0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.27
616
Hemoglobin
A few days after the baby is born, doctors conduct a laboratory blood test. This is done to check blood counts and blood type. One of the most important values in the analysis is hemoglobin HGB. In this article we will look at what kind of hemoglobin a newborn baby should have.
Taking blood from a newborn
Hemoglobin and its main task in the body
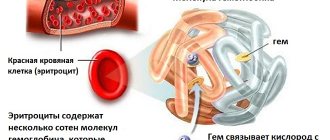
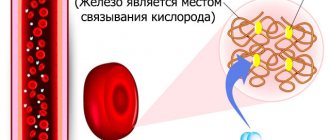
Hemoglobin is a complex protein that is part of the main blood cells, red blood cells. It consists of 2 main components: heme (iron, which gives blood its red color) and globin (protein).
Hemoglobin (new cells) is formed in the bone marrow. Its average duration is 120 days. It is then broken down in the liver and converted into bilirubin (bile pigment) and excreted from the body in feces.
The main purpose of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues , as well as to take carbon dioxide from the organs and deliver it to the pulmonary system for removal from the body. Blood saturated with oxygen has a bright scarlet color, and when carbon dioxide is transferred, the color of the blood becomes dark.
An excess or lack of hemoglobin changes the amount of oxygen in the blood, which impairs the functioning of organs. The speed of metabolic processes slows down.
Additionally, hemoglobin is involved in regulating the acid-base composition of the blood (prevents alkalization of the plasma) and retains the required amount of moisture in the tissues.
How is it determined
The most common diagnostic method is a general blood test. Its popularity is due not only to its ease of implementation, but also to its high level of information content. This method can be carried out in public medical institutions, and no financial investments are required.
Determining specific types of protein (for example, glycosylated hemoglobin) is a little more difficult. They must be tested in private laboratories.
When interpreting the results of the analysis, it is important to take into account the fact that the protein content in venous blood is ten to twenty percent lower than in capillary blood.
Methods for determining the level of hemoglobin in the blood of children
To determine the concentration of iron in a child's blood, it is necessary to donate blood from a finger. A vein sample does not provide accurate information. This analysis takes no more than 5 hours to prepare. To measure the amount of hemoglobin, the unit g/l is used (how many grams of protein per liter of blood).
What affects hemoglobin levels in the blood:
| Watch | In the morning, the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is higher than in the evening. |
| Food | Food affects the composition of the blood, the concentration of hemoglobin decreases, as it is involved in the process of digesting food |
| Physical exercise | If in the evening the child participates in active physical games for a long time, the analysis will show incorrect results. |
| Baby's position | The child must not be in a horizontal position when the analysis is taken. In this case, blood flows from the finger to the internal organs, which distorts the result. |
| Blood collection | When taking an analysis, you should not put too much pressure on your finger, as this will allow intercellular fluid to enter the blood, which will lower the hemoglobin level. |
| Location of the procedure | When taken from a vein, a tourniquet is applied to the vessels, which leads to stagnation of blood and an increase in the amount of hemoglobin. |
| Diseases accompanied by dehydration | If there is a lack of fluid in the body, there is not enough fluid in the blood plasma, and the amount of hemoglobin increases. This distorts the result. |
Doctors recommend taking a blood hemoglobin test in the morning and on an empty stomach.
In the evening you need to give the child more water so that the blood flows in the morning without the need for strong pressure on the finger.
When checking the presence of iron dynamics, parents should not change the diet, time of delivery, or activity of the child.
Features of children's hemoglobin
We all know that a child’s body has a number of its own characteristics that are different from the body of an adult. This is manifested in joint mobility, metabolic rate, and, of course, the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood.
Did you know? A special place in the study of the hemoglobin molecule and its properties in the human body was occupied by the works of the English biochemist Max Perutz, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1962. Peruts was the first to reveal the features of the spatial structure of the hemoglobin molecule.
Normal hemoglobin level in children 0-3 months
The hemoglobin level in a child after birth is high, which decreases by the 4th month of life. Due to the breakdown of large amounts of this protein, children may develop congenital jaundice, which resolves on its own on the 4th day.
Iron indicators from birth to the 3rd month:
- from birth to the end of 3 days, the indicator should vary within the range: 175-240 g/l;
- by the end of the 1st week the norm reaches: 160-210 g/l;
- when the child is 1 month old, the amount of iron is: 150-185 g/l;
- at 2 months the norm is: 100-150 g/l;
- by the end of the 3rd month the indicator reaches: 105-130 g/l.
At this age, minor deviations are not an indicator of pathology and do not require drug treatment.
Symptoms of low levels
If the hemoglobin level in children is low, then treatment should be started immediately. At this age, the child grows and his organs develop.
Iron-containing protein carries oxygen to all tissues and organs. If there is insufficient oxygen in the body, the baby will not be able to develop normally.
A baby's hemoglobin is low if parents notice the following symptoms:
- loss of appetite;
- the baby is weak and lethargic;
- the child becomes irritable;
- the skin is dry and flaky;
- immunity decreases;
- headache appears.
Anemia in a baby most often appears at 2 months. The cause may be not only some disease in the baby, but also the health of the mother.
The condition of the child and the mother are closely related. The doctor will determine a decrease in hemoglobin if a woman had anemia during pregnancy.
The percentage of babies who will experience a decrease in hemoglobin reaches 80%.
Video:
A baby born with anemia does not show activity and is very weak. During the time that the fetus is in the womb, the child’s body does not have time to form a system responsible for the level of hemoglobin. That is why up to 6 months a baby may experience reduced protein levels.
Premature birth is a serious cause of anemia in an infant. A developing fetus cannot completely form a circulatory system; it simply does not have time to receive the necessary substances for its formation.
If the mother had a multiple pregnancy, then all the nutrients that penetrate the placenta are divided between the babies. Thus, babies receive insufficient amounts of substances necessary for normal development.
A lot of effort is spent on neutralizing harmful substances, so the baby may feel weak, drowsy, and dizzy.
After taking a hemoglobin test, the norm in a 4-month-old child should correspond to the established range.
If the numbers in the decoding are below normal, then treatment should be started immediately. Anemia in a baby during the first months of life has dangerous consequences.
After surgery, a child's iron protein levels will be reduced. In this case, the blood will recover on its own after some time.
Normal hemoglobin level in children 8-12 months
From 8 months to 1 year, the hemoglobin level decreases slightly, although the limits of permissible deviations remain the same and are equal to: 110-140 g/l.
Average indicators (g/l):
- 8 months – 130;
- 9 months – 130;
- 10 months – 125;
- 11 months – 125;
- 12 months – 120.
If hemoglobin is low in children aged 8-12 months, the pediatrician may recommend giving the baby apple juice/sauce as complementary foods.
Already from this age, deviations from the norm may indicate the beginning of the development of pathology. If deviations were observed previously, the pediatrician will prescribe a retest.
Normal hemoglobin level in children aged 1 year and older
Before the child reaches the 1st year, the lack of hemoglobin could be replenished with reserves accumulated in utero. Upon reaching 12 months, the body begins to produce iron on its own. Therefore, for children after one year, adequate nutrition plays an important role.
Norms of iron in the blood from 1 year to 12 years (g/l):
- 1-2 years average reading 120, permissible deviations: 110-140;
- From 3 to 4 years, the average reading is 125, permissible deviations: 110-140;
- From 5 to 7 years, the average reading is 130, permissible deviations are 120-140;
- From 7 to 12 years old, the average value is 135, permissible deviations: 115-150.
After 12 years of age, children begin puberty. The iron level already changes depending on the gender of the child.
Normal hemoglobin level in a child by age and gender
Norm for girls (g/l):
- from 12 to 15 years the norm varies from 110-150;
- from 15 to 18 years old the limits are 115-155.
Norm for boys (g/l):
- from 12 to 15 years of age the permissible limits are 120-160;
- from 15 to 18 the value varies 115-160.
From this age, deviations from the norm in girls (with a slight change and without additional symptoms) may occur during menstruation. Therefore, the pediatrician should be informed about the presence of menstruation during the period of blood sampling.
What hemoglobin should premature babies have?
The hemoglobin level in a child born prematurely differs from that of children born on term.
This is influenced by 3 factors:
- The child did not receive enough iron reserves in utero, which are formed in the last months of development;
- The bone marrow is not fully mature to produce the required amount of iron.
In premature babies, the permissible lower limit of hemoglobin at birth is 160 g/l , while in full-term babies it is 5 g/l. higher. By the age of one year, the lower limit drops to 100 g/l, in full-term infants it is 110 g/l. A level of 85 g/l is considered critical, then the child needs an urgent blood transfusion.
Iron deficiency can appear by the 3rd month of life , which is dangerous for the child (he will begin to lag behind in mental and physical development). By the age of 3, the child’s iron level returns to normal, with proper treatment, which is determined by the pediatrician.
Factors affecting hemoglobin levels in children
In a healthy baby at birth, hemoglobin levels may begin to decrease.
Smoking and alcohol during pregnancy can not only have a negative impact on the child’s hemoglobin level, but also lead to much more serious pathologies in the baby’s health
The development of pathology may occur due to the following reasons:
- course of pregnancy. If there was a multiple pregnancy, prematurity, or the mother smoked and drank while pregnant. Mom catches a cold and takes medication. As well as difficult childbirth with injuries to the child;
- In infants, iron deficiency can develop due to improper nutrition of the mother. In formula-fed babies, the amount of iron is influenced by the feeding mixture;
- in older children, iron levels are affected by the introduction of complementary foods;
- in case of illness, hemoglobin levels decrease , so a sudden decrease in iron may signal a hidden disease;
- blood diseases can be inherited, but do not appear from birth;
- the presence of internal bleeding (open ulcer, rupture of a small vessel).
The pediatrician initially checks the hereditary factor and how the birth proceeded. When these indicators are negative, the child’s nutrition and the presence of hidden diseases are checked.
Signs of low hemoglobin
Characteristic external signs:
- Paleness, “circles” under the eyes.
- Lethargy, apathy, weakness, drowsiness, rapid onset of fatigue.
- Dizziness.
- Nails with white spots.
- Decreased appetite.
- Sleep disorders.
- Frequent infections.
- Dryness and flaking of the skin.
In severe cases, children with anemia have shortness of breath, increased heart rate (tachycardia), and impaired attention and memory.
The earlier anemia develops, and the later its treatment is started, the more clearly the child exhibits developmental delay.
Hemolytic anemia can be suspected when signs of jaundice appear.
Expert opinion
Irina Katykova
Pediatrician, pediatric neurologist
Ask a Question
Do you still have questions about your child's health? Ask them right here on the website and we will definitely answer!
High hemoglobin in a child
A change in blood composition towards an increase in hemoglobin is no less dangerous than anemia (iron deficiency). Pathology can be detected by characteristic symptoms and by taking a blood test.
Symptoms of high hemoglobin
A slight increase in the amount of iron in the blood may be temporary and go away on its own. In this case, there are no symptoms of pathology.
One of the symptoms of high hemoglobin in a child is refusal to eat or poor appetite
With a significant increase in hemoglobin over a long period of time, the child develops symptoms:
- Self-appearance of bruises on the body that take a long time to disappear. Or their formation with a light touch.
- When receiving abrasions or scratches, there is an increased viscosity of the released blood.
- Headache caused by high blood pressure.
- The child gets tired with little exercise and sleeps more than usual.
- Appetite is reduced to a minimum or completely absent.
Excessive blood and sudden appearance of bruises are the hallmark symptoms of the disease. When contacting a pediatrician, the cause of the pathology will be clarified, as well as how much the permissible level is exceeded. Blood that is too thick can cause the baby to die quickly and suddenly.
Reasons for increased hemoglobin
An increase in hemoglobin can be caused by serious pathologies or temporary factors. After they are eliminated, the blood composition returns to normal.
Active games and intense physical activity can lead to a short-term increase in hemoglobin
Reasons for a short-term increase in hemoglobin in the blood:
- intensive physical exercises, active games. In this process, the body uses more oxygen, so the brain, in order to sufficiently replenish the tissues with it, sends a signal to increase red blood cells in the blood;
- living in the mountains or places with thin air. In this case, the body experiences a deficiency of oxygen, since there is little of it in the air. To increase its concentration in the blood, more red blood cells are produced;
- long stay in a room with dry air. This leads to temporary dehydration of the body. As a result, blood thickening and hemoglobin increase;
- frequent consumption of foods high in iron;
- burns , the body produces more hemoglobin to restore the skin;
- side effects from taking medications;
- smoking in adolescence.
These causes should be excluded by the pediatrician, since treatment is not required to eliminate the pathology.
Dangerous causes of increased iron:
- infectious and endocrine diseases (rotavirus, diabetes), accompanied by loss of fluid from the body;
- impaired functioning of the lungs , accompanied by insufficient respiratory activity;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels:
- increased production of red blood cells by the bone marrow as a result of a malfunction of the body or due to neoplasms (cancer or benign tumors);
- impaired renal function.
To reduce the amount of iron, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of the disease. If the disease cannot be treated, then the pediatrician will prescribe medication.
The danger of high hemoglobin in children
A normal level of hemoglobin is necessary for the full functioning of the body. Its increase can cause the child to develop dangerous complications. Due to the increase in red cells, the blood becomes thick and viscous. As a result, oxygen is delivered more slowly to all organs , including the brain experiencing oxygen starvation.
High hemoglobin and, as a result, thick and viscous blood can cause blood clots, which is life-threatening
Thick blood can independently clog blood vessels or, due to the changed consistency, blood clots can form. Also, the vessels wear out quickly, and hemorrhage can occur not only in the form of bruises on the skin, but also in organs. Thick blood can cause a heart attack in childhood.
An increased amount of iron settles in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby disrupting the functioning of organs and increasing the likelihood of developing pathologies . Untimely treatment can result in mental retardation for the child, the development of abnormalities in the digestive tract and death.
Treatment. Medicines, folk remedies
If elevated hemoglobin is detected, the pediatrician prescribes a comprehensive treatment , which will depend on the root cause of the development of the pathology. If an increase in red blood cells is a symptom of a disease, then therapy for this disease is necessary.
The child's diet and drinking habits are adjusted. Drinking plenty of fluids will prevent dehydration and thin the blood. Additionally, during the treatment period, foods with a high iron content (pomegranate, buckwheat, liver) are excluded. The diet should contain more fish products, poultry, and legumes.
Plentiful fluid intake by a child is important not only for maintaining normal hemoglobin levels, but also for the health of the child’s body as a whole.
During the treatment of the root cause or if the increase in iron is a consequence of the disease, the child is prescribed blood thinners . Their purpose is to remove excess hemoglobin from the blood.
More often used in pediatric therapy:
- aspirin;
- chimes;
- heparin.
Vitamin preparations containing vitamins B and C are also . They promote the absorption of iron in the body. The dosage, course and type of medications are prescribed by a pediatrician; self-medication can be fatal.
For school-age children, leech therapy can be used in joint treatment. They remove “bad blood”, have a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels, and reduce the likelihood of blood clots.
You can also eliminate excess hemoglobin by bloodletting using cupping. In severe cases, bloodletting may be prescribed by cutting the veins (this procedure is performed in a hospital).
Treatment with leeches for high hemoglobin in children is permissible only in extreme cases!
Treatment with leeches and bloodletting cannot be carried out if there are contraindications:
- pathologies of heart development and low blood pressure;
- tumor formations;
- blood clotting disorder;
- in girls during menstruation;
- deviations in mental development;
- skin diseases;
- age up to 7 years.
The room should be well ventilated and with humidified air. The child should spend more time outdoors.
You can use traditional medicine recipes: flaxseed oil, tea with lemon, or just lemon water. Cranberry juice thins the blood. During treatment, you need to regularly take a blood test to check iron levels.
Features of treatment for children under one year old
When treating infants, it is necessary to provide the child with plenty of fluids. It is advisable to give water between feedings.
The diet of a nursing mother plays a huge role in the development of the baby, in particular, regarding the level of his hemoglobin
When breastfeeding, the baby can receive medications through milk, and the mother should also adhere to a diet with a reduced iron content. When artificial feeding, formulas are selected with a lower hemoglobin content.
The introduction of complementary foods should occur under the supervision of a pediatrician , with iron-containing products being introduced last. It is not recommended to exclude them completely. Additionally, mothers should spend more time walking with their children and humidify the air in the nursery.
Consequences of anemia
If low hemoglobin is not detected in time or the situation is left to chance, this threatens the child with serious health problems. Lack of hemoglobin causes insufficient oxygen supply to all tissues of the child’s body, including brain tissue.
The consequences of prolonged hypoxia will be developmental delays and deterioration of the child’s brain activity, as well as disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
The approach to treating a child with low hemoglobin should be comprehensive and based on the reason for the decrease in this blood indicator:
- If a child has iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements are indicated. They should be prescribed by a pediatrician, selecting an age-appropriate dosage. You cannot give your child any iron supplements on your own. Babies with iron deficiency are usually prescribed medications that are taken orally. They are presented in drops or syrup, for example, in the preparations Aktiferrin, Ferrum Lek Maltofer and Ferronal 35.
- If the cause of low hemoglobin is acute blood loss, the child may be given a blood transfusion. This procedure is also recommended for children with severe iron deficiency anemia.
- At the same time, the doctor will advise you to adjust the child’s diet. adding foods high in iron to it, which promotes the formation of hemoglobin in the body. Such products include meat (iron is absorbed from it much better than from any plant food), legumes, eggs, offal, cereals, pomegranates, berries, nuts and other products.
- Children with anemia are also advised to take long walks in the fresh air. since oxygen access stimulates the formation of red blood cells.
Parents should understand that it is impossible to treat anemia only by changing the child’s diet; adjusting the diet will only help supplement the treatment.
The opinion of the famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky regarding diet during the treatment of anemia can be found here:
Low hemoglobin in a child
The child’s hemoglobin level indicates his health. But the indicators may deviate downwards. In this case, the pediatrician diagnoses the development of anemia. At the same time, all organs begin to experience oxygen starvation.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
The amount of iron in the child’s body decreases gradually. Initially, the pathology occurs without visible symptoms and can be determined by taking a blood test.
Dizziness, pale and dry skin, decreased attention and memory - all this may indicate anemia
A large decrease in hemoglobin in the blood is accompanied by symptoms:
- the skin becomes pale and dry;
- decreased appetite and weight gain;
- the child becomes lethargic, sleeps more, but the sleep is restless;
- At school age, children may complain of dizziness. There is a lack of attention and memory loss;
- White spots may appear under the nail plates and on the body;
- puffiness and blueness appear under the eyes;
- The heart rate speeds up as the heart needs to pump more blood to deliver the required amount of oxygen.
Additionally, parents begin to notice the child’s developmental lag behind his peers , both physically and mentally. The disease can occur in 3 stages (mild, moderate and severe). If anemia is severe, the child may be unconscious and will require urgent donation of blood.
Causes of low hemoglobin in children
A decrease in iron can be temporary or permanent , depending on the cause of the pathology. When a pathology appears temporarily, the blood composition returns to normal after the provoking factor is eliminated. In other cases, drug treatment is required.
Anemia of the expectant mother during pregnancy can cause low hemoglobin in the child
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin:
- Anemia in the mother during pregnancy. As a result, the child does not have iron reserves and the disease can be inherited.
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the mother followed a vegetarian diet or did not eat well ; the child did not receive the necessary iron from food;
- Untimely introduction of foods containing iron (fish, meat, buckwheat porridge).
- Lack of vitamins B9 and B12 in the body.
- Impaired functioning of the digestive tract due to the development of pathology (dysbacteriosis, ulcers, gastritis).
- Tumor neoplasms.
- Infectious and autoimmune diseases.
- Side effect from taking medications.
- Bleeding , internal or external.
- Impaired blood formation may be associated with pathology in the bone marrow.
Anemia caused by poor diet can be treated with an iron-rich diet without the use of drugs. The menu and medications are prescribed by the pediatrician.
The dangers of low hemoglobin
When parents ignore symptoms or expect iron levels to be restored on their own, the child’s organs and tissues do not receive the required amount of oxygen at this time. The brain, digestive tract and muscles do not function at full capacity.
Pediatricians, with prolonged anemia, note a lag in mental development and growth, frequent colds, and poor physical development.
Treatment. Medicines, folk remedies
The hemoglobin level in a child, with a slight decrease, can be restored by adjusting the diet.
To do this, the child’s menu should include more dishes containing iron (pomegranate, buckwheat, meat), as well as drinks made from fruits and berries (rose hip decoction, compotes, milk).
When a decrease in hemoglobin is caused by a disease, the cause must first be eliminated. Next, therapy with iron-containing drugs is prescribed if the norm does not recover on its own.
With moderate severity of anemia, the child is prescribed medications:
- ferrum lek;
- totem;
- maltofer;
- Ferrous gluconate.
If taking the drug does not increase the level of hemoglobin (this is possible due to the characteristics of the child’s body), then an analogue is selected by the pediatrician. It is important to follow the exact dosage and complete the full course. Usually it is at least 3 months. During the treatment period, it is necessary to take a blood test for control.
If anemia occurs in a severe form or a sharp drop in iron, the child is prescribed a course of injections (they are dangerous for small children, as they can cause anaphylactic shock, and bumps from injections often need to be removed surgically), they are prescribed in extreme cases.
In severe cases of anemia, your doctor may prescribe a blood transfusion.
usually be prescribed . The process is less dangerous and less painful.
You can use traditional medicine together:
- daily consumption of pomegranate juice diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio. Depending on age, the amount of juice per day is adjusted by the pediatrician;
- juice from beets and carrots in a 1:1 ratio. For treatment, prepare a fresh portion each time. The drink causes stool liquefaction, so frequent consumption is not recommended;
- chewing washed dried fruits;
- rosehip drink. For 1 liter, steam 30-40 g of berries in a thermos. Add lemon juice and honey before use.
Traditional medicine will allow you to level out iron levels if the deviations are small and noted recently or are the result of an illness. For moderate and severe anemia, drug treatment is necessary. Independent choice of drugs is unacceptable.
Features of treatment for children under one year old
For treatment, infants are prescribed adjustments to the mother's diet (when breastfeeding) or formulas enriched with hemoglobin. Timely introduction of complementary foods (meat, fruits and drinks) is also mandatory.
If there are deviations in the child’s hemoglobin level, it is important to introduce complementary foods correctly and in a timely manner.
The use of medications is permitted, but the age and weight of the patient are taken into account. Additionally, parents are recommended to spend more time with their child in the fresh air, outside the city (walks through a forested area).
What is anemia, and how to overcome it?
Important! If the blood test result shows low hemoglobin, only a doctor can prescribe appropriate treatment. You cannot treat yourself on your own, since anemia occurs not only due to a lack of iron in the blood.
Anemia is divided into the following types:
- Iron deficiency. Iron is very important for hemoglobin synthesis. If a pregnant woman does not have enough of it, the baby will develop anemia. This pathology occurs in children if they receive little iron from food, or their absorption of this microelement is impaired.
- B12-deficient. Vitamin B12 also plays an important role in the synthesis of hemoglobin. The child may lack it due to the fact that the pregnant mother suffered from a lack of vitamins in the body; the baby did not receive them in sufficient quantities through breastfeeding or eating other foods.
- Folate deficiency. Folic acid deficiency also causes anemia. This element plays an important role in the synthesis of DNA and RNA. When red blood cells first begin to form, they have a nucleus. It is where DNA and RNA synthesis occurs, for which folic acid is responsible. The blood cells then lose their nucleus and take on a different shape.
- Hemolytic. This type of anemia occurs because red blood cells are actively destroyed. This is possible in children born ahead of schedule, if the blood of the mother and fetus is incompatible, dangerous poisoning of the body has occurred with heavy metal compounds, poisons, the baby was treated for a long time with certain medications.
- Dyshemopoietic. This type of anemia is rare in young children. It occurs as a consequence of impaired blood formation in the bone marrow.
- Posthemorrhagic. It is also very rarely diagnosed in children. This anemia occurs due to excessive blood loss after injury or surgery.
How long the treatment will last and how to raise hemoglobin levels is up to the doctor to decide. The basis of therapy is taking vitamins and adjusting the diet of the child and mother. It should include foods that increase hemoglobin: cereals, fruits and vegetables, cottage cheese, nuts.
Your baby may be prescribed iron supplements if iron deficiency anemia is detected. The duration of treatment is approximately two weeks, after which blood is again taken for analysis. The most popular of the drugs is Maltofer.
Iron-deficiency anemia
Menu for maintaining normal hemoglobin in children
Depending on whether the child’s hemoglobin is increased or decreased, parents should create a menu.
If there is not enough iron, then dishes with a high iron content should prevail:
- boiled meat;
- red vegetables and fruits;
- nuts;
- liver;
- buckwheat, oat and wheat cereals;
- spinach and other greens;
- products containing vitamins B9 and B12.
Products of plant origin to increase hemoglobin
If the iron content is high, foods with a low iron content should predominate in the diet:
- fish products;
- poultry meat;
- milk products;
- eggs;
- soy products;
- flour products (bread, horns).
The menu must be discussed with the pediatrician. It is necessary that the growing body does not lack nutrients. Therefore, the diet should be varied, but with the required hemoglobin content in dishes. When compiling it, the age and energy needs of the child are taken into account.
Normal hemoglobin levels
Hemoglobin (HGB) is a special blood protein whose molecules are found in red blood cells - erythrocytes.
First, it’s worth finding out which HGB readings are normal. Our table shows the limit values of this indicator, which depend on the age of the child. Age days/months/years
Hemoglobin level, g/l
HGB levels can fluctuate depending on how physically active your child is and their health. The amount of this protein is also affected by the baby’s nutrition and sleep quality. If a child does not receive enough vitamins, proteins, and microelements from his diet, moves little and does not go for a walk, his test results will be worse - hemoglobin will be underestimated.
How often should hemoglobin be checked in children?
The baby's first blood test is taken immediately after birth. Then before each vaccination. Blood donation is scheduled to occur once every 6 months (up to 3 years), if the child is healthy.
A blood test is taken from a child up to 3 years of age every six months (provided that the baby is healthy)
If there are changes in the amount of iron, the pediatrician prescribes tests once every 4 weeks. Thus, the decrease or increase in iron during treatment is monitored. If no changes are noted, the pediatrician replaces the drug.
Hemoglobin levels are monitored from birth. Pediatricians, when viewing the analysis, note an increase or decrease in iron content. If necessary, a repeat blood test is done and treatment is prescribed. Deviations in a child can cause disturbances in mental and physical development, and the performance of the organs of the whole organism decreases.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Natalie Podolskaya
Drug treatment
If the level of hemoglobin in the blood is significantly reduced, the doctor will prescribe medications that, in addition to iron, should contain manganese and copper, which help deliver it to the bone marrow cells.
For children under one year of age, the drug is prescribed in the form of drops; for complete absorption, it is taken 2 hours before meals or an hour after meals. Typically, the course of treatment for iron deficiency anemia lasts two weeks. At the end of therapy, the doctor should order a repeat blood test to monitor hemoglobin levels.
If the indicator has risen to the required values, it is necessary to further maintain it with the help of a balanced diet and a proper lifestyle.
Dr. Komarovsky believes that before prescribing drug treatment, the pediatrician must find out the reason for the decrease in hemoglobin and, based on these factors, prescribe an adequate drug for therapy.