Home » Laparoscopy » Laparoscopy and its types
March 11, 2020 Laparoscopy
Many people who have not yet had such an operation ask what it feels like after laparoscopy. In fact, each person can undergo this or that operation in his own way. The same can be said about laparoscopy. The consequences of this surgical intervention depend on the duration of the procedure, the skill of the doctor who performs the operation, postoperative care, how the patient tolerates pain and other factors. What suits one patient may not suit another at all. Doctors often tell their patients that the recovery period after surgery will only take a couple of days. But in reality this is often different from reality. Recovery may take several weeks.
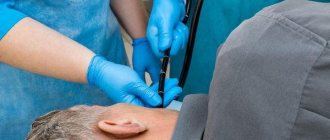
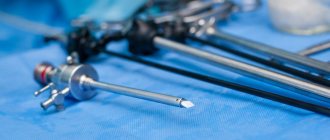
Laparoscopy is a branch of endosurgery in the abdominal area. More specifically, laparoscopy is considered a diagnostic or surgical intervention on the abdominal organs. It is carried out not through natural openings or a large incision in the front wall of the abdomen, but through special punctures. Through one of them, using an optical system (light guide), you can see the image on the monitor, and through the others, the surgeon introduces the necessary instruments for performing manipulations. The basic principles of surgical treatment do not change; thanks to endosurgery, they rise to a higher level. For patients, the operation itself is not something supernatural that could take them out of the normal rhythm of life for a long time or radically change their entire subsequent life.
In any developed country, endosurgery (laparoscopy in particular) is a one-day surgery, where the subsequent period depends on the disease, and not on the operation itself.
Laparoscopic operations are performed for diseases of the digestive tract and gynecology.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the removal of the gallbladder due to various diseases and some intervention on the extrahepatic bile ducts, which is performed under visual control using a laparoscope. Standard LCE is done under general anesthesia by a team consisting of 2 surgeons. In this case, a special endosurgical instrument is used, inserted into the abdominal cavity through 4 trocars, the diameter of which is 5-10 mm.
Laparoscopy in gynecology is performed:
- for infertility, the cause of which has not been shown by non-invasive research;
- if hormonal therapy is ineffective for infertility;
- during surgery on the ovaries (if an ovarian tumor was removed, there were cysts, sclerocystosis);
- if there is a suspicion of endometriosis, adhesive disease;
- if the patient suffers from chronic pelvic pain;
- if there is endometriosis of the ovaries, uterine appendages, pelvic cavity;
- with myomatous lesions of the uterus;
- if the fallopian tubes were ligated, there was an ectopic pregnancy, or there was a rupture of the tube;
- with torsion of the cyst, ovary, ovarian apoplexy, with internal bleeding;
- during a pelvic examination.
Stool disorders after laparoscopy: causes and treatment
Article prepared by:
Vasily Babkinsky
Doctor of the highest category
Appendicitis can be chronic or acute. The latter form is much more common. Some symptoms that occur during acute appendicitis are characteristic of a number of simple intestinal abnormalities, and therefore are easily misleading and distort the understanding of the situation. One of these symptoms is bowel dysfunction. Diarrhea with appendicitis is a serious symptom.
Diarrhea can also occur with appendicitis
Association with diarrhea before and after surgery
The inflammatory process on the appendix develops at any age, but in young children and the elderly it is much less common.
Despite the rapid development of medicine, only surgical intervention can cope with the disease - there is no gentle treatment.
It is important to promptly recognize signs of inflammation in the appendix and seek medical help, preventing pus from penetrating into the peritoneum.
Can there be diarrhea with appendicitis and should a problem with stool be considered a sure sign of inflammation? The appearance of diarrhea occurs in one case - if the appendix is located near the loop-shaped turns of the large intestine, which rarely happens. The inflammatory process spreads to the cecum, which causes liquefaction of the stool. Food is excreted in a half-digested form, as liquid absorption deteriorates.
After surgery, diarrhea appears quite often. The reason is therapy with antibacterial drugs that stimulate loose stools. The body's reaction to intoxication also ends with prolonged diarrhea. During the rehabilitation period, it is important to choose the right nutrition. If the diet includes prohibited foods, it is quite possible that stool disorders will appear.
If diarrhea after appendicitis lasts more than three days, bloody clots are observed in the stool, and the temperature rises, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What is appendicitis
The first section of the large intestine is the cecum. A special process departs from it - the appendix, 5-12 cm long - in an adult. This small appendage of the cecum performs important functions in the body:
- The lymphatic tissue concentrated in it resists harmful agents that penetrate the intestines - viruses, bacteria, yeast and mold.
- The isolated position of the appendix prevents intestinal contents from entering it. Thanks to this, it creates an ideal environment for the growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria. Microorganisms grown on a kind of “farm” quickly colonize the intestines in the event of loss of the symbiotic biocenosis after illness or treatment with antibiotics.
Blockage of the lumen of the appendage provokes rapid growth of microflora, which begins to “eat” the walls of its container, causing inflammation of the appendix of the cecum. According to doctors, the main causes of blockage of the appendiceal inlet are:
- Fecal stones due to chronic constipation.
- Intestinal neoplasms.
- Clusters of helminths.
- Adhesive processes of the abdominal and pelvic cavity organs.
As a rule, there is an acute course of the process, developing at lightning speed in 2-12 hours. Lack of surgical care threatens a complication in the form of diffuse purulent peritonitis with a fatal outcome.
What signs, besides diarrhea, indicate appendicitis?
It is not worth focusing only on diarrhea to determine the inflammatory process in the appendix. There are common signs of the disease that are easy to recognize on your own:
- painful sensations in the lower right (rare, but it happens that the pain appears on the left) part of the abdomen;
- attacks of nausea leading to vomiting;
- increase in body temperature by 1-3 degrees;
- severe dryness in the mouth;
- a thick layer of white coating on the tongue.
Diarrhea appears in the chronic form of the disease, while in acute inflammation, which lasts only two days, diarrhea simply does not have time to manifest itself. Loose stools do not affect the diagnosis in any way.
Secondary signs of appendicitis include not only diarrhea, but also constipation, which appears due to the inflammatory process in the intestines. A doctor can diagnose appendicitis with high accuracy, so you should not hesitate to contact a doctor if you experience a combination of several alarming signals from the body.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptom of appendicitis is pain. Aching dull sensations are constantly pursued, the pain does not go away. With any movement from sneezing to running, the pain intensifies. Initially, it is felt everywhere, then it is localized in the area of the appendage and remains there.
The temperature accompanies the inflammatory process without rising high. With appendicitis, the indicator does not exceed 37.5-38.5 degrees. The temperature may not rise. When the appendix ruptures, it increases sharply to critical levels.
A symptom of appendicitis is dry mouth, white coating on the tongue. The symptom is one-time vomiting, there may be diarrhea, but more often constipation occurs.
Possible complications after laparoscopy regarding gynecology
Laparoscopy helped many girls and women get rid of tumors that were debilitating the body, while others used it to cure infertility. Since this type of surgical intervention is the most gentle, all women hope that everything will go without complications.
But you also need to be aware of possible negative consequences. There were cases when surgical instruments touched the bladder and intestines during surgery. Cardiovascular damage rarely occurs. If the operation is performed incorrectly, the patient will develop adhesions. And poorly placed sutures create a risk of suppuration.
You need to call a doctor if you have the following signs:
- piercing pain in the lower abdomen;
- heat;
- severe weakness, the patient loses consciousness for a short time;
- headache, with darkening of the eyes;
- it is not possible to pass “little by little”, there is pain while the patient urinates;
- There is pus at the wound site.
I would also like to write the following: objectively evaluate your feelings. Discomfort in the area where the incision was made is one thing, and the presence of frightening pain covering the entire abdomen is another.
Constipation after surgery: what to do, easy ways to help the body with bowel movements
Often there are problematic health issues that can only be resolved through surgery. Constipation after surgery is a common and unpleasant problem for patients. How to fight and not face trouble? We will try to understand the nature of the disease and choose the appropriate treatment method.
Causes of constipation
80-90% of operations negatively affect intestinal motility, which becomes the main condition for the appearance of constipation in humans. A brief explanation of such unpleasant consequences of surgical interventions:
- After anesthesia, the body tends to experience a fundamental imbalance in functioning, muscle weakness (mainly reflected in the intestines).
- Due to postoperative sutures and injuries, tension is prohibited and defecation with straining is excluded.
- Physical passivity - lying down after surgery provokes a slowdown in bowel function. This means that the removal of contents from the body slows down.
- Changing the already habitual regime and diet (stress of the body).
- Taking a lot of medications to prepare for surgery.
The psychological factor plays an important role. After the operation, the patient experiences a stressful, sometimes depressive state, and even nervous breakdowns are possible. The described number of reasons stimulates constipation.
List of surgeries that cause constipation
Constipation usually appears after operations on the gastrointestinal tract. The list includes:
- Operations to remove appendicitis. The patient is recommended to eat small portions every 2-3 hours (porridge, puree or finely ground food). This diet will help a person quickly restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hemorrhoid removal surgery. The disease involves a number of reasons for the occurrence of obstipation, including pain, dysbacteriosis, the appearance of scars, disruption of the microflora in the intestines and fear in the operated patient about the dehiscence of the sutures. After removal of hemorrhoids, rest and proper nutrition are recommended.
- After abdominal surgery. Constipation is caused by adhesions (formations of connective tissue, which leads to gluing of the serous surfaces of organs) in the abdominal cavity. It is advisable to restore an active lifestyle (sports) as much as possible in order to get rid of the ailment. Doctors advise diversifying your diet with cereals made from coarse cereals (wheat), biokefir, vegetable salads and light soups.
- After laparoscopy (surgery by creating a small hole). The operation eliminates injury. True, this does not mean that constipation will bypass the patient. In the case of such an operation, you will need to give up physical activity (gym, dancing, running, etc.) and hot procedures (sauna). Daily care of sutures and antiseptic bandage is required.
- After resection. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy offers the removal of a poorly functioning gallbladder. On the first postoperative day, it is forbidden to drink or eat. Over the next 24 hours, you are allowed to take unsweetened rosehip decoction, switching to green tea, dried fruit compote or low-fat kefir. As for solid foods, mashed potatoes, pureed vegetable soups, and boiled fish are allowed on the fourth or fifth day. Quick recovery and treatment of constipation require adherence to the prescribed diet and proper nutrition.
- Removal of the uterus and possible adhesions. The occurrence of constipation is often associated with a long operation, a large amount of lost blood, hidden bleeding, and possible infection.
- After general anesthesia. Everyone's reaction to anesthesia is different. Some people react negatively to anesthesia. In addition, anesthesia has a bad effect on the liver and kidneys due to its inherent narcotic nature. Simple boiled water comes to the rescue.
Almost all surgical interventions in the human gastrointestinal tract lead to constipation. To get rid of the disease, you will need to follow the doctor’s recommendations and take care of your own health.
If you want to treat constipation yourself, you should follow the advice in the article (with your doctor’s permission!). Treatment methods for constipation can be divided into medicinal and traditional.
Constipation medications
Stool softeners will help solve the painful situation. Emollients normalize bowel movements. To purchase them, you do not need special prescriptions from your doctor. Medicines fill the stool with an optimal level of moisture, which makes bowel movements easier. It is recommended to take tablets 1-2 times a day.
Laxatives for constipation in combination with emollients help cope with the disease. There are stimulating and osmotic. The latter allow fluid in the body to reach the intestines. The first ones are also effective. Diarrhea and stomach cramps may occur after a stimulant laxative.
Lubricants are a lesser-known method of dealing with complicated bowel movements, which does not mean there is no result. The principle of operation is similar to softeners; easy passage of stool through the gastrointestinal tract is ensured by lubrication of the intestinal walls. Mineral oil and fish oil are considered more common and accessible.
Suppositories or enemas also help relieve constipation. In most cases, the main component of the suppository is glycerin with bisacodyl, which easily penetrates the muscular structure of the rectum, stimulating easy contraction. An enema should only be given with the permission of a doctor, since after a number of operations it is contraindicated.
Folk remedies
Regarding folk remedies in the treatment of constipation, therapy is based on proper nutrition and consumption of certain foods in higher concentrations. It is necessary to increase the level of fluid in the body.
You are supposed to drink the universal norm of water or more (from two liters per day): boiled water, coffee and decaffeinated teas (the best option is a laxative).
The consumption of carbonated drinks, fruit nectars, alcohol and energy drinks is prohibited.
Fiber in supplements softens stool and facilitates its movement through the gastrointestinal tract. Dietary fiber is consumed in different ways: in the form of capsules, chewing candies or powder - no more than twice a day with the permission of a doctor.
It is worth abstaining from foods that cause constipation:
- Foods with high concentrations of potassium and calcium.
- Milk (cheese, sour cream, yogurt, not including low-fat kefir).
- Fruits (grapes and bananas).
- Sweets (chocolate, caramel, etc.).
- Concentrated nectars.
- Flour and butter products.
- White bread and pastries (sweet and savory).
- White rice.
- Semi-finished products, etc.
Prunes are an essential component in the treatment of constipation, because their natural sugar sorbitol and fiber have a laxative effect. It is permissible to drink warm prune juice - a glass a day.
Traditional medicine suggests treating constipation with senna leaves and buckthorn bark, chamomile infusion, pumpkin or carrot juice. But no folk remedies will clear the congestion without clearly defined rules. In the case of nutrition, this is a strict diet.
Features of diets and general recommendations
Diet should be called the most effective means of combating postoperative constipation, which is prescribed by the attending physician.
And not in vain, because exclusively proper nutrition can enhance the effect of medications and give the body strength to fight the disease.
The diet consists of products whose composition is rich in certain substances, vitamins and microelements, which can easily cope with constipation:
- Oatmeal and buckwheat (in combination with pieces of prunes and a spoonful of honey are not only healthy, but also delicious).
- Whole grain bread, bran and diet bread.
- Vegetable and fruit salads (except for legumes and quince).
- Steamed lean meat (chicken or turkey).
- Boiled fish.
In addition, you can sign up for acupressure massage. By identifying and activating certain points, stagnant food moves through the gastrointestinal tract. To carry out a massage procedure, it is recommended to make an appointment with an experienced master and not to do it yourself, so as not to harm yourself.
Physical activity is seen as a key part of the diet. It is important to force yourself to move from the moment the doctor allows you to walk.
Systematic physical exercise normalizes the functioning of the colon, and light aerobics in the fresh air stimulates regular bowel movements. It is advisable to devote at least 3 hours a week to walking.
And at the same time, engage in certain sports that are allowed after the operation.
Try to visit the bathroom regularly. Listen to your body and its signs of the urge to have a bowel movement. You should not put off going to the toilet. Later, such restraints will immediately cause severe constipation. Over time, defecation will acquire an individual pattern, and the intestines will be able to be emptied daily at approximately the same time.
A timely consultation with your doctor before surgery and a discussion with your doctor about the likelihood of constipation will help prevent constipation.
Together, optimize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and exercise as much as possible. If problematic situations arise, contact a gastroenterologist without delay so as not to worsen the situation.
Maintain a stable state of health and invest physical labor in it, because this is the most valuable capital of a person.
Source: https://GastroTract.ru/simptom/zapory/zapor-posle-operatsii.html
Stool after cholecystectomy
As mentioned earlier, laparoscopy is not only done to eliminate or diagnose female diseases. It's time to talk about cholecystectomy.
For 2-4 months after gallbladder removal, patients must follow a certain food restriction (diet). Why is this so important? The body needs time to adapt to changes in the functioning of the biliary system. At this time, it is possible (but not always) for stool to loosen or become more frequent up to 2-3 times a day. So some suffer from constipation, others from frequent loose stools. It's different for everyone. If you follow a special diet, the pain during bowel movements will not last long, and then it will go away completely.
But after 4-6 months after the operation, a person can return to his usual lifestyle (almost without restrictions). But if the patient’s disease lasted for a long time, and then became complicated by damage to related organs (chronic pancreatitis, cholangitis, etc.), then some symptoms will remain even after cholecystectomy, and in the future they will need to be treated. This is an additional argument in favor of timely surgery if there is gallbladder disease.
The main reasons for the development of postoperative stool disorders
- The first reason why stool disorders develop after surgery is anesthesia. Laparoscopy requires general anesthesia, and deep sleep is achieved using strong narcotics. They have a direct toxic effect on the digestive organs, which leads to temporary disruptions in their functioning.
- Another point is general muscle atony, including intestinal muscles - this inevitably leads to disturbances in peristalsis.
- In the case when laparoscopy is performed for the purpose of cholecystectomy, that is, when the gallbladder is no longer there, the digestive system has to get used to the new mode of functioning. This is not easy, and a lot depends on proper rehabilitation and proper nutrition, following a fairly strict diet. This moment aggravates the toxic effect of anesthesia drugs, and stool disorders are inevitable.
- Changes in diet and strong medications significantly disrupt the intestinal microflora, which also negatively affects its functioning.
- In addition, it may simply be painful for the patient to go to the toilet, and he consciously avoids it. Diarrhea after cholecystectomy is associated with the constant flow of bile into the intestines, and it is a stimulant of peristalsis.
One of the complications of cholecystectomy is diarrhea.
In many cases, especially after cholecystectomy, the body independently adapts to new working conditions, but it is still not recommended to wait - on the advice of a doctor, you should follow a diet and take medications, since diarrhea quickly leads to dehydration, loss of vitamins and microelements.
Unpleasant symptoms after surgery
Sometimes the patient has pain in the lower back and middle of the abdomen after surgery. To reduce pain, you need to rest more and try not to strain yourself. If the pain does not go away after three days, contact your doctor, as this may be a sign of possible complications.
Bloating, nausea and weakness are the patient’s constant companions for three days. You should not be afraid of such symptoms, because against the background of a previous operation this is a completely normal phenomenon. Say no to junk food these days. Drink kefir and low-fat yogurt, eat crackers, chicken broth, lean meat and biscuits. Sweets, fried foods, and flour foods are prohibited during this period. The digestive system is very weakened and cannot function as usual.
After three days, return to your normal diet if the pain in the lower abdomen and heaviness go away.
Doctors say that pain in the lower abdomen is normal and there is nothing strange about it. It is present in 80% of patients after such an operation. It’s a completely different matter if there is severe pain. Then you should definitely consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous; the patient’s situation may worsen.
Constipation symptoms
If a person does not have stool in the first few days after surgery on the gastrointestinal tract, this does not mean that constipation has occurred. In the first days, patients are usually advised to drink and only on the third or fourth day are they allowed to eat grated light food. So it is quite normal that in the first 2-3 days the patient will have no stool, since the intestines simply cannot process it, and it starts when normal food begins to enter the body.
Heaviness in the abdomen, bloating and nagging pain, which indicate fullness, signal constipation.
But the following signs will signal constipation itself:
- Bloating and gas formation.
- Fatigue, fatigue may appear, and performance may decrease.
- With prolonged stagnation of the intestines, a rash appears on the face, which is evidence of intoxication of the body.
- When trying to empty the intestines, the patient experiences sharp pain in the rectal area, since the feces are already very dry and begin to irritate the intestines and can even lead to cracks in the rectum and anus.
- If the act of defecation is still successful, the patient continues to feel heaviness in the stomach and a feeling of incompleteness of the process.
- The person loses his appetite and may experience headaches, pain and nausea.
When these symptoms of constipation have already begun to appear, it is important to restore bowel function as soon as possible, before the patient’s condition worsens and constipation becomes chronic.
Constipation is also dangerous because it slows down the recovery process after surgery and can lead to complications.
What to do for constipation after laparoscopy
An important point after laparoscopic intervention is compliance with the drinking regime - you need to drink at least 7 glasses of clean, still water per day (excluding other liquids). A decoction (juice/infusion) of prunes helps a lot. There is no point in using any laxatives without a doctor’s prescription - they only have a symptomatic effect and do not eliminate the very cause of constipation. The daily diet can be enriched with:
- whole grain bread;
- bran;
- buckwheat;
- carrots.
Detailed recommendations are usually written by a doctor for a specific patient.
In the postoperative period, the microflora often suffers, and a number of measures are aimed at restoring it. There are a lot of drugs that, once in the intestines, help quickly restore the correct ratio of bacteria, which allows stool to normalize. The doctor may order a study of the acidity of gastric juice - this point also affects peristalsis. To correct the pH value, it is better to use a diet - at low values add sour fruits and berries to the diet, at high values - fermented milk products.
Diet and physical activity after laparoscopy
A strict diet is prescribed for 3-4 months, and it must be followed. This is a prerequisite for an easy recovery period. Detailed recommendations on proper nutrition should be written in the hospital upon discharge. All dishes must be boiled and pureed; steaming is allowed. Fatty foods and alcohol are also prohibited. An important point is the frequency of meals - at least 6 times a day in portions of 200-250 ml. Over time, portions gradually increase and new foods are included in the diet.
It is irrelevant to write that movement is life, but after cholecystectomy this is really true. Already in the first week after surgery, daily half-hour leisurely walks are needed, and light breathing exercises are allowed. This will keep the intestines in good shape. Then you can do general hygienic gymnastics, but without abdominal exercises. Running is not allowed, but walking time is increased to an hour. Normal activity is allowed only after six months or a year, depending on the patient’s condition.
What to do if your lower back hurts after laparoscopy?
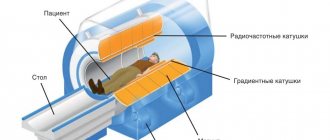
Most likely, this has nothing to do with the operation. If there is a tug in the abdominal area, then a woman may instinctively tense her back muscles and not even notice it. Hence the appearance of lower back pain. In any case, you should consult your doctor and carry out the necessary examinations (flora smear, ultrasound), as well as an X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine, since the problem may be pinched nerve fibers or osteochondrosis.
Why does constipation occur after laparoscopy?
Since carbon dioxide is introduced into the abdominal cavity during surgery, this can cause a deterioration in intestinal motility and cause constipation. This phenomenon is undesirable, since constipation after laparoscopy creates unnecessary tension in the abdominal cavity, which can cause the internal sutures to separate. To minimize constipation, it is necessary to follow a special diet that excludes the intake of “fixing” foods. You also need to drink a lot of fluids so that you don’t have problems going to the toilet in large quantities. Doctors also recommend leading an active lifestyle and moving a lot. Long walks on foot will be beneficial.
It is important to follow these rules in order to avoid hemorrhoids after laparoscopy, which provokes constipation. Laparoscopy is a rather innovative and gentle operation, but even it does not exclude the possibility of hemorrhoids (especially if this method was used to remove the uterus and/or its appendages).
Menstruation after laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
The onset of menstruation occurs in most patients on time and menstrual irregularities are usually not observed. Sometimes after laparoscopy, patients experience menstrual irregularities, which may begin delayed or, conversely, ahead of schedule.
Such violations are associated with many factors: the level of professionalism of the doctor, the characteristics of the woman’s body, age characteristics, weakened immunity, stress and more. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the processes occurring in the body, the symptoms and nature of the discharge and seek advice from a doctor. In such cases, the doctor prescribes medications and vitamins that strengthen the immune system.
To treat patients who have not had menstruation for six months or more, hormones are prescribed. After laparoscopy, ovulation reappears and pregnancy is possible after six months or a year. If ovulation does not return after several cycles, consult your doctor. Most likely, it is necessary to resort to medical treatment.
Problems with bowel movements after surgery
In that situation, if after an operation aimed at removing hemorrhoids, hernia or appendicitis, constipation occurs, then you should immediately begin treatment for it, since there is a huge likelihood of complications.
Problems with defecation can be caused by postoperative trauma, but much more often their occurrence is due to the effect of anesthesia on the body. During the process of anesthesia, almost all muscles weaken, including the intestinal muscles. In order for muscle tone to be restored, a certain time must pass, before which constipation begins to appear.
To prevent the development of constipation after surgery, it is recommended to follow certain rules:
- Before your first meal, be sure to drink 200 milliliters of cold water.
- It is advisable to use laxative medications for several weeks after surgery.
- The intestinal flora should be properly enriched with various microelements. To increase their amount in the body, you should take probiotics.
- In order for the intestines to function properly, a special diet is required. In the morning, you should give preference to porridge cooked in water. At lunchtime, it is recommended to consume fermented milk products, boiled lean meat or fish, and vegetables.
After chemotherapy, constipation may occur for the following reasons:
- insufficient amount of fluid in the body - at least 2 liters of water should be consumed per day, and during chemotherapy, this amount increases to 3 liters;
- poor quality nutrition - the patient eats food containing a large amount of fat, eating is carried out on the go;
- low intake of fiber into the body;
- drugs used in chemotherapy have a negative effect on smooth muscle and intestinal mucosa;
- there is a pathological effect of a malignant neoplasm on the process of feces formation;
- as a result of the strong influence of drugs used in chemotherapy, the intestinal microflora is destroyed, which contributes to the development of constipation;
- the mucous membrane in the area of the large intestine is affected;
- there is a negative effect on the autonomic nervous system, which controls the normal functioning of the large intestine;
- In rare cases, problems with bowel movements occur as a result of a sudden change in chemotherapy drugs.
Carrying out surgery in the intestinal area for quite a long time worsens the process of peristalsis. This leads to stagnation of intestinal contents, which provokes the development of constipation.
In some situations, constipation causes swelling of the intestines, which puts pressure on the chest from the inside. In turn, the chest affects the muscles of the heart and lungs.
If you do not promptly begin treatment for constipation after intestinal surgery, you can lead to disruption of the functioning of all body systems. The duration of therapy in this situation is about two months.
Laparoscopy is one of the most modern methods of surgery, when surgical intervention on internal organs is carried out through a small hole.
When using this operating technique, the likelihood of injury is eliminated, but the risk of constipation is high.
Treatment of constipation in such a situation should be strictly controlled by a doctor, but there are general rules of conduct. It is strictly forbidden to engage in sports, heavy physical labor and visit baths or saunas.
Removal of the uterus is a rather complex operation, which is further characterized by the formation of adhesions.
It is the adhesions that occur after removal of the fallopian tube that cause problems with bowel movements.
The formation of adhesions occurs as a result of the following factors:
- quite a long operation;
- presence of injuries during surgery;
- a large amount of lost blood;
- there is hidden bleeding;
- possible infection;
- a person has a predisposition to the development of adhesions, which is inherent in genetics.
If there is an inflammatory process in the area of the cecum, immediate surgery is required. This urgency is justified by the fact that in the event of a rupture of the appendix, the development of a life-threatening disease - peritonitis - may occur.
In the modern world, such an operation is no longer life-threatening, but certain consequences from its implementation still remain and they consist precisely in problems with defecation.
During the operation, intestinal motility is weakened, which provokes the formation of constipation.
After performing a surgical intervention aimed at removing appendicitis, the main reasons for the development of constipation are the following:
- preparatory process for surgical intervention and implementation of drug blockade;
- the effects of anesthesia or surgery;
- lack of physical activity for several days after surgery;
- the presence of postoperative adhesions;
- nervous tension before the operation and fear of developing constipation after it.
The puncture is widespread among female representatives who use the IVF procedure.
The IVF process is as follows: an egg is removed from a woman’s body, which is subjected to artificial insemination and then placed in an incubator.
Constipation in this case can occur for the following reasons:
- exposure to anesthesia and medications;
- an overactive reaction of the ovaries to the use of hormonal drugs, which leads to their rapid growth.
It was noted that in most cases, constipation is caused not by the procedure itself, but by the high-protein diet prescribed after the puncture.
Why does the ovary hurt, ache, or tug after laparoscopy?
If your ovaries hurt after laparoscopy, this is a natural process. Still, this is an operation, albeit performed using a non-laparotomy method, in which recovery is even longer and more difficult. After recovering from anesthesia, in the first hours, the right or left ovary sometimes hurts, as well as the puncture sites.
If pain after laparoscopy persists for a long time, even after the stitches are removed, then this is a good reason to contact a medical institution for additional examinations. The causes of pain in the area of the left ovary or on the right may be inflammation, improperly performed surgery, too slow tissue healing, as well as other reasons.
Why do I have loose stools (diarrhea) after laparoscopy?
This phenomenon can be caused by anesthesia, since the narcotic substances contained in it inevitably affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, general muscle atrophy can temporarily cause diarrhea.
In order to stop diarrhea as quickly as possible, it is necessary to introduce foods rich in fiber into the diet. This is bran, whole grain bread. You can also eat rice.
How to get rid of post-operative constipation?
Treatment is prescribed only after identifying the cause of this symptom. First of all, you should increase the amount of fluid consumed to 2.5-3 liters. This promotes softening and faster excretion of stool. The diet should include wholemeal bread, bran, buckwheat and oatmeal.
Laxatives allow you to quickly improve bowel movements, but each drug has side effects and contraindications. In addition, they do not help eliminate the cause of constipation. Active substances act in the large intestine, increasing osmotic pressure and enhancing peristalsis.
It is necessary to begin treatment with herbal-based drugs, available in the form of tablets, drops and suppositories. The feces soften due to the swelling of the fibers contained in the preparations. They are quickly eliminated from the body along with feces.
The drug Fortrans is indicated for long-term constipation in adults; it should not be taken if you have heart, liver or kidney diseases. The elimination of unpleasant symptoms is facilitated by the restoration of microflora with the help of probiotics, which reach the intestines in their original form. By increasing the number of beneficial bacteria and eliminating inflammation, the drugs quickly get rid of the problem. Glycerin suppositories allow you to quickly get results, but you should not abuse such drugs. The tone of the intestinal walls decreases, because of this it becomes unable to empty itself. Taking laxatives after surgery can contribute to exhaustion and dehydration. For treatment at home, you can use folk remedies for constipation.
medoperacii.ru
Diarrhea after gallbladder removal
One of the common complaints after cholecystectomy is: “I can’t go to the toilet normally.” The most common concern is diarrhea, which is a consequence of bladder removal. The first days it can be painful not only to pass a lot, but also to urinate - the condition stabilizes after 2-3 knocks. After the postoperative pain subsides and a gradual return to normal food intake, the patient is in the hospital, receives appropriate treatment and there are no problems with peristalsis. In the recommendations, the doctor should write down the specifics of the diet, but many do not pay due attention to this point.
The occurrence of diarrhea is associated with a violation of the frequency of meals, too much food and the consumption of prohibited foods. This leads to the fact that the bile duct remains open into the intestine, and the bile entering it constantly stimulates peristalsis. The result is diarrhea, loss of nutrients and minerals, and a sharp deterioration in general condition. There is no point in constantly correcting the situation with medications, so diet and the correct mode of physical activity come to the fore.
In 60% of cases when loose stools occur after laparoscopy, the patient himself is to blame. In addition to violating the diet, many people prefer to take certain medications to correct bowel movements - doing this without consulting a doctor is unacceptable, since such behavior can lead to serious complications.