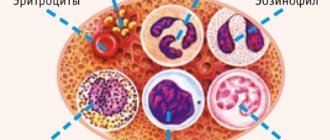
Hemostasis
Using the RFMC test, it is possible to detect the presence of fibrinomeric complexes - markers of thrombinemia. This indicator partially evaluates hemostasis (biological system for maintaining fluid state and blood clotting).
The analysis is performed during preventive examinations and diagnosis of blood pathologies. After submitting the material for research and obtaining the result, it is necessary to decipher it by a specialist. Assessing human hemostasis requires extensive experience.
If there is a violation in the hemostatic system, treatment cannot be delayed. It is required to determine with utmost precision what the problem is related to (hyper-folding, insufficient folding), the reasons for the appearance of atypical deviations, and ways to solve the problem.
It is important to know! To obtain accurate data, you need to correctly submit the material for analysis. The main rule is to donate blood on an empty stomach.
Physiological reasons for the growth of RFMK
After conceiving a child, a woman's hormonal background changes. This affects the functioning of all internal organs, and the hemostatic system is no exception. Blood clotting increases, and the formation of blood clots in the bloodstream accelerates. This phenomenon is called physiological hypercoagulation. Such changes in the hemostatic system are ensured by natural processes occurring in a woman’s body:
- implantation – implantation of an embryo into the endometrium;
- formation and development of the placenta - a structure that nourishes and protects the fetus;
- stopping natural bleeding during childbirth.
Increased blood clotting during pregnancy is due to the following mechanisms:
- formation of the third circle of blood circulation;
- increase in BCC (blood volume in vessels) by 20%;
- an increase in the number of platelets - cells responsible for the formation of blood clots;
- increase in fibrinogen and blood clotting factors.
Physiological coagulation is not dangerous for the woman and the fetus. If RFMC remains within normal limits (taking into account gestational age), treatment is not required.
When is a RFMC analysis prescribed?
The most common indications for analysis:
- pregnancy planning;
- diagnosis of thrombosis;
- screening before surgery;
- pregnancy monitoring;
- suspicion of DIC syndrome;
- planning an in vitro fertilization procedure;
- assessment of the effectiveness of the therapy.
RFMC is used as a preventive diagnostic method and a method for assessing treatment.
It doesn't take much time to analyze. During the treatment of thrombosis, this study allows you to evaluate the effect of treatment. Based on the data obtained, the treatment regimen is adjusted.
What is RFMK and D-dimer
During pregnancy, it should be slightly increased - this is how the body prepares for childbirth. But there are certain standards, exceeding which can cause a miscarriage. Therefore, every woman should be tested for RFMC and D-dimer during pregnancy in the third trimester - at 28 weeks, and, if required, according to individual indications.
To understand why you need to know RFMC during pregnancy and planning, what kind of analysis for D-dimer is, you need to understand the meaning of these indicators.
The abbreviation RFMC stands for soluble fibrin-monomer complexes - these are the remnants of small blood clots when thrombosis develops in the body.
If RFMK is higher than normal, then the blood thickens, which leads to increased thrombus formation. Blockage or narrowing of blood vessels significantly impairs the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, hypoxia may occur, and the risk of pregnancy loss increases.
D-dimers are protein substances, fibrin breakdown products. They take part in the process of hematopoiesis and are particles of blood clots. If their level in the blood is increased, this can lead to increased thrombosis.
Currently, mandatory tests for D-dimers are carried out more in the United States when planning a pregnancy or undergoing IVF. They believe that this analysis must be done to exclude the possibility of blood clots.
In the CIS countries, RFMC analysis is more often carried out and already during pregnancy.
It is quite difficult to donate blood for D-dimers to a pregnant woman - the analysis requires certain preparation. You need to fast for 12-14 hours, you can only drink a little clean water.
Therefore, the D-dimer test is used to identify dangerous conditions in people of other categories, and not in pregnant women. Moreover, it can increase in liver diseases, inflammatory and infectious diseases, and under the influence of age-related changes. That is, the indicator is not always reliable. During pregnancy, the value of this indicator should be 248 ng/ml. Above 1500 ng/ml the condition is considered abnormal.
Preparation for analysis
The material is collected according to the generally accepted scheme:
- alcohol is excluded 3 days before the test;
- if you are taking medications that affect clotting, the doctor asks you to temporarily stop using them 48 hours before the procedure;
- Do not eat for 12 hours.
There is no need to adjust your diet before the study.
It is better to go and take the material in the morning after a 12-hour fast. This way you can get reliable results. The delivery is done on an empty stomach. In the morning it is permissible to drink plain water. Any food before analysis is prohibited.
Advice. If possible, it is better to avoid heavy physical activity, emotional excitement, and smoking during the day before the scheduled test, or 1-2 hours before the test.
What is homeostasis?
To fully understand the processes of RFMK, one must first understand about the homeostasis system. This system consists of components of the blood that circulate throughout the body that help the blood clot.
Blood itself is a liquid tissue that is found in human vessels, possessing a huge variety of functions and the uniqueness of its work.
One of the main properties of blood is its timely clotting, which helps stop bleeding and restore tissue. The process of coagulation occurs through the formation of thrombi (dense blood clots).
If blood did not have this property, then a person would die from even a small injury due to blood loss.
Formed blood clots are delivered through vessels to the site of injury, which clogs the site of injury and stops both external and internal bleeding.
The healing process, in most cases, is not felt by the person, which indicates the healthy functioning of the blood circulation system.
There are three main components of the homeostasis system.
These include:
- The inner layer of blood vessels, which is covered with cells, called endothelium . Damage to it can occur under the influence of various factors, but, in many cases, the endothelium is damaged under mechanical influence on the tissue (physical trauma). Cells that have not been damaged and are located around the site of the lesion begin to actively synthesize substances that stimulate the formation of a blood clot;
- Thrombosis occurs with the direct participation of platelets, which have the ability to combine, thereby forming a blood clot . The formed thrombus is delivered to the affected tissues to block the lesion. With large scale lesions, the formation of blood clots may not be sufficient, which involves the process of blood plasma;
- Plasma contains thirteen factors . At the moments of their activation, the formation of a blood clot occurs much faster and completely covers the affected area, stopping hemorrhage (hemostasis).
Homeostasis is responsible for the normal process of blood clotting.
The operation of this system occurs with the support of two other systems. The fibrinolytic and anticoagulant systems must promptly respond to tissue deformation and involve plasma factors.
Anticoagulant blood system
Another important task of these systems is to ensure that the blood does not clot excessively, which can be fatal.
RFMK norm
The normal value is considered to be 3.38 mg/100 ml. The maximum allowable is 4.0 mg/100 ml. If the RFMC exceeds the values, there is a high risk of developing unnecessary clotting. Blood clots can form in large and small vessels.
Standards may vary slightly depending on individual characteristics. Indicators near the upper limits should alert a person. You will need to adjust your lifestyle and conduct some therapy to lower the RFMC value.
Decoding the results obtained
There is a certain standard for indicators for pregnant women, but only a doctor should make final diagnoses and prescribe the necessary treatment measures. The thing is that not only pregnancy affects the results - a woman may have some chronic diseases, deviations in the analysis will appear, but nevertheless, the pregnancy will proceed safely.
Coagulogram norms during pregnancy: table
Therefore, only a specialist can decipher everything correctly, and a pregnant woman, based on statistics, independently learns only general information. In general, the coagulogram includes 8 key indicators, by which the doctor can accurately determine even small deviations.
What is the main focus:
- Fibrinogen is a protein that forms the basis for blood clotting during clotting. Exceeding the norm leads to a tendency to thrombosis, and insufficiency may indicate toxicosis. The norm for standard cases of fibrinogen is from 2 to 4 g/l; for pregnant women, this figure is 6 (the level constantly increases as labor approaches).
- APTT is interpreted as activated partial thromboplastin time, which means the period of time during which blood clotting occurs. For a healthy ordinary person, this figure is equivalent to 24-35 seconds, and in pregnant women, due to an increase in fibrinogen, clotting occurs faster - in about 17-20 seconds.
- Thrombin time is another important indicator of the coagulogram, indicating the duration of the last coagulation period. The average statistical norm is 11-18 seconds, for pregnant women it is higher. Deviations in this parameter may indicate a malfunction of the liver.
- Prothrombin is another protein present in plasma that precedes thrombin and is also involved in clot formation. The density of the blood and its ability to clot will depend on the concentration of this protein. The optimal indicator is from 78 to 142%. If the norm in a pregnant woman is exceeded, this may be a sign of placental abruption.
- Platelets are special blood elements formed directly in the bone marrow. During pregnancy, platelet counts decrease slightly, and if the drop is strong, this indicates the presence of the disease. In this case, the normal value is from 131 to 402 thousand/µl.
- D-dimer is a factor responsible for thrombus formation in the human body. Plays an important role for timely diagnosis of thrombosis. In pregnant women, this parameter gradually increases, but if the jump is sharp, then diabetes or kidney problems may be present. The standard value is from 33 to 726 ng/ml.
- Antithrombin III is a protein that slows down the clotting process, and if it deviates by 50% or more, there is a risk of developing thrombosis. Must be present between 70 and 115%.
- Specific antibodies - this criterion determines the presence of a lupus anticoagulant in the body. It really shouldn’t happen (except for taking certain medications during pregnancy) and if such a factor was discovered, then the woman has pathologies that should be promptly identified by a doctor.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=-q3MSNmPPGE
In order to correctly decipher the analysis and give it a reliable assessment, the doctor must be aware of all the medications that the pregnant woman is taking, if something was prescribed by another specialist.
The development of abnormalities can be largely influenced by excess weight or other individual characteristics of the body.
It is extremely important to take this test and other necessary tests in a timely manner during pregnancy and to carefully prepare for them. This is the only way to protect your health and that of your unborn baby.
Factors influencing changes in RFMK
Among the factors influencing the blood count are:
- the presence of thrombosis, blockages of blood vessels;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- injuries;
- DIC syndrome.
Thrombosis can lead to dangerous complications and cause death.
There are a number of other factors that can influence the value of RFMC. The indicator may change with a pathological course of pregnancy, serious burns and surgical interventions with large blood loss.
Helpful information. If there are provoking factors, you need to get tested to determine the extent of the damage. If thrombosis of any localization is suspected, RFMC will help in diagnosis.
Reasons for level changes
An increase in temperature affects the level of the indicator
The most common increase in the level of RFMC in the blood is always associated with the activation of blood coagulation function. Coagulability increases for the following reasons:
- Stress, physical overload (the body prepares in advance to withstand injuries and blood loss);
- Infectious diseases, especially in the acute period;
- Fever, increased body temperature to 38.5 degrees or more;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system (atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease);
- Arterial hypertension;
- Conditions after myocardial infarction;
- Varicose veins;
- Oncological diseases;
- Pregnancy (especially in the prenatal period).
Anticoagulants reduce the level of fibrin complexes
The most dangerous consequence of activation of blood clotting is disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. This is a pathological condition of intravascular coagulation, when blood clots form randomly throughout the body, blocking small and large vessels, depriving blood supply and disabling healthy organs. This condition can be triggered by massive blood loss, trauma, pathological childbirth, severe bacterial or viral infection, or poisoning.
Reduced levels of RFMC occur when taking anticoagulant drugs used in the treatment of the cardiovascular system. Doctors often monitor the effectiveness of treatment precisely by changes in the level of RFMC, which allows them to quickly adjust the dosage of drugs. A decrease in the level of RFMC in other cases may indicate hematological diseases and requires a comprehensive analysis - a coagulogram.
The need for analysis
The need for examination arises in people who are at risk of developing various thromboses. Girls who are planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant should also monitor the RFMC readings. Poor or excessively good blood clotting can lead to complications during pregnancy.
People who suffer from thrombophilia also need to regularly have a coagulogram, including RFMC. By controlling the blood picture, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of complications and consequences of the disease. This examination method should also be used in preparation for planned surgical intervention.
More information about blood tests during pregnancy in the video:
Normal for pregnant women
The normal value for pregnant girls in the first trimester is up to 5.5 mg/100 ml. It is desirable that the value be in the range of 3.5-4.0 mg/100 ml.
During pregnancy, the likelihood of developing blood pathologies increases
It is worth noting that the norm for pregnant women depends on the stage of pregnancy. In normal conditions, the analysis is taken 3 times: in the first, second and third trimester. By the last trimester, the upper limit of normal increases. Thus, in the 3rd trimester, RFMC can reach 7.5 mg/100 ml, and this will not be considered a pathology.
The interpretation of the analysis is entrusted to the doctor who monitors the pregnancy. He will be able to understand how critical the results obtained are, taking into account the girl’s individual characteristics.
What does an elevated level mean?
If the level of RFMK is too high, many negative processes can occur. There is a risk of developing disorders of intrauterine development of the fetus, termination of pregnancy and premature aging of the placenta. If an increased value of fibrin complexes in the blood is detected, the doctor prescribes a number of additional studies that allow us to obtain a more accurate picture and determine the root cause of the deviation.
Among the factors that can increase RFMC in a pregnant woman’s blood are:
- smoking;
- development of liver, kidney or endocrine system disease.
- failure of metabolic processes;
- allergy to any product.
Hereditary and genetic diseases can also provoke an increased level of this indicator.
It is necessary to determine the cause of the deviation. Then choose treatment, taking into account the duration of pregnancy. In some cases, in order to avoid fetal death, childbirth is performed at an early stage of 7-8 months.
Reduced rate
A value below the norm is just as dangerous as an excessively high value. During pregnancy, a drop in RFMC is extremely rare. Among the main dangers of developing too low fibrinogen are the likelihood of bleeding and placental abruption. If necessary, adjustment of coagulation is carried out in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of a doctor.
If you have problems with clotting, any bleeding is dangerous
Indicators below reference values occur with improper use of anticoagulants, congenital hemophilia and von Willebrand disease. To draw up a scheme for influencing insufficient blood clotting, the doctor will need to take into account many nuances.
Treatment when RFMC levels are abnormal
Composing a therapy is a complex procedure. After the examination and diagnosis, the doctor selects the appropriate method of exposure. To combat high concentrations of RFMC during pregnancy, the most safe and effective means are used. The following classes of drugs may be used:
- angioprotectors;
- metabolic;
- anticoagulants.
Experts often prescribe vitamin B9 (folic acid) to prevent severe clotting. In addition, Actovegin and Curantil can be used. The duration of use and dosage of medications are determined by the attending physician. The dosage may be adjusted as treatment progresses and the condition improves.
Along with the use of medications, you must adhere to a special diet. You will definitely need to exclude fatty, fried, salted and smoked foods. You need to start consuming at least 1.5 liters of water to normalize your blood picture.
The diet should be as balanced as possible
It is recommended to go for walks in the fresh air more often. If there are no contraindications, you can visit the gymnastics center and perform complexes created specifically for pregnant women.
Normal indicators
Values characterized as normal for a blood test for RFMC have a rather small range, which is 3.38 + 0.02 mg per 100 ml of plasma, but the mark of 4 mg/100 ml will also not be considered a deviation. But its excess will become a reason for the doctor to make a decision regarding further examinations and find out the causes of this disorder, and then develop appropriate therapeutic tactics.
There are some cases (congenital or hereditary anomalies) when a reading of up to 5 mg/100 ml is considered normal, and no treatment is required. This conclusion is made after certain additional examinations confirm the sufficient functioning of the homeostasis system. In such situations, it is imperative that blood tests be carried out in the same laboratory, since sometimes there are discrepancies of almost one.
Concept and mechanism of homeostasis
Prevention of complications
To prevent complications from high RFMC (especially during pregnancy), the following actions must be taken:
- Healthy food;
- regularly take comprehensive tests at clinics;
- follow all doctor's recommendations;
- take supplements that improve blood condition.
During pregnancy, examinations are carried out as planned. Under no circumstances should they be postponed. If you feel unwell, you must seek help and undergo unscheduled examinations.
Blood monitoring is an integral part of prevention
Examinations should include not only blood tests, but also ultrasound examinations and instrumental examinations. If a girl is pregnant, then she is severely limited in her ability to use various medications due to their toxicity. That is why all actions throughout pregnancy should be aimed at preventing possible diseases.
Remember. General preventive actions will help prevent the development of many diseases. The main thing is to adhere to these standards constantly.
What are the dangers of elevated RFMC levels during pregnancy?
We do not intend to intimidate the expectant mother, but we want to remind you that the significantly increased result is not caused by harmless reasons. It can be:
- Thrombophilia, which is usually hereditary in nature and manifests itself especially aggressively during pregnancy. This pathology, creating a high risk of clot formation, interferes with the normal course of the pregnancy process (miscarriages). The task of the gynecologist in this case is to carefully consider a plan of therapeutic measures that create conditions for bearing the fetus for up to 7 months (35 - 36 weeks), when the baby, although weak, is quite viable;
- A history of thrombosis during pregnancy may reappear, so this condition is considered an indication for more frequent testing of soluble fibrin-monomer complexes;
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, which can be caused by a variety of causes (infections, shock, trauma, autoimmune diseases, neoplasms, late toxicosis, purulent inflammation, cardiovascular and other chronic pathologies), during childbirth can become an uncontrollable process with a very sad end. . The risk of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome makes it necessary to monitor the level of RFMC very often, which the expectant mother must understand and strictly follow the doctor’s prescriptions in order to save the life of herself and her child.
To avoid severe complications during childbirth (in particular, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome), unscheduled administration of additional coagulogram parameters (RFMC, D-dimer, etc.) is indicated in the presence of:
- Severe diseases of the liver, kidneys, lungs;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Cardiovascular pathology;
- Neoplasms;
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- Diseases of the endocrine system, for example, diabetes;
- Purulent inflammation;
- Gestozov;
- Increased RFMC before pregnancy;
- Bad habits (smoking – primarily, including passive smoking);
- Pregnancy that occurs after artificial insemination using IVF;
- Multiple pregnancy.
Any deviations from the normal values of hemostasiogram parameters should be carefully rechecked and studied. If the RFMC is elevated for several weeks, the gynecologist, depending on the degree of increase in the indicator, prescribes treatment, which often takes place in a hospital setting (this, first of all, applies to cases when the concentration jumps sharply and exceeds the norm several times). A pregnant woman, for her part, must be aware of her share of responsibility in order to prevent terrible complications and fully experience the happiness of motherhood. Unfortunately, there are undisciplined pregnant women who ignore doctor’s advice, do not come for tests on time, refuse hospitalization, lead an unhealthy lifestyle, and then indiscriminately make complaints to all doctors in a row.
How to reduce the increase in clotting levels?
The advantage is that if you take the right nutrition for viscous blood, you can completely do without medications. It is recommended to change your diet week by week to ensure that your body is fully saturated with different vitamins.
To effectively reduce density, and accordingly RFMK, they recommend:
- Low-fat meat (turkey and chicken);
- Fresh tomatoes;
- Pepper;
- Garlic;
- Ginger;
- Blueberry;
- Celery juice;
- Sea fish;
- Green tea;
- Fermented milk products (yogurt and kefir);
- Nuts;
- Sunflower seeds;
- Blueberry;
- Olive oil.
The products have a very beneficial effect, since during pregnancy a large number of drugs taken is not recommended.
A moderate amount of the above foods consumed in the diet will help control blood density to normal levels.
Description
PFCM (soluble fibrin monomer complexes). Quantitative determination of high molecular weight fibrin compounds with fibrinogen and its breakdown products, which appear when the coagulation system is activated. Determination of the amount of FEMC is carried out as part of the expanded coagulum. The research results are important for diagnosing and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndromes, thrombophilia, preparation for surgery and in vitro fertilization when planning pregnancy.