristics of the joint condition directly on the monitor and makes a diagnosis. The whole procedure takes no more than 5 minutes. This method is especially in demand in traumatology.
Arthrography (X-ray with contrast)
Arthrography (X-ray with contrast)
In order to clearly see not only bone tissue, but also the condition of cartilage and ligaments, the method of contrast radiography is used. To implement this method, the joint cavity is filled with air and a special liquid, increasing the size of the area under study. This technique allows you to make ligaments and cartilage tissue more visible.
Arthrography is often used to identify a tumor, joint lining tear, or meniscal injury. This method allows you to see the presence of a foreign body in the image, the consequences of an old injury.
The disadvantages of arthrography include the risk of certain complications. Some patients may have an allergic reaction to the injected contrast fluid. There is a possibility that there will be a crunch in the knee when moving. To prevent this phenomenon, it is recommended to use an elastic bandage for several days after the procedure.
How is a knee x-ray done?
X-ray technician at work
No special preparation is required for the photo. You don't need to follow any diet. During the session, the radiologist asks you to take the desired position of your leg. At the time of the picture, at the request of the doctor, you need to stop breathing for a few seconds and not move, otherwise the picture will be blurry.
The quality of the image also reflects the correct posture of the subject.
Before the session, the patient is placed in a supine position. A direct projection photograph is taken in case of illness. After an injury, additional radiography in a lateral projection or targeted is required. The quality of the image largely depends on the qualifications of the radiologist.
Where can I do it?
Despite the emergence of new examination techniques, x-rays remain the most common diagnostic method for bone articulation pathologies. If the knee begins to bother you, but a person does not know where to get an X-ray of the knee joint, you should contact a physician or surgeon at your local clinic. The doctor will issue a referral for testing.
Today, X-rays can be taken at any medical center that has special equipment. If you undergo the procedure at a clinic at your place of residence, it will be free. In private clinics, the cost ranges from one and a half to two thousand rubles, depending on the complexity of the technique and the device used. In Moscow, these are the multidisciplinary center SM-Clinic, Medkvadrat, Human Health, Dobromed, Medscan, Best Clinic and other institutions.
Functions of synovial fluid
The knee joint regularly withstands enormous loads. But as long as the connection is healthy, the person does not attach any importance to it. But many anatomical components are involved in comfortable movement and weight bearing. Articular fluid plays one of the leading roles.
The knee joint is of the synovial type, in which the bony surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage and surrounded by a connective tissue membrane reinforced by ligaments. The inner surface of the capsule secretes synovial fluid into the joint cavity.
When the norm is maintained, the biological environment has unique biophysical and chemical properties. Acts as a lubricant for the smooth movement of bone ends relative to each other. Delivers nutrients to cartilage fibers. Prevents premature thinning and destruction of joint elements.